Facial Expression Recognition Method Based on Multi-scale Detail Enhancement
-
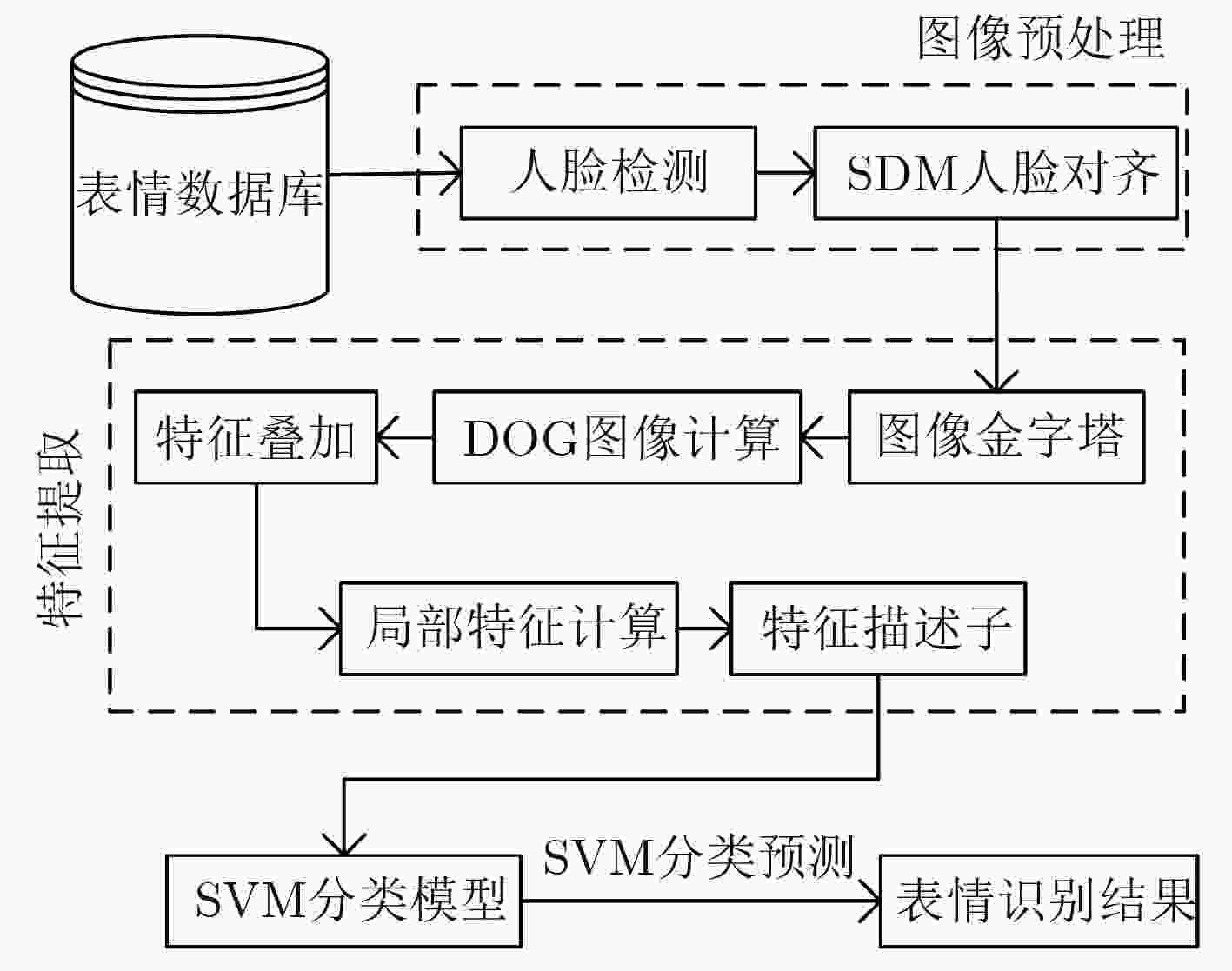
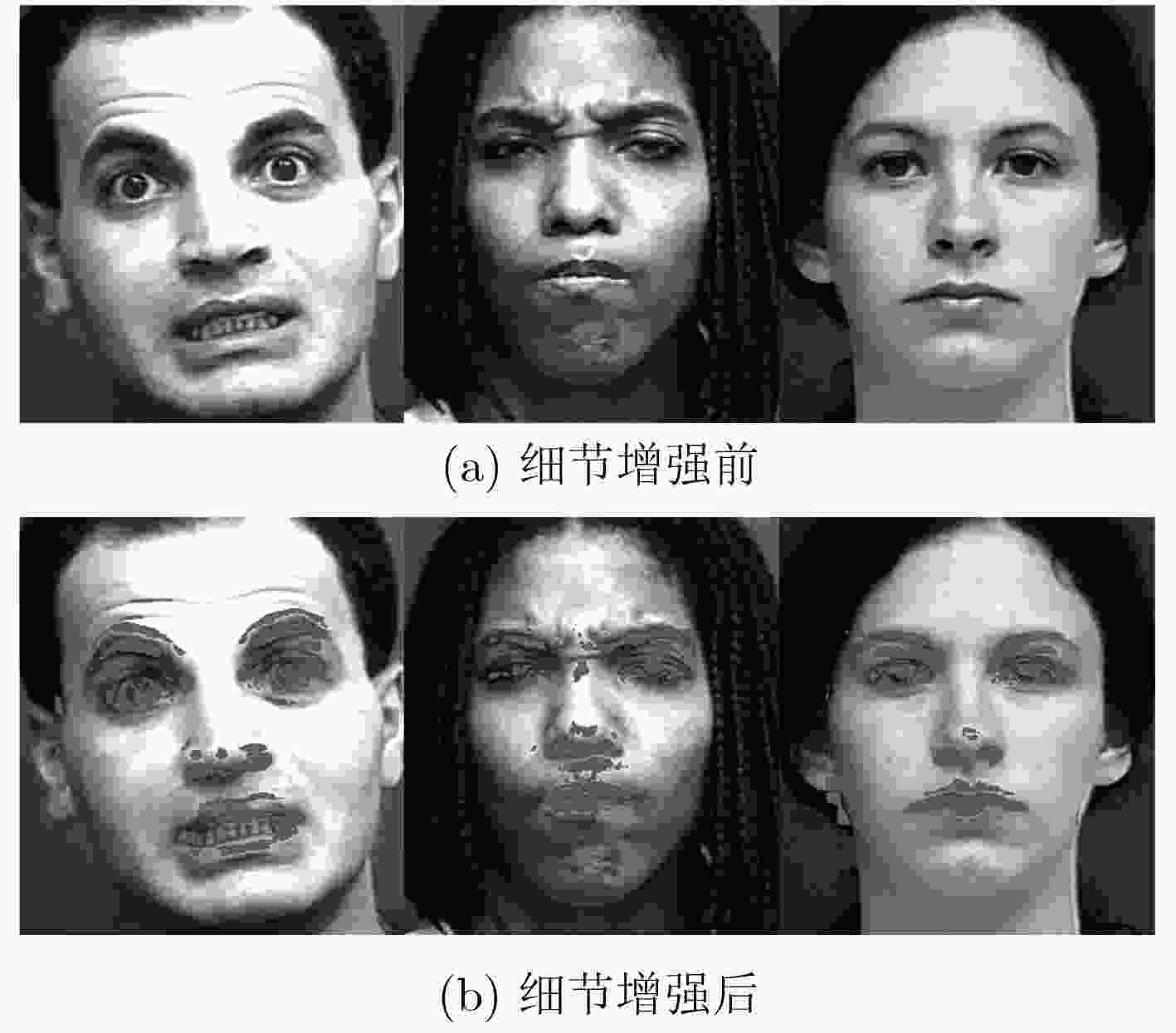
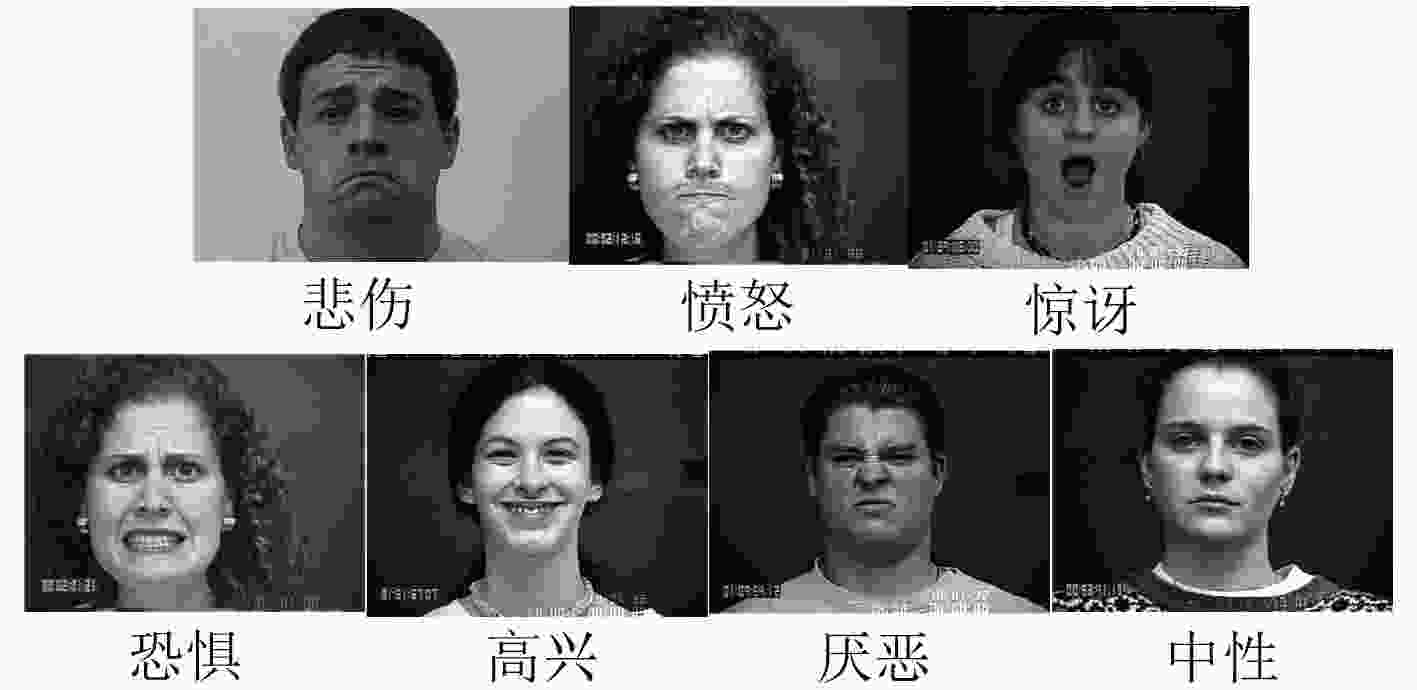
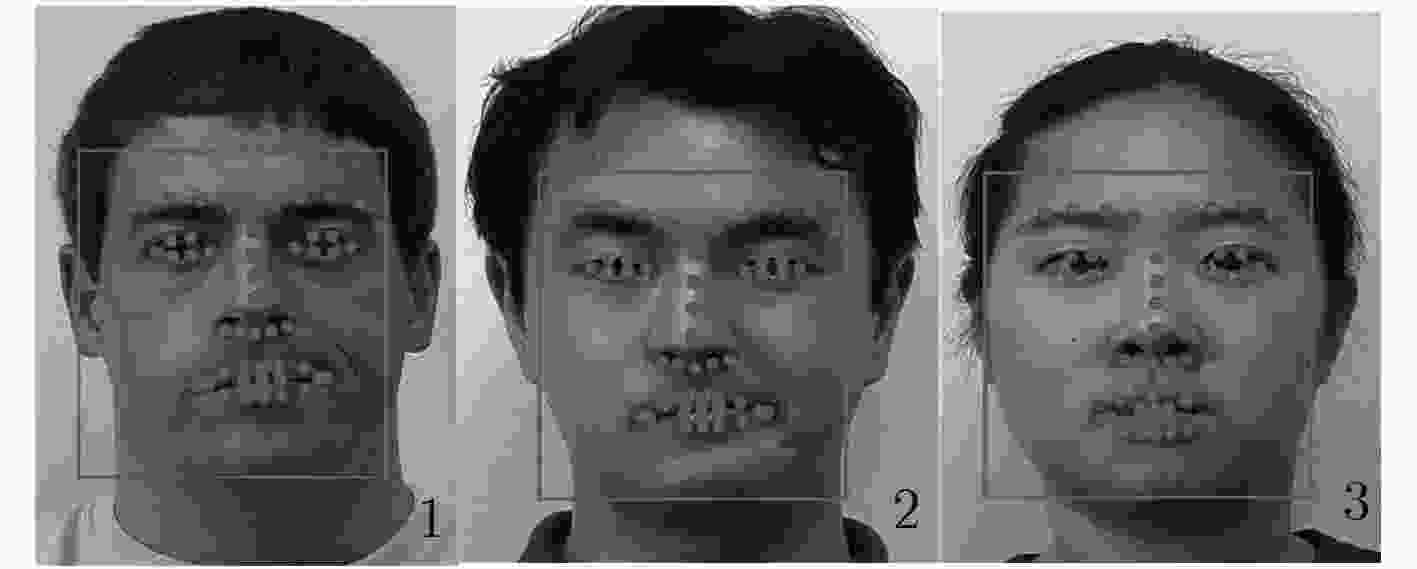
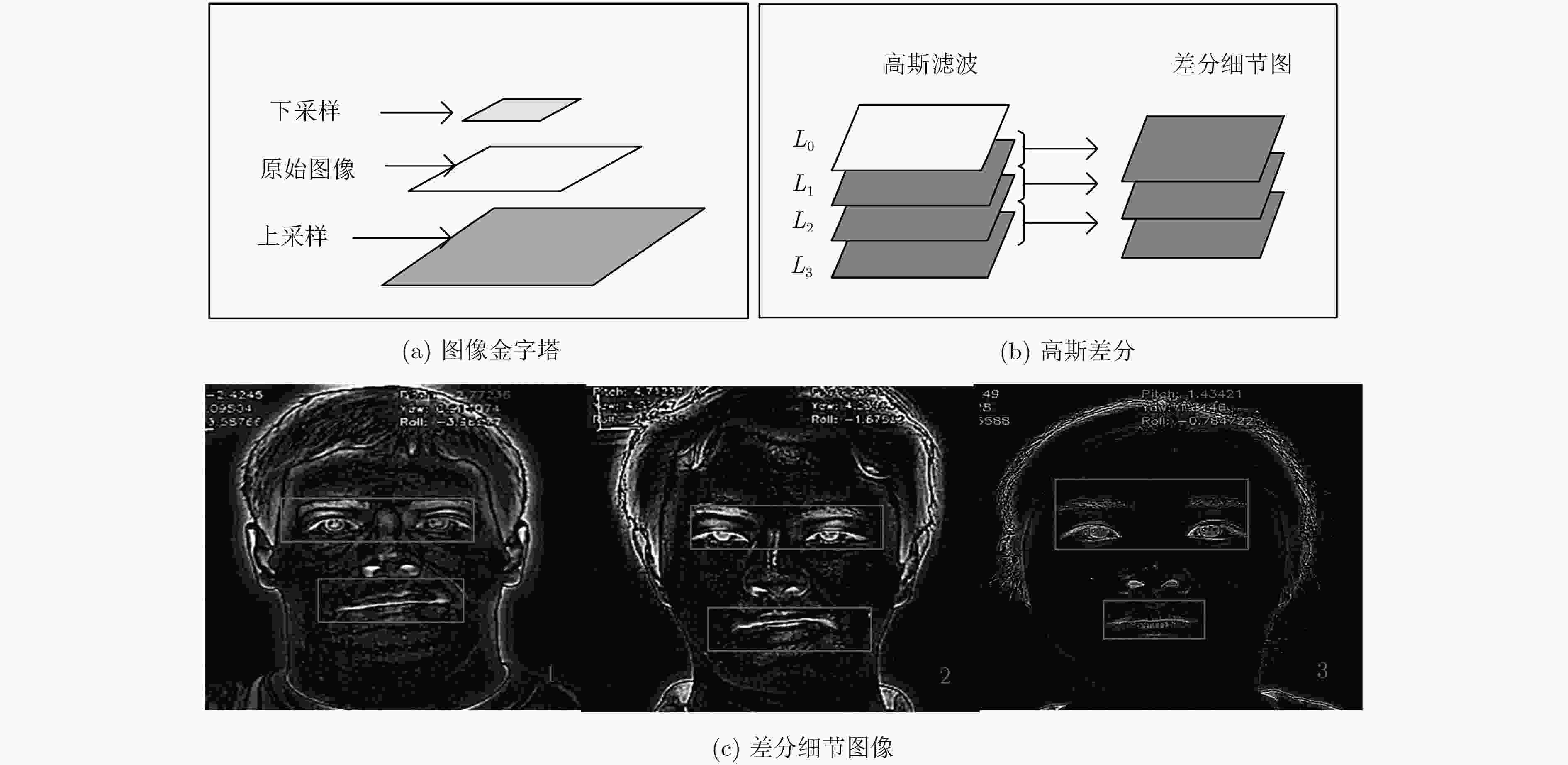
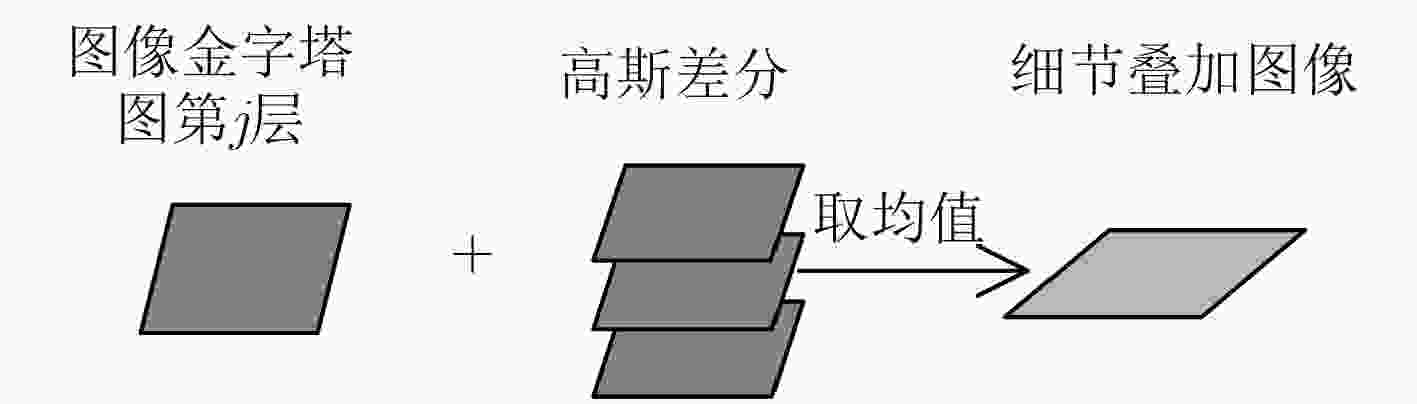
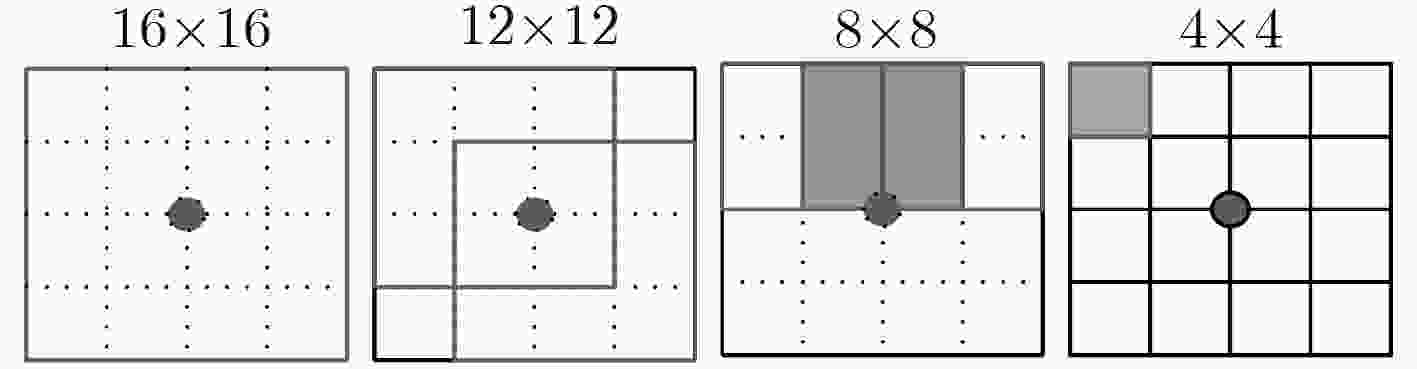
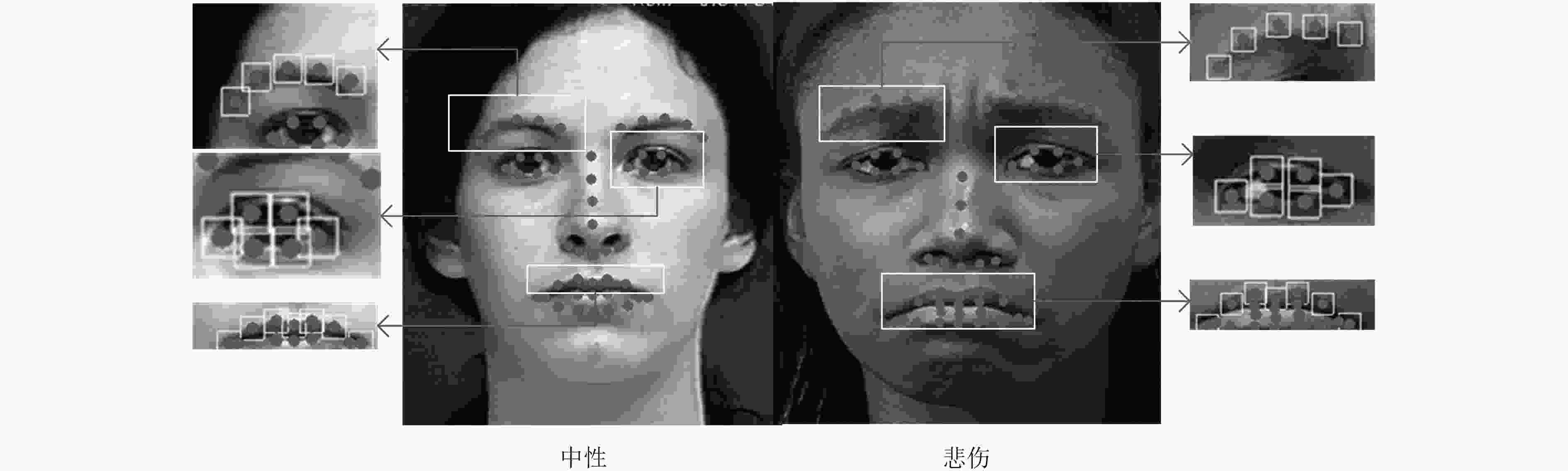
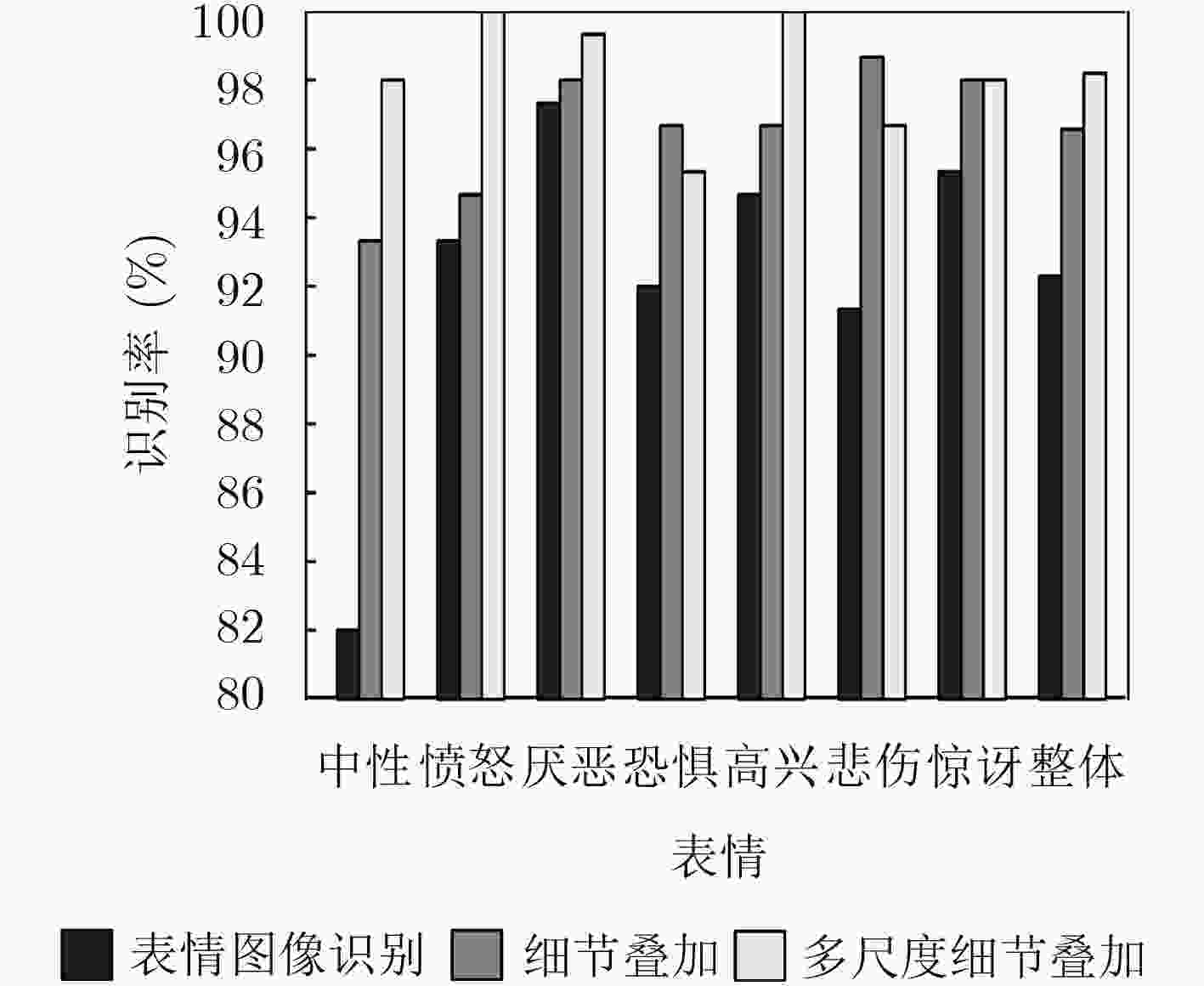
摘要: 人类面部表情是其心理情绪变化的最直观刻画,不同人的面部表情具有很大差异,现有表情识别方法均利用面部统计特征区分不同表情,其缺乏对于人脸细节信息的深度挖掘。根据心理学家对面部行为编码的定义可以看出,人脸的局部细节信息决定了其表情意义。因此该文提出一种基于多尺度细节增强的面部表情识别方法,针对面部表情受图像细节影响较大的特点,提出利用高斯金字塔提取图像细节信息,并对图像进行细节增强,从而强化人脸表情信息。针对面部表情的局部性特点,提出利用层次结构的局部梯度特征计算方法,描述面部特征点局部形状特征。最后,使用支持向量机(SVM)对面部表情进行分类。该文在CK+表情数据库中的实验结果表明,该方法不仅验证了图像细节对面部表情识别过程的重要作用,而且在小规模训练数据下也能够得到非常好的识别结果,表情平均识别率达到98.19%。Abstract: Facial expression is the most intuitive description of changes in psychological emotions, and different people have great differences in facial expressions. The existing facial expression recognition methods use facial statistical features to distinguish among different expressions, but these methods are short of deep exploration for facial detail information. According to the definition of facial behavior coding by psychologists, it can be seen that the local detail information of the face determines the meaning of facial expression. Therefore, a facial expression recognition method based on multi-scale detail enhancement is proposed, because facial expression is much more affected by the image details than other information, the method proposed in this paper extracts the image detail information with the Gaussian pyramid firstly, thus the image is enhanced in detail to enrich the facial expression information. Secondly, for the local characteristics of facial expressions, a local gradient feature calculation method is proposed based on hierarchical structure to describe the local shape features of facial feature points. Finally, facial expressions are classified using a Support Vector Machine (SVM). The experimental results in the CK+ expression database show that the method not only proves the important role of image detail in facial expression recognition, but also obtains very good recognition results under small-scale training data. The average recognition rate of expressions reaches 98.19%.
-
表 1 高斯模糊半径取值的最优识别率(%)
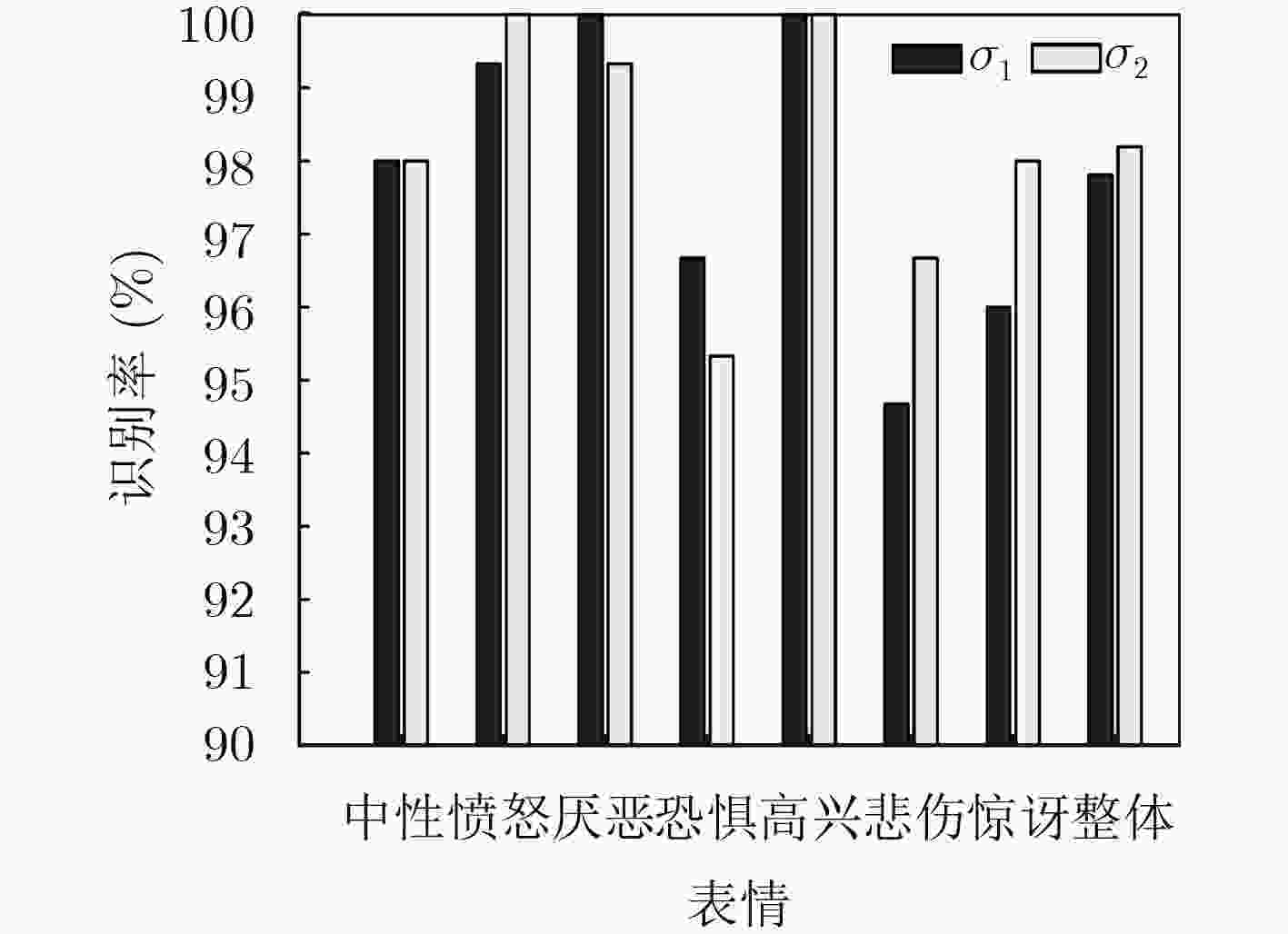
高斯核 中性 愤怒 厌恶 恐惧 微笑 悲伤 惊讶 整体 K1 98.00 99.33 100 96.67 100 94.67 96.00 97.81 K2 96.00 98.67 100 95.33 100 96.67 98.00 97.81 表 2 表情识别率分布表(%)
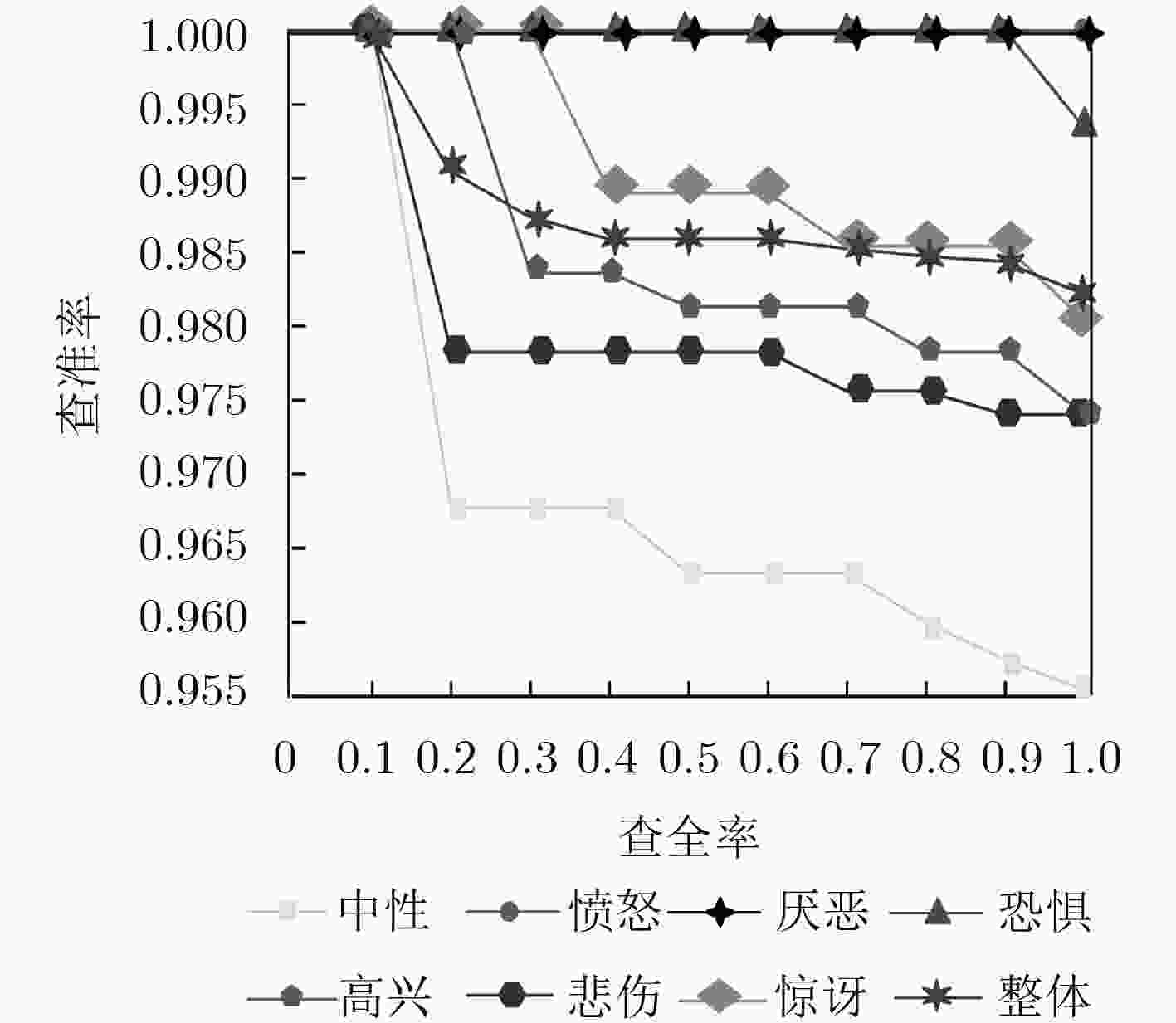
中性 愤怒 厌恶 恐惧 高兴 悲伤 惊讶 中性 98.00 0 0 0 0 2.00 0 愤怒 0 100.00 0 0 0 0 0 厌恶 0 0 99.33 0 0 0.67 0 恐惧 0 0 0 95.33 2.67 0 2.00 高兴 0 0 0 0 100 0 0 悲伤 3.33 0 0 0 0 96.67 0 惊讶 1.33 0 0 0.67 0 0 98.00 表 3 本文方法与CNN与LeNet-5方法比较(%)
-
MEHRABIAN A. Communication without words[J]. Psychology Today, 1968, 2(4): 53–56. GUO Zhenhua, ZHANG Lei, and ZHANG D. A completed modeling of local binary pattern operator for texture classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(6): 1657–1663. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2044957 王玮, 黄非非, 李见为, 等. 采用LBP金字塔的人脸描述与识别[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2009, 21(1): 94–100, 106.WANG Wei, HUANG Feifei, LI Jianwei, et al. Face description and recognition by LBP pyramid[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2009, 21(1): 94–100, 106. 钟思志. 人脸面部表情识别算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华东师范大学, 2015.ZHONG Sizhi. Research on facial expression recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], East China Normal University, 2015. 杨凡, 张磊. 基于Gabor参数矩阵与改进Adaboost的人脸表情识别[J]. 计算机应用, 2014, 34(4): 1134–1138.YANG Fan and ZHANG Lei. Facial expression recognition based on Gabor parameters matrix and improved Adaboost[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2014, 34(4): 1134–1138. 童莹. 基于空间多尺度HOG特征的人脸表情识别方法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2014, 35(11): 3918–3922, 3979. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2014.11.041TONG Ying. Facial expression recognition algorithm based on spatial multi-scaled HOG feature[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2014, 35(11): 3918–3922, 3979. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2014.11.041 TURAN C and LAM K M. Region-based feature fusion for facial-expression recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 2014: 5966–5970. SAEED A, AL-HAMADI A, and NIESE R. The effectiveness of using geometrical features for facial expression recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2013: 122–127. CHEN Junkai, CHEN Zenghai, CHI Zheru, et al. Facial expression recognition in video with multiple feature fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2018, 9(1): 38–50. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2016.2593719 任福继, 于曼丽, 胡敏, 等. 融合表情和BVP生理信号的双模态视频情感识别[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(5): 688–697.REN Fuji, YU Manli, HU Min, et al. Dual-modality video emotion recognition based on facial expression and BVP physiological signal[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(5): 688–697. LOPES A T, DE AGUIAR E, DE SOUZA A F, et al. Facial expression recognition with convolutional neural networks: Coping with few data and the training sample order[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 610–628. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.026 ZHANG Chongsheng, WANG Pengyou, CHEN Ke, et al. Identity-aware convolutional neural networks for facial expression recognition[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28(4): 784–792. LUCEY P, COHN J F, KANADE T, et al. The extended cohn-kanade dataset (CK+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression[C]. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 94–101. YAO Yongqiang, HUANG Di, YANG Xudong, et al. Texture and geometry scattering representation-based facial expression recognition in 2D+3D videos[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2018, 14(1S): 18. 李勇, 林小竹, 蒋梦莹. 基于跨连接LeNet-5网络的面部表情识别[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(1): 176–182.LI Yong, LIN Xiaozhu, and JIANG Mengying. Facial expression recognition with cross-connect LeNet-5 network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(1): 176–182. JIA Qi, GAO Xinkai, GUO He, et al. Multi-layer sparse representation for weighted LBP-patches based facial expression recognition[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(3): 6719–6739. doi: 10.3390/s150306719 ZHOU Jun, ZHANG Sue, MEI Hongyan, et al. A method of facial expression recognition based on Gabor and NMF[J]. Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 2016, 26(1): 119–124. doi: 10.1134/S1054661815040070 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
