Total Variation Regularized Reconstruction Algorithms for Block Compressive Sensing
-
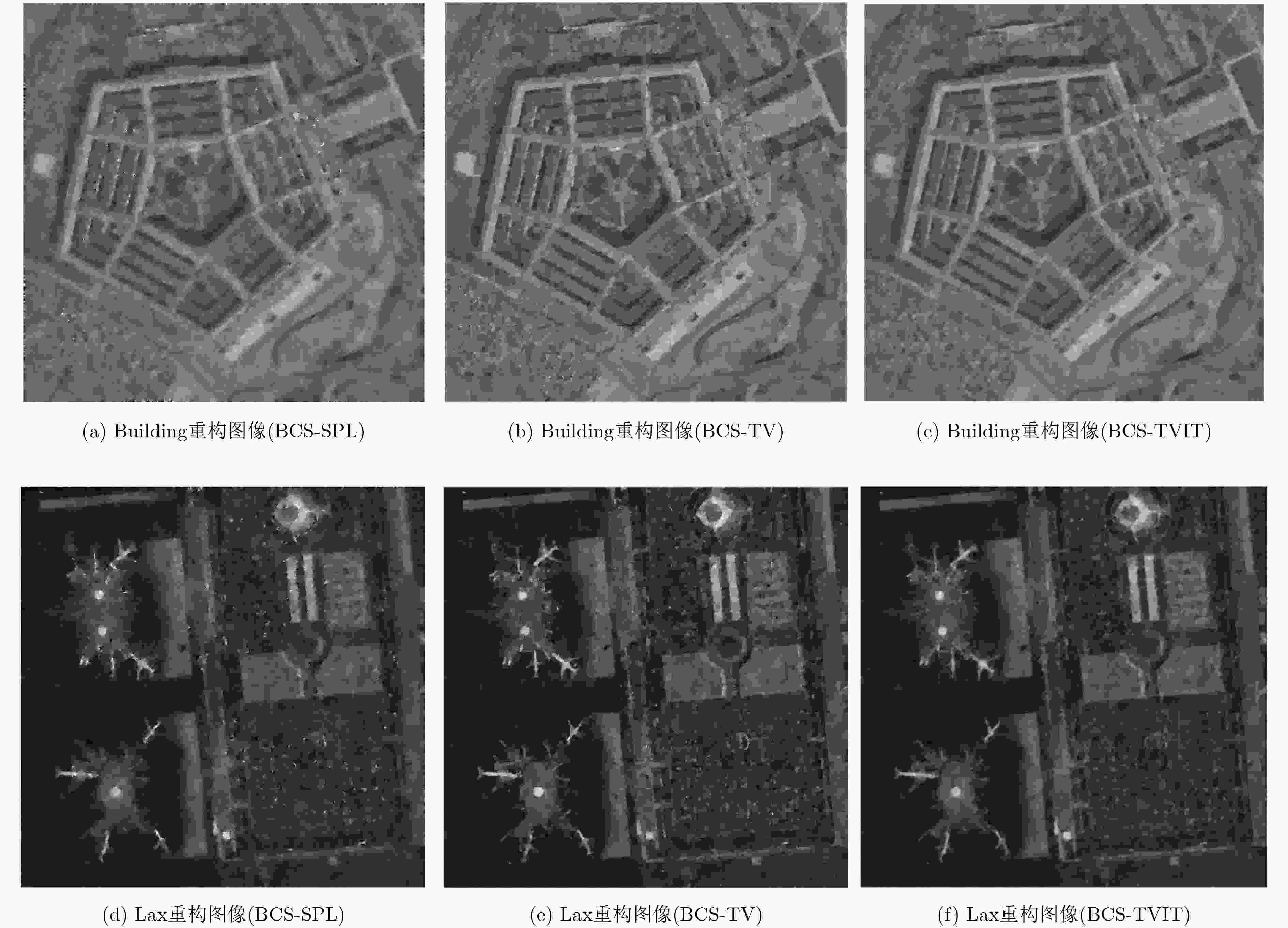
摘要: 针对分块压缩感知(BCS)重建图像质量较差问题,该文提出一种最小化l0范数的分块压缩感知全变差(TV)正则化迭代阈值图像重构算法(BCS-TVIT)。BCS-TVIT算法考虑图像的局部平滑、有界变差等性质,将最小化l0范数与图像的全变差TV正则项结合,构建目标函数。针对目标函数中l0范数项和分块测量约束项无法直接优化问题,采用迭代阈值法使重构图像l0范数最小化,并通过凸集投影保证满足约束条件,完成了目标函数的优化求解。实验表明,与基于l0范数最小化的分块压缩感知平滑投影算法(BCS-SPL)相比,BCS-TVIT算法重构图像峰值信噪比提高2 dB,能消除BCS-SPL的“亮斑”效应,且在视觉效果上明显优于BCS-SPL算法;与最小全变差算法相比,BCS-TVIT算法重构图像峰值信噪比提升1 dB,且能降低重构时间约2个数量级。Abstract: In order to improve the quality of reconstruction image by Block Compressed Sensing (BCS), a Total Variation Iterative Threshold regularization image reconstruction algorithm (BCS-TVIT) is proposed. Combining the properties of local smoothing and bounded variation of the image, BCS-TVIT uses the minimization l0 norm and total variation to construct the objective function. To solve the problem that l0 norm term and the block measurement constraint can not be optimized directly, the iterative threshold method is used to minimize the l0 norm of the reconstructed image, and the convex set projection is employed to guarantee the block measurement constraint condition. Experiments show that BCS-TVIT has better performance than BCS-SPL in PSNR by 2 dB. Meanwhile, BCS-TVIT can eliminate the " bright spot” effect of BCS-SPL, having better visual effect. Comparing with the minimum total variation, the proposed algorithm increases PSNR by 1 dB, and the reconstruction time is reduced by two orders of magnitude.
-
表 1 各算法的重构PSNR (dB)
算法 采样率 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 BCS-SPL[6] 22.50 24.02 25.64 27.28 28.91 Barbara BCS-TV[15] 22.38 23.52 24.48 25.56 26.73 BCS-TVIT 22.67 24.41 26.46 28.73 31.58 BCS-SPL[6] 23.73 25.30 26.57 27.72 29.01 Lax BCS-TV[15] 23.75 26.05 28.06 29.93 31.77 BCS-TVIT 24.16 26.88 28.69 30.50 32.28 BCS-SPL[6] 25.54 27.10 28.27 29.39 30.59 Building BCS-TV[15] 25.45 27.99 29.88 31.69 33.50 BCS-TVIT 26.28 28.99 30.63 32.19 33.74 BCS-SPL[6] 23.37 25.32 26.80 28.31 29.56 Aerial BCS-TV[15] 23.22 25.63 27.67 29.42 31.41 BCS-TVIT 24.02 27.28 29.57 31.56 33.26 表 2 各算法的重构时间(s)
算法 采样率 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 BCS-SPL[6] 52 16 12 12 9 Barbara BCS-TV[15] 1210 1514 1759 2136 2690 BCS-TVIT 70 57 32 21 21 BCS-SPL[6] 35 28 27 25 24 Lax BCS-TV[15] 1179 1499 1737 2097 2638 BCS-TVIT 39 30 28 29 25 BCS-SPL[6] 51 35 25 24 21 Building BCS-TV[15] 1222 1539 1781 2153 2684 BCS-TVIT 53 38 26 26 22 BCS-SPL[6] 50 30 26 24 18 Aerial BCS-TV[15] 1170 1492 1750 2125 2666 BCS-TVIT 51 30 28 23 19 表 3 重构图像PSNR (dB)
-
CANDÈS E J, ELDAR Y C, NEEDELL D, et al. Compressed sensing with coherent and redundant dictionaries[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2010, 31(1): 59–73. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2010.10.002 KABANAVA M and RAUHUT H. Cosparsity in Compressed Sensing[M]. Cham: Birkhäuser, 2015: 315–339. ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, ZHANG Y D, et al. Compressive sensing-based coprime array direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(11): 1719–1724. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2016.1048 GAN Lu. Block compressed sensing of natural images[C]. 2007 5th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Cardiff, UK, 2007: 403–406. VAN CHIEN T, DINH K Q, JEON B, et al. Block compressive sensing of image and video with nonlocal Lagrangian multiplier and patch-based sparse representation[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2017, 54: 93–106. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2017.02.012 MUN S and FOWLER J E. Block compressed sensing of images using directional transforms[C]. The 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Cairo, Egypt, 2009: 3021–3024. 唐朝伟, 王雪锋, 杜永光. 一种稀疏度自适应分段正交匹配追踪算法[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(3): 784–792. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.03.011TANG Chaowei, WANG Xuefeng, and DU Yongguang. A sparsity adaptive stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) , 2016, 47(3): 784–792. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.03.011 CANDES E J and TAO T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(12): 5406–5425. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.885507 EFTEKHARI A and WAKIN M B. New analysis of manifold embeddings and signal recovery from compressive measurements[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2015, 39(1): 67–109. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2014.08.005 陈勇, 吴春婷, 刘焕淋. 基于改进压缩感知的缺损光纤Bragg光栅传感信号修复方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(2): 386–393. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170424CHEN Yong, WU Chunting, and LIU Huanlin. A repaired algorithm based on improved compressed sensing to repair damaged fiber bragg grating sensing signal[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(2): 386–393. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170424 BLUMENSATH T and DAVIES M E. Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 27(3): 265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2009.04.002 宋和平, 王国利. 稀疏信号重构的阈值化迭代检测估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(10): 2431–2437. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01696SONG Hepin and WANG Guoli. Sparse signal recovery via iterative detection estimation with thresholding[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(10): 2431–2437. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01696 XIAO Yunhai, YANG Junfeng, and YUAN Xiaoming. Alternating algorithms for total variation image reconstruction from random projections[J]. Inverse Problems & Imaging, 2012, 6(3): 547–563. doi: 10.3934/ipi.2012.6.547 CANDES E J, ROMBERG J, and TAO T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489–509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 CANDÈS E J, ROMBERG J K, and TAO T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2006, 59(8): 1207–1223. doi: 10.1002/cpa.20124 CHEN Gao, LI Gang, and ZHANG Jiashu. Tensor compressed video sensing reconstruction by combination of fractional-order total variation and sparsifying transform[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2017, 55: 146–156. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2017.03.021 USC. The USC-SIPI image database[EB/OL]. http://sipi.usc.edu/database/database.php?volume=misc&image=12, 2018. CHEN Duo, WAN Suiren, XIANG Jing, et al. A high-performance seizure detection algorithm based on Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and EEG[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(3): e0173138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173138 YANG Jingyu, XU Wenli, DAI Qionghai, et al. Image compression using 2D Dual-tree Discrete Wavelet Transform (DDWT)[C]. 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2007: 297–300. SAI N S T and PATIL R C. Image retrieval using 2D dual-tree discrete wavelet transform[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2011, 14(6): 1–8. doi: 10.5120/1891-2513 SENDUR L and SELESNICK I W. Bivariate shrinkage functions for wavelet-based denoising exploiting interscale dependency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(11): 2744–2756. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.804091 GOMATHI R, and SELVAKUMARAN S. A new bivariate shrinkage denoising of remotely sensed images with Discrete Shearlet Transform (DST)[C]. 2018 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 2018: 173–175. ZHANG Fuqiang and LIU Zengli. Image denoising based on the bivariate model of dual tree complex wavelet transform[C]. The 11th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Shenzhen, China, 2015: 171–174. doi: 10.1109/CIS.2015.49. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
