Adaptive Strategy Fusion Target Tracking Based on Multi-layer Convolutional Features
-
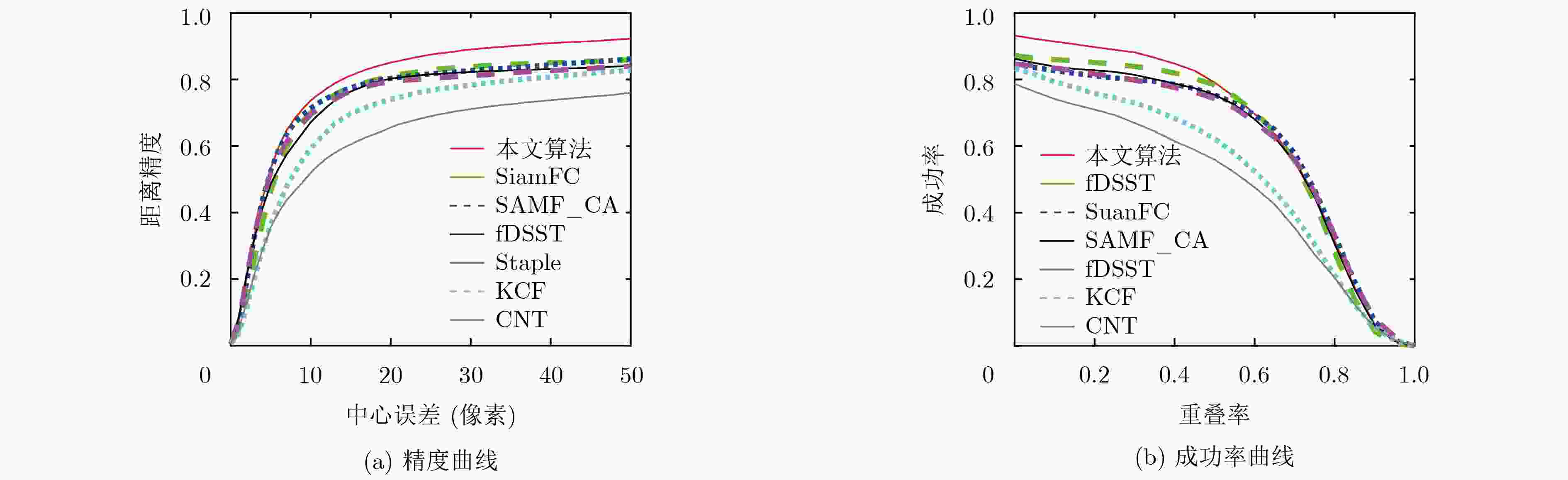
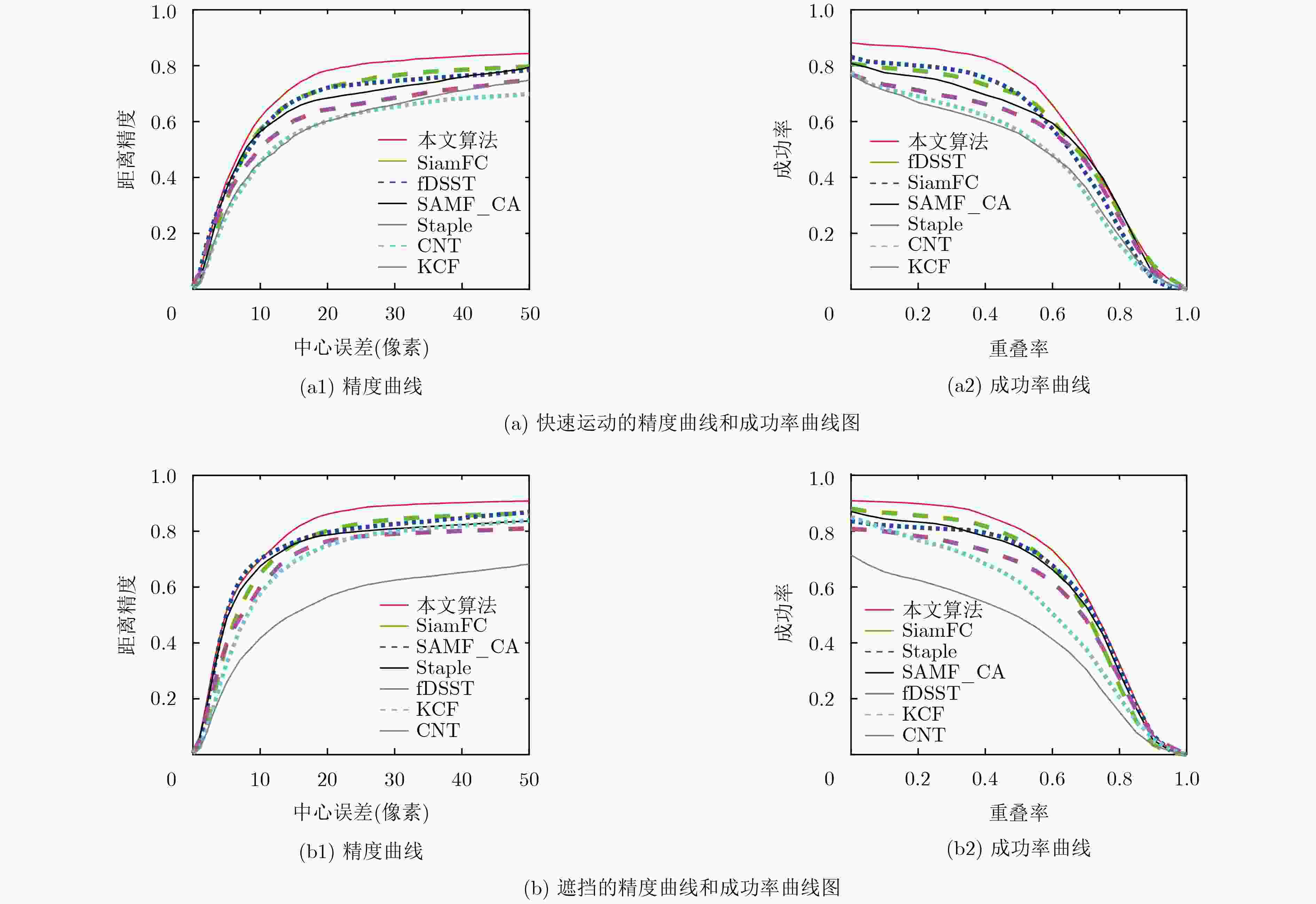
摘要: 针对目标快速运动、遮挡等复杂视频场景中目标跟踪鲁棒性差和跟踪精度低的问题,该文提出一种基于多层卷积特征的自适应决策融合目标跟踪算法(ASFTT)。首先提取卷积神经网络(CNN)中帧图像的多层卷积特征,避免网络单层特征表征目标信息不全面的缺陷,增强算法的泛化能力;使用多层特征计算帧图像相关性响应,提高算法的跟踪精度;最后该文使用自适应决策融合算法将所有响应中目标位置决策动态融合以定位目标,融合算法综合考虑生成响应的各跟踪器的历史决策信息和当前决策信息,以保证算法的鲁棒性。采用标准数据集OTB2013对该文算法和6种当前主流跟踪算法进行了仿真对比,结果表明该文算法具有更加优秀的跟踪性能。Abstract: To solve the problems of low robustness and tracking accuracy in target tracking when interference factors occur such as target fast motion and occlusion in complex video scenes, an Adaptive Strategy Fusion Target Tracking algorithm (ASFTT) is proposed based on multi-layer convolutional features. Firstly, the multi-layer convolutional features of frame images in Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) are extracted, which avoids the defect that the target information of the network is not comprehensive enough, so as to increase the generalization ability of the algorithm. Secondly, in order to improve the tracking accuracy of the algorithm, the multi-layer features are performed to calculate the correlation responses, which improves the tracking accuracy. Finally, the target position strategy in all responses are dynamically merged to locate the target through the adaptive strategy fusion algorithm in this paper. It comprehensively considers the historical strategy information and current strategy information of each responsive tracker to ensure the robustness. Experiments performed on the OTB2013 evaluation benchmark show that that the performance of the proposed algorithm are better than those of the other six state-of-the-art methods.
-
表 1 基于多层卷积特征的自适应决策融合目标跟踪算法
输入:视频序列第1帧的目标位置;初始各决策权重$w_1^1,w_1^2, ·\!·\!· ,w_1^m$; $R_1^m = 0$,$l_1^m = 0$。 输出:每帧图像的目标位置$({a_t},{b_t})$。 (1) //权重初始化。使用式(4)计算$k$个跟踪器的初始权重; (2) for t=2 to T(T是视频的总帧数): (3) //提取网络多层特征。提取网络中待检测图像$k$层的特征$x_t^k$和模板分支最后一层特征${u'_1}$; (4) //响应值计算。使用式(6)和式(8)计算$k$个相关滤波响应值$R_t^k$和相似性响应值${R'_t}$; (5) //自适应响应决策融合。计算目标位置首先使用式(7)和式(9)计算步骤(4)中每个决策者预测的目标位置$(a_t^m,b_t^m)$;通过式(10)计算最终的 目标位置$({a_t},{b_t})$; (6) //更新权重值,用于下一帧检测。首先通过式(11)和式(12)计算各决策者的损失$L_t^m$和当前代价函数$p_t^m$;其次使用式(13)和式(14)更新稳 定性模型并计算每个决策者的稳定性度量值$r_t^m$;使用式(15b)和式(15a)计算每个决策者当前代价函数$p_t^m$的$\alpha _t^m$比例值和每个决策者 的累积代价函数$S_t^m$;并使用式(16)更新每个决策者所对应的权重$w_{t + 1}^m$;最后通过式(5)更新$k$个跟踪器的权重; (7) end for; 表 2 测试视频序列包含的影响因素
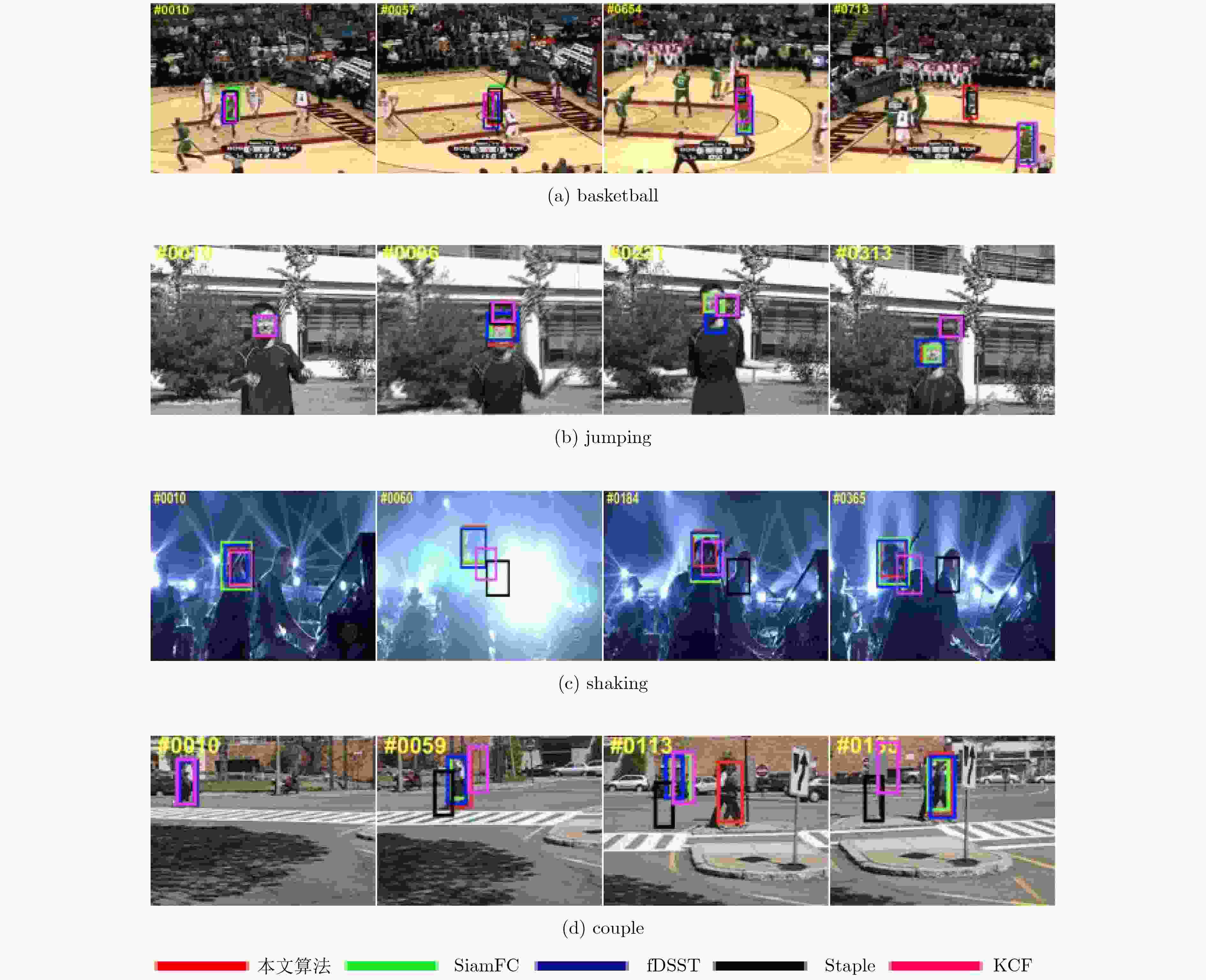
序列 帧数 影响因素 basketball 725 形变、遮挡、光照变化、背景杂波等 jumping 313 运动模糊、快速运动 shaking 365 光照变化、背景杂波、尺度变化等 couple 140 平面外旋转、尺度变化、形变等 -
侯志强, 张浪, 余旺盛, 等. 基于快速傅里叶变换的局部分块视觉跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(10): 2397–2404. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150183HOU Zhiqiang, ZHANG Lang, YU Wangsheng, et al. Local patch tracking algorithm based on fast fourier transform[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(10): 2397–2404. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150183 HUANG C, LUCEY S, and RAMANAN D. Learning policies for adaptive tracking with deep feature cascades[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 105–114. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 2012: 1097–1105. WANG Linzhao, WANG Lijun, LU Huchuan, et al. Saliency detection with recurrent fully convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of the 14th Computer Vision European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 825–841. LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. DANELLJAN M, ROBINSON A, KHAN F S, et al. Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking[M]. LEIBE B, MATAS J, SEBE N, et al. Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. Cham: Springer, 2016: 472–488. WANG Naiyan and YEUNG D Y. Learning a deep compact image representation for visual tracking[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 2013: 809–817. BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]. Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 850–865. DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. TIAN Gang, HU Ruimin, WANG Zhongyuan, et al. Improved object tracking algorithm based on new hsv color probability model[M]. YU Wen, HE Haibo, ZHANG Nian. Advances in Neural Networks – ISNN 2009. Berlin Heidelberg, Springer, 2009: 1145–1151. 孙航, 李晶, 杜博, 等. 基于多阶段学习的相关滤波目标跟踪[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(10): 2337–2342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.10.004SUN Hang, LI Jing, DU Bo, et al. Correlation filtering target tracking based on online multi-lifespan learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(10): 2337–2342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.10.004 DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking[C]. Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 2014: 65.1–65.11. HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]. Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 702–715. HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2014.2345390 HELD D, THRUN S, and SAVARESE S. Learning to track at 100 FPS with deep regression networks[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 749–765. TAO Ran, GAVVES E, and SMEULDERS A W M. Siamese instance search for tracking[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1420–1429. ZHANG Hainan, SUN Yanjing, LI Song, et al. Long-term tracking based on multi-feature adaptive fusion for video target[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2018. CHAUDHURI K, FREUND Y, and HSU D. A parameter-free hedging algorithm[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 2009: 297–305. WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Online object tracking: a benchmark[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 2411–2418. MUELLER M, SMITH N, and GHANEM B. Context-aware correlation filter tracking[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1387–1395. DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Discriminative scale space tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1561–1575. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609928 BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, GOLODETZ S, et al. Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1401–1409. ZHANG Kaihua, LIU Qingshan, WU Yi, et al. Robust visual tracking via convolutional networks without training[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1779–1792. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
