Robust Visual Tracking Algorithm Based on Siamese Network with Dual Templates
-
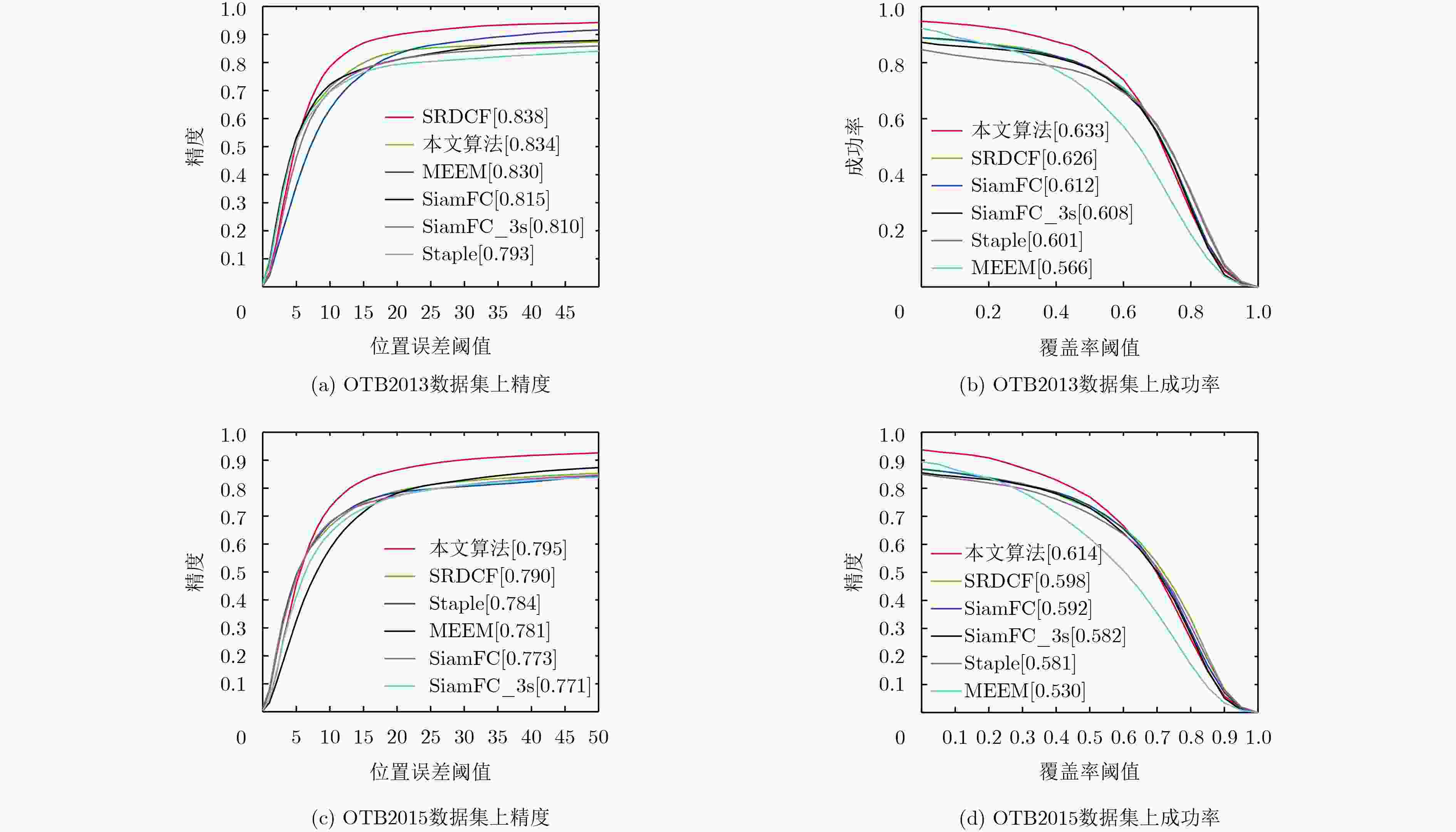
摘要: 近年来,Siamese网络由于其良好的跟踪精度和较快的跟踪速度,在视觉跟踪领域引起极大关注,但大多数Siamese网络并未考虑模型更新,从而引起跟踪错误。针对这一不足,该文提出一种基于双模板Siamese网络的视觉跟踪算法。首先,保留响应图中响应值稳定的初始帧作为基准模板R,同时使用改进的APCEs模型更新策略确定动态模板T。然后,通过对候选目标区域与2个模板匹配度结果的综合分析,对结果响应图进行融合,以得到更加准确的跟踪结果。在OTB2013和OTB2015数据集上的实验结果表明,与当前5种主流跟踪算法相比,该文算法的跟踪精度和成功率具有明显优势,不仅在尺度变化、平面内旋转、平面外旋转、遮挡、光照变化情况下具有较好的跟踪效果,而且达到了46 帧/s的跟踪速度。Abstract: In recent years, the Siamese networks has drawn great attention in visual tracking community due to its balanced accuracy and speed. However, most Siamese networks model are not updated, which causes tracking errors. In view of this deficiency, an algorithm based on the Siamese network with double templates is proposed. First, the base template R which is the initial frame target with stable response map score and the dynamic template T which is using the improved APCEs model update strategy to determine are kept. Then, the candidate targets region and the two template matching results are analyzed, meanwhile the result response maps are fused, which could ensure more accurate tracking results. The experimental results on the OTB2013 and OTB2015 datasets show that comparing with the 5 current mainstream tracking algorithms, the tracking accuracy and success rate of the proposed algorithm are superior. The proposed algorithm not only displays better tracking effects under the conditions of scale variation, in-plane rotation, out-of-plane rotation, occlusion, and illumination variation, but also achieves real-time tracking by a speed of 46 frames per second.
-
Key words:
- Siamese network /
- Object tracking /
- Dual templates /
- Template update
-
表 1
$\text{λ} $ 取值对精度、成功率的影响(OTB2015)$\lambda $ 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.850 0.90 1.00 1.10 成功率 0.447 0.513 0.587 0.603 0.614 0.605 0.585 0.591 精度 0.642 0.697 0.742 0.779 0.793 0.761 0.761 0.774 表 2 基于Siamese网络下的双模版跟踪算法
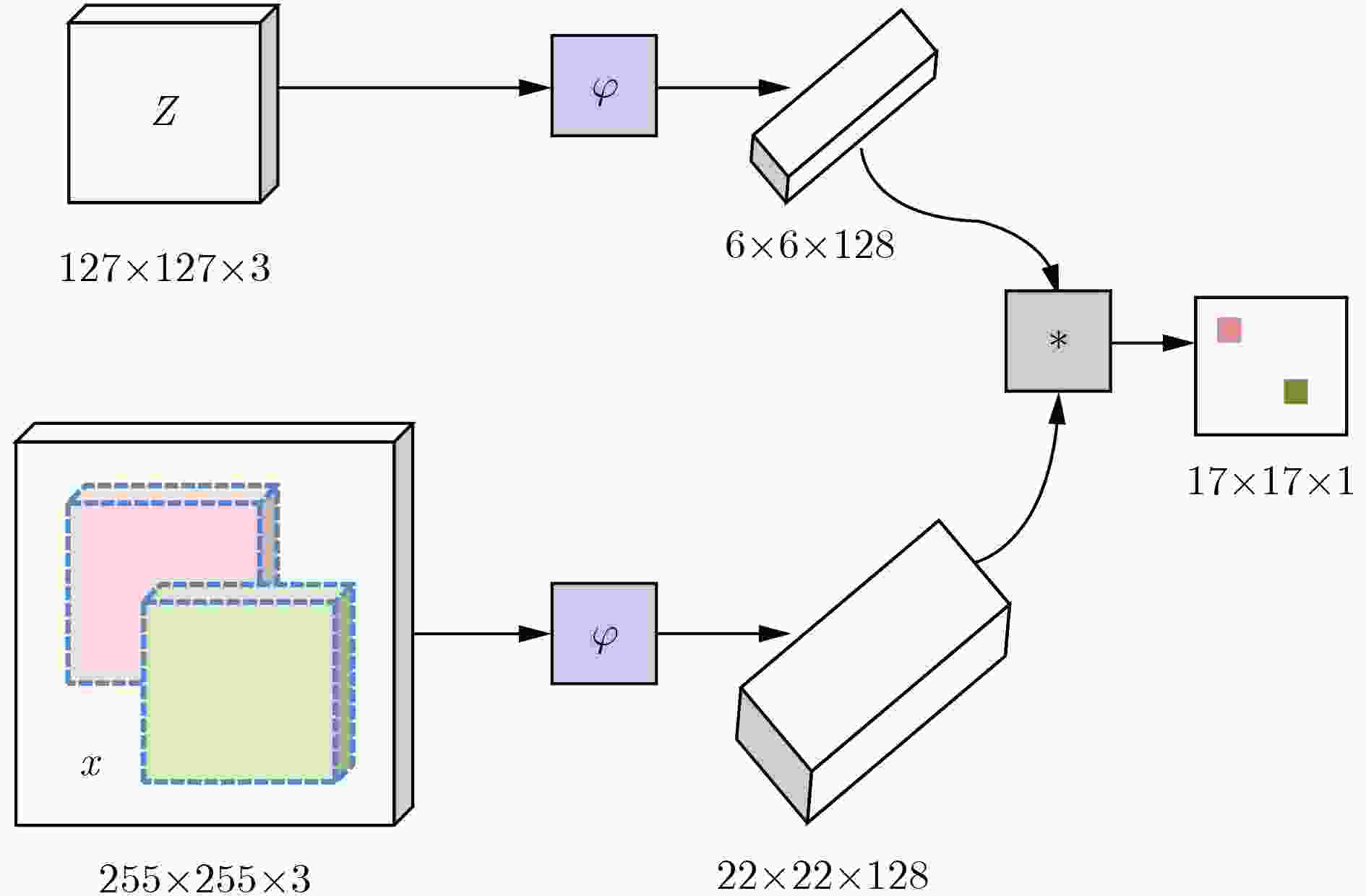
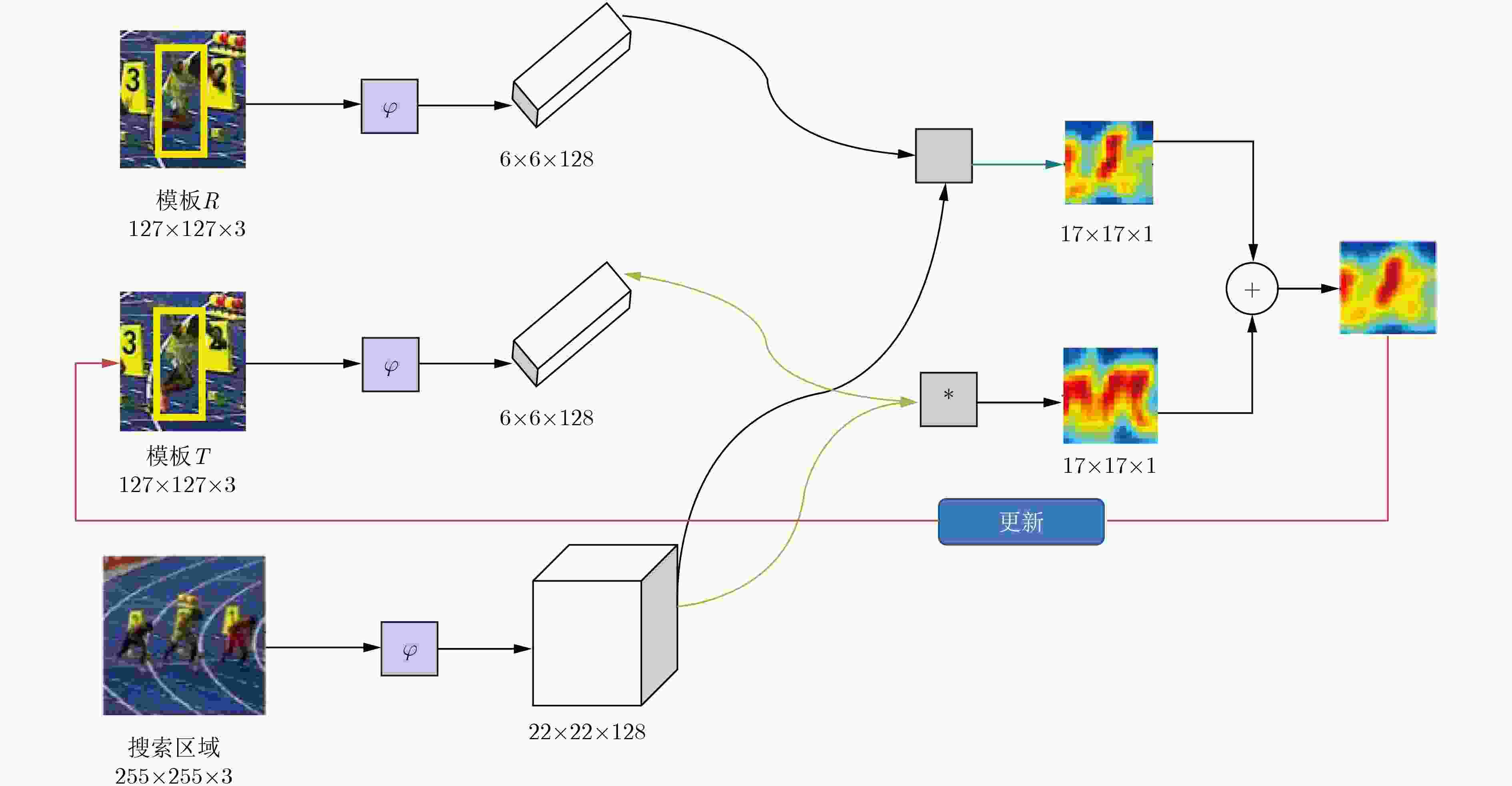
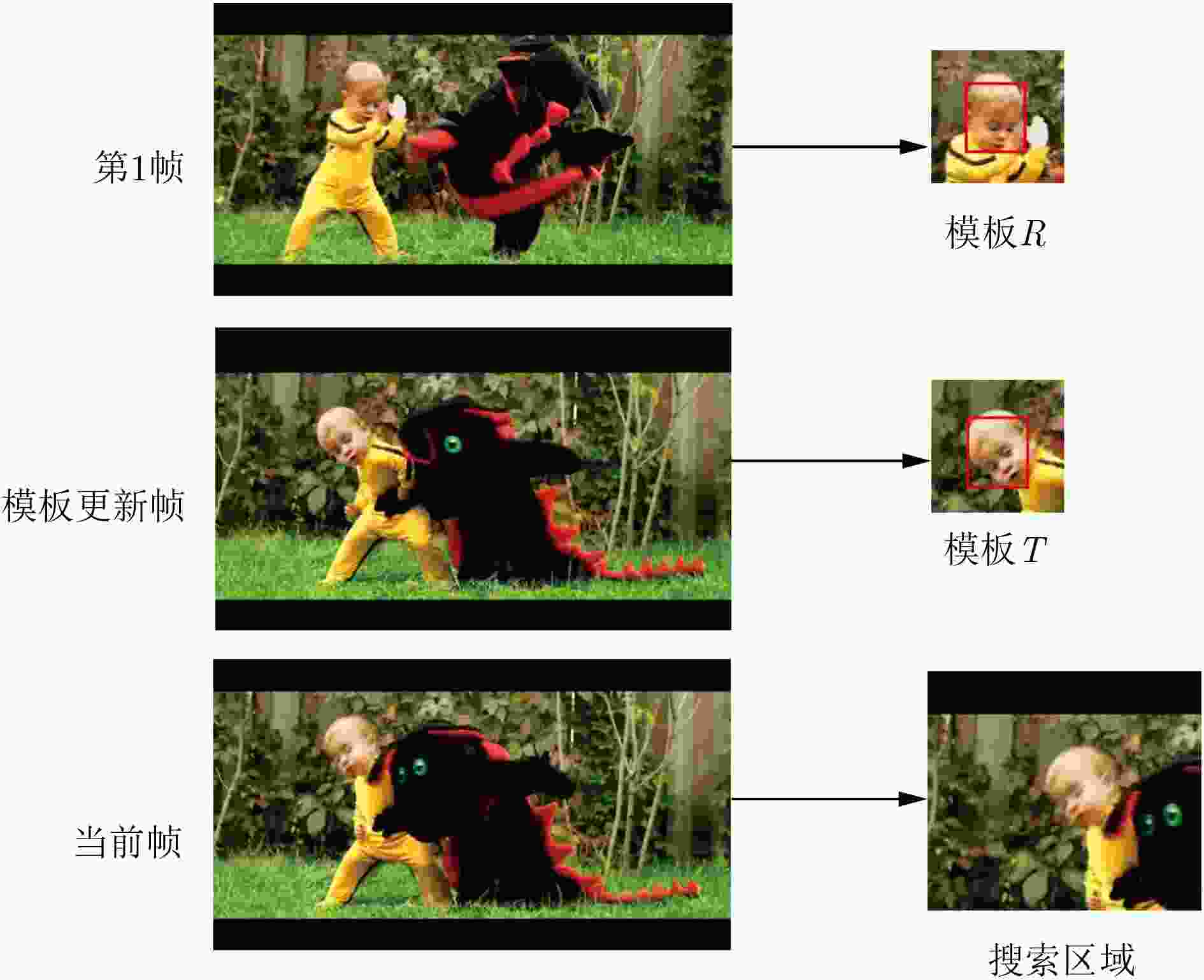
输入: 图像序列: I1, I2, In; 初始目标位置: ${P_0} = ({x_0},{y_0})$, 初始目标大小: ${s_0} = ({w_0},{h_0})$ 输出: 预估目标位置: ${P_{\rm{e}}} = ({x_{\rm{e}}},{y_{\rm{e}}})$, 预估目标大小: ${s_{\rm{e}}} = ({w_{\rm{e}}},{h_{\rm{e}}})$. for t=1, 2,···,n, do: 步骤1 跟踪目标 (1) 以上一帧中心位置${P_{t{\rm{ - 1}}}}$裁剪第t帧中的感兴趣区域ROI,放大为搜索区域; (2) 提取基准模板R,动态模板T和搜索区域的特征; (3) 使用式(4)计算两个模板特征与搜索区域特征的相似性,得到结果响应图,响应图中最高响应点即为预估目标位置。 步骤2 模型更新 (1) 使用式(5)计算跟踪置信度${\rm{APCEs}}$; (2) 计算${F_{{\rm{max}}}}$和${\rm{APCEs}}$的平均值${\rm{m}}{{\rm{F}}_{{\rm{max}}}}$和${\rm{mAPCEs}}$; (3) 如果${F_{{\rm{max}}}}{\rm{ > }}\lambda {\rm{m}}{{\rm{F}}_{{\rm{max}}}}$且${\rm{APCEs}} > \lambda {\rm{mAPCEs}}$,更新动态模板T; Until图像序列的结束。 表 3 不同属性下算法的跟踪成功率对比结果
算法 SV(64) OPR(63) IPR(51) OCC(49) DEF(44) FM(39) IV(38) BC(31) MB(29) OV(14) LR(9) 本文算法 0.577 0.596 0.595 0.613 0.573 0.607 0.605 0.577 0.633 0.538 0.460 SiameseFC 0.553 0.549 0.579 0.564 0.510 0.569 0.550 0.572 0.525 0.467 0.584 SiameseFC_3S 0.552 0.558 0.557 0.567 0.506 0.568 0.568 0.523 0.550 0.506 0.618 SRDCF 0.561 0.550 0.544 0.569 0.544 0.597 0.613 0.583 0.595 0.460 0.514 Staple 0.525 0.535 0.552 0.561 0.554 0.537 0.598 0.574 0.546 0.481 0.459 MEEM 0.470 0.526 0.529 0.495 0.489 0.542 0.517 0.519 0.557 0.488 0.382 表 4 不同属性下算法的跟踪精度对比结果
算法 SV(64) OPR(63) IPR(51) OCC(49) DEF(44) FM(39) IV(38) BC(31) MB(29) OV(14) LR(9) 本文算法 0.781 0.796 0.815 0.811 0.804 0.816 0.801 0.770 0.749 0.717 0.878 SiameseFC 0.732 0.744 0.780 0.720 0.690 0.735 0.711 0.748 0.654 0.615 0.805 SiameseFC_3S 0.735 0.757 0.742 0.722 0.690 0.743 0.736 0.690 0.705 0.669 0.900 SRDCF 0.745 0.571 0.745 0.735 0.734 0.769 0.792 0.775 0.767 0.597 0.765 Staple 0.727 0.738 0.770 0.726 0.748 0.697 0.792 0.766 0.708 0.661 0.695 MEEM 0.736 0.795 0.794 0.741 0.754 0.752 0.740 0.746 0.731 0.685 0.808 表 5 本文算法与5种算法跟踪速度对比
本文算法 SiameseFC SiameseFC_3S SRDCF Staple MEEM Code M+C M+C M+C M+C M+C M+C PlatformFPS GPU46(Y) GPU58(Y) GPU86(Y) GPU5(N) CPU80(Y) CPU10(N) -
侯志强, 韩崇昭. 视觉跟踪技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2006, 32(4): 603–617.HOU Zhiqiang and HAN Chongzhao. A survey of visual tracking[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2006, 32(4): 603–617. WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834–1848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 HE Anfeng, LUO Chong, TIAN Xinmei, et al. A twofold Siamese network for real-time object tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4834–4843. TAO Ran, GAVVES E, and SMEULDERS A W M. Siamese instance search for tracking[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1420–1429. BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking[C]. 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 850–865. WANG Qiang, TENG Zhu, XING Junliang, et al. Learning attentions: Residual attentional Siamese network for high performance online visual tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4854–4863. ZHU Zheng, WU Wei, ZOU Wei, et al. End-to-end flow correlation tracking with spatial-temporal attention[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 548–557. VALMADRE J, BERTINETTO L, HENRIQUES J, et al. End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5000–5008. GUO Qing, FENG Wei, ZHOU Ce, et al. Learning dynamic Siamese network for visual object tracking[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1781–1789. WANG Qiang, ZHANG Mengdan, XING Junliang, et al. Do not lose the details: Reinforced representation learning for high performance visual tracking[C]. 2018 International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Swedish, 2018. LI Bo, YAN Junjie, WU Wei, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8971–8980. ZHU Zheng, WANG Qiang, LI Bo, et al. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 103–119. RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG Jia, SU Hao, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211–252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y REAL E, SHLENS J, MAZZOCCHI S, et al. YouTube-boundingboxes: A large high-precision human-annotated data set for object detection in video[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7464–7473. HERMANS A, BEYER L, and LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07737, 2017. WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Online object tracking: A benchmark[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 2411–2418. KRISTAN M, MATAS J, LEONARDIS A, et al. The visual object tracking VOT2015 challenge results[J]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 564–586. SMEULDERS A W M, CHU D M, CUCCHIARA R, et al. Visual tracking: An experimental survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(7): 1442–1468. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.230 WANG Mengmeng, LIU Yong, and HUANG Zeyi. Large margin object tracking with circulant feature maps[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4800–4808. ZHANG Jianming, MA Shugao, and SCLAROFF S. MEEM: Robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 188–203. BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, GOLODETZ S, et al. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1401–1409. DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310–4318. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.490. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 LI Bo, WU Wei, WANG Qiang, et al. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.11703.pdf, 2018. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
