Adaptive Recognition Method for Unknown Interference Based on Hilbert Signal Space
-
摘要: 针对大样本下未知干扰类型的分类识别问题,该文提出一种基于信号特征空间的未知干扰自适应识别方法。首先,基于Hilbert信号空间理论对干扰信号进行处理,建立干扰信号特征空间,进而利用投影定理对未知干扰进行最佳逼近,提出基于信号特征空间的概率神经网络(PNN)分类算法,并设计了未知干扰分类识别器的处理流程。仿真结果表明,与两种传统方法相比,该方法在已知干扰的分类精度方面分别提高了12.2%和2.8%;满足条件的未知干扰最佳逼近效果随功率强度呈线性变化,设计的分类识别器在满足最佳逼近的各类干扰中总体识别率达到91.27%,处理干扰识别的速度明显改善;在信噪比达到4 dB时,对未知干扰识别准确率达到92%以上。
-
关键词:
- 无人机通信 /
- 未知干扰 /
- 自适应识别 /
- Hilbert信号空间 /
- 概率神经网络
Abstract: In order to solve the problem of classification and recognition of unknown interference types under large samples, an adaptive recognition method for unknown interference based on signal feature space is proposed. Firstly, the interference signal is processed and the interference signal feature space is established with the Hilbert signal space theory. Then the projection theorem is used to approximate the unknown interference. The classification algorithm based on signal feature space with Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN) is proposed, and the processing flow of unknown interference classifier is designed. The simulation results show that compared with two kinds of traditional methods, the proposed method improves the classification accuracy of the known interference by 12.2% and 2.8% respectively. The optimal approximation effect of the unknown interference varies linearly with the power intensity in the condition, and the overall recognition rate of the designed classifier reaches 91.27% in the various types of interference satisfying the optimal approximation, and the speed of processing interference recognition is improved significantly. When the signal-to-noise ratio reaches 4 dB, the accuracy of unknown interference recognition is more than 92%. -
表 1 干扰信号参数
干扰类型 干扰参数 数值 单音干扰 干扰频点(MHz) 150 多音干扰 干扰频点(MHz) 50, 100, ···, 250 部分频带干扰 覆盖带宽(MHz) 250~400 脉冲干扰 占空比(%) 10 线性调频干扰
(单分量)初始频率(MHz) 150 调频率 500 梳状谱干扰 分量数目 3 带宽(MHz) 800 表 2 干扰分类算法识别率比较
信号空间数据集 识别率(%) 单音干扰 多音干扰 部分频带 线性调频 脉冲干扰 梳状谱 总体识别率 传统SVM分类器 85.0 98.7 100 82.5 90 81.2 86.3 文献[12] 100 98.7 100 98.7 100 98.7 95.7 本文算法 100 100 100 91.0 100 100 98.5 表 3 多分类算法性能比较(%)
干扰空间数据集 分类识别率 训练识别率 测试识别率 本文算法 传统算法 本文算法 传统算法 本文算法 传统算法 单音干扰 92.41 47.55 92.59 50.85 91.27 46.24 多音干扰 98.73 45.37 部分频带 81.01 45.99 线性调频 100 45.37 脉冲干扰 74.36 45.86 梳状谱 98.72 46.94 未知干扰 93.59 46.62 -
POISEL R A. Modern Communications Jamming Principles and Techniques[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2011: 279–288. HU Su, BI Guoan, GUAN Yongliang, et al. TDCS-based cognitive radio networks with multiuser interference avoidance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(12): 4828–4835. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.111313.130261 ERHAN D, SZEGEDY C, TOSHEV A, et al. Scalable object detection using deep neural networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 2155–2162. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.276. OQUAB M, BOTTOU L, LAPTEV I, et al. Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 1717–1724. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.222. WATT N and DU PLESSIS M C. Dropout algorithms for recurrent neural networks[C]. The Annual Conference of the South African Institute of Computer Scientists and Information Technologists, Port Elizabeth, South Africa, 2018: 72–78. doi: 10.1145/3278681.3278691. WANG Shangxing, LIU Hanpeng, GOMES P H, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for dynamic multichannel access in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(2): 257–265. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2809722 张彪, 闫晓鹏, 栗苹, 等. 基于支持向量机的无线电引信抗扫频式干扰研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(4): 635–640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.04.009ZHANG Biao, YAN Xiaopeng, LI Ping, et al. Research on anti-frequency sweeping jamming of radio fuze based on support vector machine[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(4): 635–640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.04.009 王国宏, 白杰, 张翔宇, 等. 基于FRFT域特征差异的压制干扰检测与分类算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(6): 1124–1132. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0423WANG Guohong, BAI Jie, ZHANG Xiangyu, et al. Detection and classification algorithm of suppression interference based on characteristic differences of FRFT domain[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(6): 1124–1132. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0423 刘明骞, 李兵兵, 曹超凤, 等. 认知无线电中非高斯噪声下数字调制信号识别方法[J]. 通信学报, 2014, 35(1): 82–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.01.010LIU Mingqian, LI Bingbing, CAO Chaofeng, et al. Recognition method of digital modulation signals over non-Gaussian noise in cognitive radio[J]. Journal on Communications, 2014, 35(1): 82–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.01.010 YANG Zeyi, TAO Ran, WANG Yue, et al. A novel multi-carrier order division multi-access communication system based on TDCS with fractional Fourier transform scheme[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2014, 79(2): 1301–1320. doi: 10.1007/s11277-014-1931-8 KUZOVNIKOV A V. Study of the methods for developing jamming-immune communications systems with the use of wavelet-modulated signals[J]. Journal of Communications Technology and Electronics, 2014, 59(1): 61–70. doi: 10.1134/S1064226914010069 王桂胜, 任清华, 姜志刚, 等. 基于信号特征空间的TDCS干扰分类识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(9): 1950–1958. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.09.06WANG Guisheng, REN Qinghua, JIANG Zhigang, et al. Jamming classification and recognition in transform domain communication system based on signal feature space[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(9): 1950–1958. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.09.06 TAO Chao, PAN Hongbo, LI Yansheng, et al. Unsupervised spectral-spatial feature learning with stacked sparse autoencoder for hyperspectral imagery classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(12): 2438–2442. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2482520 郭立民, 寇韵涵, 陈涛, 等. 基于栈式稀疏自编码器的低信噪比下低截获概率雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 875–881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170588GUO Limin, KOU Yunhan, CHEN Tao, et al. Low probability of intercept radar signal recognition based on stacked sparse auto-encoder[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 875–881. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170588 DONOHO D L, TSAIG Y, DRORI I, et al. Sparse solution of underdetermined systems of linear equations by stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(2): 1094–1121. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2011.2173241 王磊, 周乐囡, 姬红兵, 等. 一种面向信号分类的匹配追踪新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(6): 1299–1306. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00942WANG Lei, ZHOU Lenan, JI Hongbing, et al. A new matching pursuit algorithm for signal classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(6): 1299–1306. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00942 GONZÁLEZ-CAMACHO J M, CROSSA J, PÉREZ-RODRÍGUEZ P, et al. Genome-enabled prediction using probabilistic neural network classifiers[J]. BMC Genomics, 2016, 17: 208. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2553-1 张国亮, 杨春玲, 王暕来. 基于优化概率神经网络和红外多光谱融合的大气层外空间弹道目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 896–902. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00623ZHANG Guoliang, YANG Chunling, and WANG Jianlai. Discrimination of exo-atmospheric targets based on optimization of probabilistic neural network and IR multispectral fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 896–902. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00623 GIRYES R and NEEDELL D. Near oracle performance and block analysis of signal space greedy methods[J]. Journal of Approximation Theory, 2015, 194: 157–174. doi: 10.1016/j.jat.2015.02.007 GIRYES R and NEEDELL D. Greedy signal space methods for incoherence and beyond[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2015, 39(1): 1–20. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2014.07.004 胡广书. 数字信号处理—理论、算法与实现[M]. 第3版, 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012: 169–175.HU Guangshu. Digital Signal Processing—Theory, Algorithm and Implementation[M]. 3rd ed, Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2012: 169–175. -





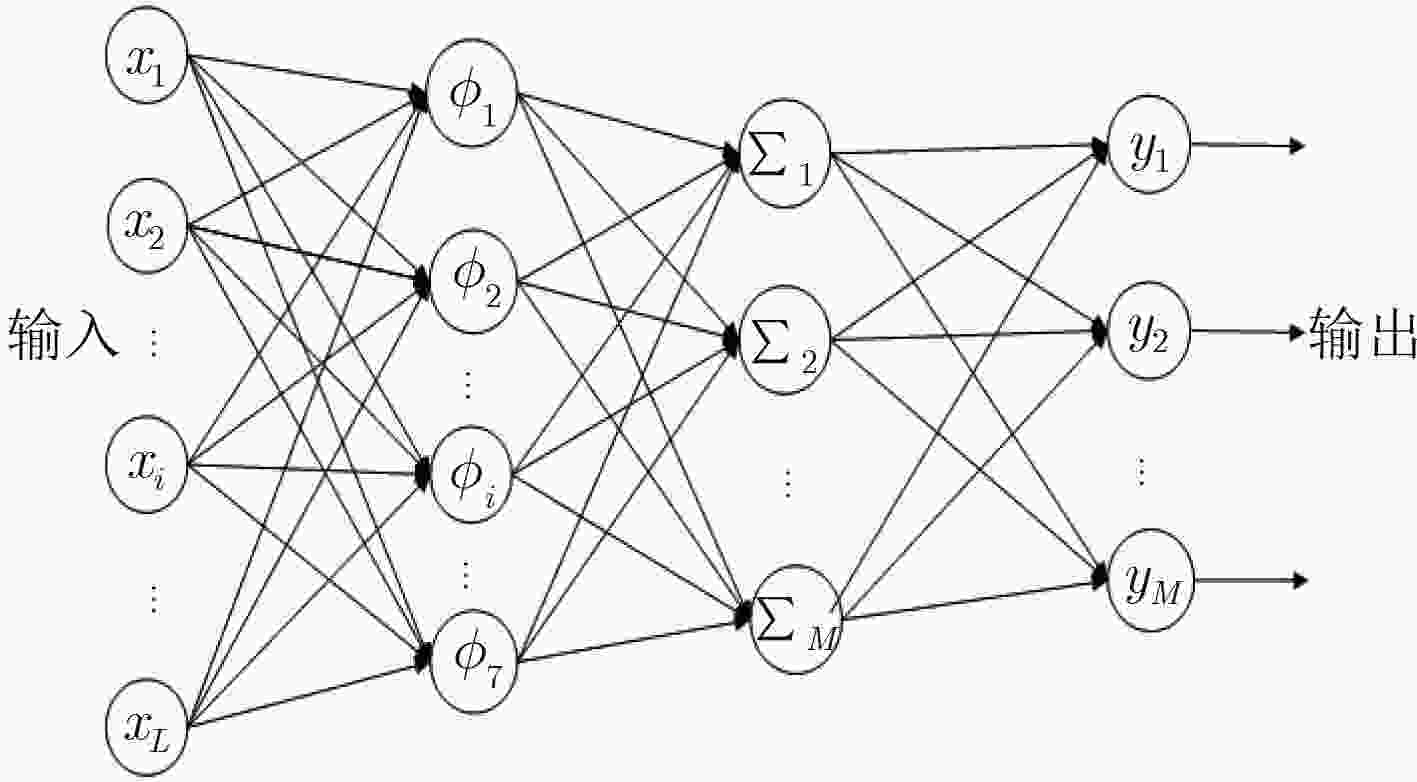
 下载:
下载:
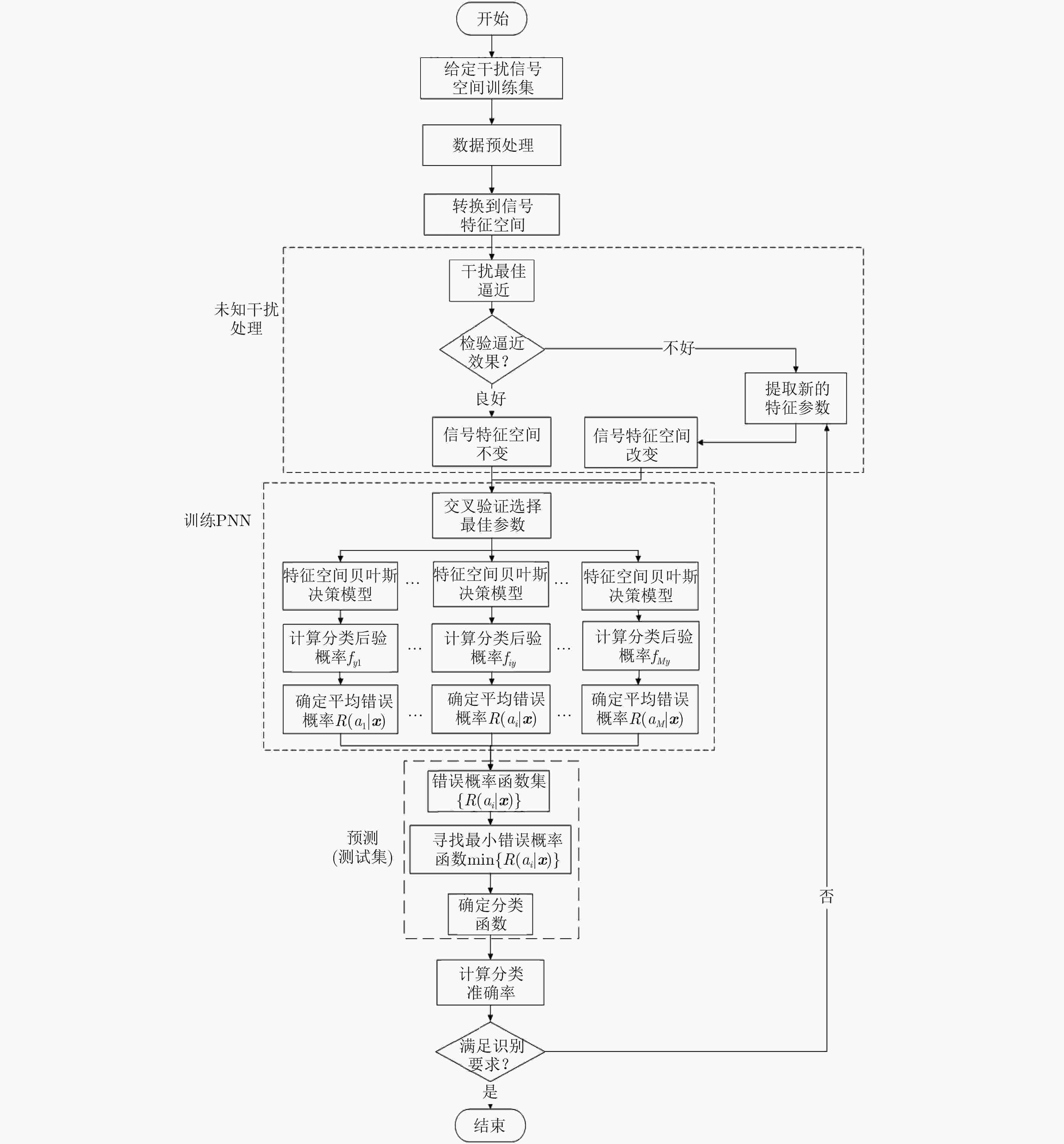
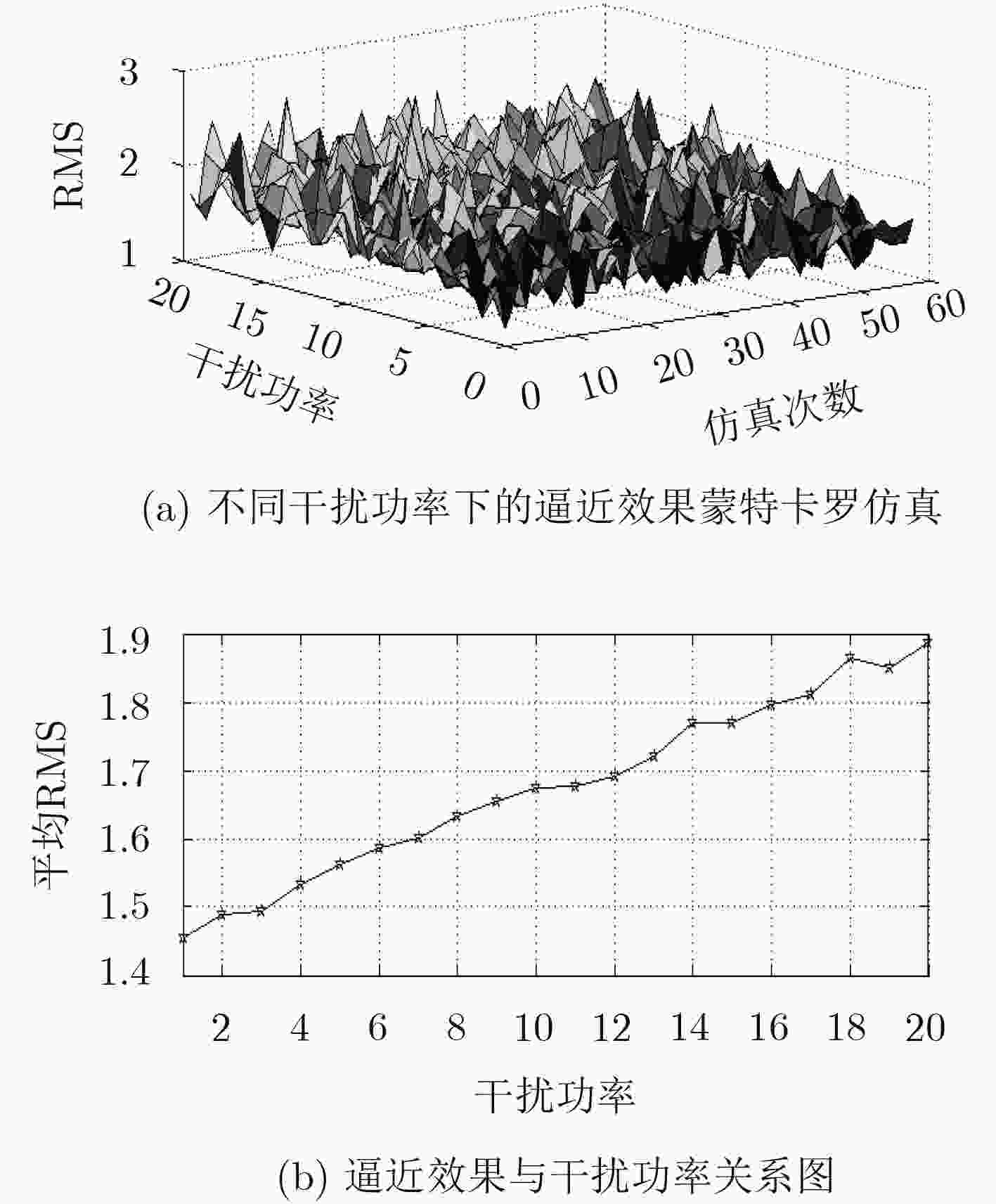
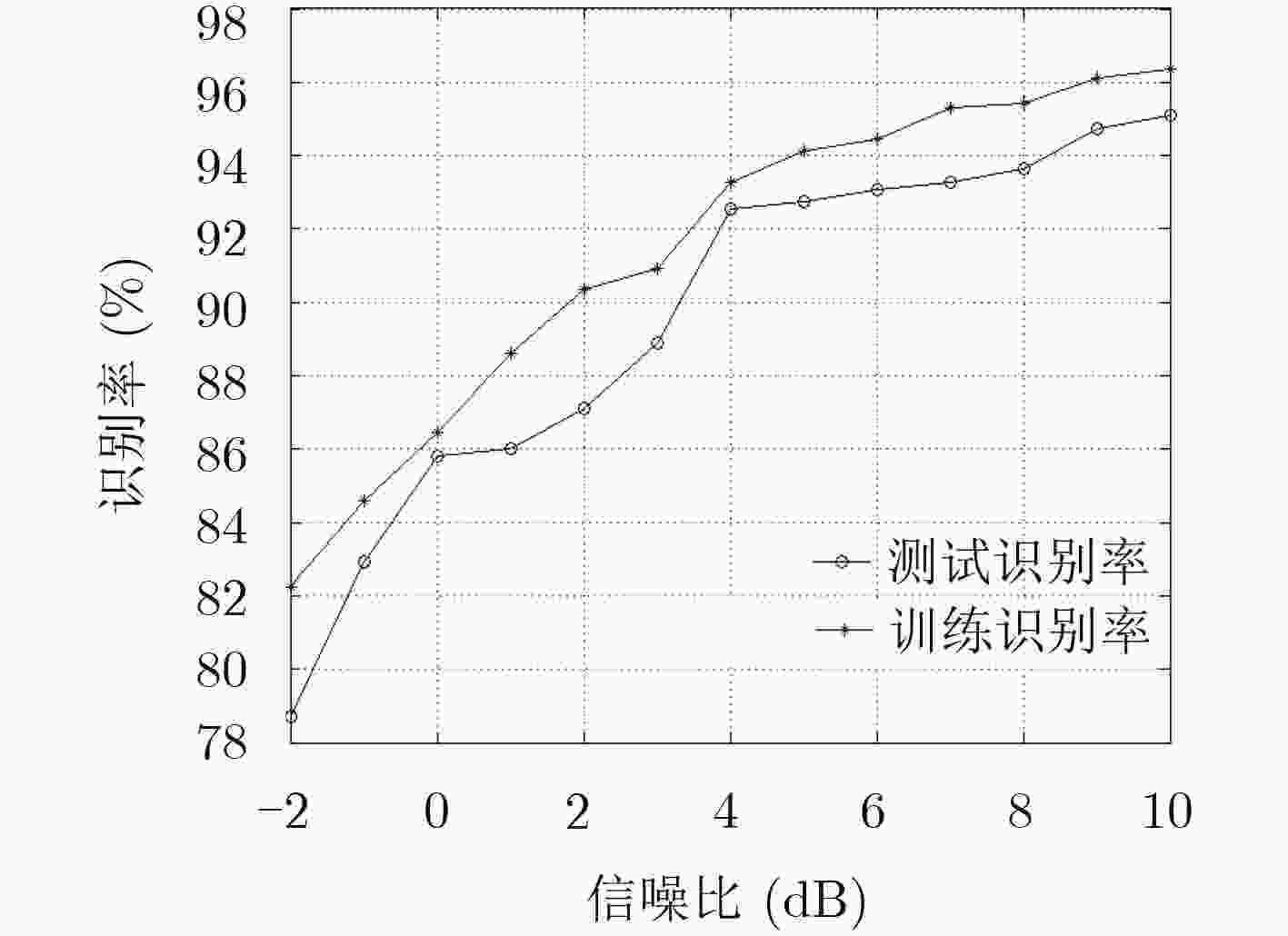


 下载:
下载:
