Adaptive Regularized Correlation Filters for Visual Tracking Based on Sample Quality Estimation
-
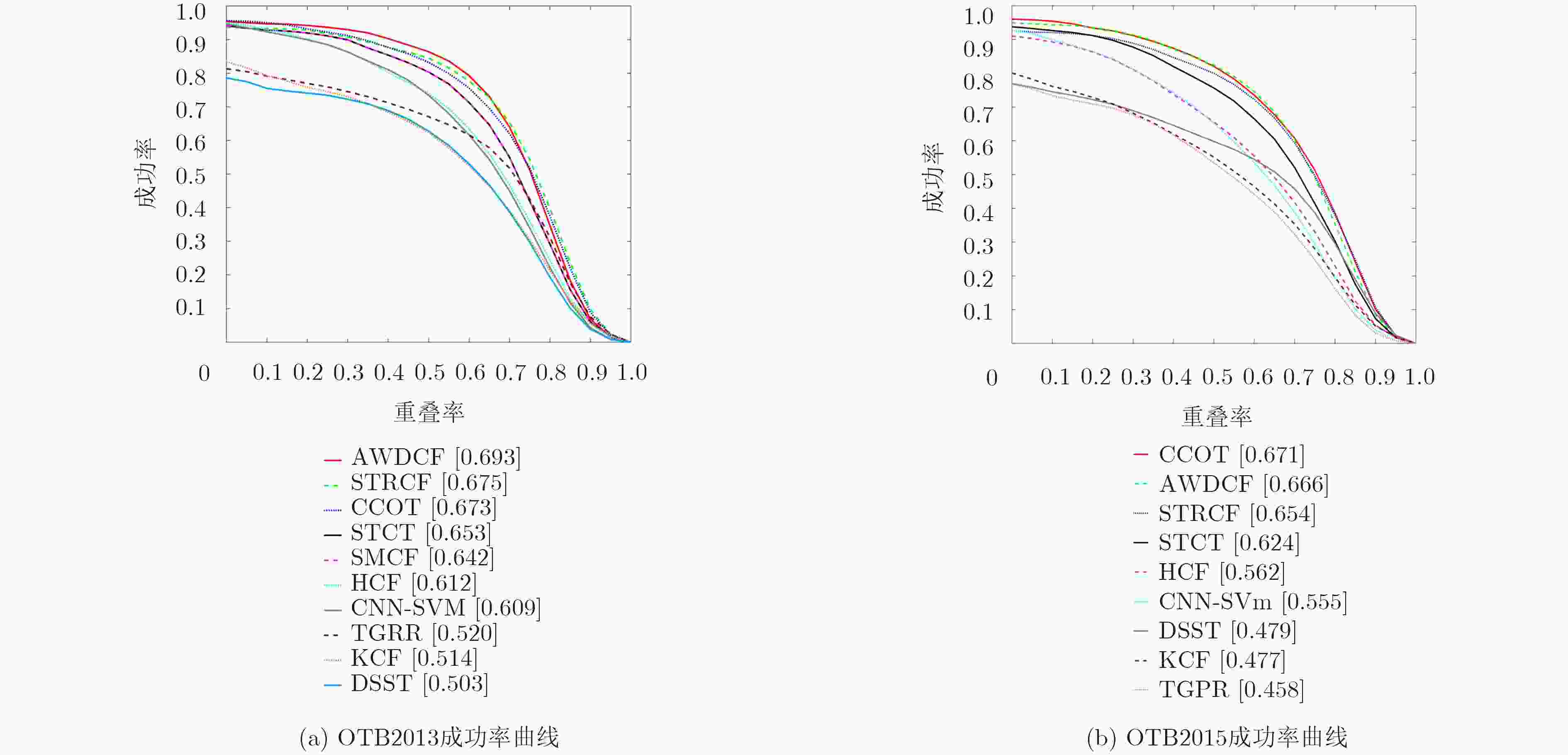
摘要: 相关滤波(CF)方法应用于视觉跟踪领域中效果显著,但是由于边界效应的影响,导致跟踪效果受到限制,针对这一问题,该文提出一种基于样本质量估计的正则化自适应的相关滤波视觉跟踪算法。首先,该算法在滤波器的训练过程中加入空间惩罚项,构建目标与背景的颜色及灰度直方图模板并计算样本质量系数,使得空间正则项根据样本质量系数自适应变化,不同质量的样本受到不同程度的惩罚,减小了边界效应对跟踪的影响;其次,通过对样本质量系数的判定,合理优化跟踪结果及模型更新,提高了跟踪的可靠性和准确性。在OTB2013和OTB2015数据平台上的实验数据表明,与近几年主流的跟踪算法相比,该文算法的成功率均为最高,且与空间正则化相关滤波(SRDCF)算法相比分别提高了9.3%和9.9%。Abstract: Correlation Filters (CF) are efficient in visual tracking, but their performance is badly affected by boundary effects. Focusing on this problem, the adaptive regularized correlation filters for visual tracking based on sample quality estimation are proposed. Firstly, the proposed algorithm adds spatial regularization matrix to the training process of the filters, and constructs color and gray histogram templates to compute the sample quality factor. Then, the regularization term adaptively changes with the sample quality coefficient, so that the samples of different quality are subject to different degrees of punishment. Then, by thresholding the sample quality coefficient, the tracking results and model update strategy are optimized. The experimental results on OTB2013 and OTB2015 indicate that, compared with the state-of-the-art tracking algorithm, the average success ratio of the proposed algorithm is the highest. The success ratio is raised by 9.3% and 9.9% contrasted with Spatially RegularizeD Correlation Filters(SRDCF) algorithm respectively on OTB2013 and OTB2015.
-
表 1 自适应正则化的相关滤波视觉跟踪算法
输入:图像序列${{{I}}_1},{{{I}}_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{{{I}}_n}$,目标初始位置${{{p}}_0} = ({x_0},{y_0})$,目标
初始尺度${{{s}}_0} = ({w_0},{h_0})$。输出:每帧图像的跟踪结果,即目标位置${{{p}}_t} = ({x_t},{y_t})$,目标尺度
估计${{{s}}_t} = ({w_t},{h_t})$对于$t = 1,2, ·\!·\!· ,n$, do: (1) 目标定位及尺度估计 (a) 利用前一帧目标位置${{{p}}_{t - 1}}$以及尺度${{{s}}_{t - 1}}$确定第$t$帧ROI区 域; (b) 提取多尺度样本${{{I}}_s} = \{ {{{I}}_{{s_1}}},{{{I}}_{{s_2}}}, ·\!·\!· {{{I}}_{{s_S}}}\} $; (c) 根据响应图确定第$t$帧中目标的中心位置${{{p}}_t}$以及尺度${{{s}}_t}$; (2) 样本质量估计及正则化自适应 (a) 根据目标中心位置及尺度提取目标及背景统计直方图; (b) 利用式(8)计算样本质量系数$Q$;之后,利用样本质量系数 计算空间正则化项; (3) 模型更新 (a) 利用式(19)更新跟踪滤波器模型${{{ω}}_t}$; (b) 利用式(17)、式(18)更新统计信息模型${{{h}}_t}$; 结束 表 2 阈值
${τ}$ 的选取与OTB2015实验结果的对比分析阈值${\rm{\tau }}$ 2500 2750 3000 3250 3500 3750 OTB2015跟踪成功率 0.820 0.779 0.871 0.855 0.817 0.795 表 3 8组测试序列的中心误差(像素)和成功率(%)
算法 CNN-SVM STRCF TGPR HCF KCF STCT DSST C-COT SMCF Girl2 7.6(98.0) 11.3(89.0) 30.9(87.0) 110.0(56.0) 118.8(8.0) 264.6(7.0) 319.1(8.0) 46.4(54.0) 8.4(96.0) 7.9(97.0) Soccer 17.5(81.0) 260(24.0) 19.6(62.0) 60.7(14.0) 13.5(53.0) 15.6(46.0) 46.9(18.0) 14.3(43.0) 12.1(83.0) 14.5(84.0) Bolt2 6.4(90.0) 151.4(48.0) 7.8(71.0) 304.0(1.0) 8.3(88.0) 329.8(1.0) 6.3(95.0) 115.5(1.0) 7.0(92.0) 6.8(90.0) KiteSurf 2.3(99.0) 25.2(51.0) 66.7(45.0) 61.7(38.0) 59.8(45.0) 40.6(31.0) 7.8(70.0) 56.7(43.0) 2.1(99.0) 2.3(99.0) Sylvester 5.5(96.0) 5.0(98.0) 5.5(96.0) 5.7(91.0) 12.9(83.0) 13.3(81.0) 14.8(82.0) 14.8(70.0) 4.5(99.0) 7.5(99.0) Basketball 3.8(99.0) 21.4(48.0) 14.1(11.0) 9.4(90.0) 3.7(100.0) 8.1(90.0) 3.9(98.0) 111.6(14.0) 5.0(97.0) 4.1(98.0) Dog1 3.0(100.0) 7.2(58.0) 3.6(100.0) 5.9(69.0) 4.4(67.0) 4.1(64.0) 4.7(97.0) 4.6(66.0) 4.0(98.0) 4.8(96.0) CarScale 7.4(77.0) 19.8(53.0) 8.7(72.0) 21.4(46.0) 29.3(73.0) 16.1(55.0) 15.2(77.0) 18.8(51.0) 5.3(87.0) 8.7(77.0) 平均 5.8(94.0) 51.7(58.0) 16.2(74.2) 70.6(62.0) 26.6(62.0) 71.3(50.8) 42.5(57.0) 38.9(47.0) 5.4(93.9) 6.1(93.5) 表 4 不同属性下算法跟踪成功率对此结果
IV (40) OPR (64) SV (66) OCC (50) DEF (44) MB (31) FM (41) IPR (31) OV (14) BC (33) LR (10) 本文算法 0.659 0.644 0.640 0.641 0.624 0.672 0.646 0.622 0.600 0.655 0.570 CNN-SVM 0.532 0.546 0.492 0.513 0.547 0.568 0.530 0.545 0.488 0.543 0.419 STRCF 0.646 0.628 0.637 0.618 0.607 0.666 0.634 0.604 0.585 0.639 0.561 TGPR 0.449 0.454 0.400 0.429 0.412 0.409 0.398 0.461 0.373 0.426 0.378 HCF 0.535 0.532 0.487 0.523 0.530 0.573 0.555 0.557 0.474 0.575 0.424 KCF 0.469 0.449 0.399 0.438 0.436 0.456 0.452 0.464 0.393 0.489 0.306 STCT 0.636 0.584 0.596 0.592 0.603 0.625 0.616 0.570 0.530 0.625 0.527 DSST 0.476 0.448 0.414 0.426 0.412 0.465 0.442 0.484 0.374 0.463 0.311 C-COT 0.641 0.637 0.654 0.639 0.637 0.688 0.610 0.635 0.613 0.666 0.583 SMCF 0.672 0.653 0.632 0.653 0.612 0.665 0.632 0.610 0.608 0.663 0.579 -
SMEULDERS A W M, CHU D M, CUCCHIARA R, et al. Visual tracking: An experimental survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(7): 1442–1468. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.230 WANG Naiyan, SHI Jianping, YEUNG D Y, et al. Understanding and diagnosing visual tracking systems[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3101–3109. 黄立勤, 朱飘. 车载视频下改进的核相关滤波跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1887–1894. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171109HUANG Liqin and ZHU Piao. Improved kernel correlation filtering tracking for vehicle video[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1887–1894. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171109 BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2544–2550. HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 FELZENSZWALB P F, GIRSHICK R B, MCALLESTER D, et al. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1627–1645. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 DANELLJAN M, KHAN F S, FELSBERG M, et al. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 1090–1097. ZHANG Kaihua, ZHANG Lei, LIU Qingshan, et al. Fast visual tracking via dense spatio-temporal context learning[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 127–141. MA Chao, HUANG Jiabin, YANG Xiaokang, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3074–2082. NAM H and HAN B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4293–4302. BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]. Computer Vision – ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2016: 850–865. DANELLJAN M, ROBINSON A, KHAN F S, et al. Beyond correlation filters: Learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 472–488. MA Chao, YANG Xiaokang, ZHANG Chongyang, et al. Long-term correlation tracking[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5388–5396. DANELLJAN M, HAGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Discriminative scale space tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(8): 1561–1575. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2609928 LI Feng, YAO Yingjie, LI Peihua, et al. Integrating boundary and center correlation filters for visual tracking with aspect ratio variation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2001–2009. WANG Xin, HOU Zhiqiang, YU Wangsheng, et al. Online scale adaptive visual tracking based on multilayer convolutional features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(1): 146–158. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2768570 DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310–4318. LI Feng, TIAN Cheng, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4904–4913. 毕笃彦, 库涛, 查宇飞, 等. 基于颜色属性直方图的尺度目标跟踪算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(5): 1099–1106. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150921BI Duyan, KU Tao, ZHA Yufei, et al. Scale-adaptive Object tracking based on color names histogram[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(5): 1099–1106. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150921 WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Online object tracking: A benchmark[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 2411–2418. WU Yi, LIM J, and YANG M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834–1848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 MA Chao, HUANG Jiabin, YANG Xiaokang, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3074–3082. WANG Lijun, OUYANG Wanli, WANG Xiaogang, et al. STCT: sequentially training convolutional networks for visual tracking[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1373–1381. HONG S, YOU T, KWAK S, et al. Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 597–606. GAO Jin, LING Haibin, HU Weiming, et al. Transfer learning based visual tracking with Gaussian processes regression[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 188–203. -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
