3D Human Motion Prediction Based on Bi-directionalGated Recurrent Unit
-
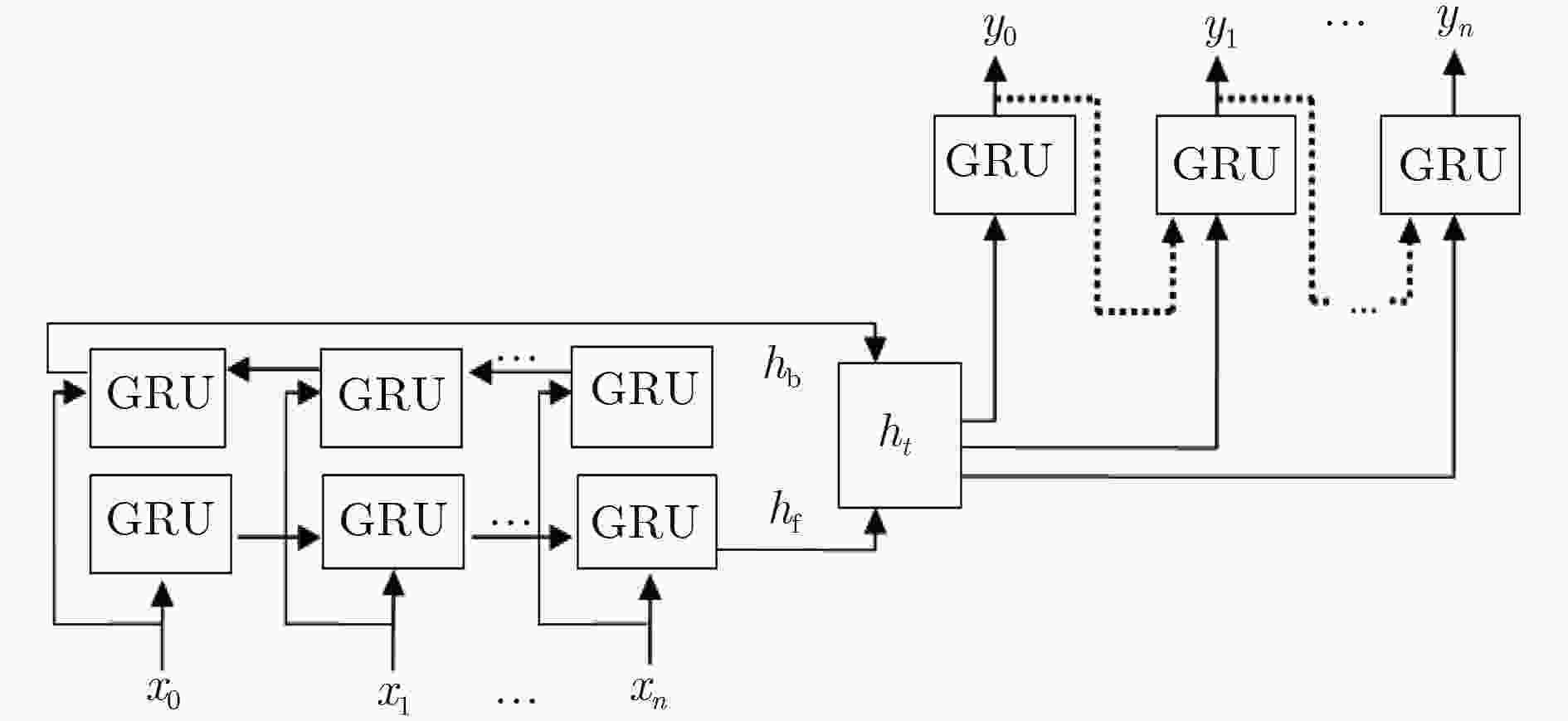
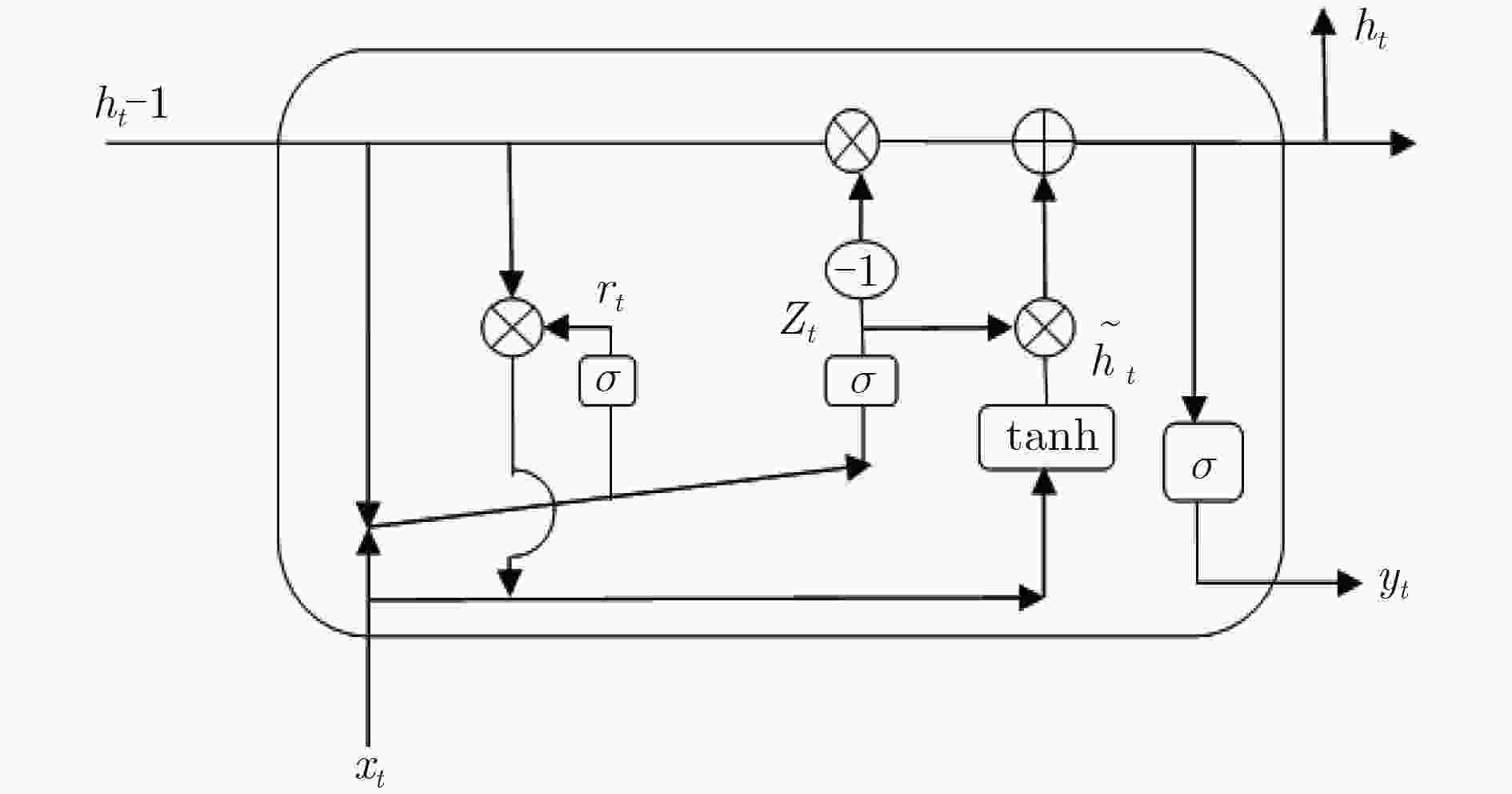
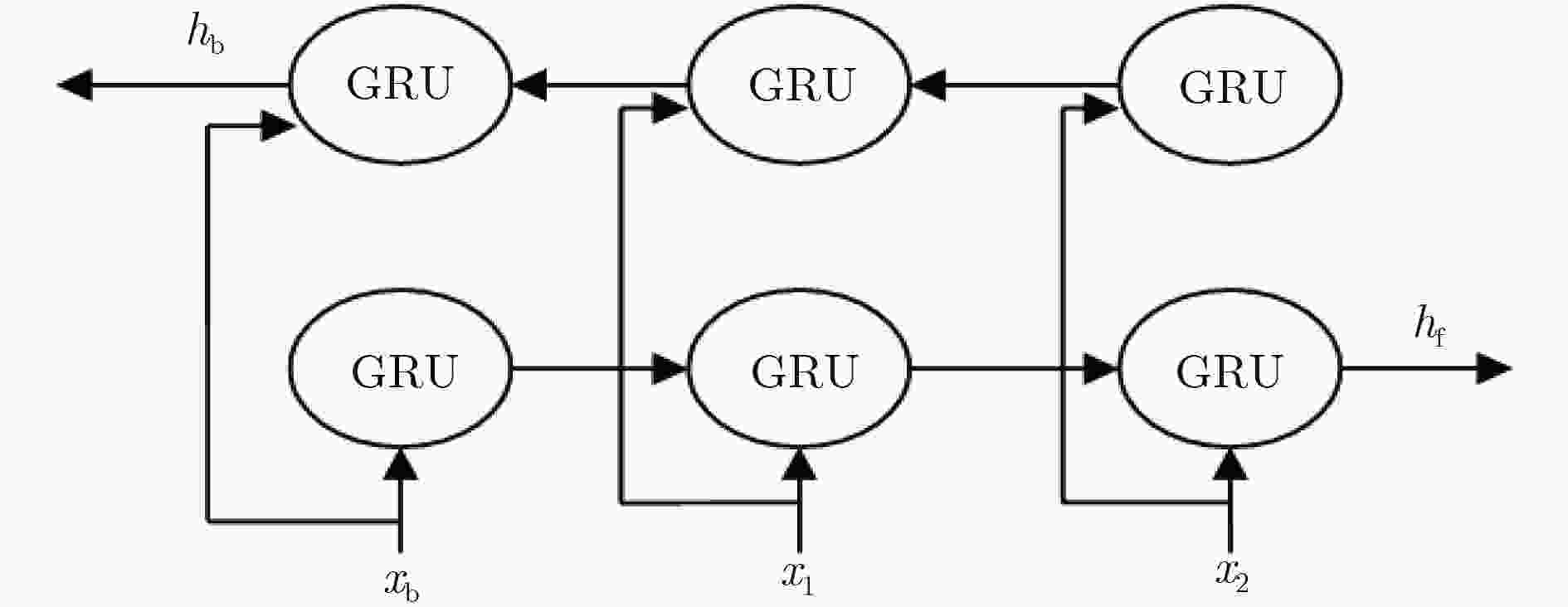
摘要: 在机器视觉领域,预测人体运动对于及时的人机交互及人员跟踪等是非常有必要的。为了改善人机交互及人员跟踪等的性能,该文提出一种基于双向门控循环单元(GRU)的编-解码器模型(EBiGRU-D)来学习3D人体运动并给出一段时间内的运动预测。EBiGRU-D是一种深递归神经网络(RNN),其中编码器是一个双向GRU (BiGRU)单元,解码器是一个单向GRU单元。BiGRU使原始数据从正反两个方向同时输入并进行编码,编成一个状态向量然后送入解码器进行解码。BiGRU将当前的输出与前后时刻的状态关联起来,使输出充分考虑了前后时刻的特征,从而使预测更加准确。在human3.6m数据集上的实验表明EBiGRU-D不仅极大地改善了3D人体运动预测的误差还大大地增加了准确预测的时间。Abstract: In the field of computer vision, predicting human motion is very necessary for timely human–computer interaction and personnel tracking. In order to improve the performance of human–computer interaction and personnel tracking, an encoder-decoder model called Bi–directional Gated Recurrent Unit Encoder–Decoder (EBiGRU–D) based on Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) is proposed to learn 3D human motion and give a prediction of motion over a period of time. EBiGRU–D is a deep Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) in which the encoder is a Bidirectional GRU (BiGRU) unit and the decoder is a unidirectional GRU unit. BiGRU allows raw data to be simultaneously input from both the forward and reverse directions and then encoded into a state vector, which is then sent to the decoder for decoding. BiGRU associates the current output with the state of the front and rear time, so that the output fully considers the characteristics of the time before and after, so that the prediction is more accurate. Experimental results on the human3.6m dataset demonstrate that EBiGRU–D not only improves greatly the error of 3D human motion prediction but also increases greatly the time for accurate prediction.
-
表 1 human3.6m数据集下1 s内各模型预测误差的对比(ms)
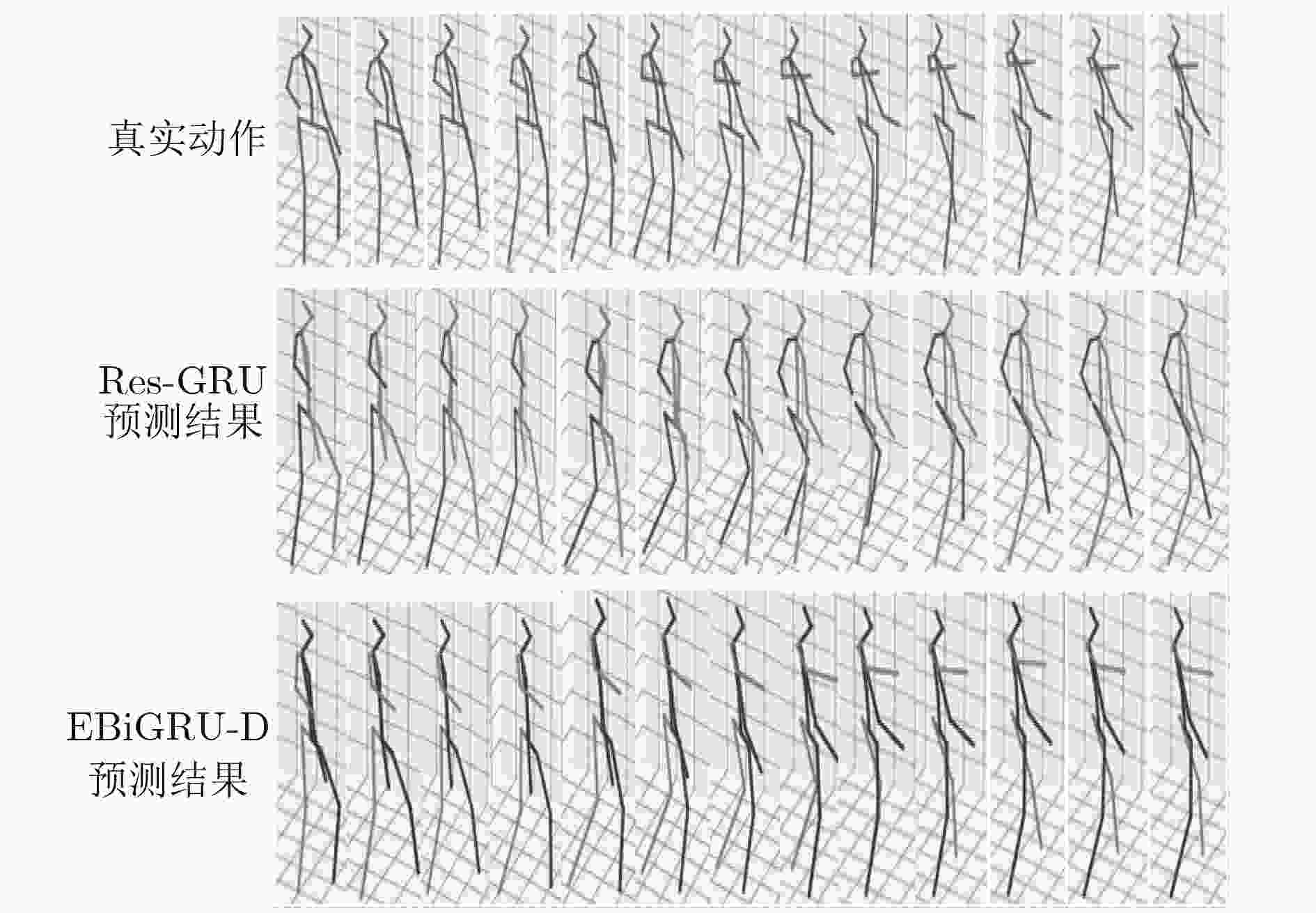
预测时间(ms) 80 160 320 400 560 640 720 1000 Walking ERD[10] 0.77 0.90 1.12 1.25 1.44 1.45 1.46 1.49 LSTM-3LR[10] 0.73 0.81 1.05 1.18 1.34 1.36 1.37 1.36 Res-GRU[13] 0.39 0.68 0.99 1.15 1.35 1.37 1.37 1.32 MHU[14] 0.32 0.53 0.69 0.77 0.90 0.94 0.97 1.06 EBiGRU-D 0.31 0.31 0.33 0.35 0.35 0.36 0.36 0.37 Greeting ERD[10] 0.85 1.09 1.45 1.64 1.93 1.89 1.92 1.98 LSTM-3LR[10] 0.80 0.99 1.37 1.54 1.81 1.76 1.79 1.85 Res-GRU[13] 0.52 0.86 1.30 1.47 1.78 1.75 1.82 1.96 MHU[14] 0.54 0.87 1.27 1.45 1.75 1.71 1.74 1.87 EBiGRU-D 0.48 0.44 0.49 0.49 0.52 0.51 0.52 0.49 Walkingdog ERD[10] 0.91 1.07 1.39 1.53 1.81 1.85 1.90 2.03 LSTM-3LR[10] 0.80 0.99 1.37 1.54 1.81 1.76 1.79 2.00 Res-GRU[13] 0.56 0.95 1.33 1.48 1.78 1.81 1.88 1.96 MHU[14] 0.56 0.88 1.21 1.37 1.67 1.72 1.81 1.90 EBiGRU-D 0.51 0.64 0.61 0.62 0.62 0.59 0.61 0.60 Discussion ERD[10] 0.76 0.96 1.17 1.24 1.57 1.70 1.84 2.04 LSTM-3LR[10] 0.71 0.84 1.02 1.11 1.49 1.62 1.76 1.99 Res-GRU[13] 0.31 0.69 1.03 1.12 1.52 1.61 1.70 1.87 MHU[14] 0.31 0.67 0.93 1.00 1.37 1.56 1.66 1.88 EBiGRU-D 0.33 0.44 0.50 0.45 0.48 1.51 0.50 0.49 表 2 human3.6m数据集下2 s内EBiGRU-D网络和Res-GRU网络预测误差的对比(ms)
预测时间(ms) 80 320 560 720 1000 1080 1320 1560 1720 2000 Walking Res-GRU[13] 0.42 0.89 1.02 1.16 1.37 1.39 1.46 1.59 1.65 1.89 EBiGRU-D 0.36 0.35 0.36 0.39 0.41 0.41 0.44 0.47 0.48 0.48 Greeting Res-GRU[13] 0.65 0.89 1.21 1.35 1.56 1.77 1.85 2.02 2.16 2.22 EBiGRU-D 0.45 0.46 0.50 0.51 0.55 0.54 0.56 0.56 0.55 0.56 Walkingdog Res-GRU[13] 0.66 1.20 1.73 1.95 2.20 2.27 2.34 2.41 2.51 2.52 EBiGRU-D 0.49 0.58 0.60 0.60 0.61 0.60 0.59 0.60 0.61 0.61 Discussion Res-GRU[13] 0.89 1.23 1.56 1.69 1.85 2.01 2.12 2.32 2.49 2.56 EBiGRU-D 0.42 0.43 0.43 0.45 0.49 0.50 0.55 0.55 0.54 0.56 -
FOKA A F and TRAHANIAS P E. Probabilistic autonomous robot navigation in dynamic environments with human motion prediction[J]. International Journal of Social Robotics, 2010, 2(1): 79–94. doi: 10.1007/s12369-009-0037-z MAINPRICE J and BERENSON D. Human–robot collaborative manipulation planning using early prediction of human motion[C]. 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 2013: 299–306. BÜTEPAGE J, BLACK M J, KRAGIC D, et al. Deep representation learning for human motion prediction and classification[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1591–1599. TEKIN B, MÁRQUEZ–NEILA P, SALZMANN M, et al. Learning to fuse 2D and 3D image cues for monocular body pose estimation[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3961–3970. YASIN H, IQBAL U, KRÜGER B, et al. A dual–source approach for 3D pose estimation from a single image[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4948–4956. 肖俊, 庄越挺, 吴飞. 三维人体运动特征可视化与交互式运动分割[J]. 软件学报, 2008, 19(8): 1995–2003.XIAO Jun, ZHUANG Yueting, and WU Fei. Feature visualization and interactive segmentation of 3D human motion[J]. Journal of Software, 2008, 19(8): 1995–2003. 潘红, 肖俊, 吴飞, 等. 基于关键帧的三维人体运动检索[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2009, 21(2): 214–222.PAN Hong, XIAO Jun, WU Fei, et al. 3D human motion retrieval based on key-frames[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2009, 21(2): 214–222. LI Rui, LIU Zhenyu, and TAN Jianrong. Human motion segmentation using collaborative representations of 3D skeletal sequences[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2018, 12(4): 434–442. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2016.0385 TAYLOR G W, HINTON G E, and ROWEIS S. Modeling human motion using binary latent variables[C]. The 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Hong Kong, China, 2006: 1345–1352. FRAGKIADAKI K, LEVINE S, FELSEN P, et al. Recurrent network models for human dynamics[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4346–4354. HOLDEN D, SAITO J, and KOMURA T. A deep learning framework for character motion synthesis and editing[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(4): 1–11. ASHESH J, ZAMIR A R, SAVARESE S, et al. Structural-RNN: Deep learning on spatio–temporal graphs[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 5308–5317. MARTINEZ J, BLACK M J, and ROMERO J. On human motion prediction using recurrent neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4674–4683. TANG Yongyi, MA Lin, LIU Wei, et al. Long–term human motion prediction by modeling motion context and enhancing motion dynamic[J/OL]. arXiv: 1805.02513. http://arxiv.org/abs/1805.02513, 2018. ZHANG Yachao, LIU Kaipei, QIN Liang, et al. Deterministic and probabilistic interval prediction for short&-term wind power generation based on variational mode decomposition and machine learning methods[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 112: 208–219. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.023 CHO K, VAN MERRIENBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[J/OL]. arXiv: 1406.1078, 2014. -





 下载:
下载:
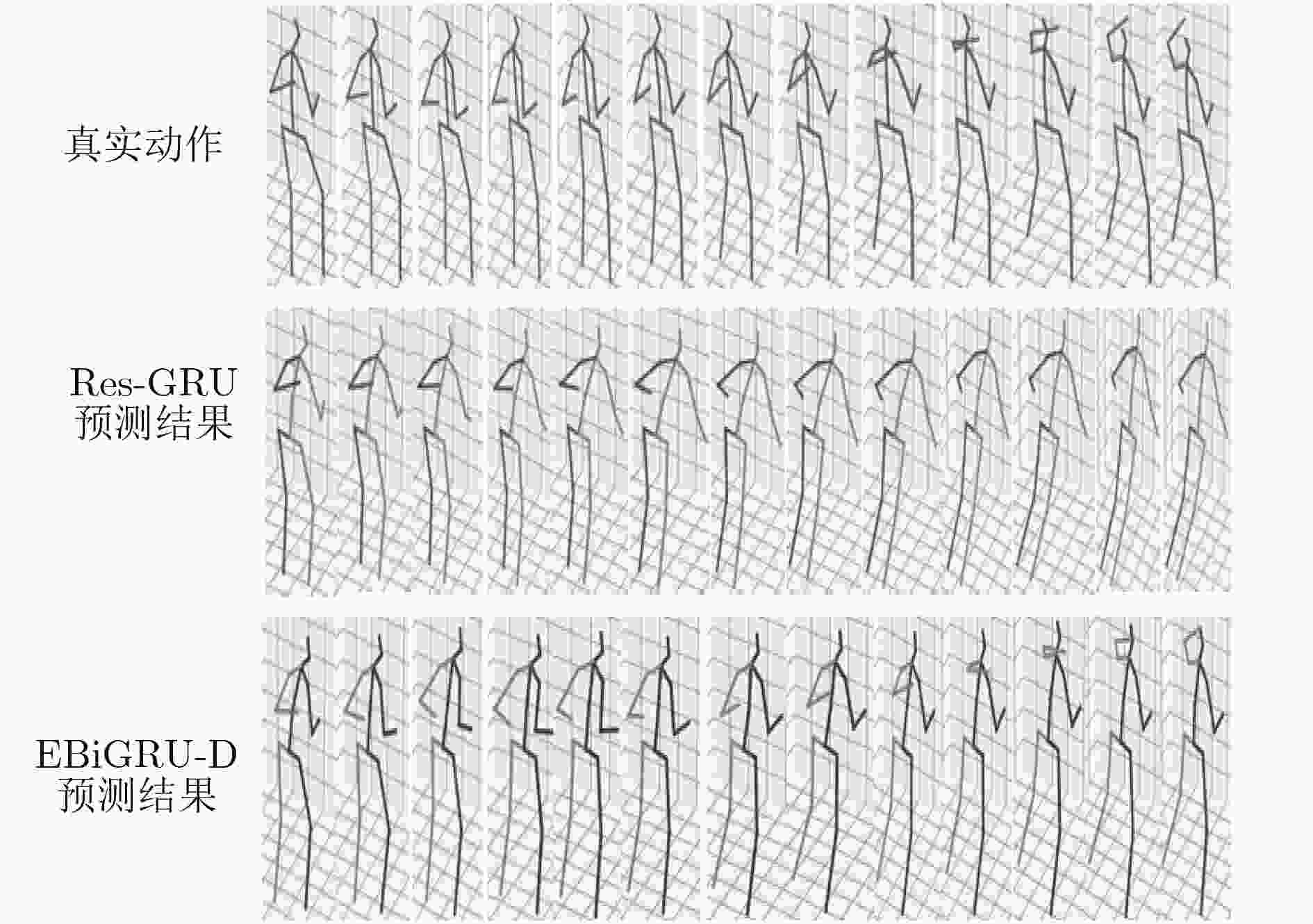
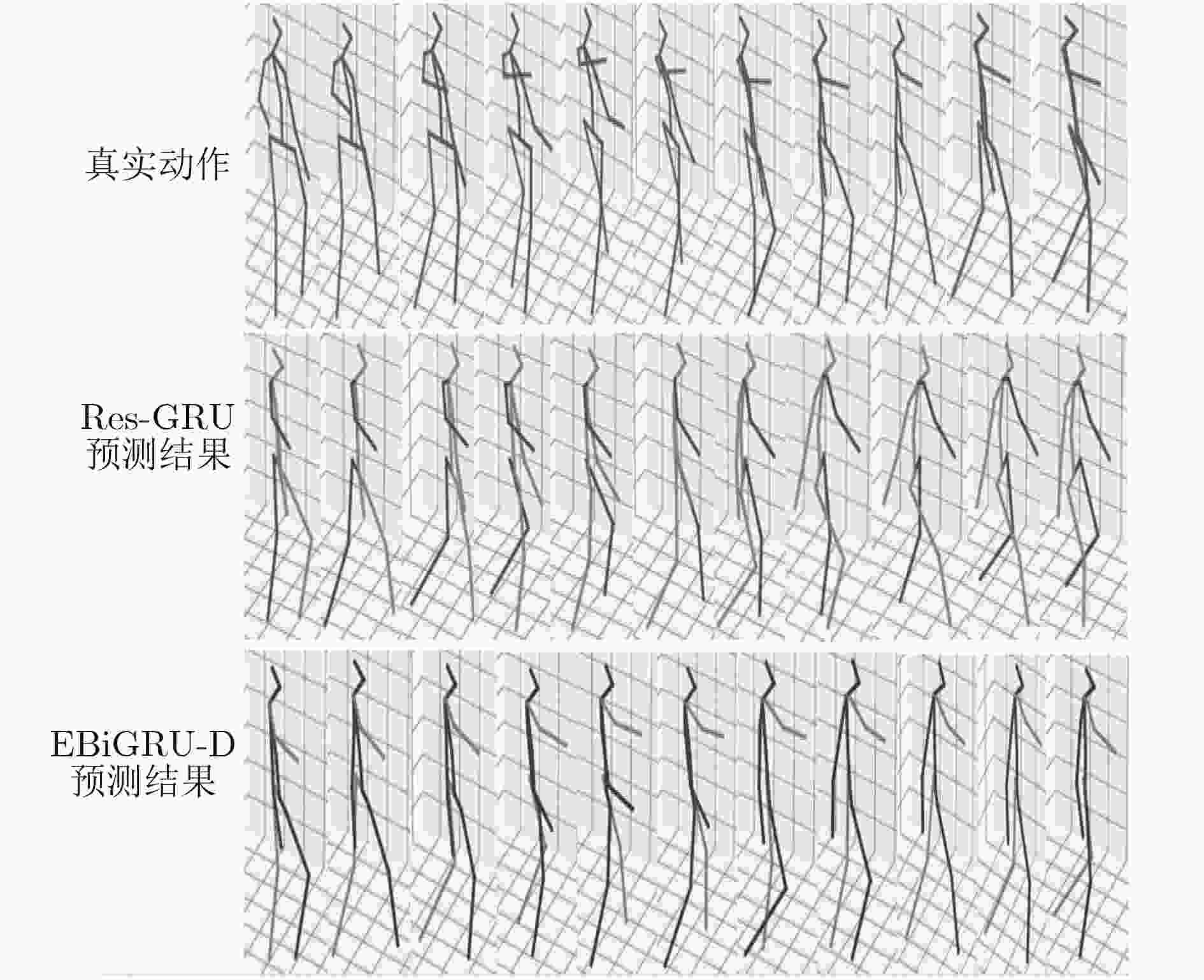
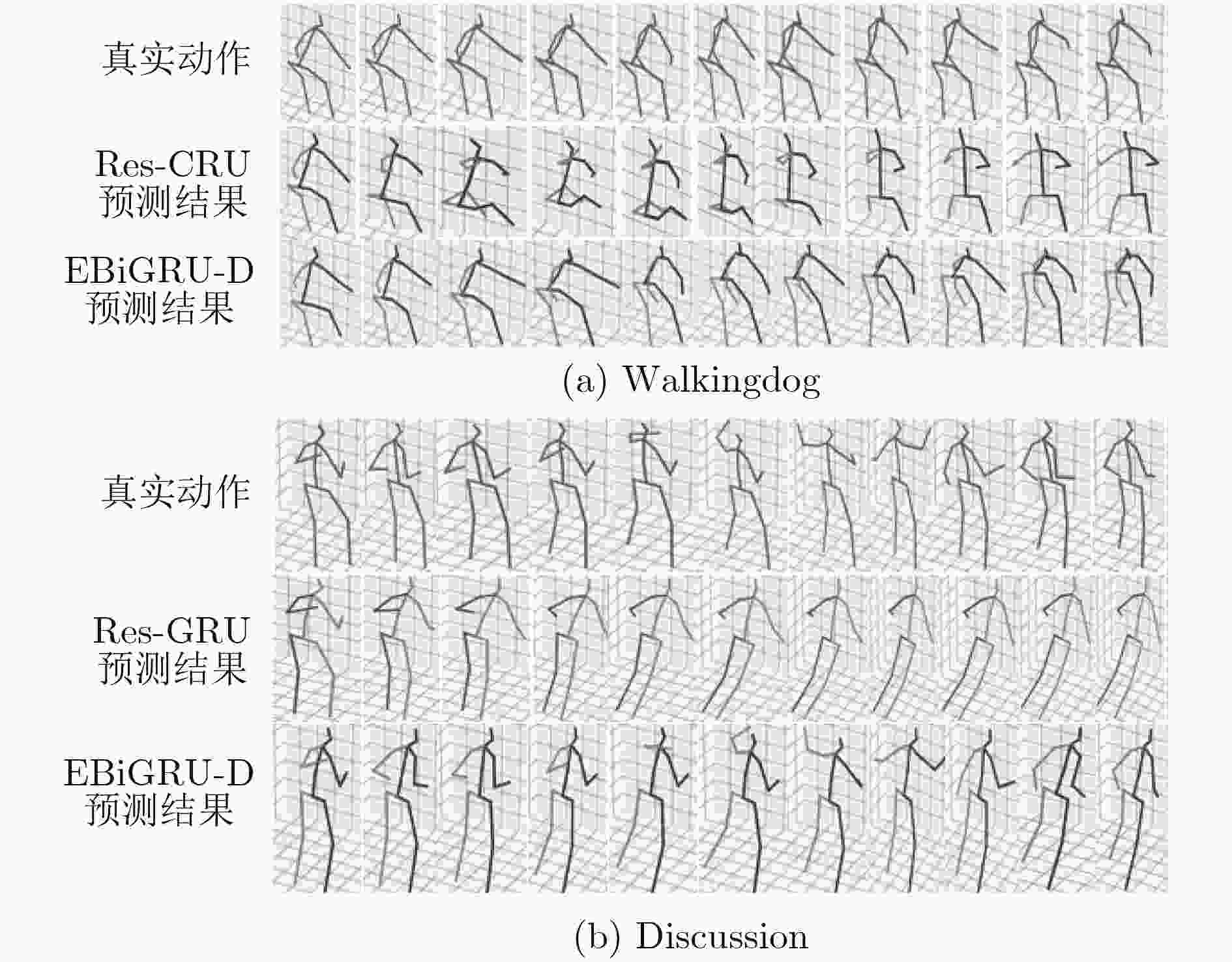
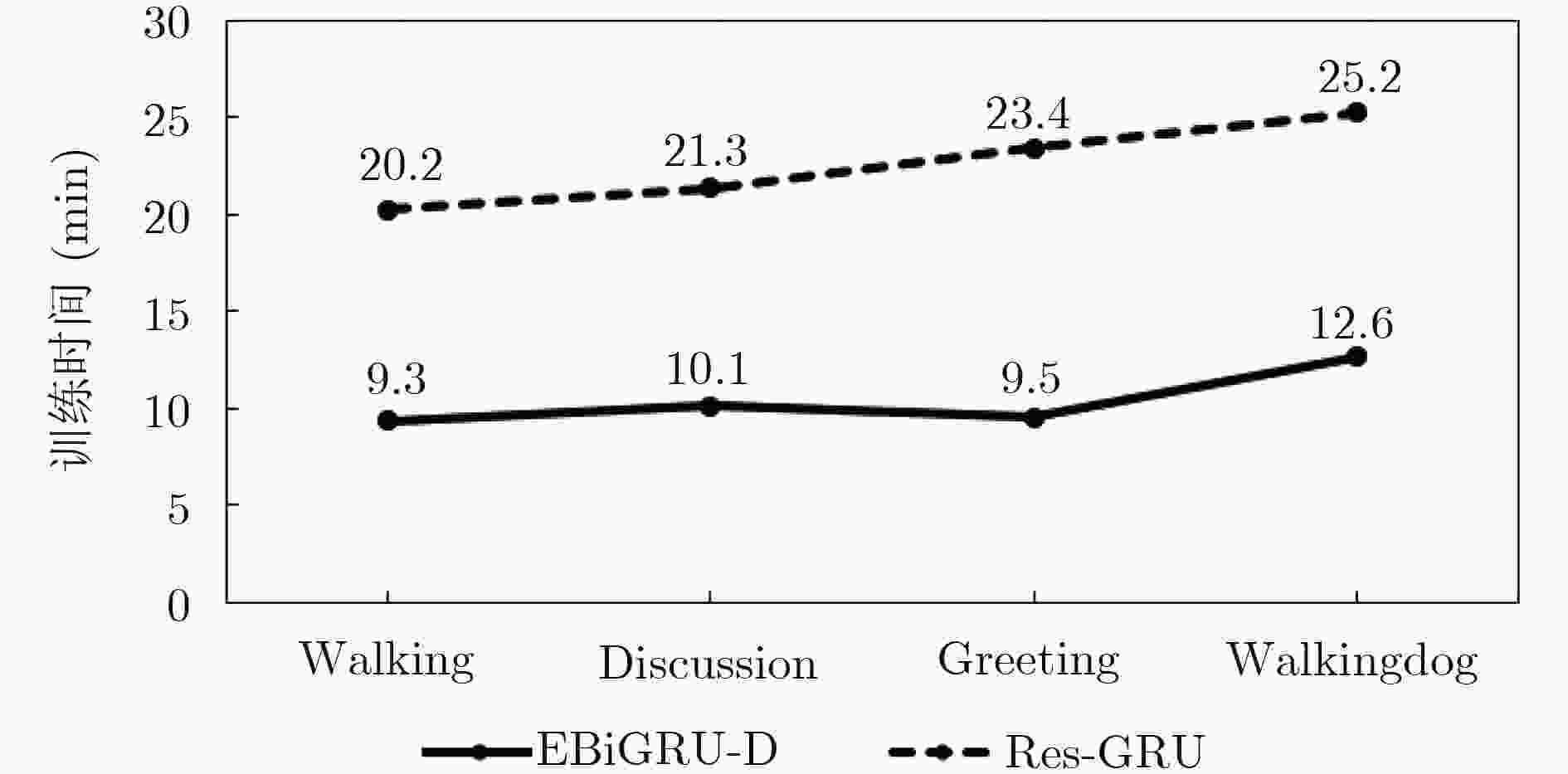


 下载:
下载:
