A Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation Mechanism Based on Minimizing Devices Energy Consumption and System Delay
-
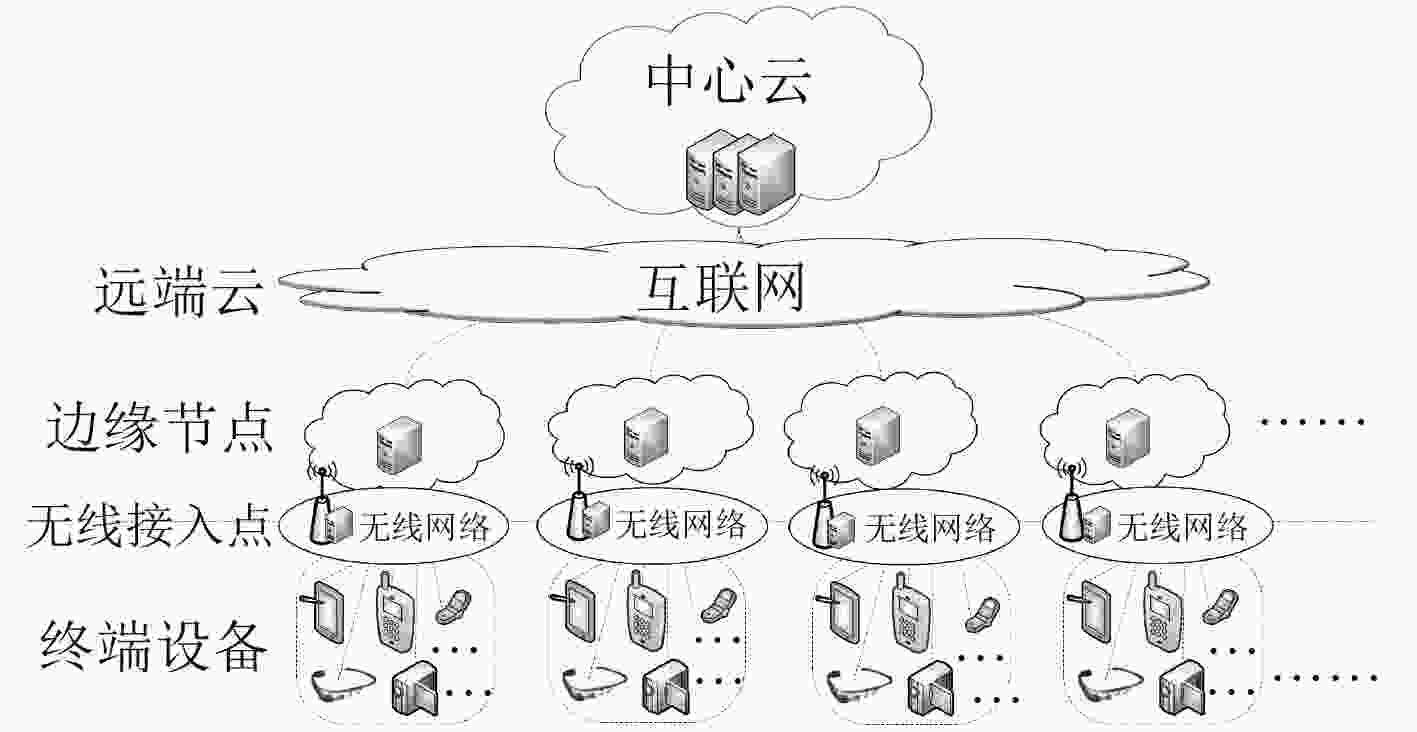
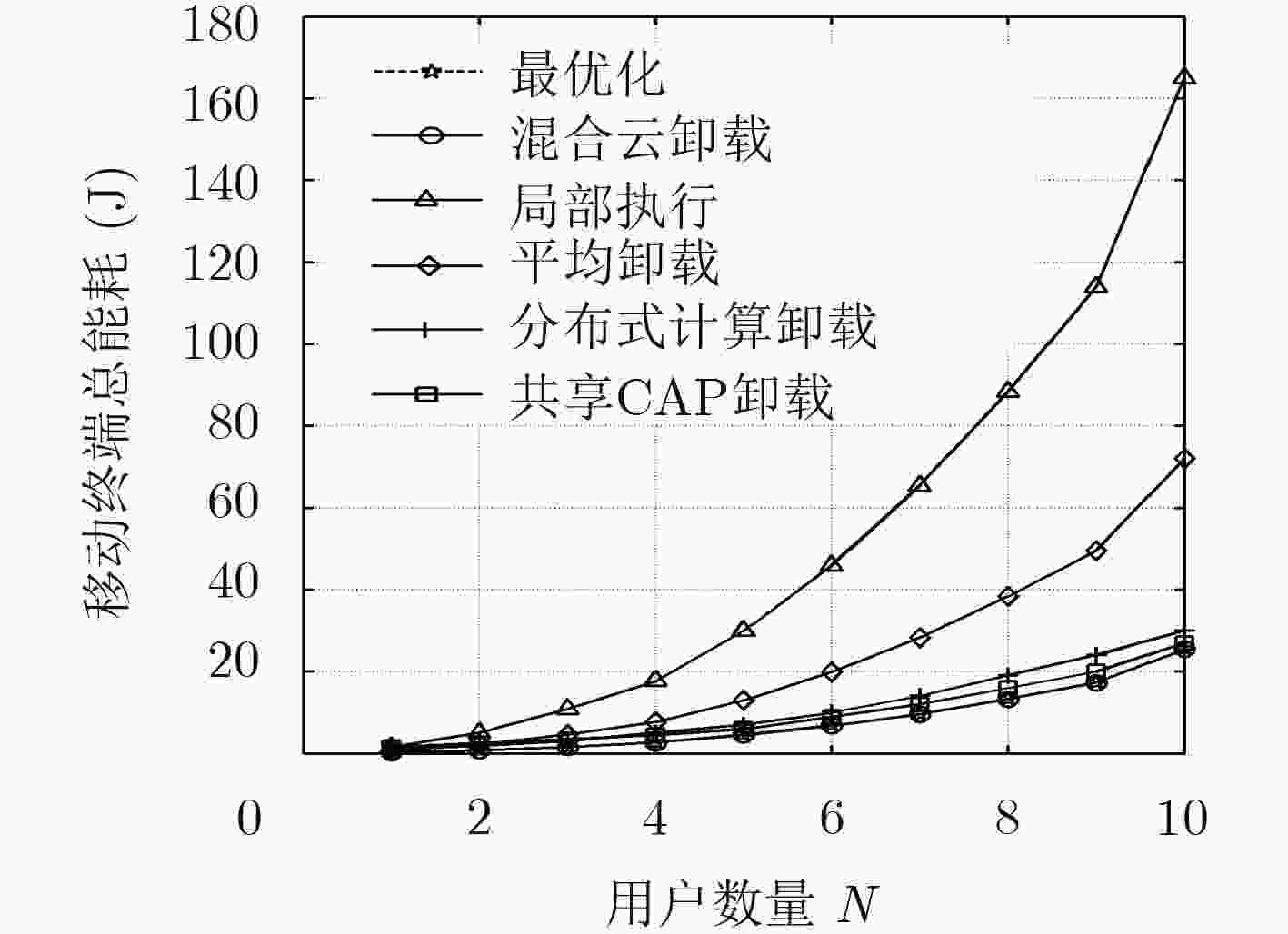
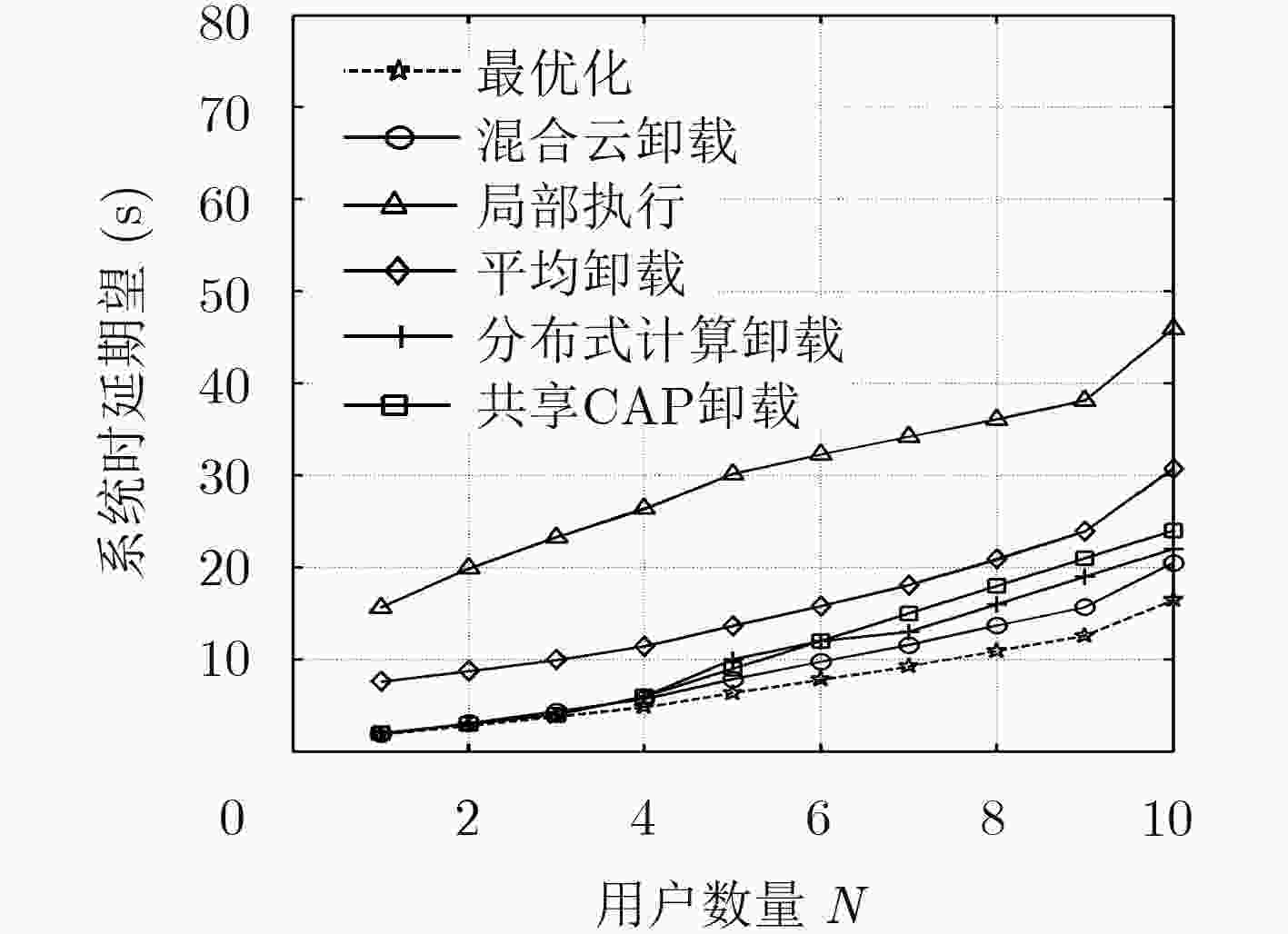
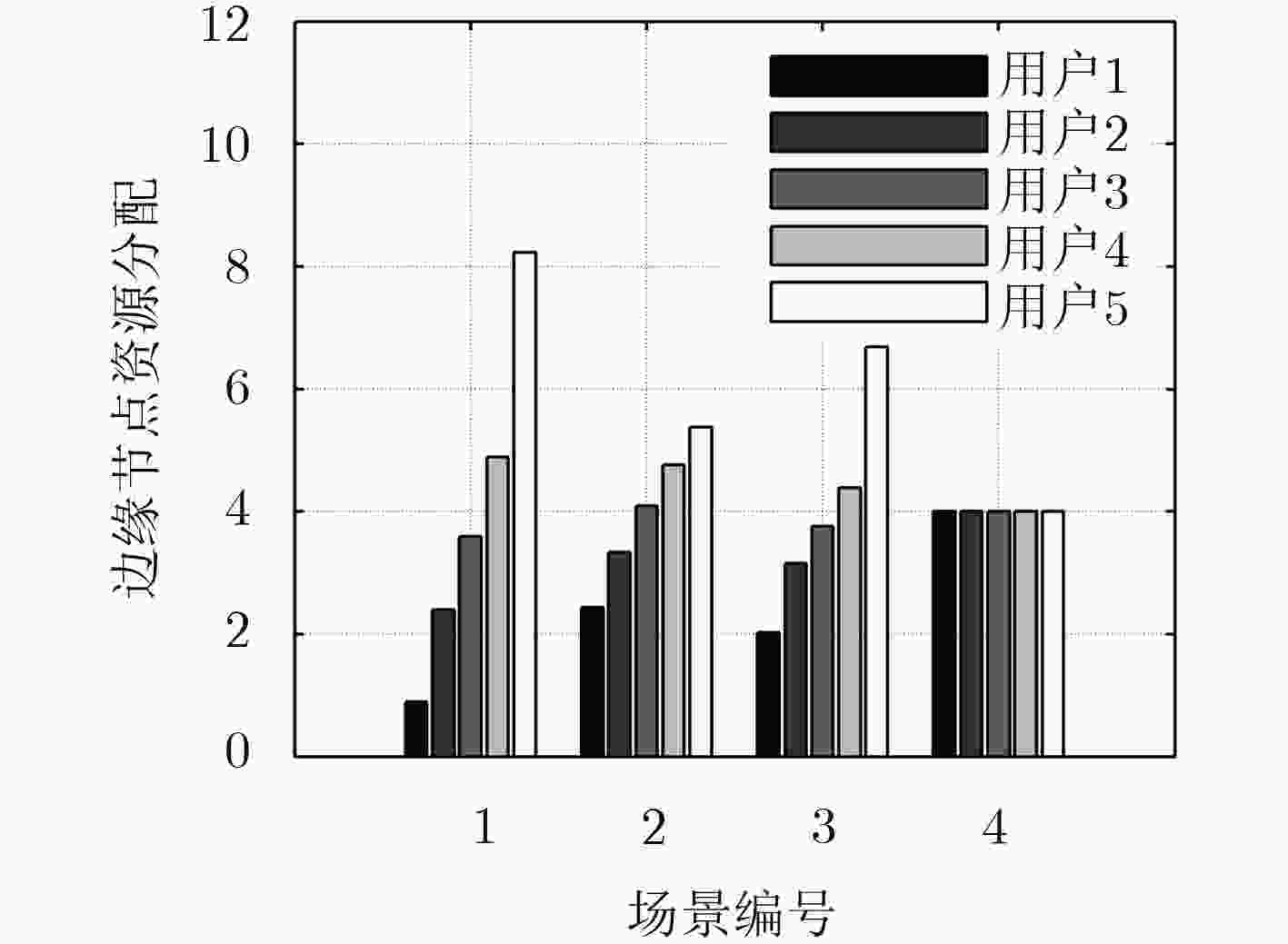
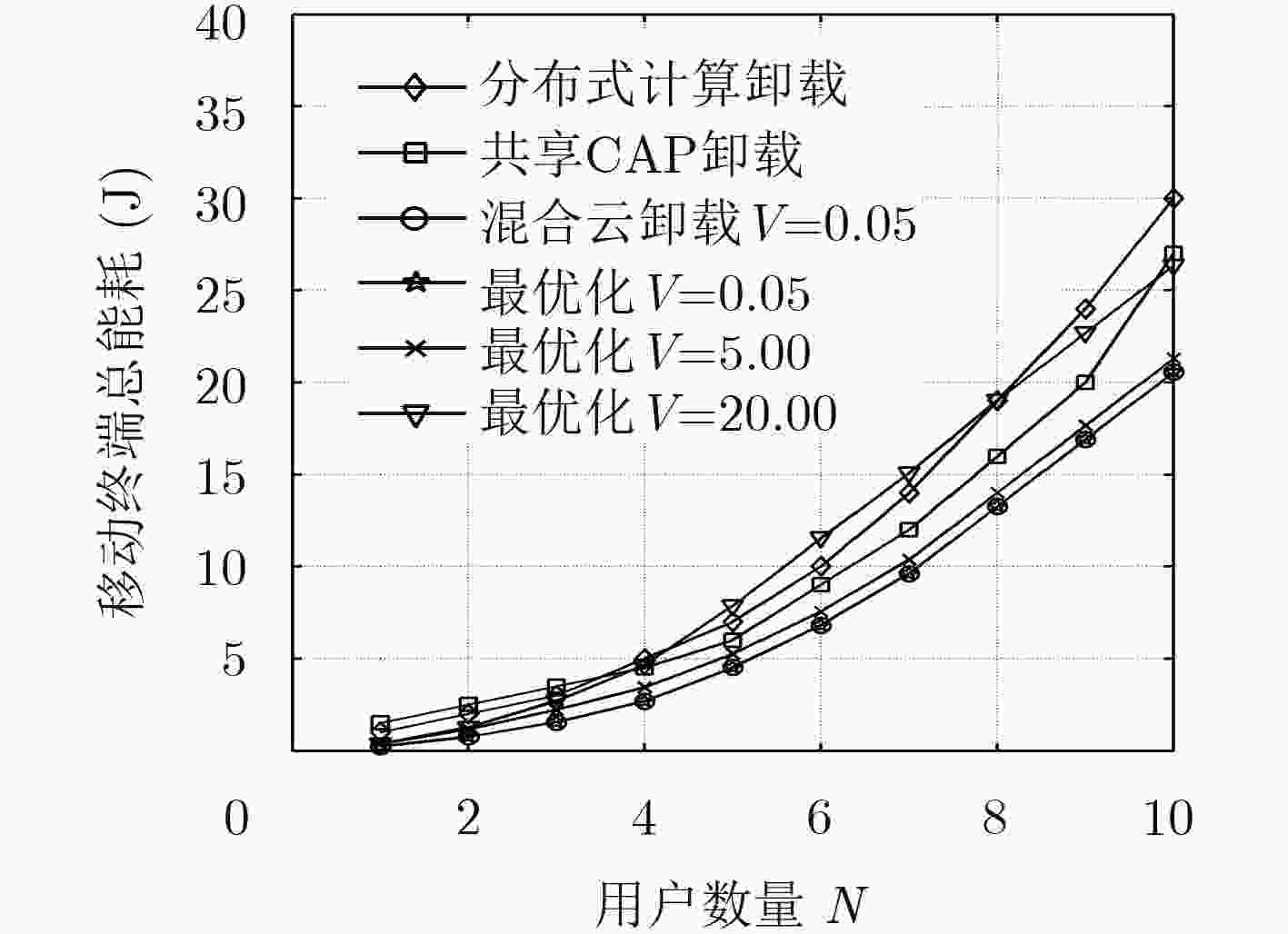
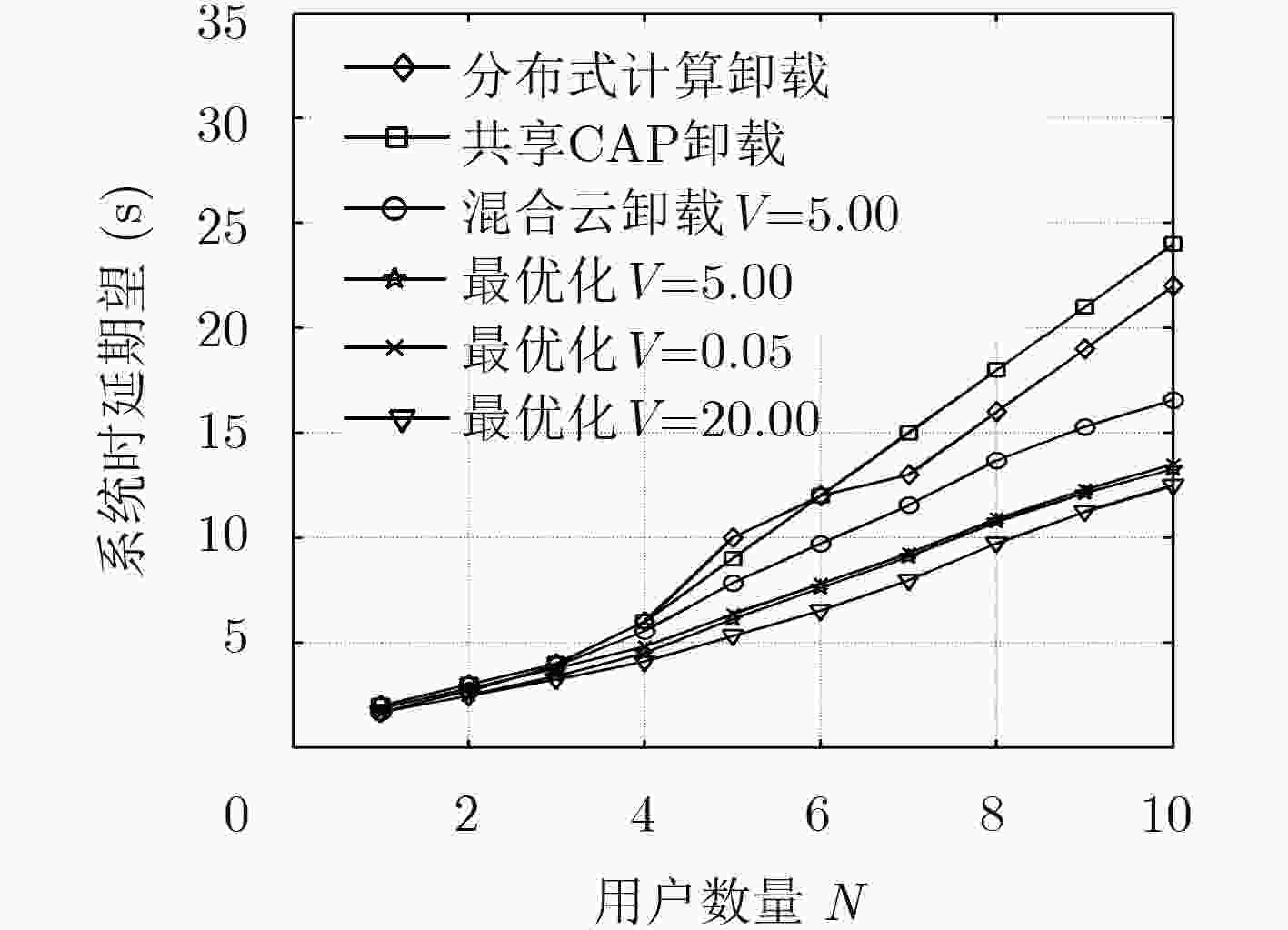
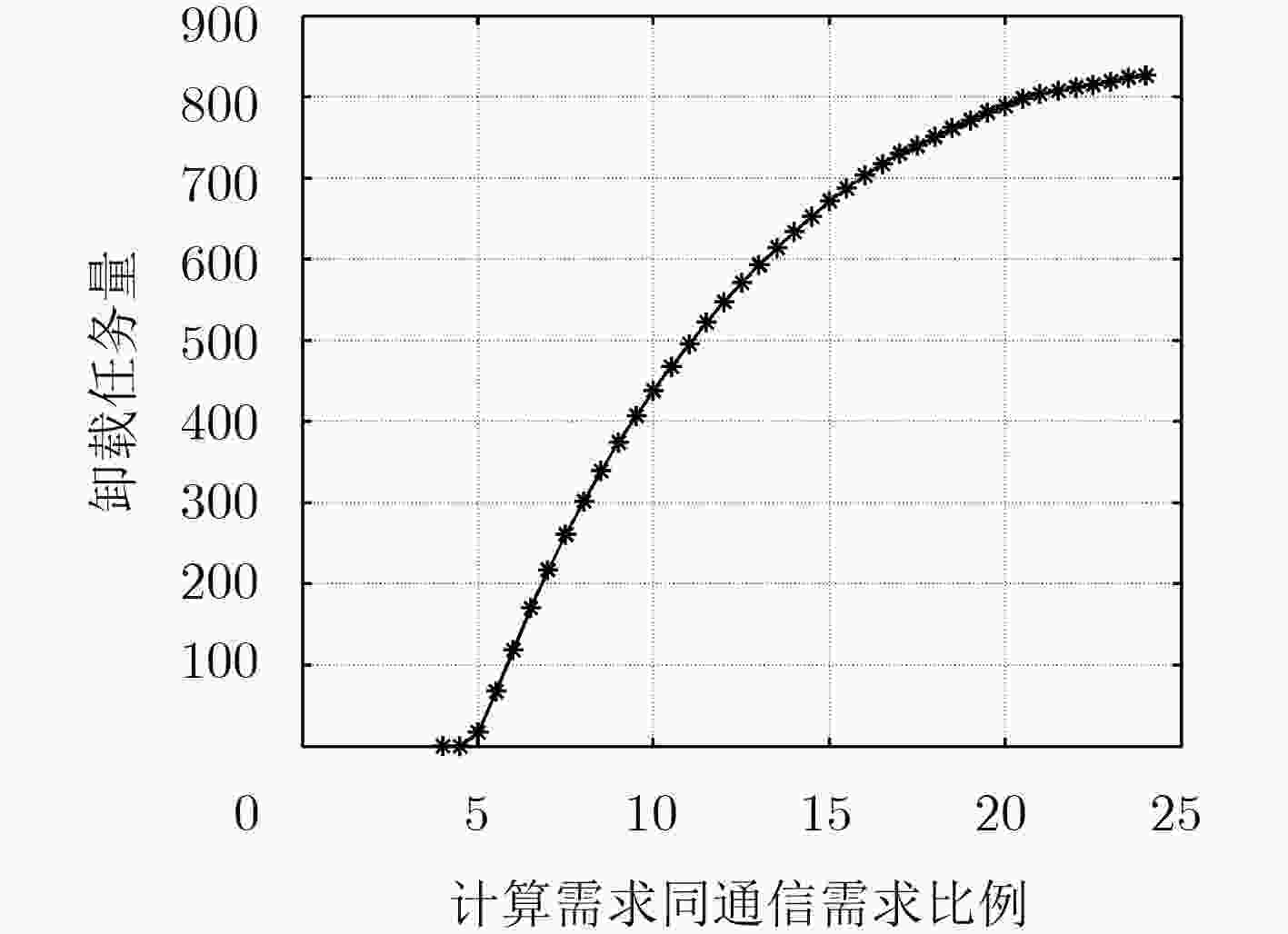
摘要: 通过移动边缘计算下移云端的应用功能和处理能力支撑计算密集或时延敏感任务的执行成为当前的发展趋势。但面对众多移动终端用户时,如何有效利用计算资源有限的边缘节点来保障终端用户服务质量(QoS)成为关键问题。为此,该文融合边缘云与远端云构建了一种分层的边缘云计算架构,以此架构为基础,以最小化移动设备能耗和任务执行时间为目标,将问题形式化描述为资源约束下的最小化能耗和时延加权和的凸优化问题,并提出基于乘子法的计算卸载及资源分配机制解决该问题。实验结果表明,在计算任务量很大的情况下,提出的计算卸载及资源分配机制能够有效降低移动终端能耗,并在任务执行时延方面较局部计算与计算卸载机制分别降低最高60%与10%,提高系统性能。Abstract: To support the execution of computation-intensive, delay-sensitive computing task by moving down the computing and processing capability in mobile edge computing becomes the current trend. However, when serving a large number of mobile users, how to use effectively the edge nodes with limited computing resources to ensure Quality of service (QoS) of end-user has become a key issue. To solve this problem, the edge cloud and remote cloud are combined to build a layered edge cloud computing architecture. Based on this architecture, with the goal of minimizing mobile device energy consumption and task execution time, the problem which is proved to be convex is formulated to minimize the weight sum of energy and delay. A computation offloading and resource allocation mechanism based on multiplier method is proposed. Simulations are conducted to evaluate the proposed mechanism. Compared with local computing and computation offloading mechanism, the proposed mechanism can effectively reduce the energy consumption of mobile device and the delay of system by up to 60% and 10%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- Edge computing /
- Computing offloading /
- Resource allocation /
- Energy consumption /
- Delay of system
-
表 1 多用户计算卸载
初始化:各移动终端数量$n$及计算能力${C_i}$,边缘节点计算能力
${C_{{\rm{edge}}}}$,远端云节点计算能力${C_{{\rm{cloud}}}}$,无线带宽资源$B$,权值$V\,$, $S = \varnothing $;输入:各用户终端计算任务请求REQ($\left[ {{\lambda _1}, {\lambda _2}, ·\!·\!· , {\lambda _n}} \right]$); 输出:最优卸载决策$S = {X^*}$; $C_i^{{\ \rm{edge}}} = {{{C_{{\rm{edge}}}}} / n}$; while TRUE do; 接收用户计算卸载请求REQ,提取请求中的对应任务信息: $B_i^{{\rm{in}}}, {V_i}, B_i^{{\rm{out}}}, P_i^{\rm{c}}, P_i^{{\rm{up}}}, {\lambda _i}$; for each $i \in \left\{ {1, 2, ·\!·\!· , n} \right\}$ do; 引入拉格朗日函数,求得满足KKT条件的最优解
$ < {x_i}, x_i^{{\rm{edge}}}, x_i^{{\rm{cloud}}} > $;最优解向下取整,得整数解$ < x' + {1_i}, x_i^{'{\rm{edge}}}, x_i^{'{\rm{cloud}}} > $, $ < {x'_i}, x_i^{'{\rm{edge}}} + 1, x_i^{'{\rm{cloud}}} > $, $ < {x'_i}, x_i^{'{\rm{edge}}}, x_i^{'{\rm{cloud}}} + 1 > $; 将整数可行解代入目标函数,取使目标函数最小的整数解为最优 整数解; end for; 回传最优解${X^*}$,移动终端接收卸载决策,执行任务; end while. 表 2 多用户计算卸载及资源分配机制
初始化:$n$, ${C_i}$, ${C_{{\rm{edge}}}}$, ${C_{{\rm{cloud}}}}$, $B$,权值$V\,$, $S = \varnothing $ 输入:各用户终端计算任务请求REQ($\left[ {{\lambda _1}, {\lambda _2}, ·\!·\!· , {\lambda _n}} \right]$) 输出:最优卸载决策$S = {X^*}$ $C_i^{{\ \rm{edge}}} = {{{C_{{\rm{edge}}}}} / n}$, ${C_0} = < C_1^{{\ \rm{edge}}}, C_2^{{\ \rm{edge}}}, ·\!·\!· , C_n^{{\ \rm{edge}}} > $; while TRUE do; 接收用户计算卸载请求REQ,提取任务信息:
$B_i^{{\rm{in}}}, {V_i}, B_i^{{\rm{out}}}, P_i^{\rm{c}}, P_i^{{\rm{up}}}, {\lambda _i}$;for each $i \in \left\{ {1, 2, ·\!·\!· , n} \right\}$ do; 引入拉格朗日函数,求得满足KKT条件的最优解
$ < {x_i}, x_i^{{\rm{edge}}}, x_i^{{\rm{cloud}}} > $;end for; 得到平均资源分配条件下的初始最优解${X^*}$, ${X_0} = {X^*}$; ${S_0} = < {X_0}, {C_0} > $; ${\mu ^{\left( 1 \right)}} = \left( {1, 1, ·\!·\!· , 1} \right)$, ${\eta ^{\left( 1 \right)}} = \left( {1, 1, ·\!·\!· , 1} \right)$, $\varepsilon = {10^{ - 5}}$, $M = 2$,
$\theta = 0.8$, $\alpha = 2$;$k = k + 1$; ${S_1} = {\rm{BFGS}}\left( {\varphi \left( {S, \mu , \eta , M} \right)} \right)$; ${\beta _k} = {\left\{ {\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{h_i}^2\left( {{S_k}} \right)} + \sum\limits_{j = 1}^{4n + 1} {{{\left[ {\left( {\min {g_j}\left( {{S_k}} \right), \frac{{{{\left( {{\eta ^{\left( K \right)}}} \right)}_j}}}{M}} \right)} \right]}^2}} } \right\}^{{1 / 2}}}$; while ${\beta _k} > \varepsilon $ do; 更新罚函数:若${\beta _k} > \theta \cdot {\beta _k}$,则$M = \alpha \cdot M$,否则$M$不变; 更新乘子向量${\mu ^{\left( k \right)}}$, ${\eta ^{\left( k \right)}}$; $k = k + 1$; ${S_k} = {\rm{BFGS}}\left( {\varphi \left( {S, \mu , \eta , M} \right)} \right)$; 依据上述公式计算${\beta _k}$值; end while; 对$ < {x_i}, x_i^{{\rm{edge}}}, x_i^{{\rm{cloud}}} > $求最优整数解,返回${S_k}^* = < {X_k}^*, {C_k}^* > $,
按${X_k}^*$进行计算卸载,按${C_k}^*$进行计算资源分配;end while. -
CHEN T Y H, RAVINDRANATH L, DENG Shuo, et al. Glimpse: Continuous, real-time object recognition on mobile devices[C]. Proceedings of the 13th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Seoul, South Korea, 2015: 155–168. LEE H S and LEE J W. Task offloading in heterogeneous mobile cloud computing: Modeling, analysis, and cloudlet deployment[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 14908–14925. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2812144 VAN DEN BOSSCHE R, VANMECHELEN K, and BROECKHOVE J. Cost-optimal scheduling in hybrid IaaS clouds for deadline constrained workloads[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cloud Computing, Miami, USA, 2010: 228–235. TONG Liang, LI Yong, and GAO Wei. A hierarchical edge cloud architecture for mobile computing[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2016- the 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–9. DU Jianbo, ZHAO Liqiang, FENG Jie, et al. Computation offloading and resource allocation in mixed fog/cloud computing systems with Min-Max fairness guarantee[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(4): 1594–1608. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2787700 AHMAD A, PAUL A, KHAN M, et al. Energy efficient hierarchical resource management for mobile cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Computing, 2017, 2(2): 100–112. doi: 10.1109/TSUSC.2017.2714344 KAO Y H, KRISHNAMACHARI B, RA M R, et al. Hermes: Latency optimal task assignment for resource-constrained mobile computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(11): 3056–3069. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2679712 WU Huaming, KNOTTENBELT W, WOLTER K, et al. An Optimal Offloading Partitioning Algorithm in Mobile Cloud Computing[M]. Cham, Springer, 2016: 311–328. DINH T Q, TANG Jianhua, LA Q D, et al. Offloading in mobile edge computing: task allocation and computational frequency scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(8): 3571–3584. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2699660 MENG Xianling, WANG Wei, and ZHANG Zhaoyang. Delay-constrained hybrid computation offloading with cloud and fog computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 21355–21367. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2748140 WANG Yanting, SHENG Min, WANG Xijun, et al. Mobile-edge computing: partial computation offloading using dynamic voltage scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(10): 4268–4282. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2016.2599530 CHEN Xu, JIAO Lei, LI Wenzhong, et al. Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2016, 24(5): 2795–2808. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2015.2487344 CHEN Xu. Decentralized computation offloading game for mobile cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2015, 26(4): 974–983. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2014.2316834 CARDELLINI V, DE NITTO PERSONÉ V, DI VALERIO V, et al. A game-theoretic approach to computation offloading in mobile cloud computing[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2016, 157(2): 421–449. doi: 10.1007/s10107-015-0881-6 CHEN Menghsi, DONG Min, and LIANG Ben. Joint offloading decision and resource allocation for mobile cloud with computing access point[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 3516–3520. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
