Research on Dynamic Threat Tracking and Quantitative Analysis Technology Based on Attribute Attack Graph
-
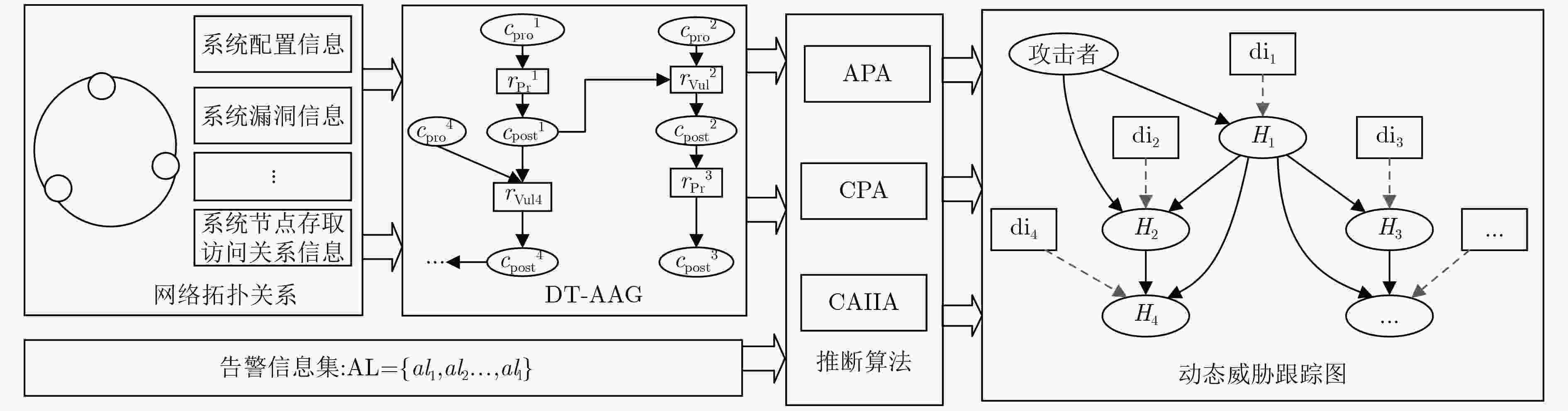
摘要: 网络多告警信息融合处理是有效实施网络动态威胁分析的主要手段之一。基于此该文提出一种利用网络系统多告警信息进行动态威胁跟踪与量化分析的机制。该机制首先利用攻击图理论构建系统动态威胁属性攻击图;其次基于权限提升原则设计了前件推断算法(APA)、后件预测算法(CPA)和综合告警信息推断算法(CAIIA)进行多告警信息的融合与威胁分析,生成网络动态威胁跟踪图进行威胁变化态势的可视化展示。最后通过实验验证了该机制和算法的有效性。Abstract: Network multi-alarm information fusion processing is one of the most important methods to implement effectively network dynamic threat analysis. Focusing on this, a mechanism for dynamic threat tracking and quantitative analysis by using network system multi-alarm information is proposed. Firstly, the attack graph theory is used to construct the system dynamic threat attribute attack graph. Secondly, based on the privilege escalation principle, Antecedent Predictive Algorithm(APA), the Consequent Predictive Algorithm(CPA) and the Comprehensive Alarm Information Inference Algorithm(CAIIA) are designed to integrate the multi-alarm information fusion and do threat analysis. Then, the network dynamic threat tracking graph is generated to visualize the threat change situation. Finally, the effectiveness of the mechanism and algorithm is validates through experiments.
-
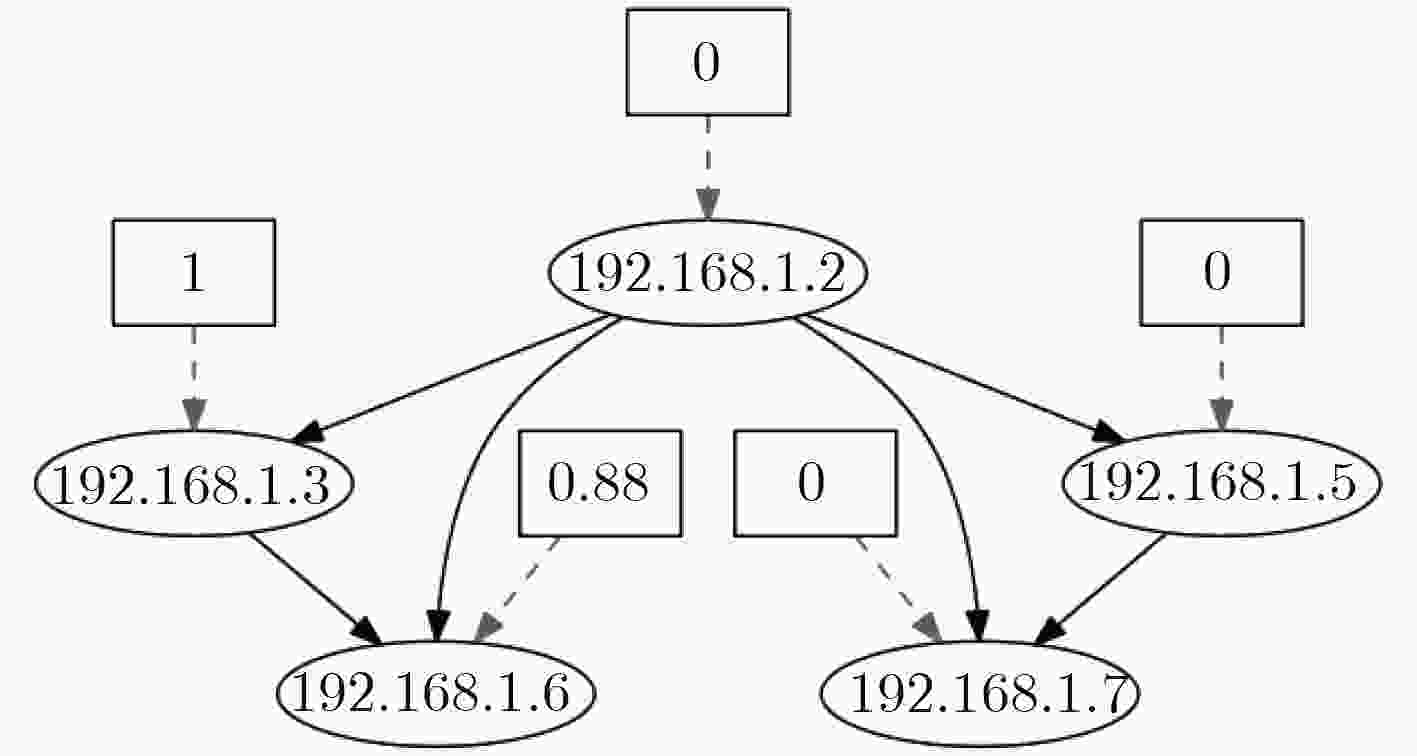
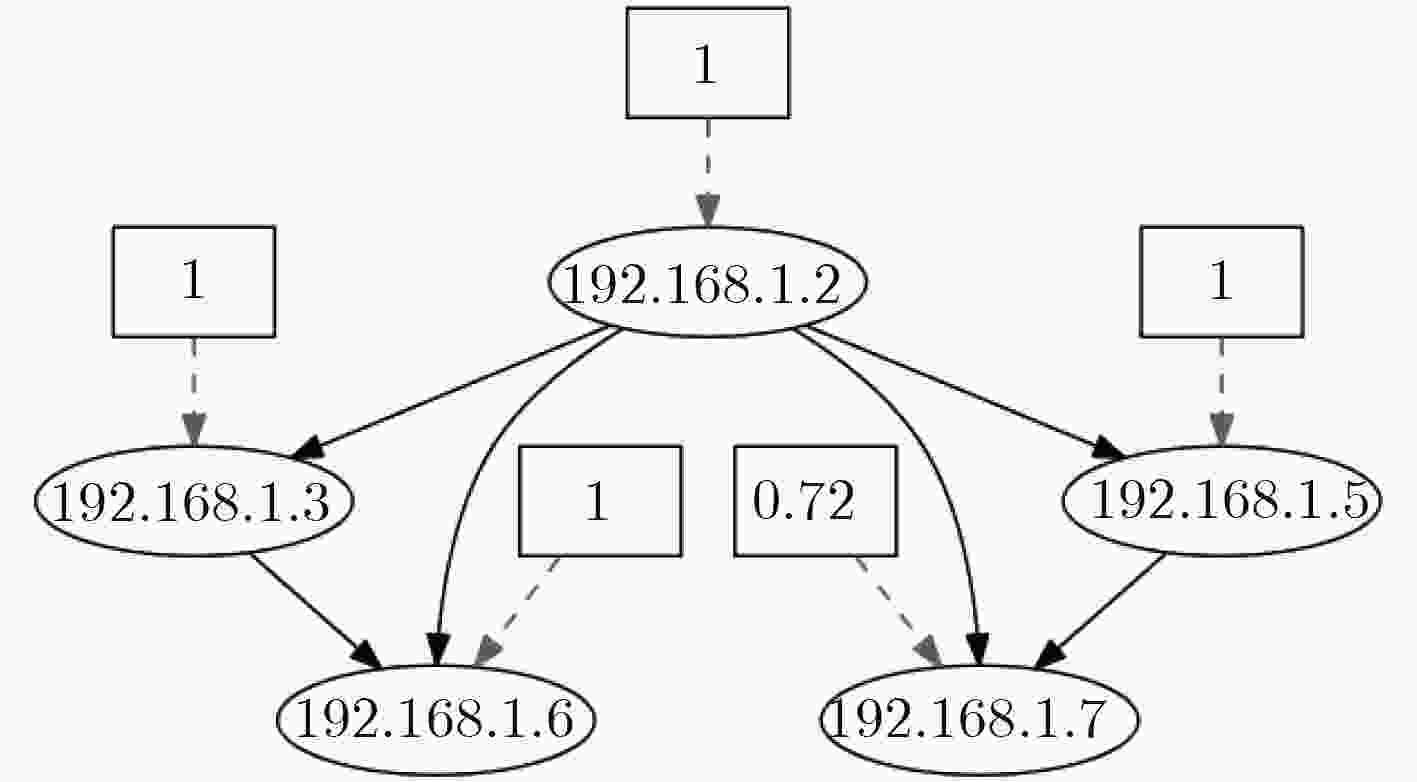
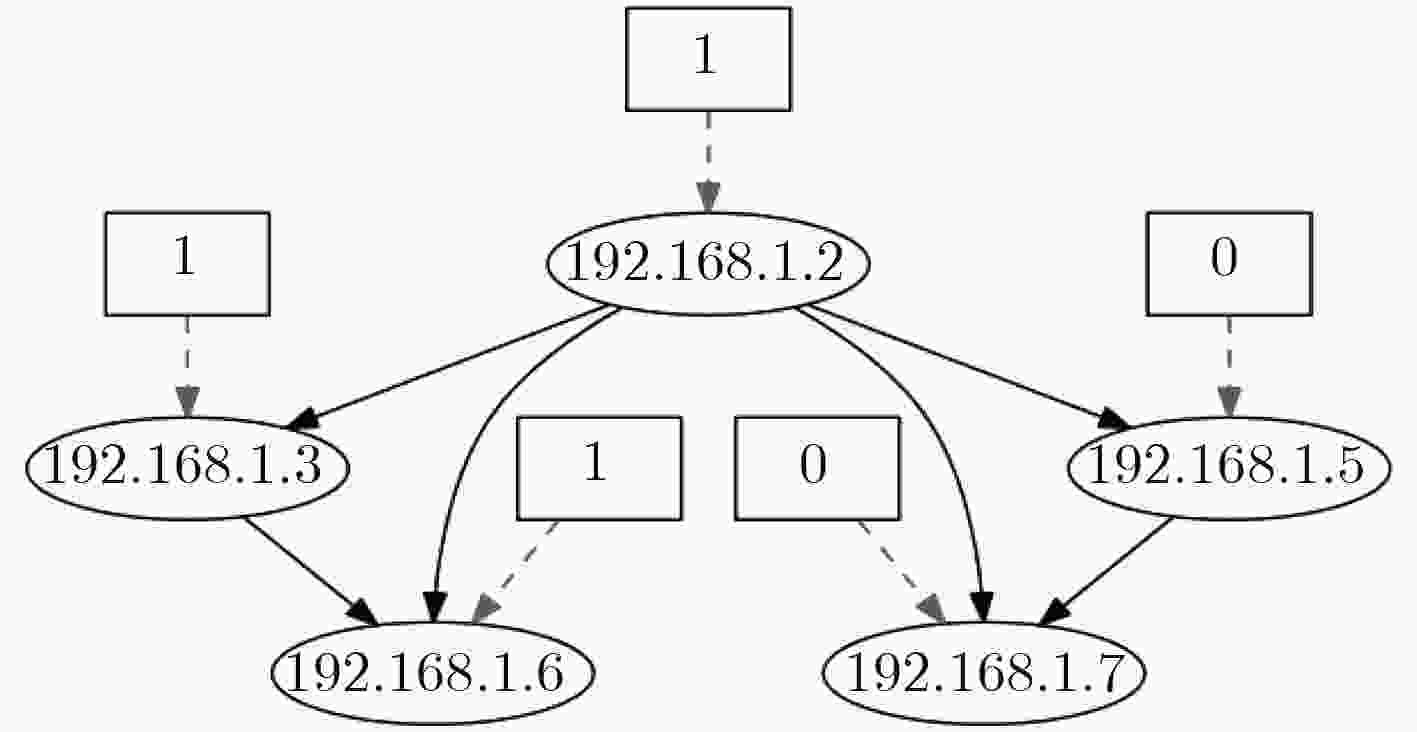
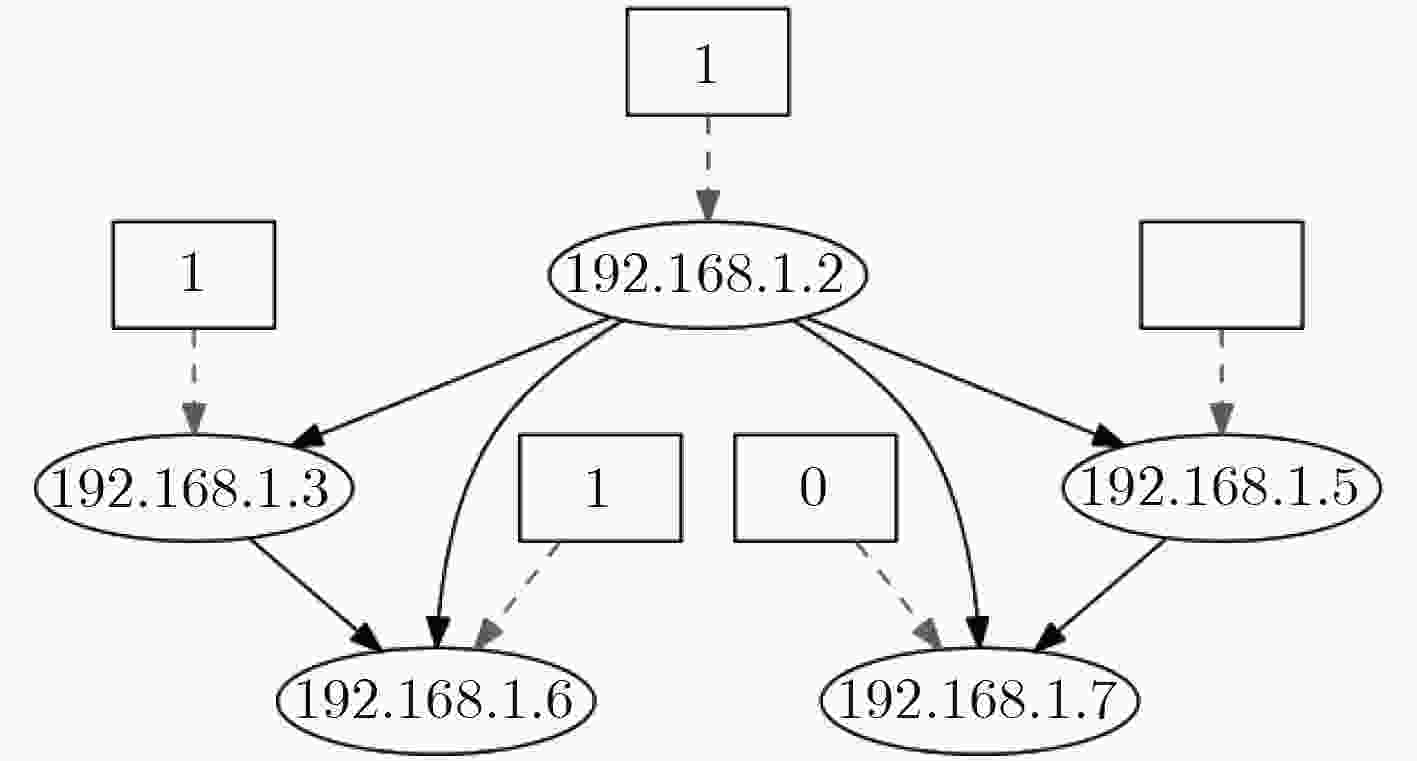
图 10 文献[17]
${\rm{tim}}{{\rm{e}}_1}$ 威胁状态图图 11 文献[17]
${\rm{tim}}{{\rm{e}}_2}$ 威胁状态图表 1 前件推断算法
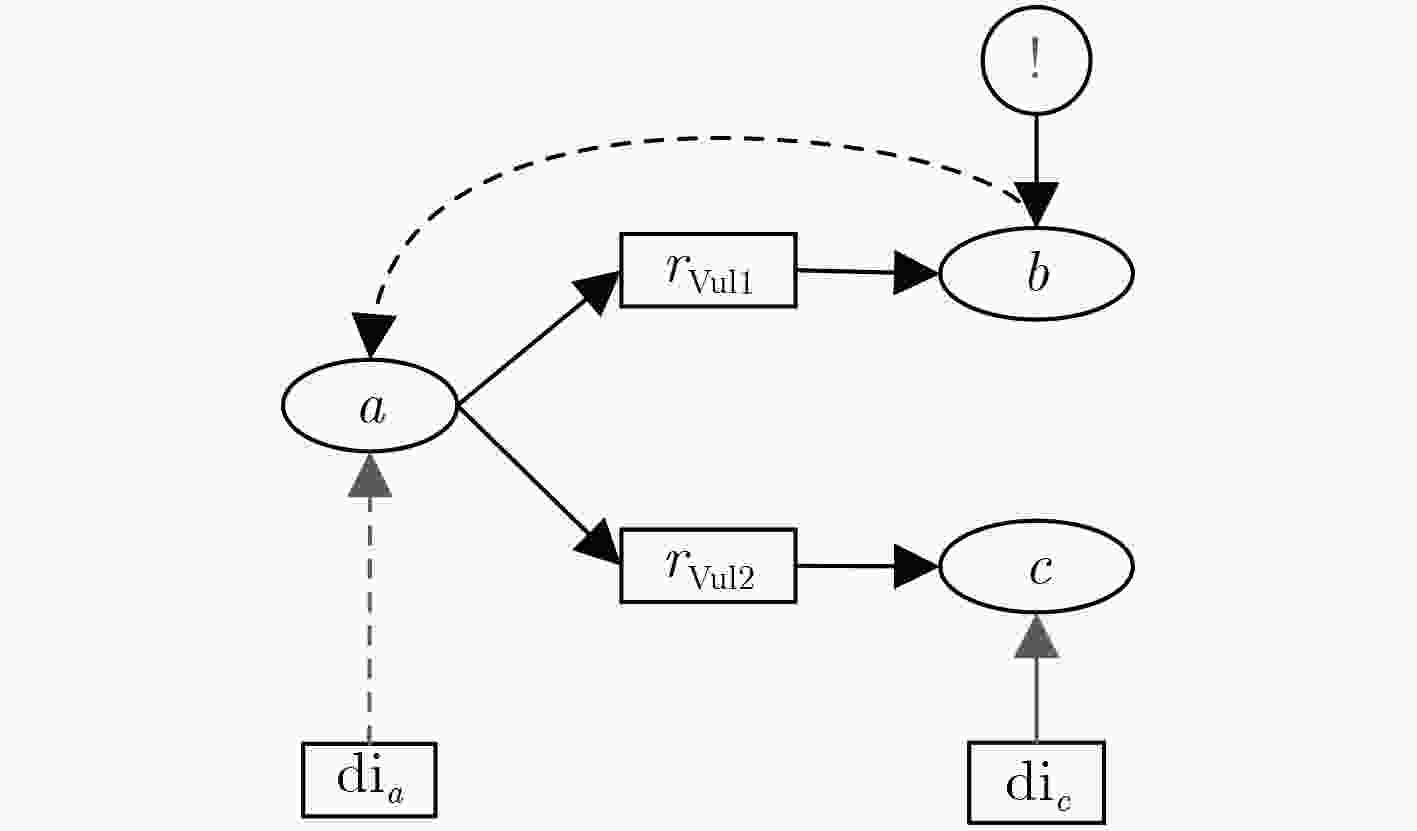
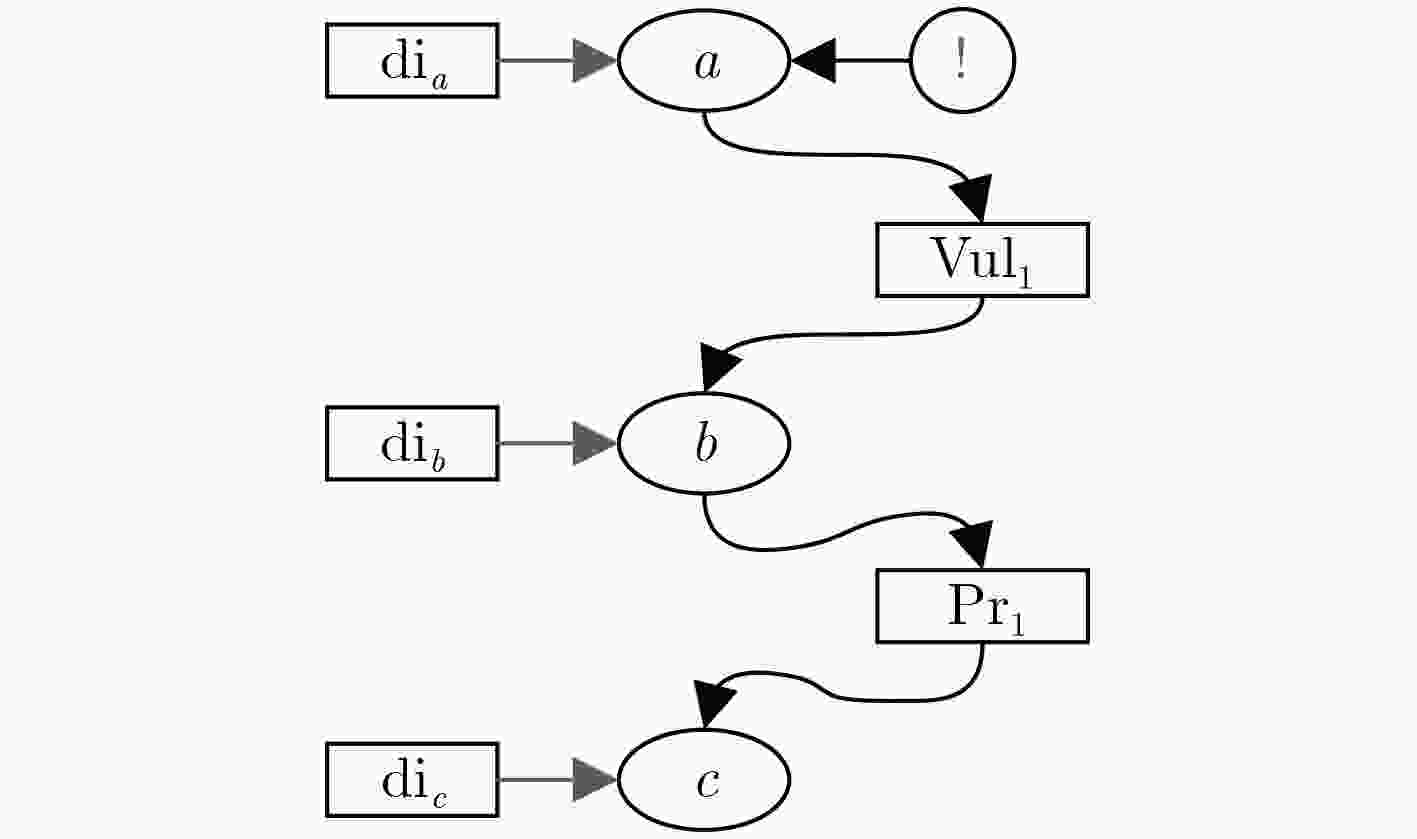
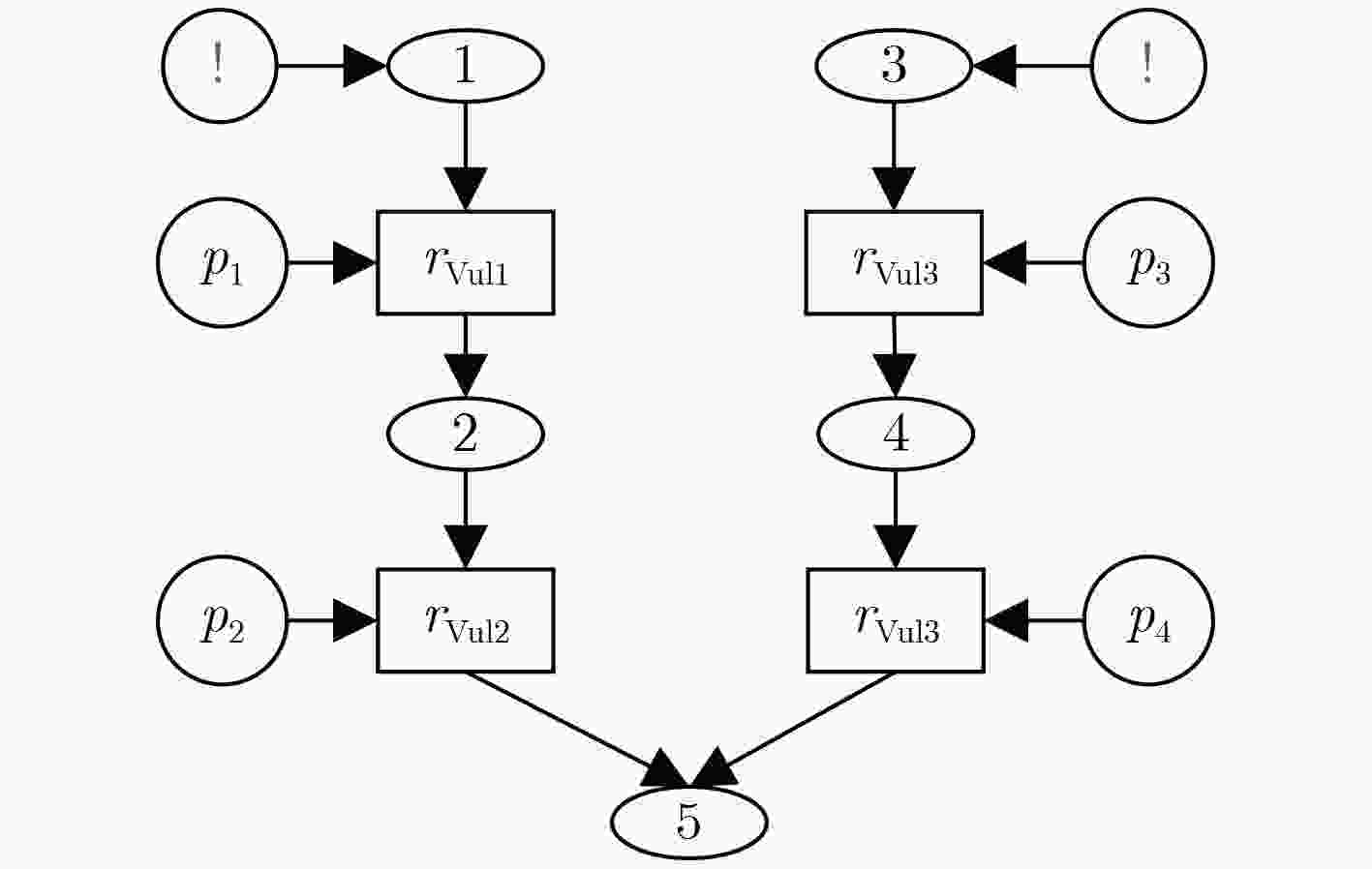
算法1:前件推断算法(${\rm{APA}}$) 输入:${\rm{DT - AAG}}$, ${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_l}$ 输出:${\rm{DI}}$ (1) ${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_l} = ({\rm{tim}}{{\rm{e}}_l},{\rm{IPpr}}{{\rm{o}}_l},{\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_l},{\rm{clas}}{{\rm{s}}_l})$; (2) if ${\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_l} = {\rm{IP}}{'_l}$, set ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_l} = 1$; //根据IP地址确定攻击图中产生告警信息的节点; (3) set l –1, l, l+1,···, l+m; //按照攻击图中关于节点l 的路径的节点权限排序; (4) if ${\rm{IPpr}}{{\rm{o}}_l} = {\rm{IP}}{'_{l - 1}}$, set ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l - 1}} = 1$; //如果该告警信息的源IP在系统中,表示攻击者已经获得该 节点的前件节点的权限; (5) { if not only ${c_{l - 1}} \to {c_l}$; //节点l–1的后置条件包含不止节点l; (6) { set $l' - 1,l',l' + 1,···,l' + n$($n \le m - 1$); //设置节点l-1的后件节点中非包含l节点路径的其余节点的顺 序; (7) ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l' - 1}} = {\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l - 1}} = 1$; (8) DO { ${\rm{CPA}}(l' - 1)$; // 对节点$l' - 1$执行后件预测算法; (9) }}} (10) else (11) set ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l - 1}} = 0$; //该告警节点与其所处攻击图中的前件节点无关,因此设置 其前件节点推断强度为0; (12) return DI 表 2 后件预测算法
算法2:后件预测算法(${\rm{CPA}}$) 输入:${\rm{DT - AAG}}$, ${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_l}$ 输出:${\rm{DI}}$ (1) ${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_l} = ({\rm{tim}}{{\rm{e}}_l},{\rm{IPpr}}{{\rm{o}}_l},{\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_l},{\rm{clas}}{{\rm{s}}_l})$; (2) if ${\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_l} = {\rm{IP}}{'_l}$, set ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_l} = 1$; (3) set l –1, l, l+1,···, l+m; (4) for(i=1, ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l + i}} \ge \lambda $&&$i \le m$, i++)
(5) {${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l + i}} = \prod\limits_{j = 1}^i {{p_{l + j}}} \times {\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_l}$; }(6) when ${\rm{D}}{{\rm{I}}_{l + i}} = \{ {\rm{di}}_{l + i}^1,{\rm{di}}_{l + i}^2,···,{\rm{di}}_{l + i}^n\}$; //从节点$l$到节点$l + i$有n条路径,${\rm{D}}{{\rm{I}}_{l + i}}$的元素都是由${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_l}$推断; (7) DO { (8) ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_{l + i}} = \max ({\rm{di}}_{l + i}^1,{\rm{di}}_{l + i}^2,···,{\rm{di}}_{l + i}^n)$; } //取单个告警不同路径中推断强度最大的值; (9) Return ${\rm{DI}}$ 表 3 综合告警信息推断算法
算法3:综合告警信息推断算法(${\rm{CAIIA}}$) 输入:${\rm{DT - AAG}}$, ${\rm{AL}}$ 输出:${\rm{DI}}$ (1) ${\rm{AL}} \ne \varnothing $; //告警信息不为空; (2) ${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_i} \in {\rm{AL}}$; (3) for each (4) ${\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_i} = ({\rm{tim}}{{\rm{e}}_i},{\rm{IPpr}}{{\rm{o}}_i},{\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_i},{\rm{clas}}{{\rm{s}}_i})$; (5) if ${\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_i} = {\rm{IP}}{'_i}$, set ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_i} = 1$; (6) DO { APA(i); // 对节点i 执行前件推断算法; (7) ${\rm{CPA}}(i)$ //对节点i执行后件预测算法 }
(8) if ${\rm{I}}{{\rm{P}}_j} \notin \bigcup\limits_{{\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_i} \in {\rm{AL}}} {{\rm{IPpos}}{{\rm{t}}_i}} $;(9) { ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_j} = \sum\limits_{{\rm{a}}{{\rm{l}}_k} \in {\rm{AL}}} {{\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_k}}$; //计算产生告警节点推断未产生告警的节点的推断强度; (10) if ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_j} > 1$, let ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_j} = 1$;} //表示将推强度大于1的值确定为1; (11) else (12) set ${\rm{d}}{{\rm{i}}_i} = 1$; (13) return DI 表 4 系统漏洞、协议关系表
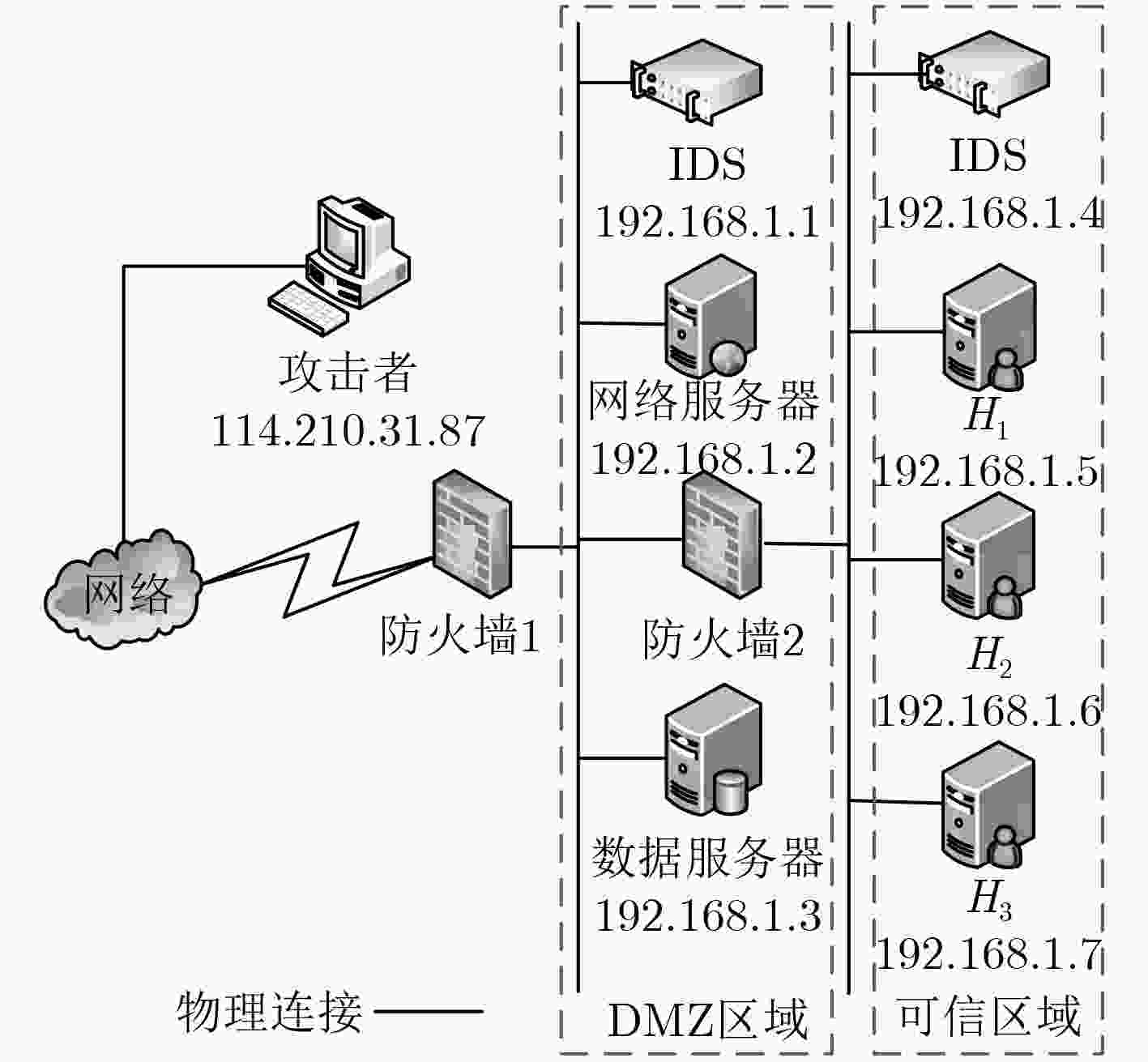
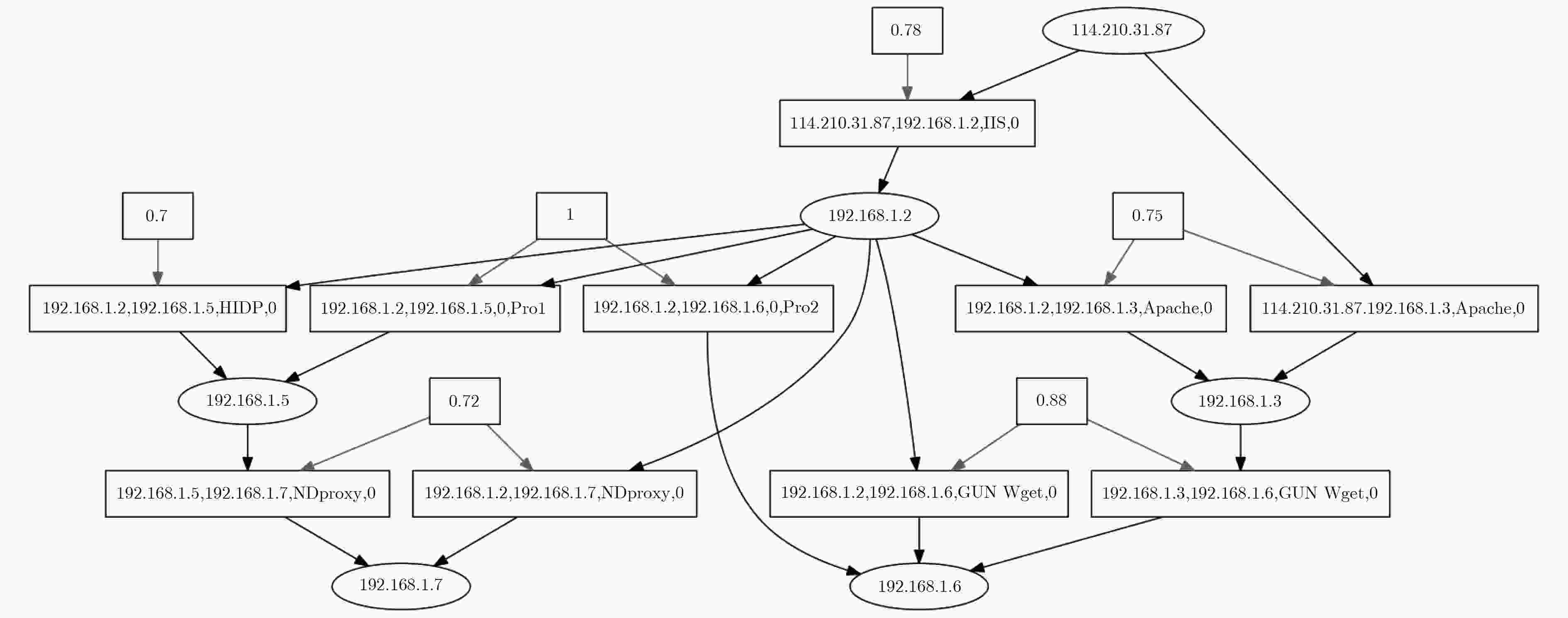
Host/Server Protocol/Vulnerability Port Web Protocol with H1&H2 /IIS 445&80 Data Apache 80 H1 Protocol with Web /HIDP 445 H2 Protocol with Web/GUN Wget 80 H3 NDproxy 445 表 5 漏洞信息表
Vul. CVE Num. Vul. Risklevel IIS CVE-2015-7597 7.8 Apache CVE-2018-8015 7.5 HIDP CVE-2018-8169 7.0 GUN Wget CVE-2016-4971 8.8 NDproxy CVE-2013-5065 7.2 -
韦勇. 网络安全态势评估模型研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2009.WEI Yong. Research on network security situational awareness model[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2009. 梅海彬, 龚俭, 张明华. 基于警报序列聚类的多步攻击模式发现研究[J]. 通信学报, 2011, 32(5): 63–69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2011.05.009MEI Haibin, GONG Jian, and ZHANG Minghua. Research on discovering multi-step attack patterns based on clustering IDS alert sequences[J]. Journal on Communications, 2011, 32(5): 63–69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2011.05.009 PHILLIPS C and SWILER L P. A graph-based system for network-vulnerability analysis[C]. The 1998 Workshop on New Security Paradigms, Charlottesville, USA, 1998: 71–79. SWILER L P, PHILLIPS C, ELLIS D, et al. Computer-attack graph generation tool[C]. The 2nd DARPA Information Survivability Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, USA, 2001: 307–321. 王会梅, 鲜明, 王国玉. 基于扩展网络攻击图的网络攻击策略生成算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(12): 3015–3021. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00414WANG Huimei, XIAN Ming, and WANG Guoyu. A network attack decision-making algorithm based on the extended attack graph[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(12): 3015–3021. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00414 苏婷婷, 潘晓中, 肖海燕, 等. 基于属性邻接矩阵的攻击图表示方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(7): 1744–1747. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00261SU Tingting, PAN Xiaozhong, XIAO Haiyan, et al. Research on attack graph based on attributes adjacncy matrix[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(7): 1744–1747. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00261 黄永洪, 吴一凡, 杨豪璞, 等. 基于攻击图的APT脆弱节点评估方法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 29(4): 535–541. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2017.04.017HUANG Yonghong, WU Yifan, YANG Haopu, et al. Graph-based vulnerability assessment for APT attack[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2017, 29(4): 535–541. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2017.04.017 叶子维, 郭渊博, 王宸东, 等. 攻击图技术应用研究综述[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(11): 121–132. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017213YE Ziwei, GUO Yuanbo, WANG Chendong, et al. Survey on application of attack graph technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(11): 121–132. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017213 HU Hao, LIU Yulin, ZHANG Hongqi, et al. Security metric methods for network multistep attacks using AMC and big data correlation analysis[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2018, 2018: 5787102. doi: 10.1155/2018/5787102 WANG Huan, CHEN Zhanfang, ZHAO Jianping, et al. A vulnerability assessment method in industrial internet of things based on attack graph and maximum flow[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 8599–8609. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2805690 胡浩, 叶润国, 张红旗, 等. 面向漏洞生命周期的安全风险度量方法[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(5): 1213–1229. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005507HU Hao, YE Runguo, ZHANG Hongqi, et al. Vulnerability life cycle oriented security risk metric method[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(5): 1213–1229. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005507 WANG Lingyu, LIU Anyi, and JAJODIA S. Using attack craphs for correlating, hypothesizing, and predicting intrusion alerts[J]. Computer Communications, 2006, 29(15): 2917–2933. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2006.04.001 ROSCHKE S, CHENG F, and MEINEL C. A New Alert Correlation Algorithm Based on Attack Graph[M]. HERRERO Á, CORCHADO E. Computational Intelligence in Security for Information Systems. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2011: 58–67. ROSCHKE S, CHENG F, and MEINEL C. High-quality attack graph-based IDS correlation[J]. Logic Journal of the IGPL, 2013, 21(4): 571–591. doi: 10.1093/jigpal/jzs034 AHMADINEJAD S H, JALILI S, and ABADI M. A hybrid model for correlating alerts of known and unknown attack scenarios and updating attack graphs[J]. Computer Networks, 2011, 55(9): 2221–2240. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2011.03.005 吕慧颖, 彭武, 王瑞梅, 等. 基于时空关联分析的网络实时威胁识别与评估[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2014, 51(5): 1039–1049. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2014.20120816Huiying, PENG Wu, WANG Ruimei, et al. A real-time network threat recognition and assessment method based on association analysis of time and space[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2014, 51(5): 1039–1049. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2014.20120816 刘威歆, 郑康锋, 武斌, 等. 基于攻击图的多源告警关联分析方法[J]. 通信学报, 2015, 36(9): 135–144. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015193LIU Weixin, ZHENG Kangfeng, WU Bin, et al. Alert processing based on attack graph and multi-source analyzing[J]. Journal on Communications, 2015, 36(9): 135–144. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2015193 王硕, 汤光明, 寇广, 等. 基于因果知识网络的攻击路径预测方法[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(10): 188–198. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016210WANG Shuo, TANG Guangming, KOU Guang, et al. Attack path prediction method based on causal knowledge net[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(10): 188–198. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016210 LIANG Wei, CHEN Zuo, YAN Xiaolong, et al. Multiscale entropy-based weighted hidden Markov network security situation prediction model[C]. 2017 IEEE International Congress on Internet Of Things (ICIOT), Honolulu, USA 2017: 97–104. CVE. Common vulnerabilities and exposures[EB/OL]. http://cve.mitre.org/, 2018. NIST. National vulnerability database[EB/OL]. https://nvd.nist.gov/, 2018. CVSS v3.0: specification document[EB/OL]. -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
