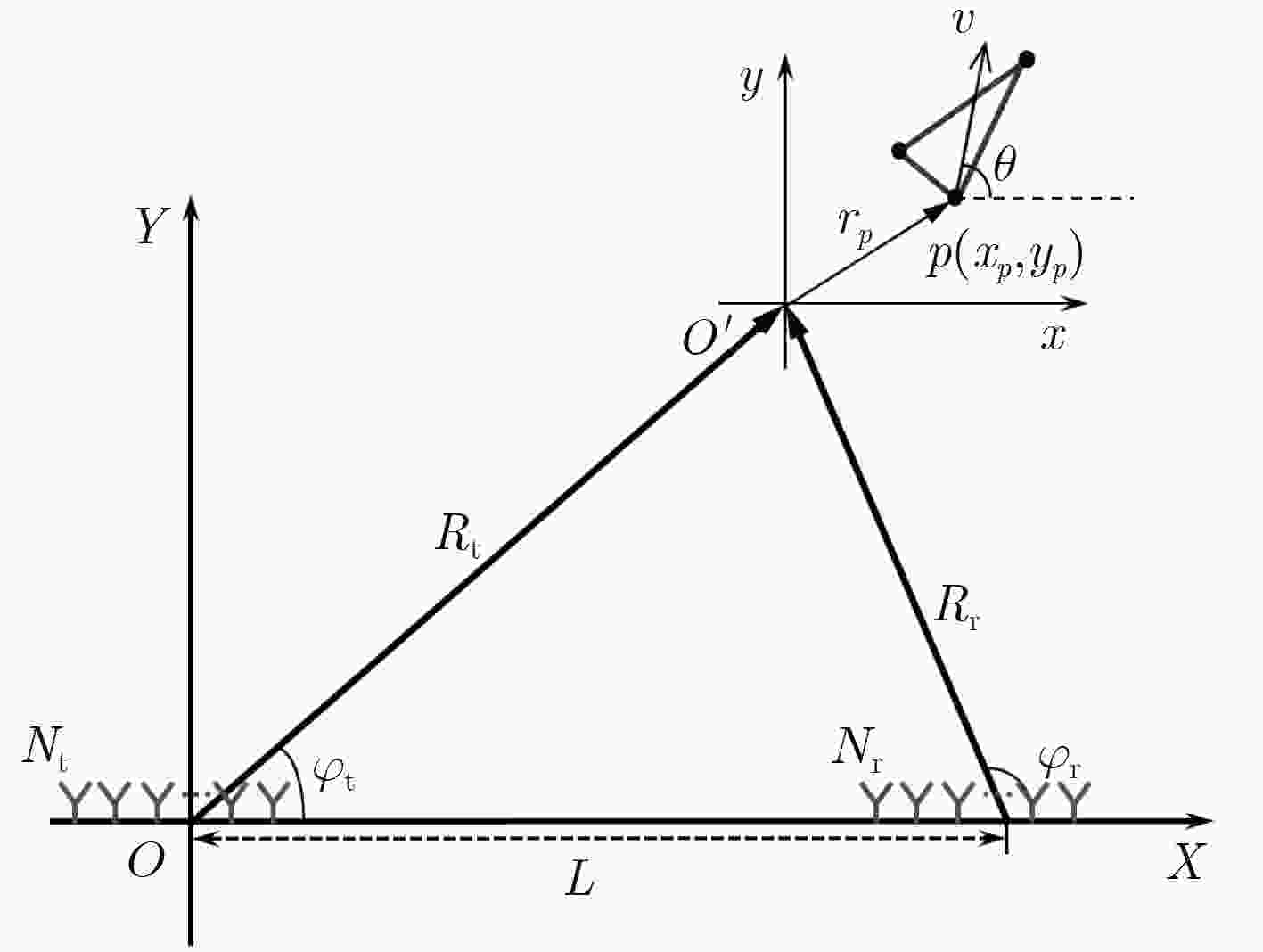
Bistatic Radar Coincidence Imaging Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning
-
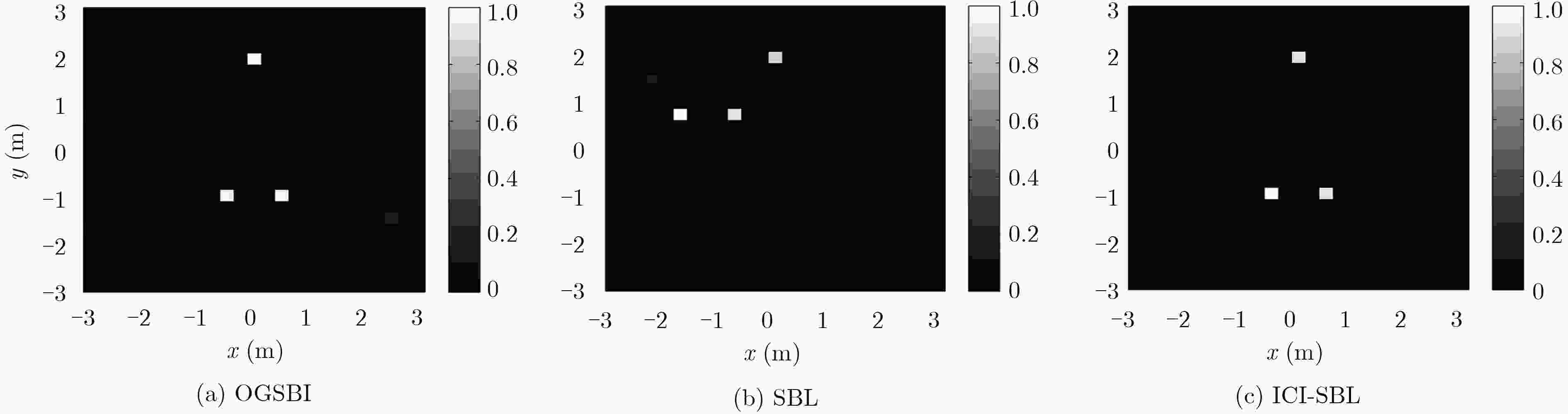
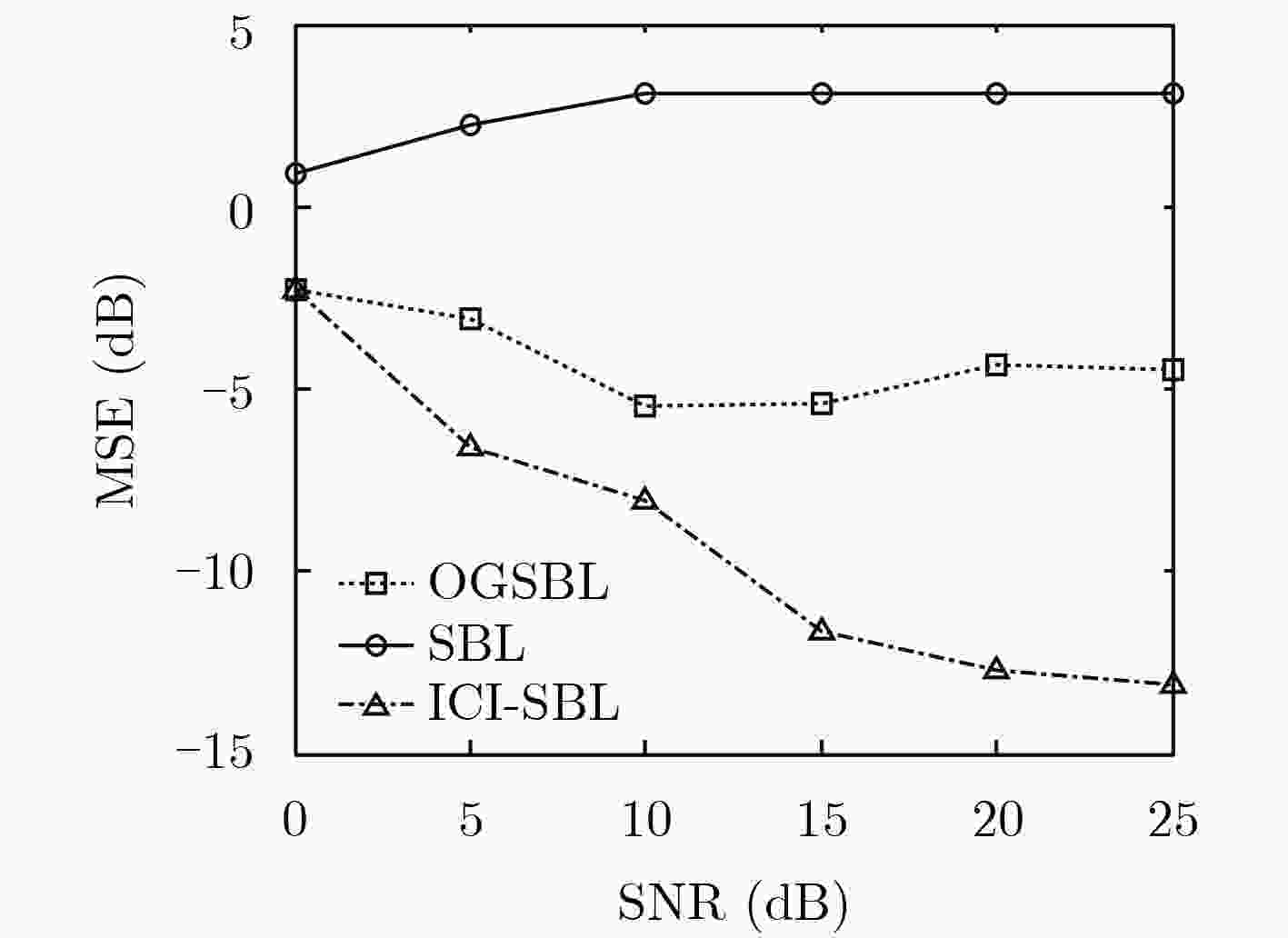
摘要: 双基雷达具有隐蔽性高、抗干扰性能强等优点,在现代电子战中发挥重要作用。基于雷达关联成像原理,该文研究运动目标双基雷达关联成像问题。首先,针对采用均匀线性阵列作为收发天线的双基雷达系统,在发射随机频率调制信号条件下,分析运动目标雷达回波信号特点,建立双基雷达关联成像参数化稀疏表征模型;其次,针对建立的参数化稀疏表征模型,提出一种基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的迭代关联成像算法。该算法在建立贝叶斯模型基础上,通过贝叶斯推理,得到稀疏重构信号,从而实现对运动目标成像和运动参数的精确估计。最后,通过仿真实验验证所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Bistatic radar has the advantages of high concealment and strong anti-interference performance, and plays an important role in modern electronic warfare. Based on the principle of radar coincidence imaging, the problem of bistatic radar coincidence imaging of moving targets is studied. Firstly, based on the bistatic radar system that uses uniform linear array as the transmitting and receiving antenna, the characteristics of the moving target radar echo signal are analyzed under the condition of transmitting random frequency modulation signal, and a bistatic radar coincidence imaging parametric sparse representation model is established. Secondly, an iterative coincidence imaging algorithm based on sparse Bayesian learning is proposed for the parametric sparse representation model established. Based on the Bayesian model, the sparse reconstructed signal is obtained by Bayesian inference, so that the moving target imaging and accurate estimation of motion parameters can be achieved. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by simulation experiments.
-
表 1 ICI-SBL算法步骤
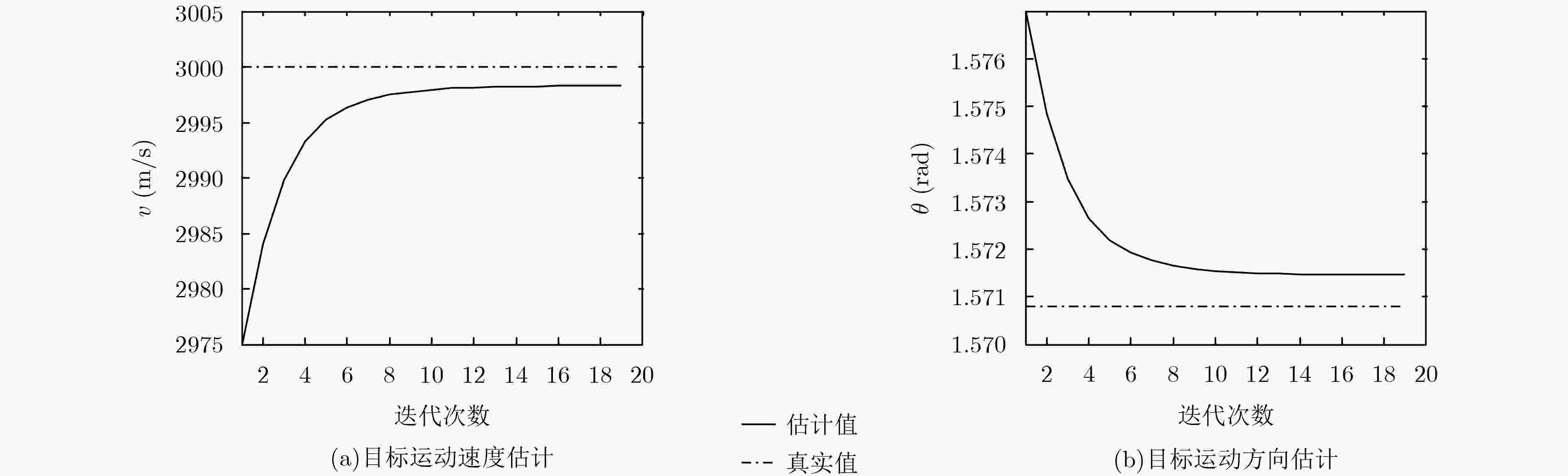
ICI-SBL算法步骤 输入:输入${\text{y}}$, ${{\text{S}}_0}$, ${{\text{S}}_1}$和${{\text{S}}_2}$; (1) 迭代次数$k = 0$,初始化相关参数$\alpha _0^0$和${{\text{α}}^0}$,令$\rm{\rho } = 0.01$, $\rm{a} = \rm{b} = {10^{ - 4}}$, $v = {v_0}$, $\theta = {\theta _0}$,并设置终止迭代次数$K = 2000$,成像区域散射
强度矢量重构精度${\varepsilon _{{\text{σ}}}} = {10^{ - 2}}$,目标运动速度估计精度${\varepsilon _v} = {10^{ - 4}}$,目标运动方向估计精度${\varepsilon _\theta } = {10^{ - 6}}$;(2) 令$k = k + 1$; (3) 根据式(17)和式(18),计算并更新第$k$次的成像区域散射强度矢量${{\text{σ}}^k}$后验分布的协方差${\text{Σ}}_{{\text{σ}}}^k$和均值${\text{μ}}_{{\text{σ}}}^k$; (4) 目标运动参数更新过程:根据式(22)和式(23),计算并更新第$k$次的目标运动参数${v^k}$和${\theta ^k}$; (5) 判断是否满足终止条件:若$k > K$,或者$\left| {{\text{μ}}_{{\text{σ}}}^k - {\text{μ}}_{{\text{σ}}}^{k - 1}} \right| < {\varepsilon _{{\text{σ}}}}$,或者$\left| {{v^k} - {v^{k - 1}}} \right| < {\varepsilon _v}$且$\left| {{\theta ^k} - {\theta ^{k - 1}}} \right| < {\varepsilon _\theta }$,输出结果。否则,继续步骤(6); (6) 环境参数即噪声功率更新过程:根据式(24),计算并更新噪声功率的倒数$\alpha _0^k$; (7) 成像区域散射强度矢量${{{\text{σ}}}^k}$先验协方差矩阵更新过程:根据式(25),计算并更新参数${{{\text{α}}}^k}$,跳转步骤(2)。 输出:输出成像区域散射强度矢量重构结果$\hat {{\text{σ}}} = {\text{μ}}_{{\text{σ}}}^k$,目标运动速度$\hat v = {v^k}$,目标运动方向$\hat \theta = {\theta ^k}$。 表 2 不同发射机天线阵元数目的条件数结果
发射机天线阵元数目${N_{\rm t}}$ 3 5 7 9 11 条件数($ \times {10^8}$) 2.1451 1.3506 0.8652 0.7393 0.5546 表 3 不同接收机天线阵元数目的条件数结果
接收机天线阵元数目${N_{\rm r}}$ 1 2 4 8 16 条件数($ \times {10^{10}}$) 1.3644 0.0695 0.0057 0.0027 2.9464 -
刘玉春. 双基雷达成像算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2013.LIU Yuchun. Study on imaging algorithms for bistatic radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2013. 胡程, 刘长江, 曾涛. 双基地前向散射雷达探测与成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 229–243. doi: 10.12000/JR16058HU Cheng, LIU Changjiang, and ZENG Tao. Bistatic forward scattering radar detection and imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 229–243. doi: 10.12000/JR16058 曾涛. 双基地合成孔径雷达发展现状与趋势分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 329–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20093ZENG Tao. Bistatic SAR: State of the art and development trend[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 329–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20093 朱小鹏, 颜佳冰, 张群, 等. 基于双基ISAR的空间高速目标成像分析[J]. 空军工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 12(6): 44–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2011.06.009ZHU Xiaopeng, YAN Jiabing, ZHANG Qun, et al. The imaging analysis of high speed space targets in Bi-ISAR system[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University:Natural Science Edition, 2011, 12(6): 44–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2011.06.009 ZHANG Shunsheng, SUN Sibo, ZHANG Wei, et al. High-resolution bistatic ISAR image formation for high-speed and complex-motion targets[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3520–3531. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2417192 JIANG Yicheng, SUN Sibo, YEO T S, et al. Bistatic ISAR distortion and defocusing analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(3): 1168–1182. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140028 KANG M S, KANG B S, LEE S H, et al. Bistatic-ISAR distortion correction and range and cross-range scaling[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(16): 5068–5078. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2713804 KANG B S, BAE J H, KANG M S, et al. Bistatic-ISAR cross-range scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(4): 1962–1973. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2677798 ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, and LI Xiang. Bayesian bistatic ISAR imaging for targets with complex motion under low SNR condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(5): 2447–2460. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2803300 陈文峰, 吕明久, 夏赛强, 等. 低信噪比下双基地ISAR一维距离成像分辨率增强方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2484–2490. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180081CHEN Wenfeng, LÜ Mingjiu, XIA Saiqiang, et al. Resolution enhancement method for bistatic ISAR one-dimensional range profile under low SNR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2484–2490. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180081 BAE J H, KANG B S, LEE S H, et al. Bistatic ISAR image reconstruction using sparse-recovery interpolation of missing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(3): 1155–1167. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.150245 DENG Donghu, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. Resolution and micro-Doppler effect in Bi-ISAR system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 152–167. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13039 ZHAO Lizhi, GAO Meiguo, MARTORELLA M, et al. Bistatic three-dimensional interferometric ISAR image reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 951–961. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130702 WANG Yong and LI Xuelu. Three-dimensional interferometric ISAR imaging for the ship target under the bi-static configuration[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(4): 1505–1520. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2513774 STAGLIANÒ D, GIUSTI E, LISCHI S, et al. Bistatic three-dimensional interferometric ISAR[J]. IET IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(1): 63–75. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0131 李东泽. 雷达关联成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014.LI Dongze. Radar coincidence imaging technique research[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014. LI Dongze, LI Xiang, QIN Yuliang, et al. Radar coincidence imaging: An instantaneous imaging technique with stochastic signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(4): 2261–2277. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2258929 何学智. 微波凝视关联成像的信息处理方法与仿真[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2013.HE Xuezhi. The information processing methods and simulations in microwave staring correlated imaging[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2013. 查国峰. 运动目标微波关联成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2016.ZHA Guofeng. Microwave coincidence imaging technique research for moving target[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2016. 张群, 罗迎. 雷达目标微多普勒效应[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: 50–51.ZHANG Qun and LUO Ying. Micro-Doppler Effect of Radar Targets[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: 50–51. CHEN Yichang, LI Gang, ZHAN Qun, et al. Refocusing of moving targets in SAR images via parametric sparse representation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 795. doi: 10.3390/rs9080795 YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 38–43. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222378 LIU Kang, LI Xiang, GAO Yue, et al. High-resolution electromagnetic vortex imaging based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(21): 6918–6917. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2754554 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
