Adaptive Knowledge Transfer Based on Classification-error Consensus Regularization
-
摘要: 目前大多数迁移学习方法在利用源域数据辅助目标域数据建模时,通常假设源域中的数据均与目标域数据相关。然而在实际应用中,源域中的数据并非都与目标域数据的相关程度一致,若基于上述假设往往会导致负迁移效应。为此,该文首先提出分类误差一致性准则(CCR),对源域与目标域分类误差的概率分布积分平方误差进行最小化度量。此外,该文提出一种基于CCR的自适应知识迁移学习方法(CATL),该方法可以快速地从源域中自动确定出与目标域相关的数据及其权重,以辅助目标域模型的构建,使其能在提高知识迁移效率的同时缓解负迁移学习效应。在真实图像以及文本数据集上的实验结果验证了CATL方法的优势。Abstract: Most current transfer learning methods are modeled by utilizing the source data with the assumption that all data in the source domain are equally related to the target domain. In many practical applications, however, this assumption may induce negative learning effect when it becomes invalid. To tackle this issue, by minimizing the integrated squared error of the probability distribution of the source and target domain classification errors, the Classification-error Consensus Regularization (CCR) is proposed. Furthermore, CCR-based Adaptive knowledge Transfer Learning (CATL) method is developed to quickly determine the correlative source data and the corresponding weights. The proposed method can alleviate the negative transfer learning effect while improving the efficiency of knowledge transfer. The experimental results on the real image and text datasets validate the advantages of the CATL method.
-
表 1 图像数据集USPS及MNIST中源域数据与目标域数据的详细设置
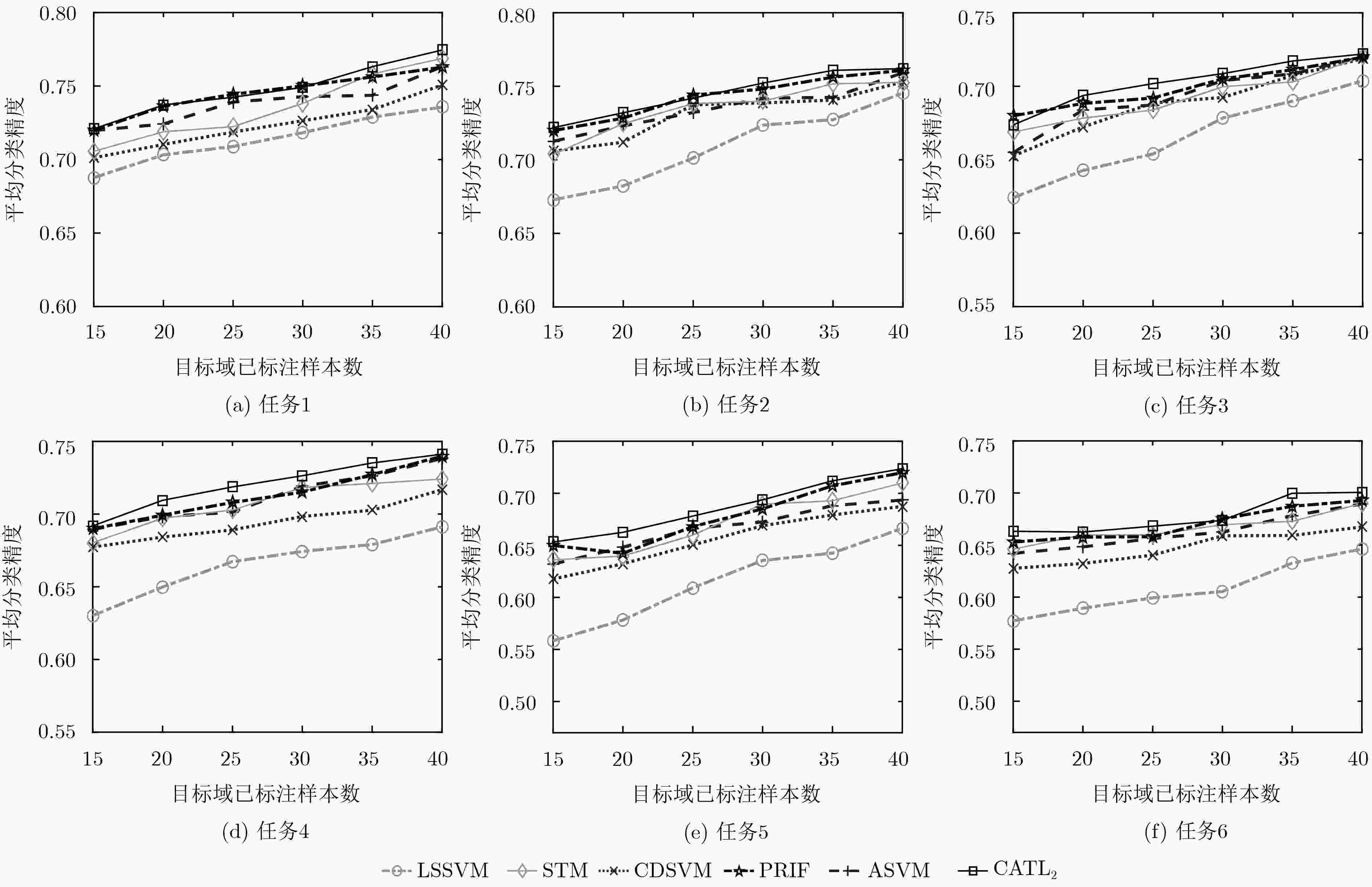
任务 源域数据 目标域数据 正类 负类 正类 负类 1 USPS7 USPS9 MNIST7 MNIST9 2 USPS4 USPS9 MNIST4 MNIST9 3 USPS0 USPS6 MNIST0 MNIST6 表 2 文本数据集20-Newsgroups中源域数据与目标域数据的详细设置
任务 源域数据 目标域数据 正类 负类 正类 负类 1 comp.graphics rec.autos comp.os.ms-windows.misc rec.motorcycles 2 comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware rec.sport.baseball comp.sys.mac.hardware rec.sport.hokey 3 sci.crypt talk.politics.guns sci.electronics talk.politics.mideast 4 sci.med talk.politics.misc sci.space talk.religion.misc 5 rec.autos talk.politics.guns rec.motorcycles talk.politics.mideast 6 rec.sport.baseball talk.politics.misc rec.sport.hokey talk.religion.misc 表 3 各种算法在图像任务上的分类精度
任务 已标注样本 LSSVM CDSVM ASVM TrAdaBoost STM PRIF CATL2 1 4 0.5287 0.5611 0.5913 0.5799 0.6018 0.6245 0.6359 6 0.5520 0.5800 0.6094 0.6133 0.6298 0.6384 0.6477 8 0.5897 0.6112 0.6266 0.6007 0.6319 0.6421 0.6528 10 0.6030 0.6392 0.6502 0.6213 0.6487 0.6539 0.6672 12 0.6381 0.6461 0.6383 0.6588 0.6643 0.6753 0.6791 14 0.6541 0.6587 0.6754 0.6682 0.6901 0.6982 0.7014 2 4 0.5354 0.5743 0.5998 0.5887 0.5983 0.6223 0.6133 6 0.5897 0.5992 0.6293 0.5903 0.6426 0.6478 0.6520 8 0.6276 0.6387 0.6492 0.6690 0.6803 0.6893 0.6927 10 0.6508 0.6641 0.6843 0.6905 0.7067 0.7029 0.7168 12 0.6892 0.6698 0.6988 0.7123 0.7234 0.7326 0.7387 14 0.7098 0.7156 0.7207 0.7076 0.7266 0.7391 0.7421 3 4 0.6578 0.6903 0.7026 0.6873 0.7235 0.7472 0.7492 6 0.7013 0.7445 0.7529 0.7354 0.7541 0.7632 0.7726 8 0.7452 0.7695 0.7721 0.7455 0.7618 07726 0.7829 10 0.7762 0.7803 0.7789 0.7836 0.7928 0.7918 0.8193 12 0.7923 0.7944 0.8034 0.7994 0.8288 0.8172 0.8301 14 0.8234 0.8213 0.8178 0.8145 0.8397 0.8263 0.8452 -
DENG Zhaohong, JIANG Yizhang, CHOI K S, et al. Knowledge-leverage-based TSK fuzzy system modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2013, 24(8): 1200–1212. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2253617 DAI Wenyuan, YANG Qiang, XUE Guirong, et al. Boosting for transfer learning[C]. The 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, Corvalis, USA, 2007: 193–200. JIANG Yizhang, DENG Zhaohong, CHUNG F L, et al. Recognition of epileptic EEG signals using a novel multiview TSK fuzzy system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(1): 3–20. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2637405 ZHUANG Fuzhen, LUO Ping, DU Changying, et al. Triplex transfer learning: Exploiting both shared and distinct concepts for text classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(7): 1191–1203. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2013.2281451 PAN S J, NI Xiaochuan, SUN Jiantao, et al. Cross-domain sentiment classification via spectral feature alignment[C]. Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, Raleigh, USA, 2010: 751–760. ZANG Shaofei, CHENG Yuhu, WANG Xuesong, et al. Semi-supervised transfer discriminant analysis based on cross-domain mean constraint[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2018, 49(4): 581–595. doi: 10.1007/s10462-016-9533-3 WANG Guanjin, ZHANG Guangquan, CHOI K S, et al. Deep additive least squares support vector machines for classification with model transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(7): 1527–1540. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2759090 YANG Jun, YAN Rong, and HAUPTMANN A G. Adapting SVM classifiers to data with shifted distributions[C]. The Seventh IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Omaha, USA, 2007: 69–76. JIANG Yizhang, DENG Zhaohong, CHUNG F L, et al. Realizing two-view TSK fuzzy classification system by using collaborative learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 47(1): 145–160. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2577558 CHU Wensheng, DE LA TORRE F, and COHN J F. Selective transfer machine for personalized facial action unit detection[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3515–3522. GRETTON A, SMOLA A, HUANG Jiayuan, et al. Covariate Shift by Kernel Mean Matching[M]. QUIÑONERO-CANDELA J, SUGIYAMA M, SCHWAIGHOFER A, et al. Dataset Shift in Machine Learning. Cambridge, USA: MIT Press, 2009: 131–160. CHENG Yuhu, WANG Xuesong, and CAO Ge. Multi-source tri-training transfer learning[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2014, E97-D(6): 1668–1672. doi: 10.1587/transinf.e97.d.1668 WANG Yunyun, ZHAI Jie, LI Yun, et al. Transfer learning with partial related " instance-feature” knowledge[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 310: 115–124. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.029 CHEN Minmin, XU Zhixiang, WEINBERGER K Q, et al. Marginalized denoising autoencoders for domain adaptation[C]. The 29th International Conference on Machine Learning, Edinburgh, Scotland, 2012: 1627–1634. ZHOU J T, PAN S J, TSANG I W, et al. Hybrid heterogeneous transfer learning through deep learning[C]. The 28th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec City, Canada, 2014: 2213–2219. GLOROT X, BORDES A, and BENGIO Y. Domain adaptation for large-scale sentiment classification: A deep learning approach[C]. The 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, Bellevue, Washington, USA, 2011: 513–520. LONG Mingsheng, WANG Jianmin, CAO Yue, et al. Deep learning of transferable representation for scalable domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28(8): 2027–2040. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2016.2554549 PARZEN E. On estimation of a probability density function and mode[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1962, 33(3): 1065–1076. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177704472 DENG Zhaohong, CHUNG F L, and WANG Shitong. FRSDE: Fast reduced set density estimator using minimal enclosing ball approximation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(4): 1363–1372. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.09.013 TOMMASI T, ORABONA F, and CAPUTO B. Learning categories from few examples with multi model knowledge transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(5): 928–941. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.197 LACOSTE-JULIEN S, SCHMIDT M, and BACH F. A simpler approach to obtaining an O(1/t) convergence rate for the projected stochastic subgradient method[J]. arXiv:1212.2002, 2012. LONG Mingsheng, WANG Jianmin, DING Guiguang, et al. Transfer learning with graph co-regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 26(7): 1805–1818. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2013.97 SUYKENS J A K and VANDEWALLE J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 1999, 9(3): 293–300. doi: 10.1023/a:1018628609742 BART E and ULLMAN S. Cross-generalization: Learning novel classes from a single example by feature replacement[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 672–679. GU Xiaoqing, CHUNG F L, and WANG Shitong. Bayesian Takagi-Sugeno-Kang fuzzy classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(6): 1655–1671. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2617377 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
