Traffic Flow Prediction Based on Hybrid Model of Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average and Genetic Particle Swarm Optimization Wavelet Neural Network
-
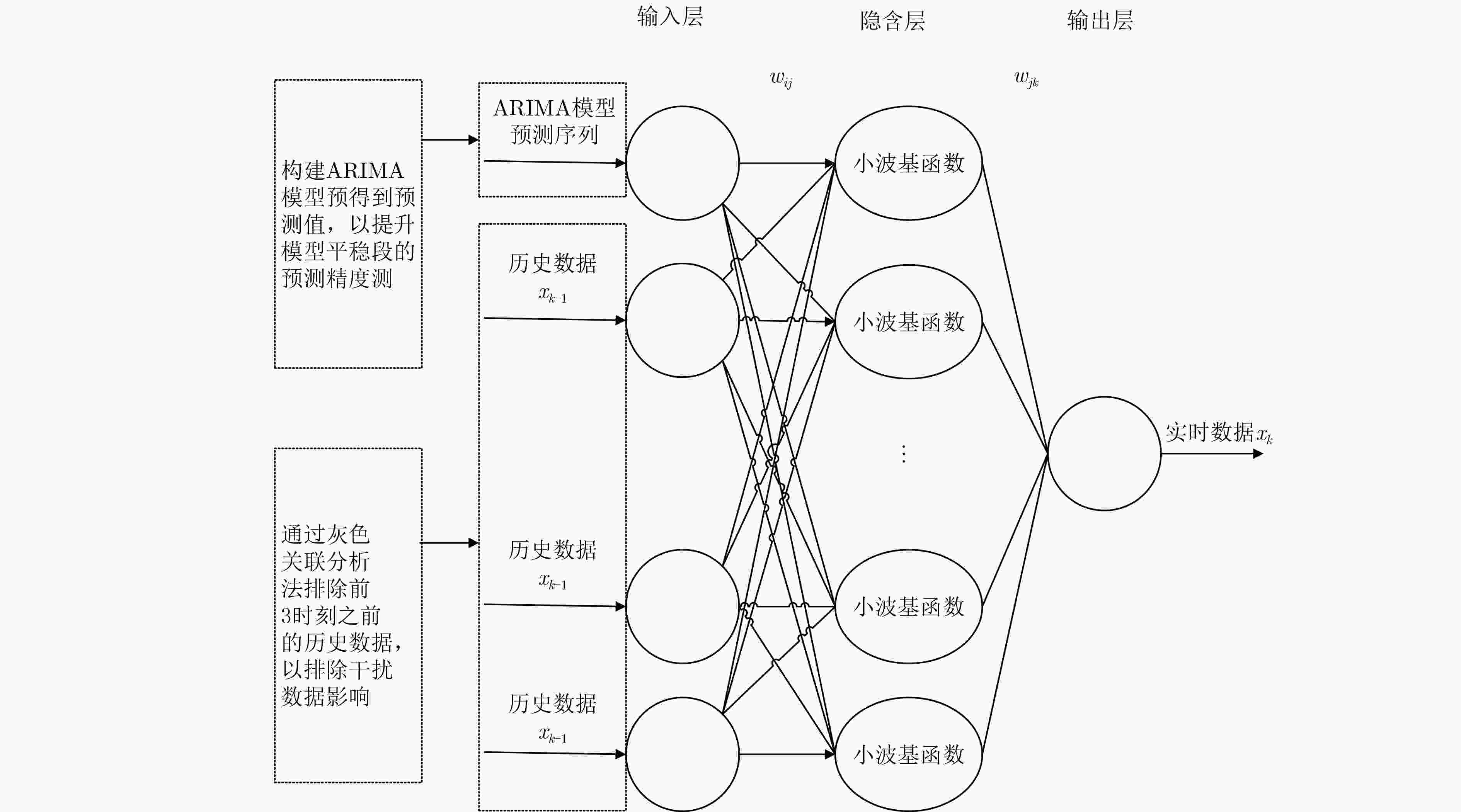
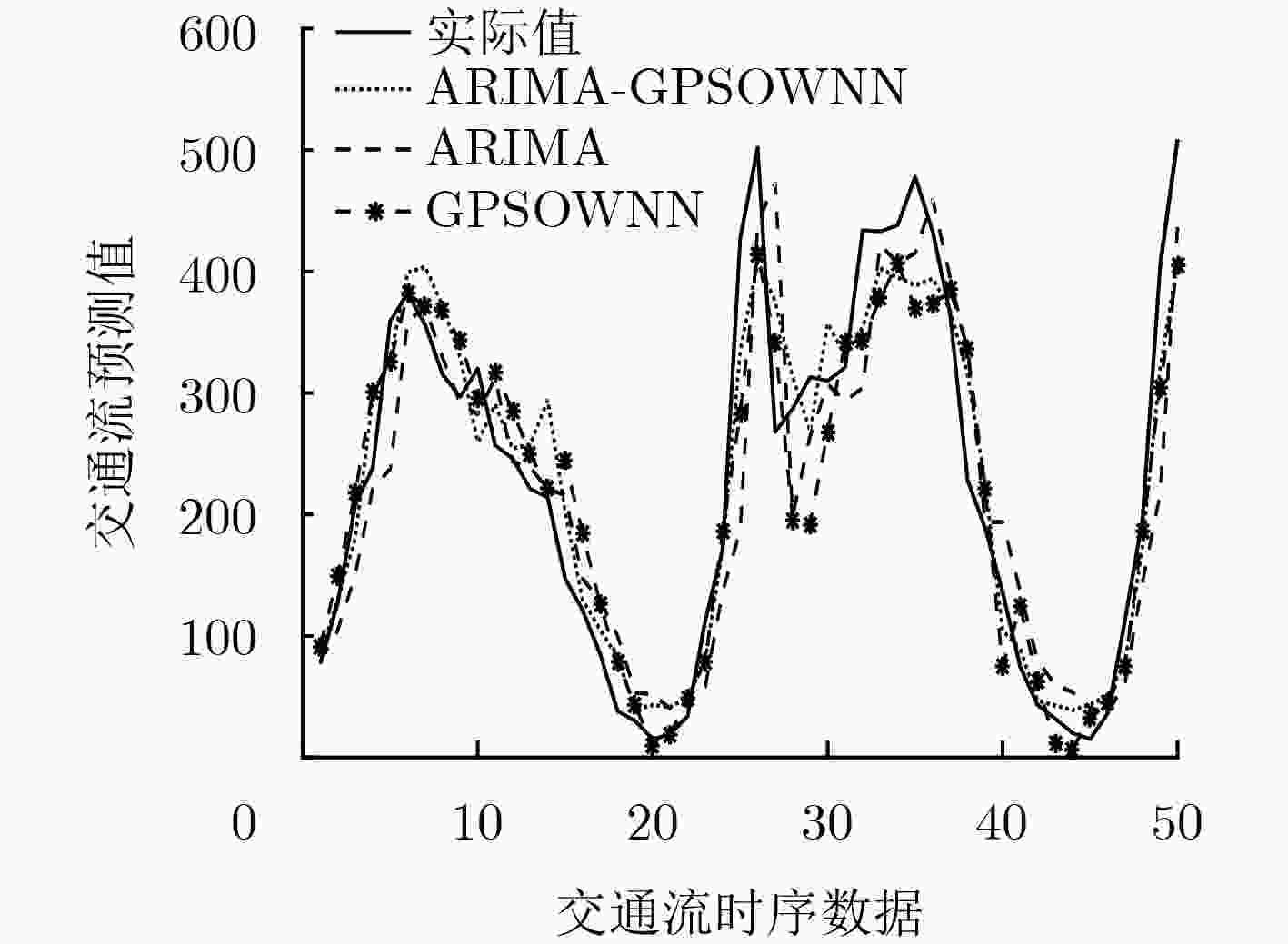
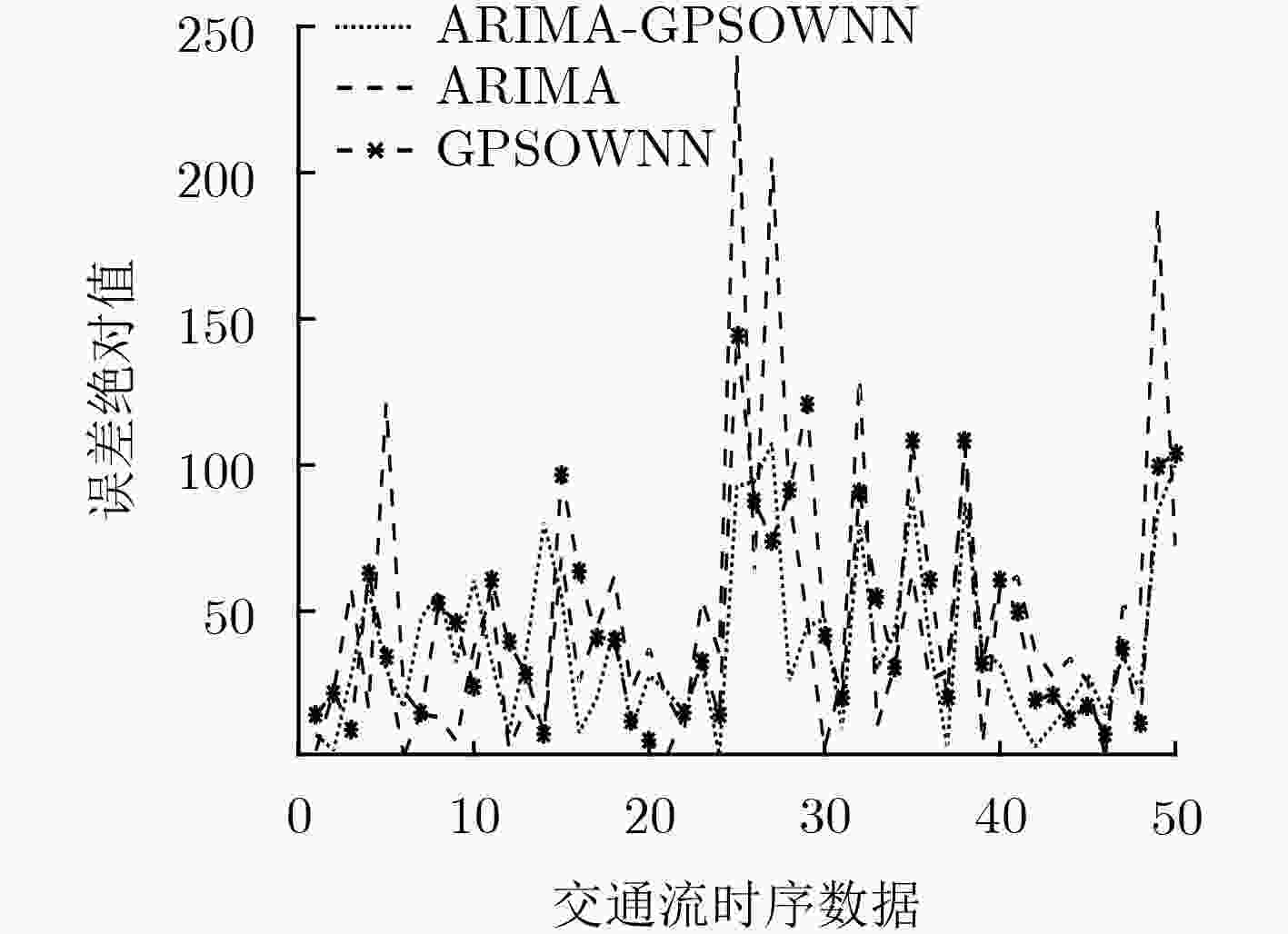
摘要: 针对短时交通流数据的非线性和随机性特点,为提高它的预测精度和收敛速度,该文从模型构建和算法两方面提出一种整合移动平均自回归(ARIMA)模型和遗传粒子群算法优化小波神经网络(GPSOWNN)相结合的预测模型和算法。在模型构建方面,将ARIMA模型预测值和灰色关联系数大于0.6的相关性强的前3个时刻的历史数据作为小波神经网络(WNN)的输入,在兼顾历史数据的平稳和非平稳的情况下,进行了模型结构简化。在算法方面,通过遗传粒子群算法对小波神经网络的参数初始值进行最优选取,可使其结果在不易陷入局部最优的条件下加快网络训练收敛速度。实验结果表明,在预测精度方面,该方法的模型明显优于整合移动平均自回归模型和遗传粒子群算法优化小波神经网络,在收敛速度方面,用遗传粒子群算法优化模型明显优于仅用遗传算法优化模型。
-
关键词:
- 短时交通流预测 /
- 灰色关联分析法 /
- 整合移动平均自回归 /
- 遗传粒子群优化小波神经网络
Abstract: In view of the nonlinear and stochastic characteristics of short-term traffic flow data, this article proposes a prediction model and algorithm based on hybrid Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Genetic Particle Swarm Optimization Wavelet Neural Network (GPSOWNN) in order to improve its prediction accuracy and rate of convergence. In terms of model construction, the ARIMA model prediction value and the historical data of the first three moments with strong correlation with gray correlation coefficient greater than 0.6 are used as input of the Wavelet Neural Network(WNN), and the structure of the model is simplified considering both the stationary and non-stationary historical data. In terms of algorithm, by using the genetic particle swarm optimization algorithm to select optimally the initial values of the wavelet neural network, the results can speed up the convergence of network training under the condition that it is not easy to fall into local optimum. The experimental results show that the proposed model is superior to hybrid ARIMA and GPSOWNN in terms of prediction accuracy, the genetic particle swarm optimization algorithm is superior to the genetic algorithm optimization model in terms of convergence speed. -
表 1 4组模型的AIC值
模型 AIC值 ARIMA(1, 1, 2) 7.210306 ARIMA(2, 1, 2) 7.426953 ARIMA(1, 1, 3) 7.250197 ARIMA(2, 1, 3) 7.509981 表 2 实时时刻与历史时刻的灰色关联系数
交通流历史时刻时间
序列${x_{k - i}}$ ($i$=1, 2, ···, 7)与${x_k}$的灰色关联系数 ${x_{k - 1}}$ 0.8271 ${x_{k - 2}}$ 0.8155 ${x_{k - 3}}$ 0.6546 ${x_{k - 4}}$ 0.5346 ${x_{k - 5}}$ 0.5146 ${x_{k - 6}}$ 0.5126 ${x_{k - 7}}$ 0.5453 表 3 3种模型的总标准误差
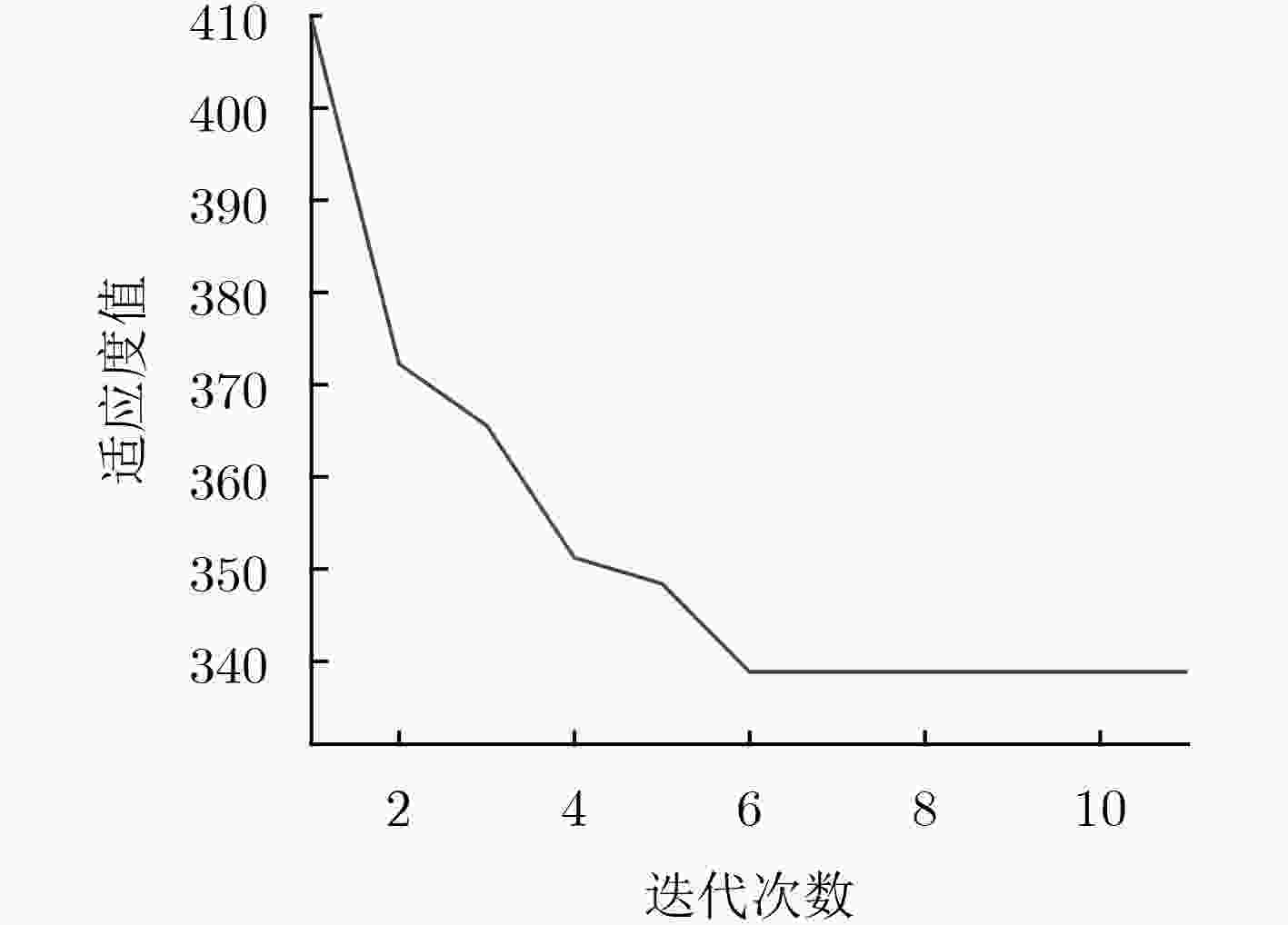
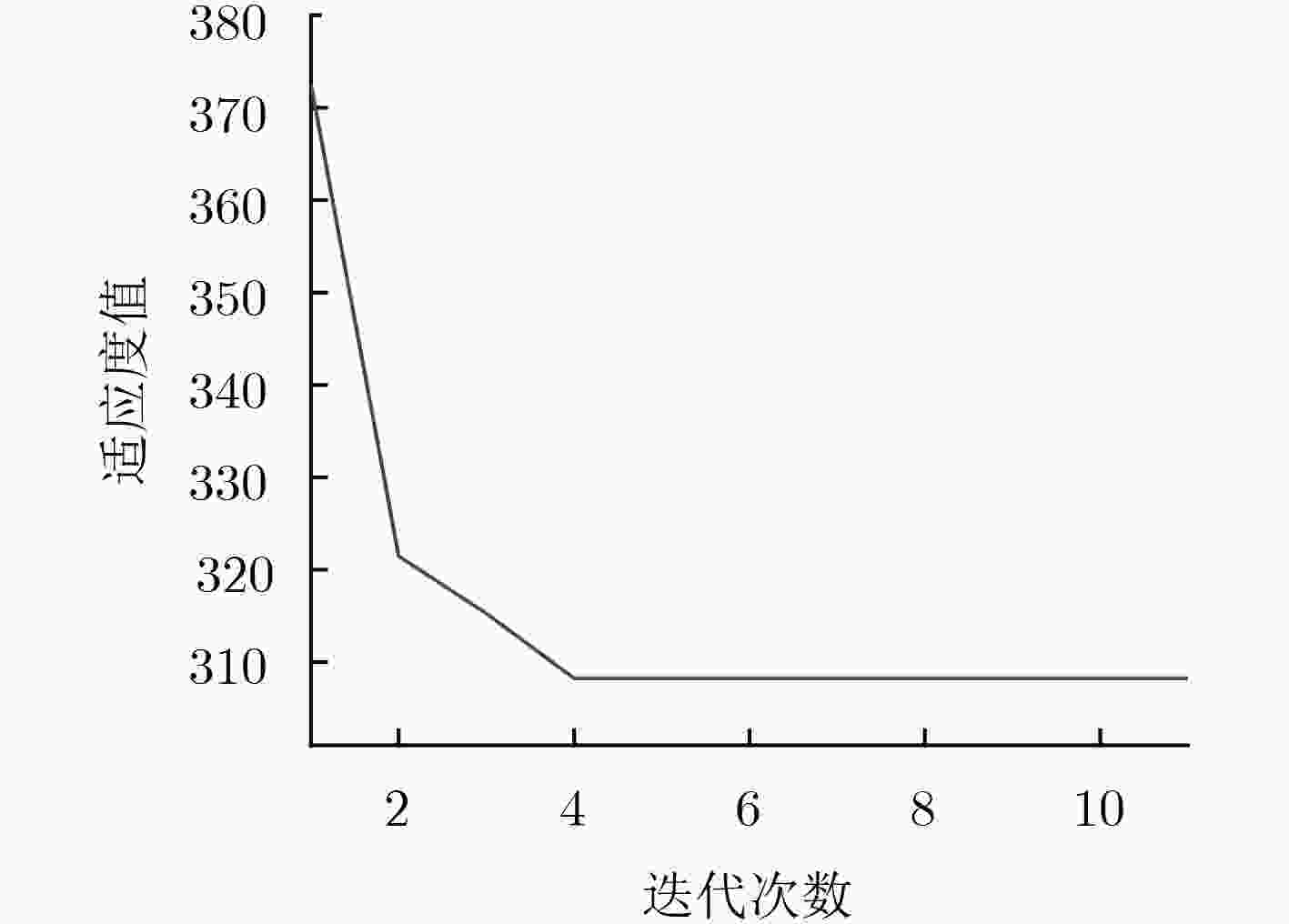
模型 总标准误差 GPSOWNN和ARIMA组合模型 294.5303 GPSOWNN模型 369.7026 ARIMA模型 459.0784 -
DARAGHMI Y A, YI C W, and CHIANG T C. Negative binomial additive models for short-term traffic flow forecasting in urban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(2): 784–793. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2287512 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国交通工程学术研究综述·2016[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(6): 1–161. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2016.06.001Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China’s traffic engineering research progress·2016[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(6): 1–161. doi: 10.19721/j.cnki.1001-7372.2016.06.001 TSELENTIS D I, VLAHOGIANNI E I, and KARLAFTIS M G. Improving short-term traffic forecasts: to combine models or not to combine?[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2014, 9(2): 193–201. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2013.0191 LIPPI M, BERTINI M, and FRASCONI P. Short-term traffic flow forecasting: An experimental comparison of time-series analysis and supervised learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(2): 871–882. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2013.2247040 李松, 刘力军, 解永乐. 遗传算法优化BP神经网络的短时交通流混沌预测[J]. 控制与决策, 2011, 26(10): 1581–1585. doi: 10.13195/j.cd.2011.10.144.lis.006LI Song, LIU Lijun, and XIE Yongle. Chaotic prediction for short-term traffic flow of optimized BP neural network based on genetic algorithm[J]. Control and Decision, 2011, 26(10): 1581–1585. doi: 10.13195/j.cd.2011.10.144.lis.006 谭满春, 冯荦斌, 徐建闽. 基于ARIMA与人工神经网络组合模型的交通流预测[J]. 中国公路学报, 2007, 20(4): 118–121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2007.04.021TAN Manchun, FENG Luobin, and XU Jianmin. Traffic flow prediction based on hybrid ARIMA and ANN model[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2007, 20(4): 118–121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2007.04.021 崔青华, 夏井新. 基于ARIMA-GARCH模型的城市主干道行程时间时变置信区间预测[J]. 东南大学学报 (英文版), 2014, 30(3): 358–362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2014.03.019CUI Qinghua and XIA Jinxin. Time-varying confidence interval forecasting of travel time for urban arterials using ARIMA-GARCH model[J]. Journal of Southeast University (English Edition) , 2014, 30(3): 358–362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2014.03.019 STOEAN R, STOEAN C, and SANDITA A. Evolutionary regressor selection in ARIMA model for stock price time s-eries forecasting[C]. International Conference on Intelligent Decision Technologies, Sorrento, Italy, 2017: 117–126. PAVLYUK D. Short-term traffic forecasting using multivariate autoregressive models[C]. Procedia Engineering, Riga, Latvia, 2017: 57–66. LUO Xianglong, NIU Liyao, and ZHANG Shengrui. An algorithm for traffic flow prediction based on improved SARIMA and GA[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2018, 22(10): 4107–4115. doi: 10.1007/s12205-018-0429-4 HU Wenbin, YAN Liping, LIU Kaizeng, et al. A short-term traffic flow forecasting method based on the hybrid PSO-SVR[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2016, 43(1): 155–172. doi: 10.1007/s11063-015-9409-6 ZHANG Hong, WANG Xiaoming, Cao Jie, et al. A multivariate short-term traffic flow forecasting method based on wavelet analysis and seasonal time series[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2018, 48(10): 3827–3838. doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-1181-7 HANG Yang, ZOU Yajie, WANG Zhouyu, et al. A hybrid method for short-term freeway travel time prediction based on wavelet neural network and markov chain[J]. Canadian Journ-al of Civil Engineering, 2018, 45(2): 77–86. doi: 10.1139/cjce-2017-0231 刘思峰, 蔡华, 杨英杰, 等. 灰色关联分析模型研究进展[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2013, 33(8): 2041–2046. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2013.08.018LIU Sifeng, CAI Hua, YANG Yingjie, et al. Advance in grey incidence analysis modelling[J]. Systems Engineering Theory and Practice, 2013, 33(8): 2041–2046. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2013.08.018 -





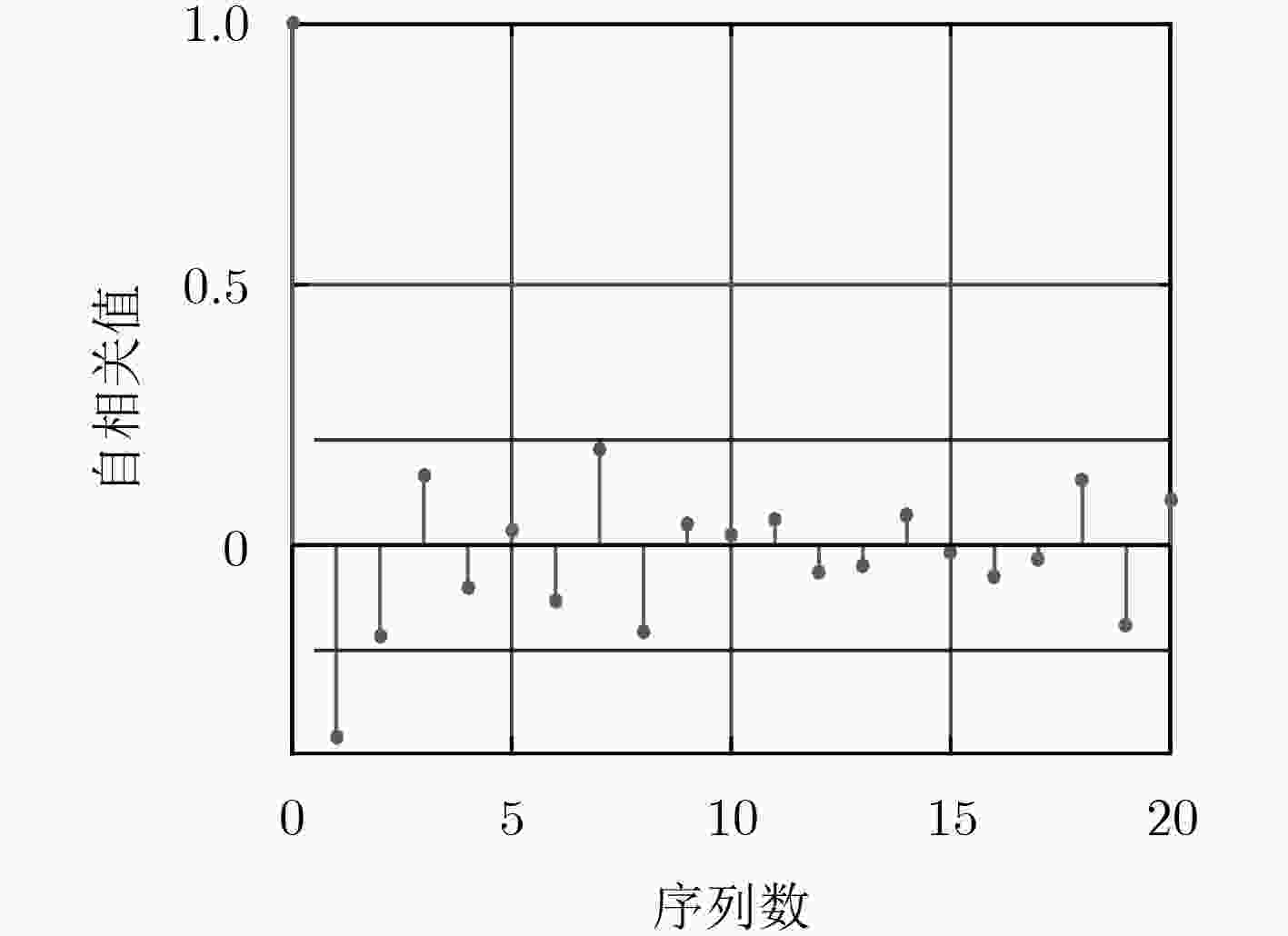
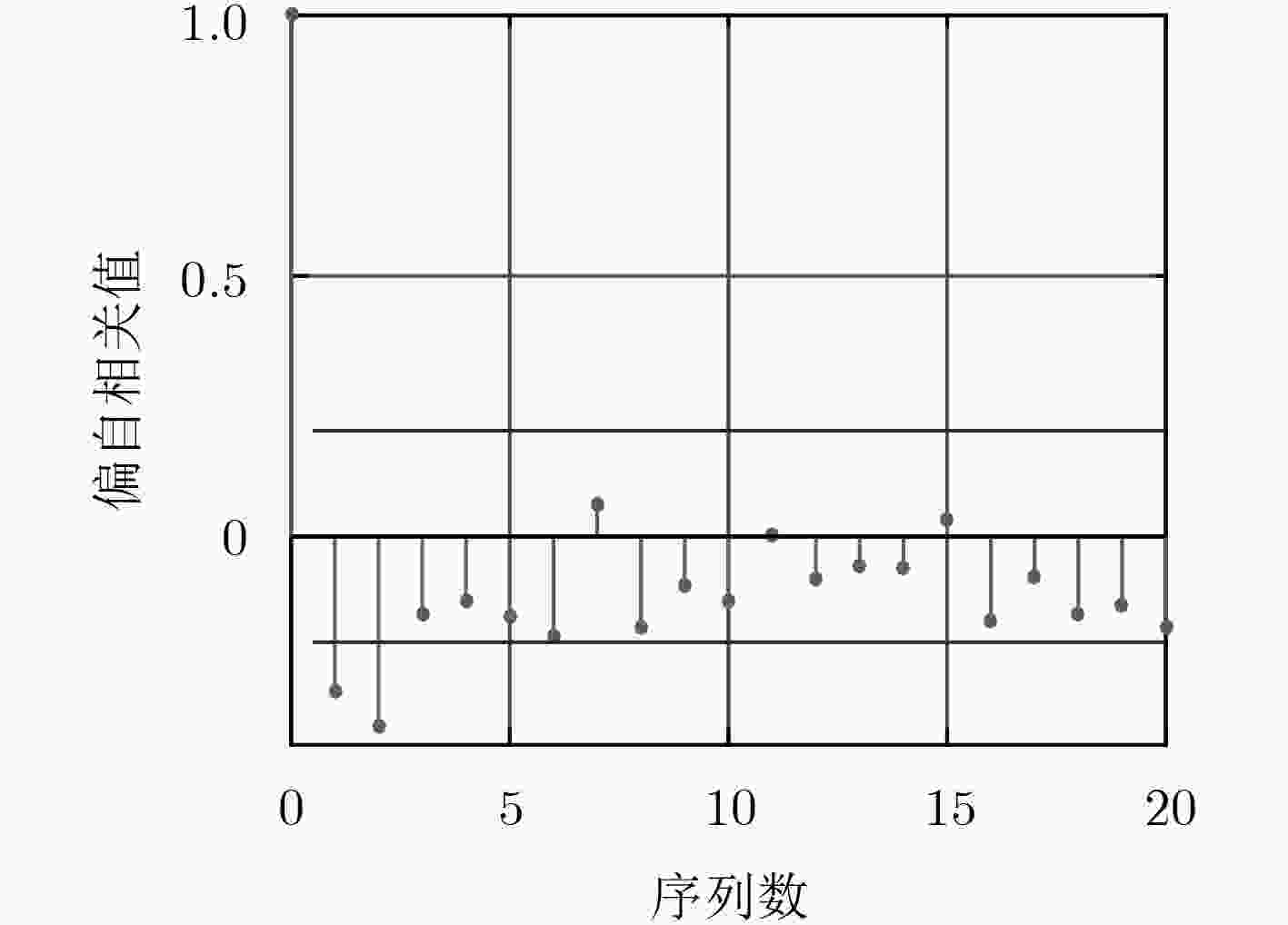
 下载:
下载:

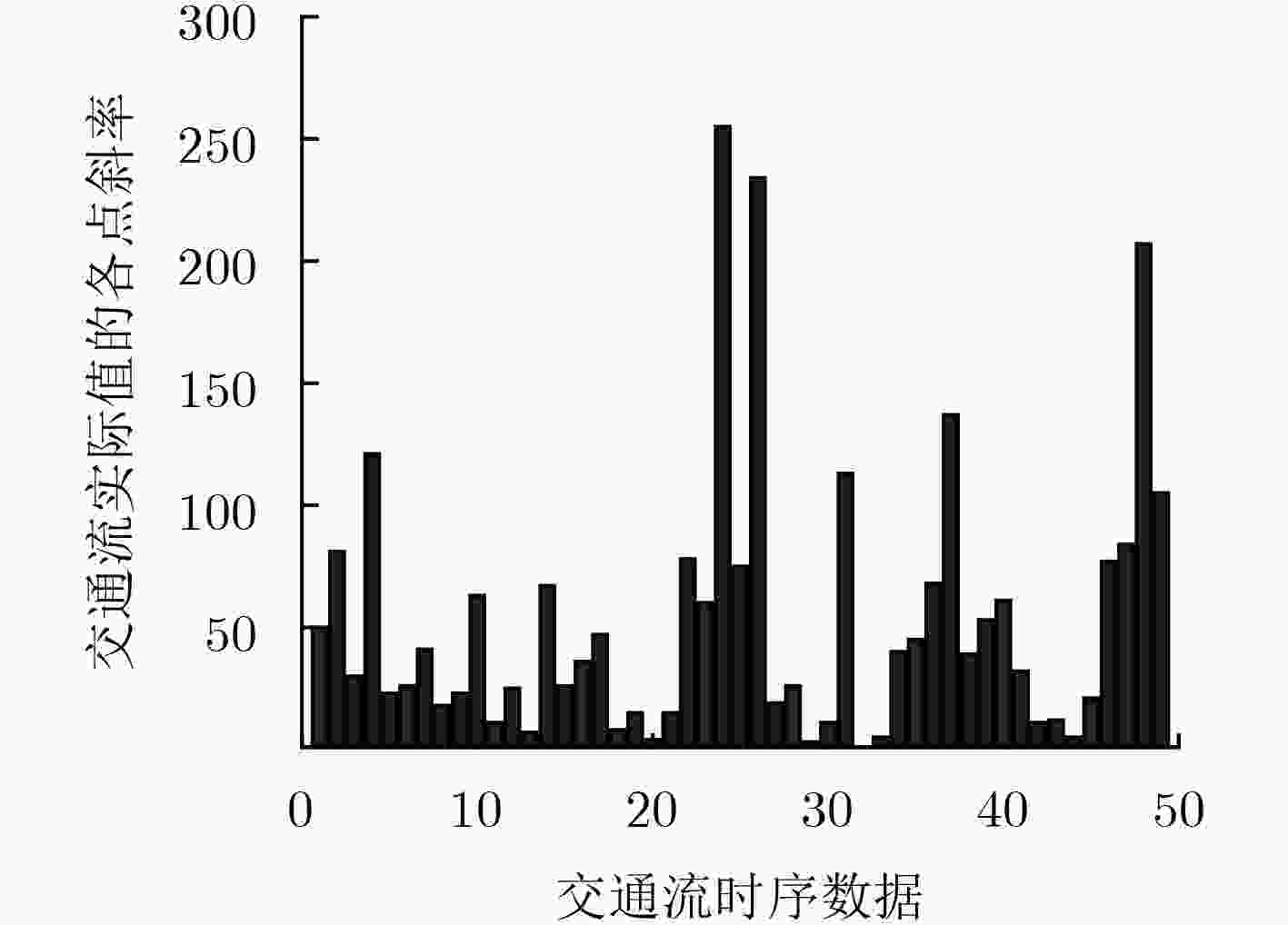
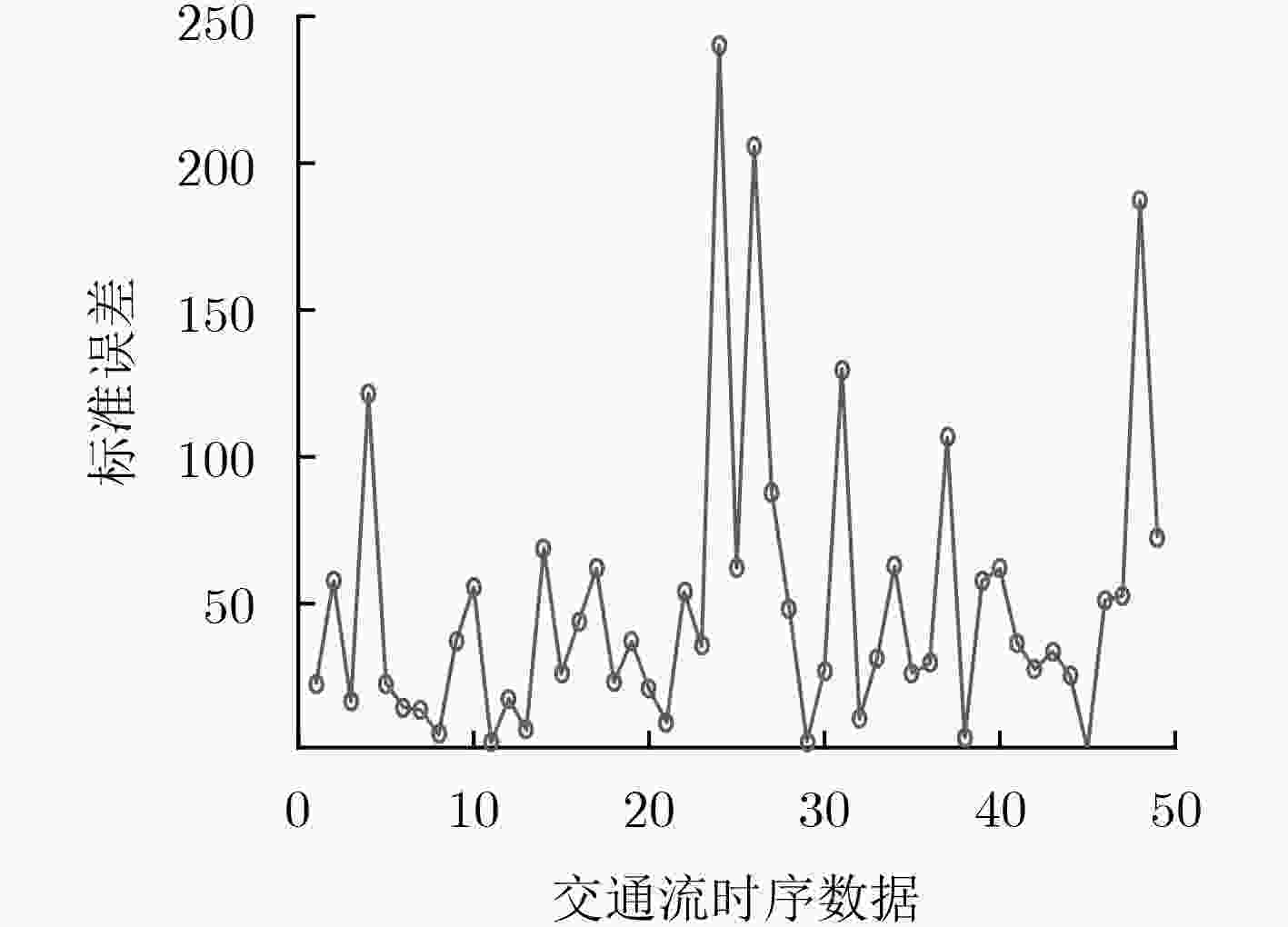


 下载:
下载:
