Passive Fingerprint Indoor Positioning Based on CSI Amplitude-phase
-
摘要:
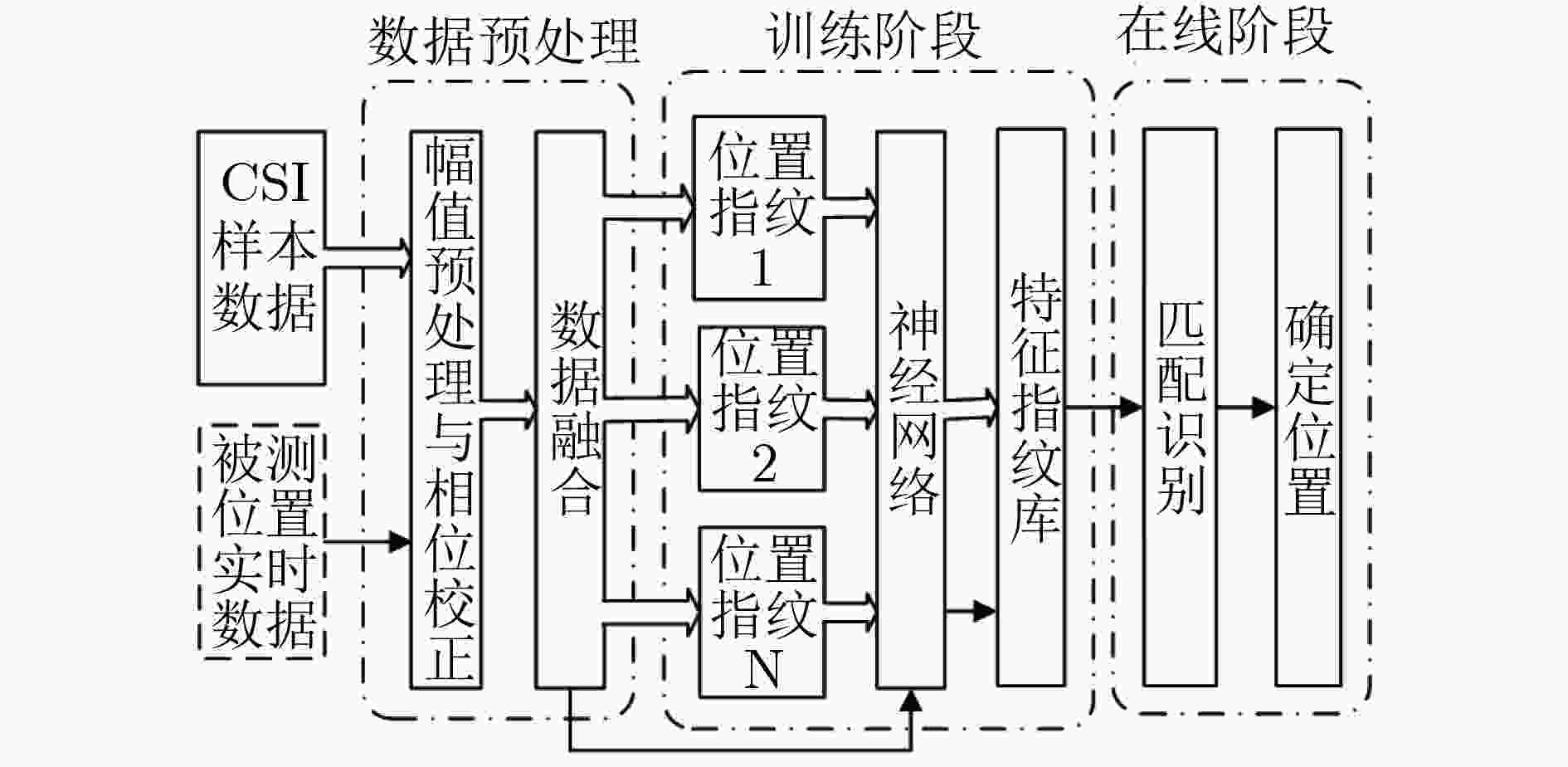
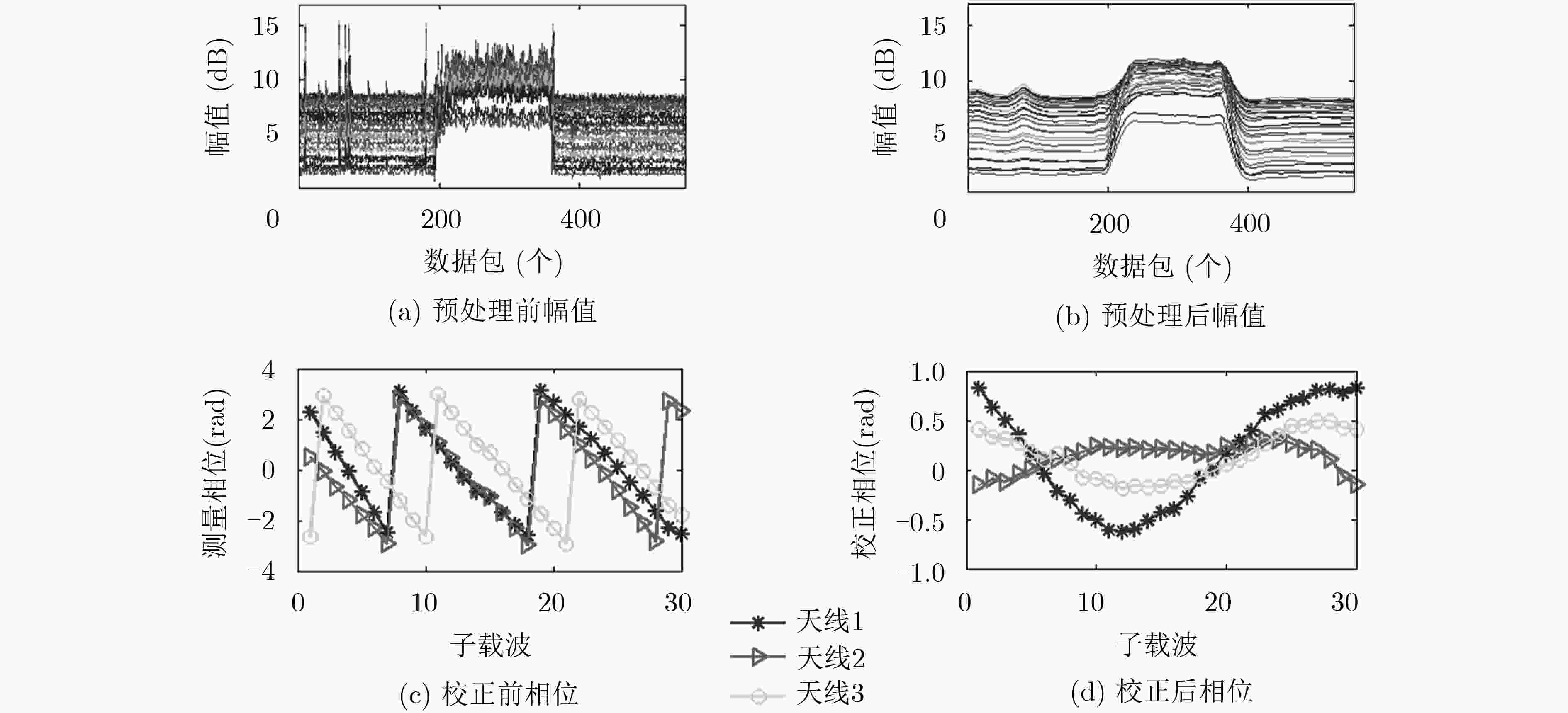
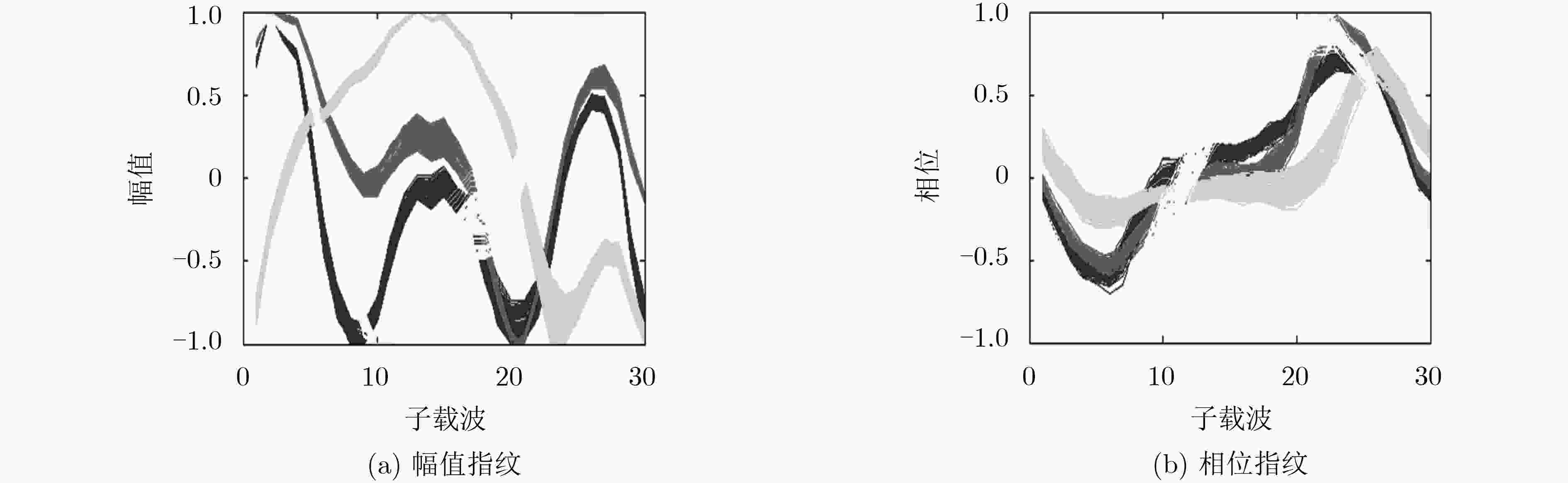
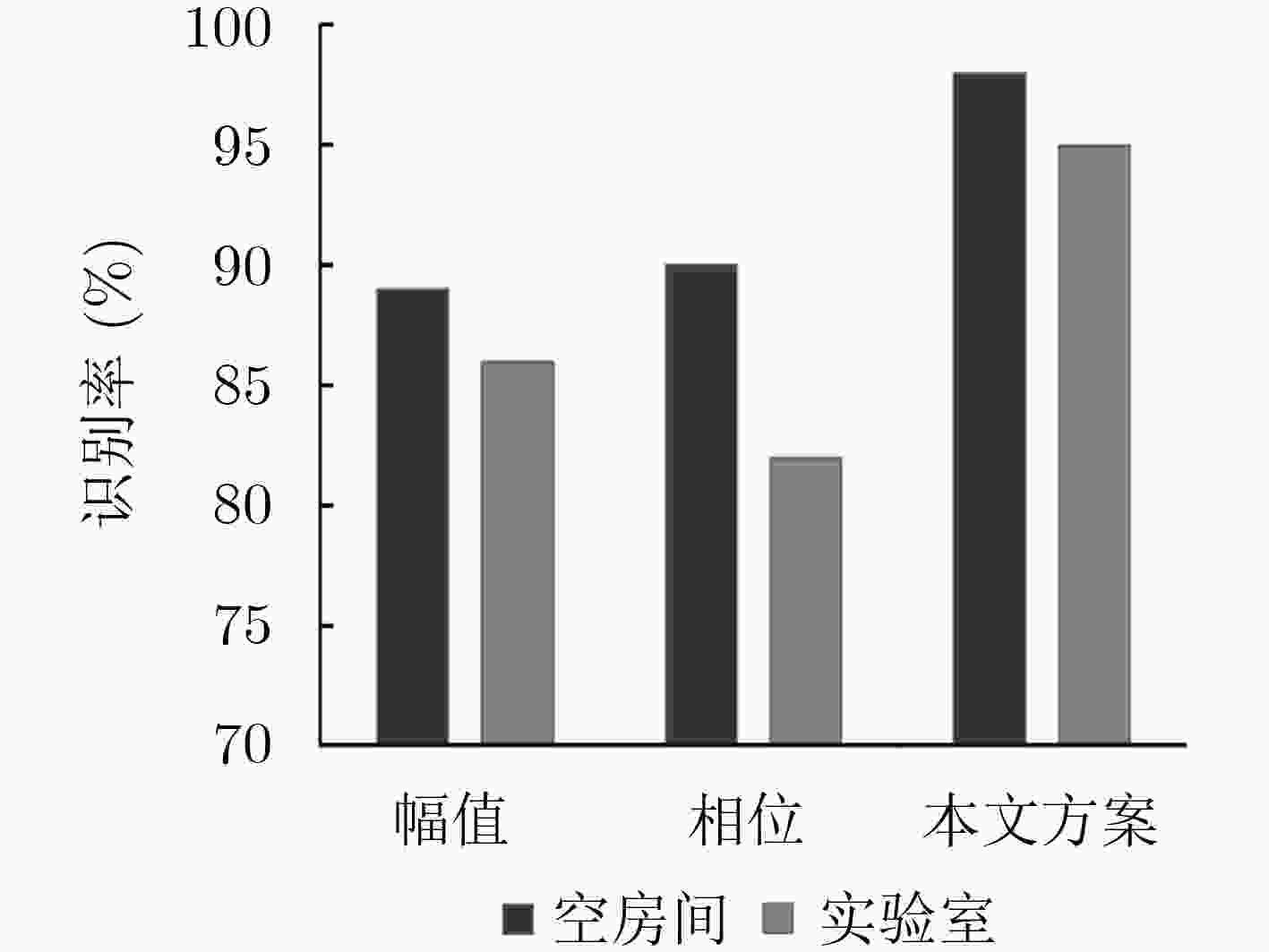
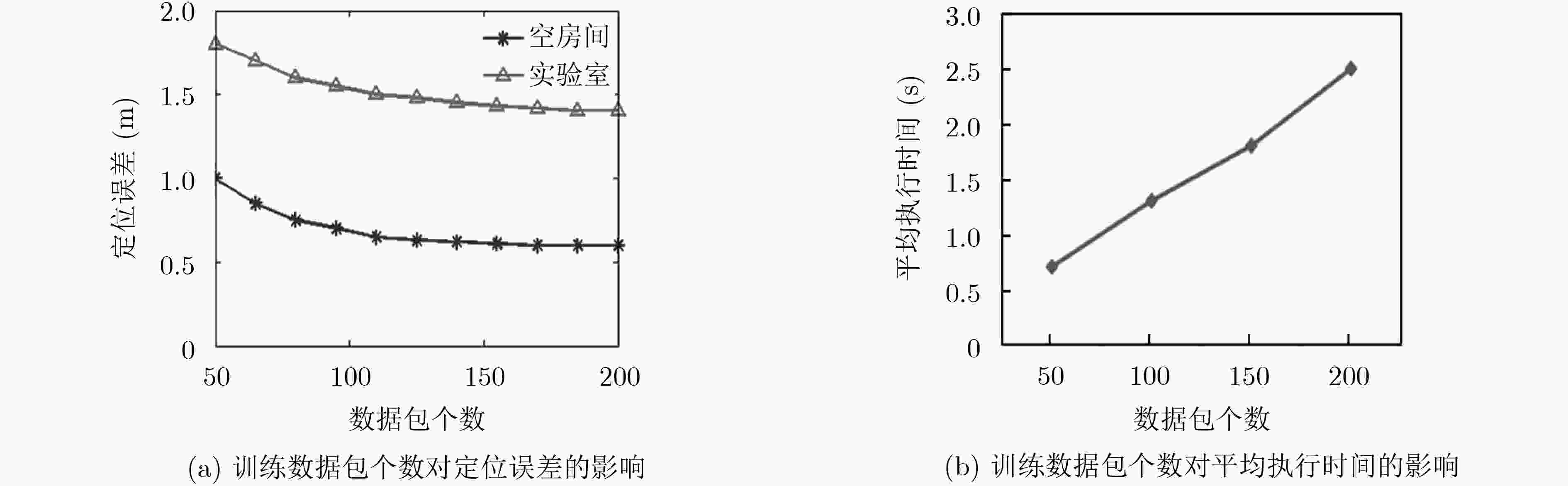
基于信道状态信息(CSI)的室内定位技术近几年备受关注。已提出的室内定位方案主要在适用性和定位精度等方面进行不断地创新和改进。该文提出一种被动式的1发2收指纹室内定位系统。用两个固定接收端采集CSI数据,信号预处理阶段对CSI幅值进行奇异值去除与低通滤波,用线性拟合的方法对CSI相位进行校正,将两个接收端采集处理得到的CSI幅值和相位信息共同作为指纹,最终通过全连接神经网络对指纹样本进行训练,并与采集到的实时数据进行匹配识别。实验表明,采用两个接收端以及幅值和相位结合定位的方法,匹配识别率达到了98%,定位精度达到0.69 m。证明该系统能精确有效地实现室内定位。
Abstract:Indoor positioning technology based on Channel State Information (CSI) receives much attention in recent years. The existing indoor positioning solution is continuously innovative and improved in terms of deployment implementation and positioning accuracy. This paper proposes a passive one-transmitter two-receivers fingerprint indoor positioning system. The CSI data is collected by two fixed receiving end-devices. In the signal preprocessing stage, the CSI amplitude is singular value removed and low pass filtered, and the CSI phase is corrected by a linear fitting method, and the CSI amplitude and phase information obtained by the two receiving ends are collectively used as fingerprint samples. The fingerprint samples are finally trained through the fully connected neural network, and matched with the collected real-time data. Experiments show that the matching recognition rate reaches 98% by using two receivers and the combination of amplitude and phase positioning, and the positioning accuracy is 0.69 m. It proves that the system can accurately and effectively achieve indoor positioning.
-
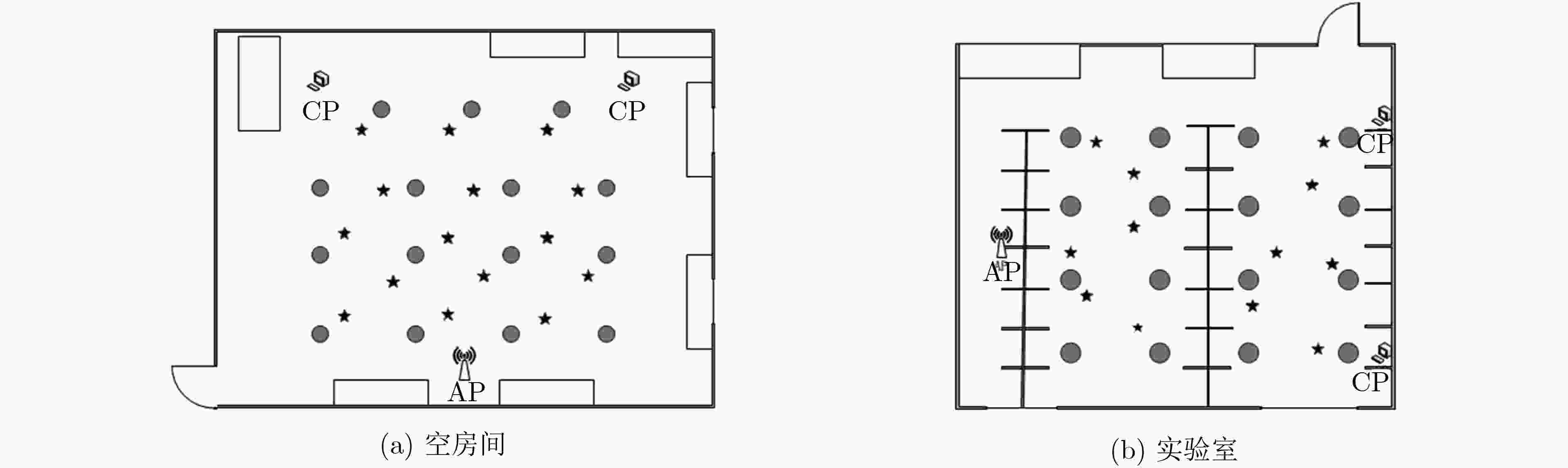
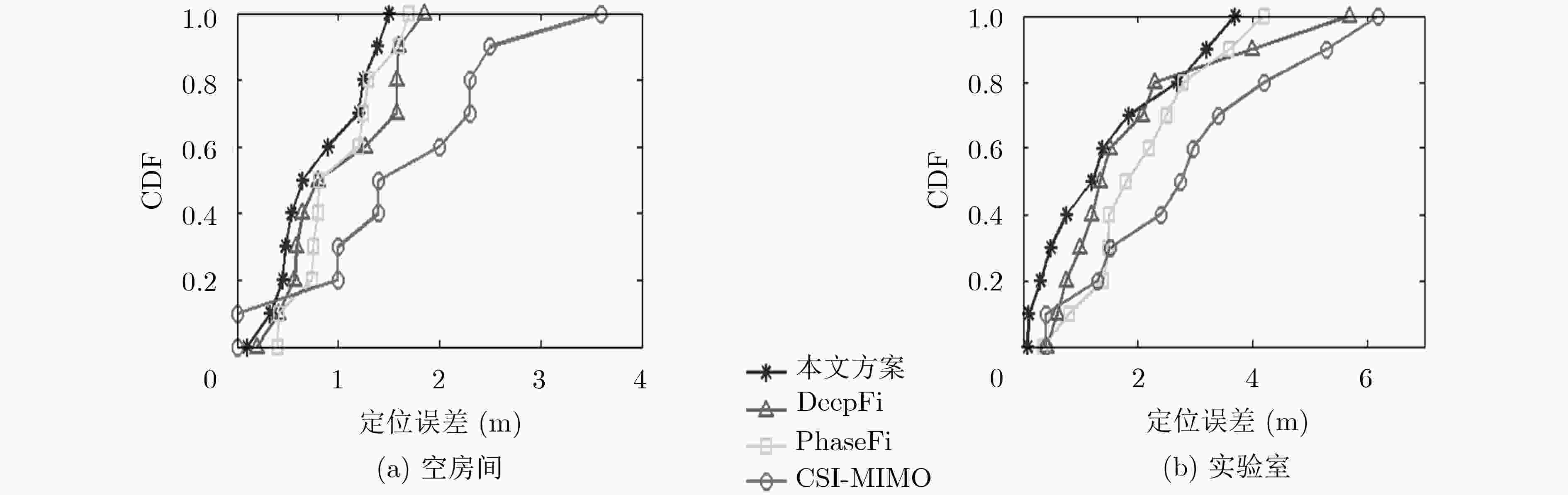
表 1 不同算法在不同场景定位误差(m)
空房间 实验室 平均误差 误差方差 平均误差 误差方差 本文方案 0.69 0.36 1.25 1.01 PhaseFi 0.94 0.56 1.81 1.34 DeepFi 1.08 0.41 2.01 1.01 CSI-MIMO 1.55 0.62 2.70 1.42 -
ZHUANG Yuan, YANG Jun, LI You, et al. Smartphone-based indoor localization with bluetooth low energy beacons[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(5): No. 596. doi: 10.3390/s16050596 BANDIRMALI N and TORLAK M. ERLAK: On the cooperative estimation of the real-time RSSI based location and k constant term[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 95(4): 3923–3932. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4032-7 KOO J and CHA Hojung. Localizing WiFi access points using signal strength[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15(2): 187–189. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2011.121410.101379 LI Jinsong, LI Yunzhou, and JI Xinsheng. A novel method of Wi-Fi indoor localization based on channel state information[C]. The 8th International Conference on Wireless Communications & Signal Processing, Yangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. WU Yang, GONG Liangyi, MAN Dapeng, et al. Enhancing the performance of indoor device-free passive localization[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 2015: 256162. doi: 10.1155/2015/256162 WANG Xuyu, GAO Lingjun, MAO Shiwen, et al. DeepFi: Deep learning for indoor fingerprinting using channel state information[C]. 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, New Orleans, USA, 2015: 1666–1671. WANG Xuyu, GAO Lingjun, and MAO Shiwen. CSI phase fingerprinting for indoor localization with a deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(6): 1113–1123. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2558659 ZHOU Rui, LU Xiang, ZHAO Pengbiao, et al. Device-free presence detection and localization with SVM and CSI fingerprinting[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(23): 7990–7999. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2762428 CHAPRE Y, IGNJATOVIC A, SENEVIRATNE A, et al. CSI-MIMO: Indoor Wi-Fi fingerprinting system[C]. The 39th Annual IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Edmonton, Canada, 2014: 202–209. YANG Zheng, ZHOU Zimu, and LIU Yunhao. From RSSI to CSI: Indoor localization via channel response[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2013, 46(2): No. 25. doi: 10.1145/2543581.2543592 WU Chenshu, YANG Zheng, and LIU Yunhao. Smartphones based crowdsourcing for indoor localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2015, 14(2): 444–457. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2014.2320254 WANG Yan, LIU Jian, CHEN Yingying, et al. E-eyes: Device-free location-oriented activity identification using fine-grained WiFi signatures[C]. The 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, USA, 2014: 617–628. ZHOU Yiwei, ZHU Hongzi, XUE Hua, et al. Perceiving accurate CSI phases with commodity WiFi devices[C]. IEEE NFOCOM 2017-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Atlanta, USA, 2017: 1–9. WANG Xuyu, YANG Chao, and MAO Shiwen. TensorBeat: Tensor decomposition for monitoring multiperson breathing beats with commodity WiFi[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2018, 9(1): No. 8. doi: 10.1145/3078855 BRUNATO M and BATTITI R. Statistical learning theory for location fingerprinting in wireless LANs[J]. Computer Networks, 2005, 47(6): 825–845. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2004.09.004 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
