A Mobile Charging and Data Collecting Algorithm Based on Multi-objective Optimization
-
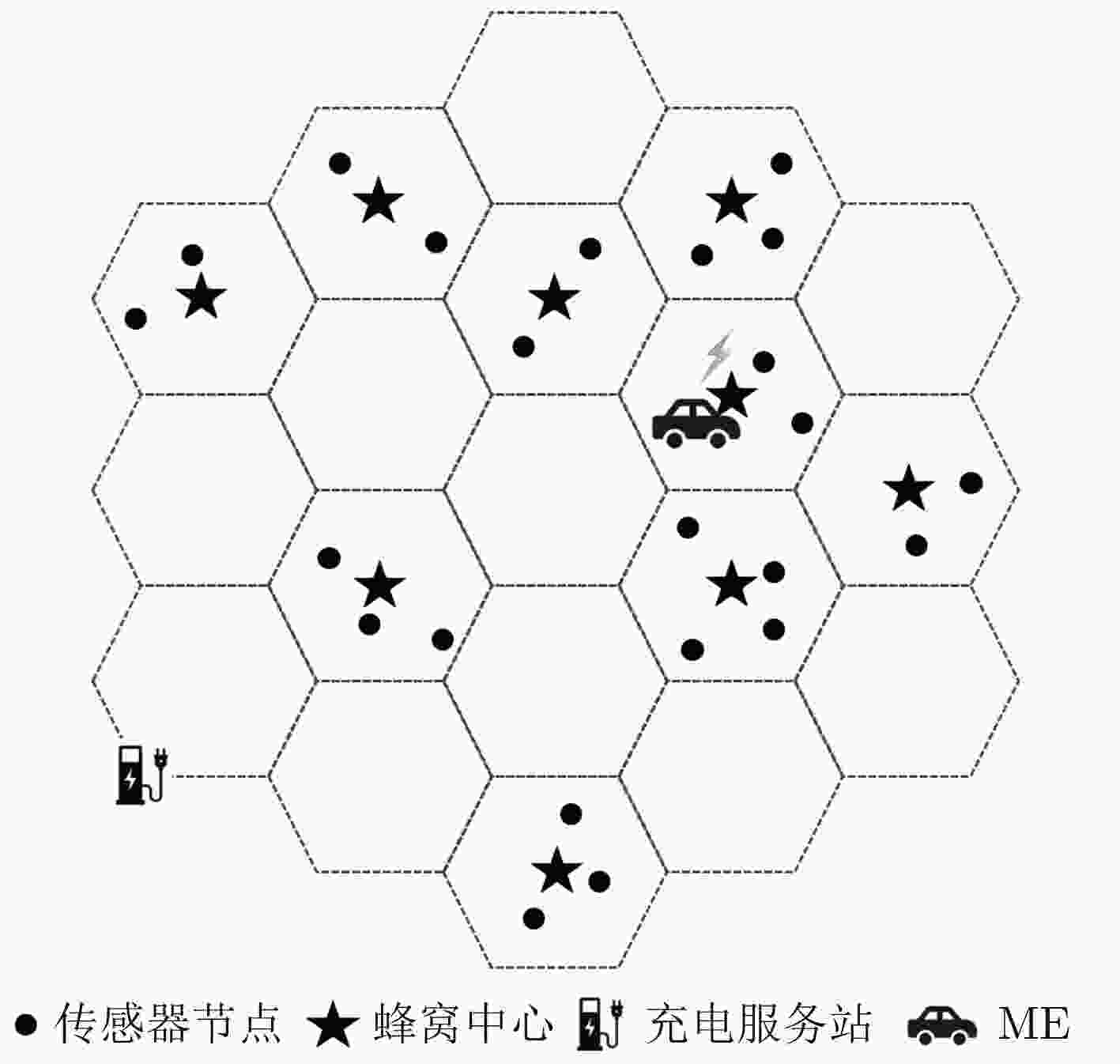
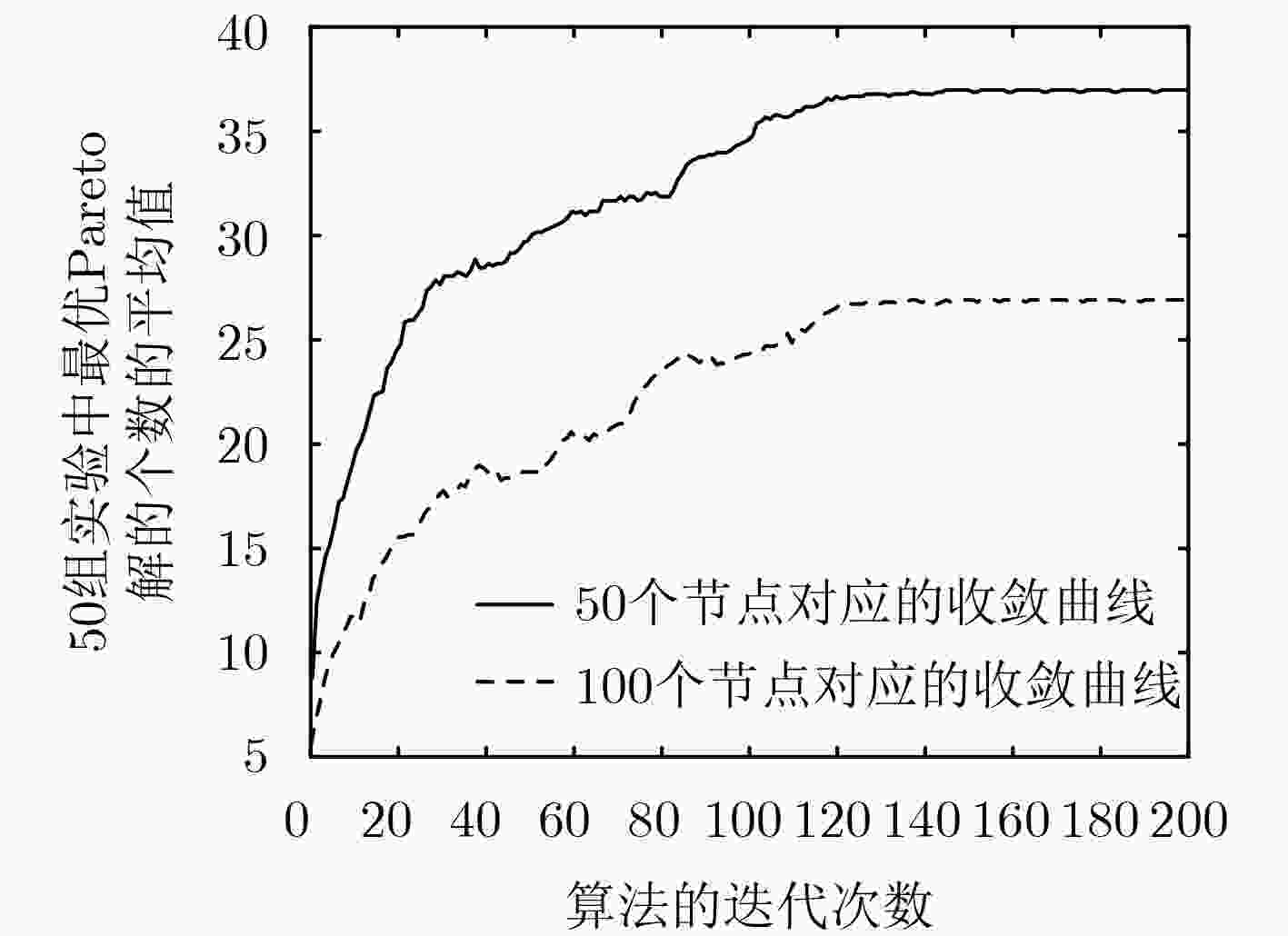
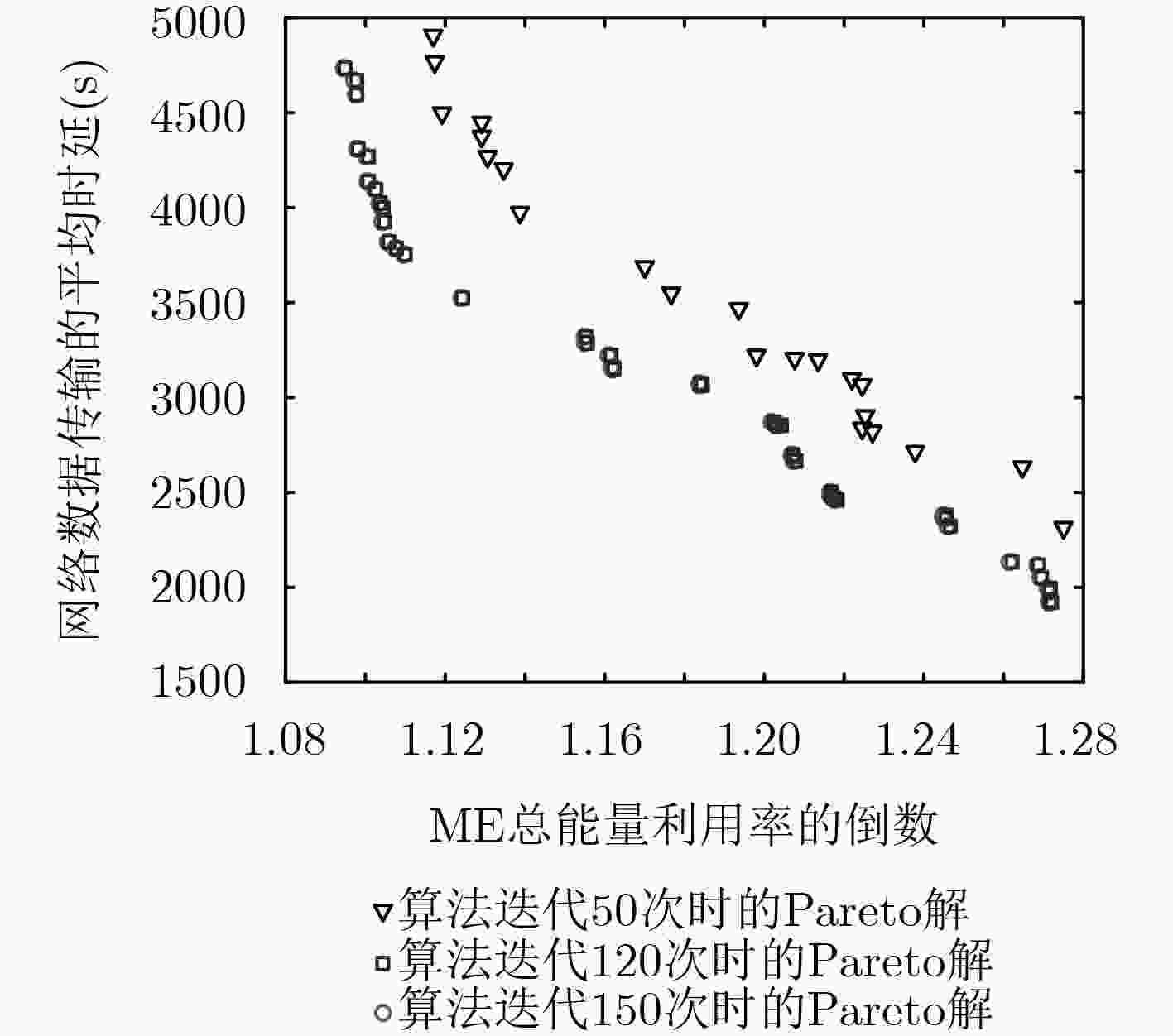
摘要: 近年来,通过引入移动设备(ME)为无线传感器网络(WSNs)进行无线充电和数据收集成为一个研究热点。传统方法一般先根据节点的充电需求优先级确定移动路径,再根据该路径依次对节点进行数据收集。该文同时考虑充电需求和数据收集两个维度,以最大化ME的总能量利用率和最小化数据收集平均时延为目标,建立多目标一对多充电及数据收集模型。在ME携带的行驶能量和充电能量不足的前提下,设计路径规划策略和均衡化充电策略,并改进多目标蚁群算法对该文问题进行求解。实验结果表明,该文算法在多种场景下的目标值、Pareto解的数量、Pareto解集的均匀性、分布范围等性能指标均优于NSGA-II算法。
-
关键词:
- 无线可充电传感器网络 /
- 数据收集 /
- 多目标优化
Abstract: Recently, the mobile charging and data collecting by using Mobile Equipment (ME) in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) is a hot topic. Existing studies determine usually the traveling path of ME according to the charging requirements of sensor nodes firstly, and then handle the data collecting. In this paper, charging requirement and data collecting are taken into consideration simultaneously. A one-to-many charging and data collecting model for ME is established with two optimization objectives, maximizing the total energy utilization and minimizing the average delay of data collecting. Due to the limited energy of the ME, the path planning strategy and the equalization charging strategy are designed. An improved multi-objective ant colony algorithm is proposed to solve the problem. Experiments show that the objective values, the number of Pareto solutions, the homogeneity of Pareto solutions and the distribution of Pareto solutions obtained by the proposed algorithm are all superior over NSGA-II algorithm. -
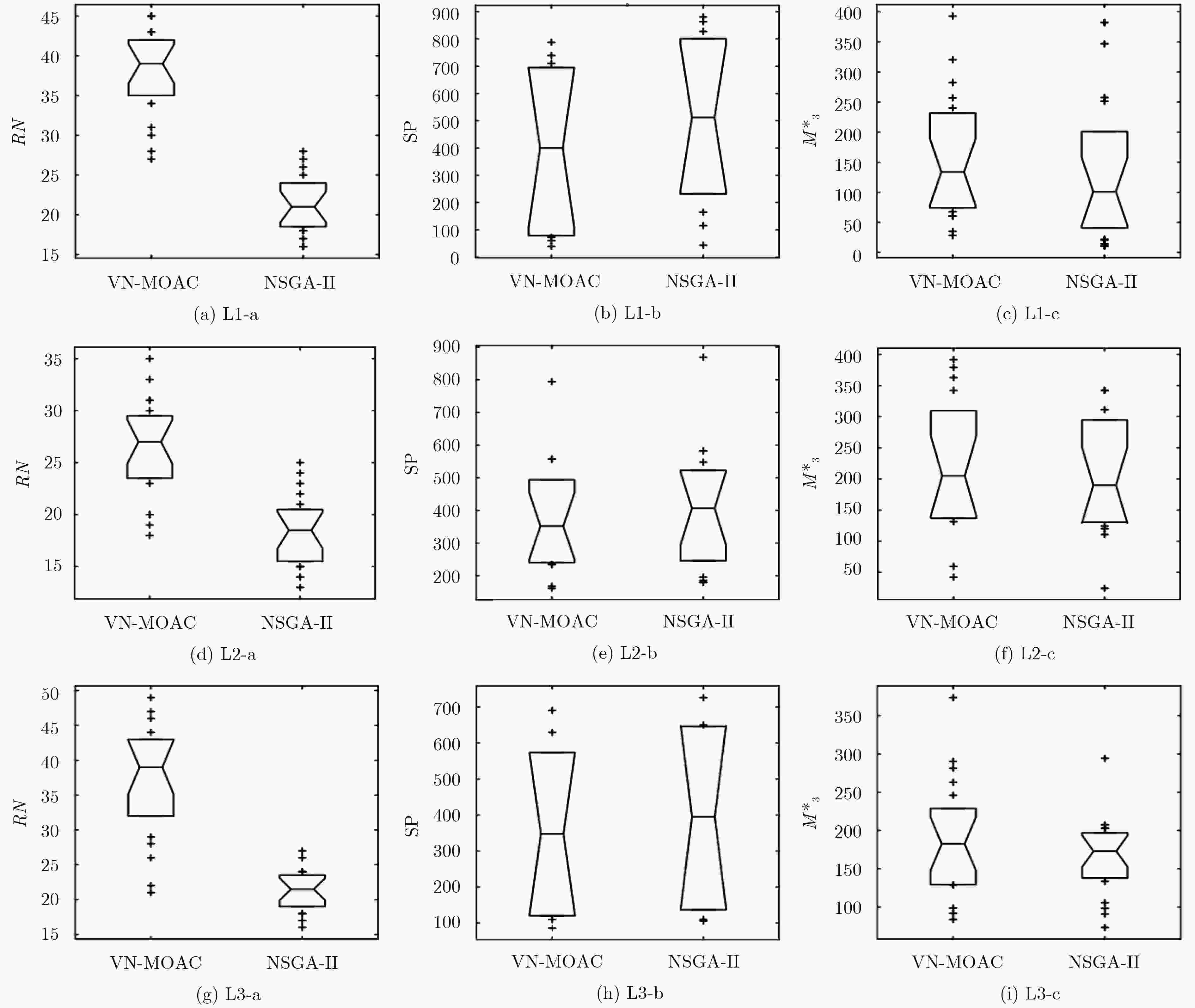
表 1 VN-MOAC算法和NSGA-II算法计算结果比较
指标 网络场景 $\phi $ (%) $\overline {\Delta \tau } $ (s) ${\rm{RN}}$ ${\rm{SP}}$ $M_3^*$ VN-MOAC NSGA-II VN-MOAC NSGA-II VN-MOAC NSGA-II VN-MOAC NSGA-II VN-MOAC NSGA-II 最优值 L1 94.02 92.31 1663.82 1812.30 45 29 38.50 45.67 392.65 378.86 L2 88.94 85.78 769.24 1176.02 35 25 161.93 180.14 391.60 342.24 L3 95.85 93.36 1608.94 1813.72 49 27 85.69 105.50 373.73 294.36 最差值 L1 75.98 73.75 5184.72 5361.46 26 17 790.03 883.10 31.59 20.73 L2 69.30 67.16 3784.31 3898.69 18 13 794.47 869.26 42.25 24.29 L3 76.35 71.24 5197.55 5408.48 21 12 690.69 726.31 83.73 73.19 平均值 L1 85.01 83.47 3145.27 3359.45 38 21 389.43 510.69 192.43 167.94 L2 80.17 75.44 2189.46 2411.95 26 18 391.85 416.68 220.62 202.72 L3 85.98 82.76 3268.98 3333.71 37 20 363.16 393.92 187.60 166.90 中值 L1 84.86 82.84 3137.80 3145.03 38 22 410.53 527.60 125.62 95.47 L2 82.34 74.66 2285.31 2329.71 27 19 352.32 406.76 204.86 171.06 L3 87.81 82.48 3308.81 3365.68 38 21 347.66 384.47 182.56 172.99 -
钱志鸿, 王义君. 面向物联网的无线传感器网络综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(1): 215–227. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00876QIAN Zhihong and WANG Yijun. Internet of things-oriented wireless Sensor networks review[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(1): 215–227. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00876 KURS A, KARALIS A, MOFFATT R, et al. Wireless power transfer via strongly coupled magnetic resonances[J]. Science, 2007, 317(5834): 83–86. doi: 10.1126/science.1143254 XIE Liguang, SHI Yi, HOU Y T, et al. Wireless power transfer and applications to sensor networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2013, 20(4): 140–145. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2013.6590061 王文华, 王田, 吴群, 等. 传感网中时延受限的移动式数据收集方法综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2017, 54(3): 474–492. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2017.20150953WANG Wenhua, WANG Tian, WU Qun, et al. Survey of delay-constrained data collection with mobile elements in WSNs[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2017, 54(3): 474–492. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2017.20150953 WANG Cong, LI Ji, and YANG Yuanyuan. Low-latency mobile data collection for wireless rechargeable sensor networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications, London, UK, 2015: 6524–6529. ZHONG Ping, LI Yating, LIU Weirong, et al. Joint mobile data collection and wireless energy transfer in wireless rechargeable sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(8): 1881. doi: 10.3390/s17081881 WANG Cong, LI Ji, YE Fan, et al. A mobile data gathering framework for wireless rechargeable sensor networks with vehicle movement costs and capacity constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(8): 2411–2427. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2490060 GUO Songtao, WANG Cong, and YANG Yuanyuan. Mobile data gathering with wireless energy replenishment in rechargeable sensor networks[C]. 2013 IEEE INFOCOM, Turin, Italy, 2013: 1932–1940. GUO Songtao, WANG Cong, and YANG Yuanyuan. Joint mobile data gathering and energy provisioning in wireless rechargeable sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2014, 13(12): 2836–2852. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2014.2307332 XIE Liguang, SHI Yi, HOU Y T, et al. A mobile platform for wireless charging and data collection in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33(8): 1521–1533. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2391631 ZHAO Miao, LI Ji, and YANG Yuanyuan. A framework of joint mobile energy replenishment and data gathering in wireless rechargeable sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2014, 13(12): 2689–2705. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2014.2307335 NIKOLETSEAS S, YANG Yuanyuan, and GEORGIADIS A. Wireless Power Transfer Algorithms, Technologies and Applications in Ad Hoc Communication Networks[M]. Cham: Springer, 2016: 667–700. XIE Liguang, SHI Yi, HOU Y T, et al. Multi-node wireless energy charging in sensor networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2015, 23(2): 437–450. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2014.2303979 HE Shibo, CHEN Jiming, JIANG Fachang, et al. Energy provisioning in wireless rechargeable sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(10): 1931–1942. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.161 卢先领, 王莹莹. 时延受限的移动sink数据收集算法[J]. 通信学报, 2014, 35(10): 107–116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.10.013LU Xianling and WANG Yingying. Data collection algorithm for mobile sink in delay-constrained network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2014, 35(10): 107–116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.10.013 XU Junyi, YUAN Xiaohui, WEI Zhenchun, et al. A wireless sensor network recharging strategy by balancing lifespan of sensor nodes[C]. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. YU Chansu, SHIN K G, and LEE B. Power-stepped protocol: Enhancing spatial utilization in a clustered mobile ad hoc network[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2004, 22(7): 1322–1334. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2004.829349 DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182–197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
