Frequency-hopping Transmitter Classification Based on Chaotic Attractor Reconstruction and Low-rank Clustering
-
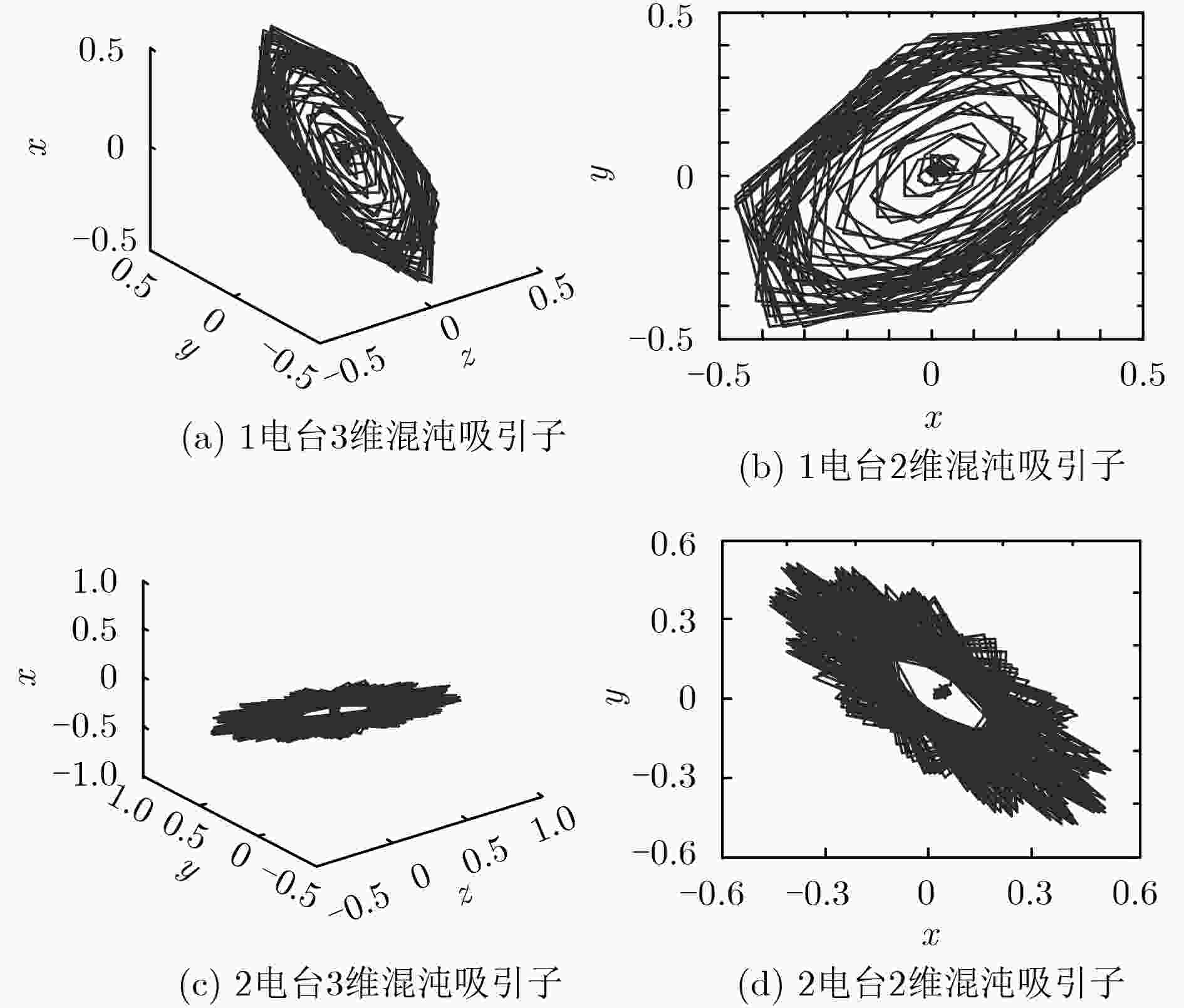
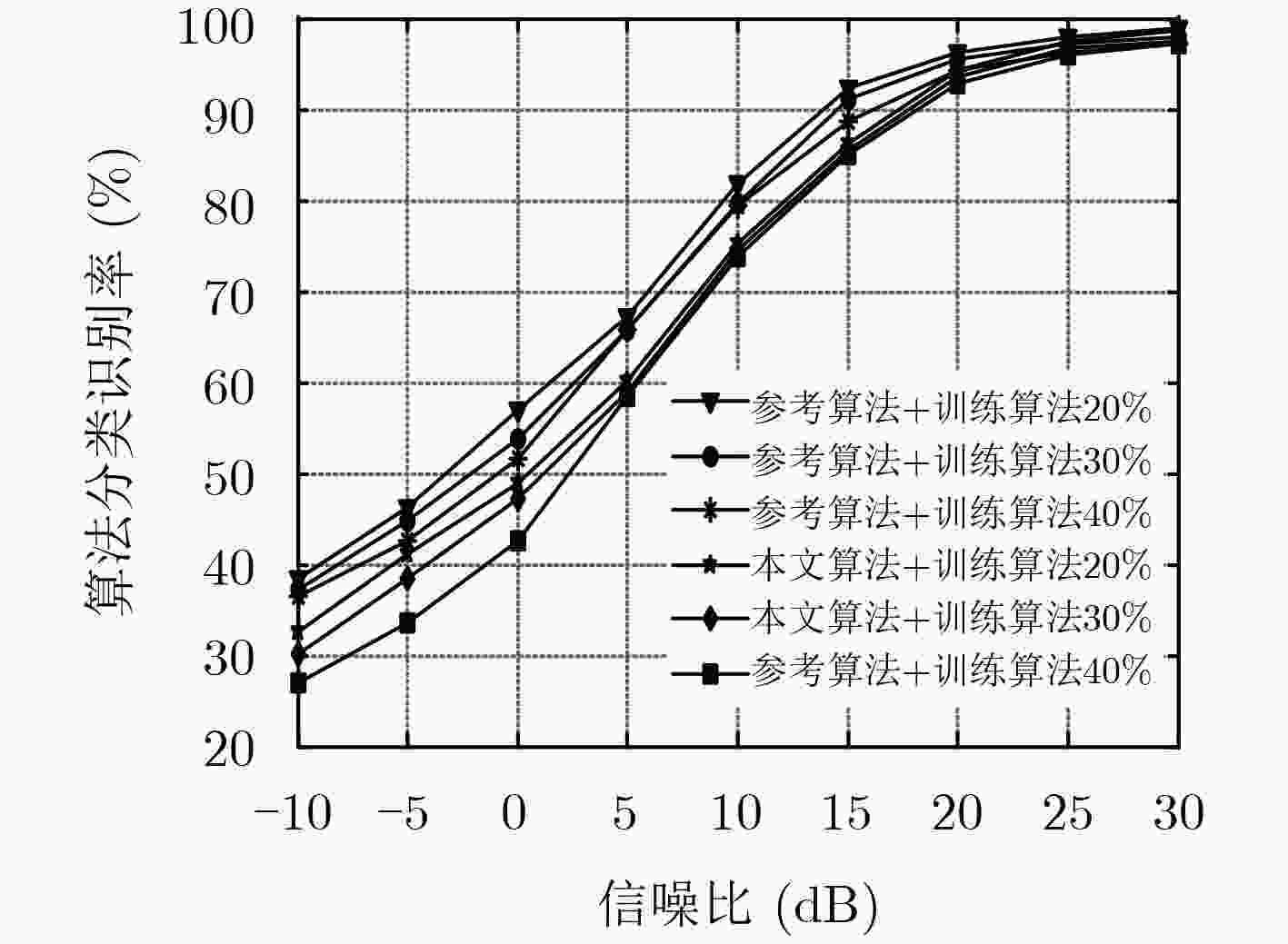
摘要: 辐射源无调制信息的暂态信号能够表征辐射源发射机的无意调制特性,对该暂态信号分析可实现辐射源识别。而跳频电台在开机以及频率转换瞬间,都存在一个无信息传送的暂态调整时间,该暂态调整瞬间,电台发射的信号是无调制信息的非线性、非平稳和非高斯信号。该暂态时间序列可反映跳频电台的器件特性,同时该序列往往呈现复杂的混沌特性。因此,借鉴混沌时间序列分析的思想,同时利用暂态信号的Low-rank特性,该文提出了一种基于暂态信号混沌吸引子重构和Low-rank聚类的跳频信号电台分选算法。实验测试表明:跳频电台的暂态信号时间序列属于混沌时间序列,同时实测多跳频信号的电台分选结果证明了Low-rank聚类算法在跳频电台分选上的可行性。
-
关键词:
- 跳频电台 /
- 暂态信号 /
- 混沌吸引子 /
- Low-rank聚类
Abstract: The transient signal without modulation information of the radiation source can characterize the unintentional modulation characteristics of the radiation source. The analysis of the transient signal can realize the radiation source identification. In the switching on and frequency conversion process of the frequency-hopping signal, there is a transient adjustment time without information transmission. In the transient adjustment moment, the signal transmitted by the transmitter is a non-linear, non-stationary and non-Gaussian signal without modulation information. This transient time series can reflect the device characteristics of the frequency-hopping transmitter, and the sequence often exhibits complex chaotic characteristics. Therefore, from the idea of chaotic time series analysis and Low-rank characteristics of transient signal, a frequency-hopping transmitter classification algorithm is proposed based on chaotic attractor reconstruction and Low-rank clustering. The experimental tests show that the transient signal of the frequency-hopping transmitter belongs to the chaotic time series. At the same time, the classification results of the frequency-hopping signals demonstrate the feasibility of the Low-rank clustering algorithm in frequency-hopping transmitter classification. -
表 1 暂态信号混沌吸引子的分形特征量
电台类别 分形特征量 Kolmogorov熵 Lyapunov指数 相关维数 电台1 0.5667 0.0312 3.2658 电台2 0.4610 0.1372 4.9878 电台3 0.9925 0.2207 1.4193 电台4 0.2919 0.1632 2.7587 -
齐昶, 王斌, 丁海军. 基于KHM聚类算法的跳频信号分选[J]. 声学技术, 2011, 30(6): 547–551. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2011.06.017QI Chang, WANG Bin, and DING Haijun. Identification of frequency hopping signals based on clustering[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2011, 30(6): 547–551. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2011.06.017 姚瑶, 赵知劲, 尚俊娜. 一种跳频信号网台分选方法[J]. 杭州电子科技大学学报, 2009, 29(1): 33–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9146.2009.01.009YAO Yao, ZHAO Zhijin, and SHANG Junna. A method for FH signal network-station sorting[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2009, 29(1): 33–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9146.2009.01.009 于欣永, 郭英, 张坤峰, 等. 基于盲源分离的多跳频信号网台分选算法[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(8): 1082–1089. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.08.008YU Xinyong, GUO Ying, ZHANG Kunfeng, et al. A network sorting algorithm based on blind source separation of multi-FH signal[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(8): 1082–1089. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.08.008 ELLIS K J and SERINKEN N. Characteristics of radio transmitter fingerprints[J]. Radio Science, 2016, 36(4): 585–597. doi: 10.1029/2000rs002345 SUI Ping, GUO Ying, ZHANG Kunfeng, et al. Frequency-hopping transmitter fingerprint feature classification based on kernel collaborative representation classifier[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2017, 2017: 9403590. doi: 10.1155/2017/9403590 顾晓辉, 刘永强, 杨绍普, 等. 基于混沌吸引子特征量的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 石家庄铁道大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 28(1): 91–95. doi: 10.13319/j.cnki.sjztddxxbzrb.2015.01.19GU Xiaohui, LIU Yongqiang, YANG Shaopu, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on characteristic auantities of chaotic attractor[J]. Journal of Shijiazhuang Tiedao University:Natural Science Edition, 2015, 28(1): 91–95. doi: 10.13319/j.cnki.sjztddxxbzrb.2015.01.19 相征, 张太镒, 孙建成. 基于混沌吸引子的快衰落信道预测算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 33(1): 145–149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2006.01.034XIANG Zheng, ZHANG Taiyi, and SUN Jiancheng. Prediction algorithm for fast fading channels based on the chaotic attractor[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2006, 33(1): 145–149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2006.01.034 王皓石. 图像的混沌吸引子研究[D]. [硕士论文], 吉林大学, 2015.WANG Haoshi. Study on the chaotic attractor of image[D]. [Master dissertation], Jinlin University, 2015. TAKENS F. Detecting Strange Attractors in Turbulence[M]. RAND D and YOUNG L S. Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Berlin, Gemany, Springer-Verlag, 1981: 366–381. KUGIUMTZIS D. State space reconstruction parameters in the analysis of chaotic time series - the role of the time window length[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1996, 95(1): 13–28. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(96)00054-1 SUN L, KINSNER W, and SERINKEN N. Characterization and feature extraction of transient signals using multifractal measures[C]. 1999 IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Edmonton, Canada, 1999: 781–785. SHAW D and KINSNER W. Multifractal modelling of radio transmitter transients for classification[C]. IEEE WESCANEX 97 Communications, Power and Computing. Conference Proceedings, Winnipeg, Canada, 2002: 306–312. FRASER A M and SWINNEY H L. Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information[J]. Physical Review A, 1986, 33(2): 1134–1140. doi: 10.1103/physreva.33.1134 KENNEL M B, BROWN R, and ABARBANEL H D. Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(6): 3403–3411. doi: 10.1103/physreva.45.3403 LIU Guangcan, LIN Zhouchen, YAN Shuicheng, et al. Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 171–184. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2012.88 YANG Junfeng and ZHANG Yin. Alternating direction algorithms for L1-problems in compressive sensing[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2011, 33(1): 250–278. doi: 10.1137/090777761 ZHANG Haixian, ZHANG Yi, and XI Peng. fLRR: Fast Low-rank representation using Frobenius-norm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(13): 936–938. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.1396 -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
