A Method of Establishing Mine Target Fingerprint Database Based on Distributed Compressed Sensing
-
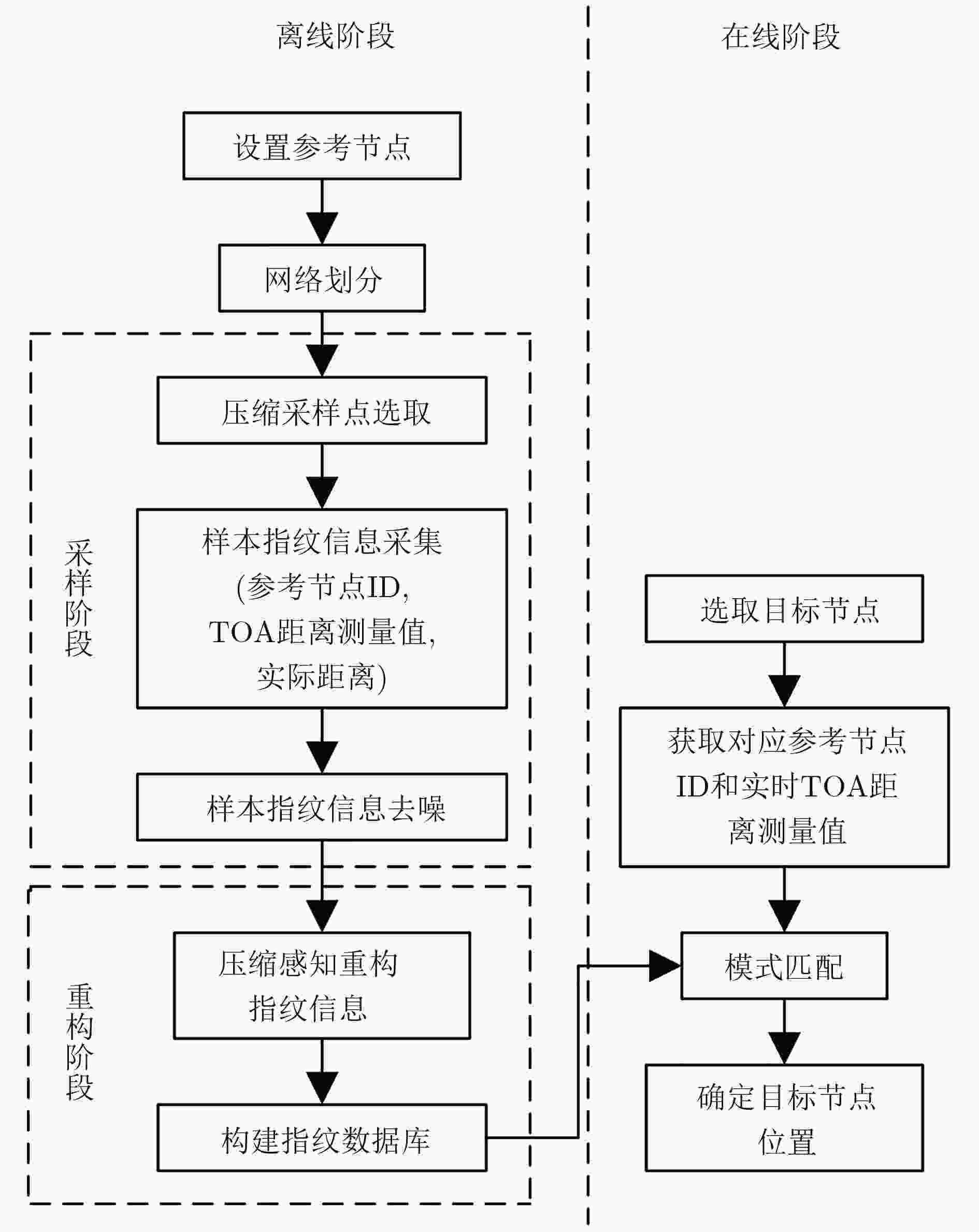
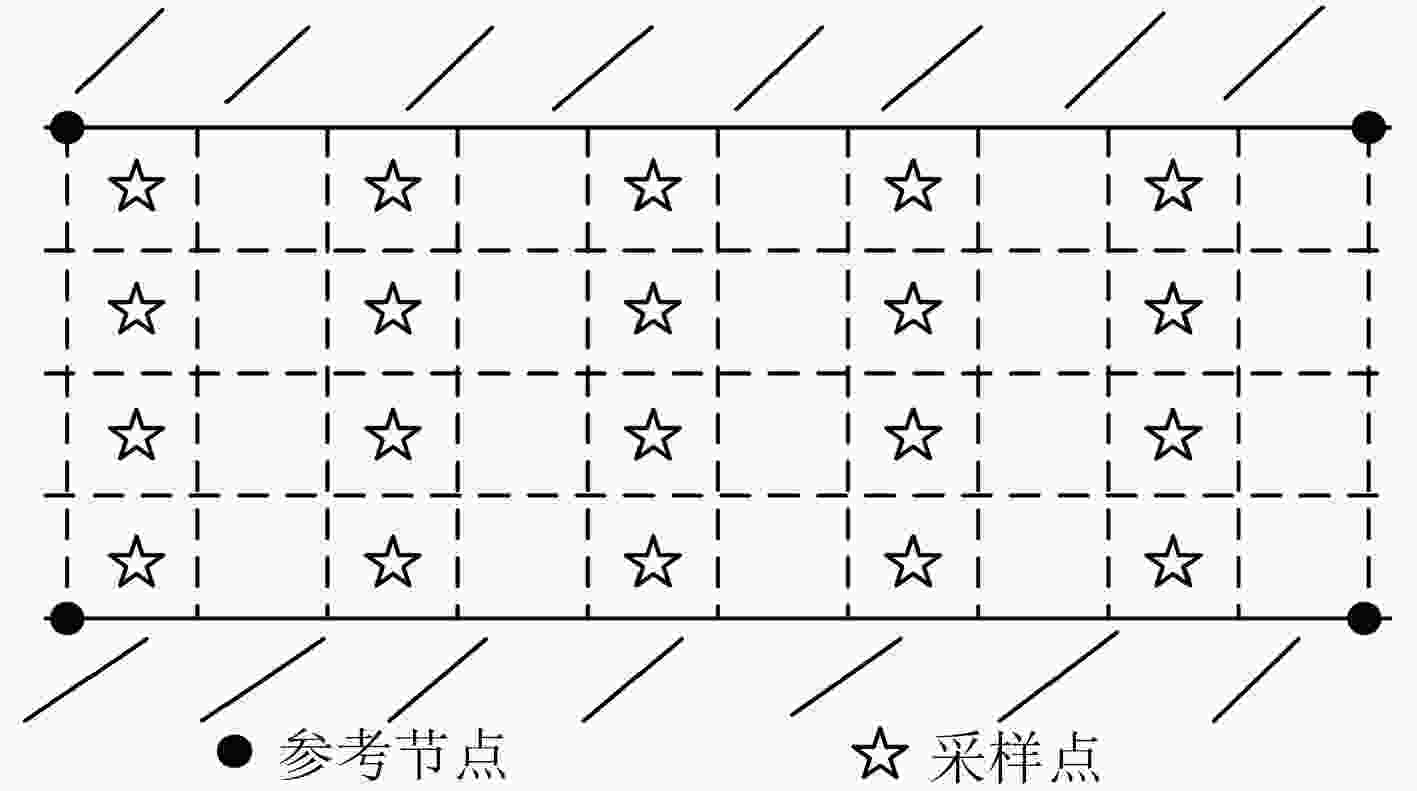
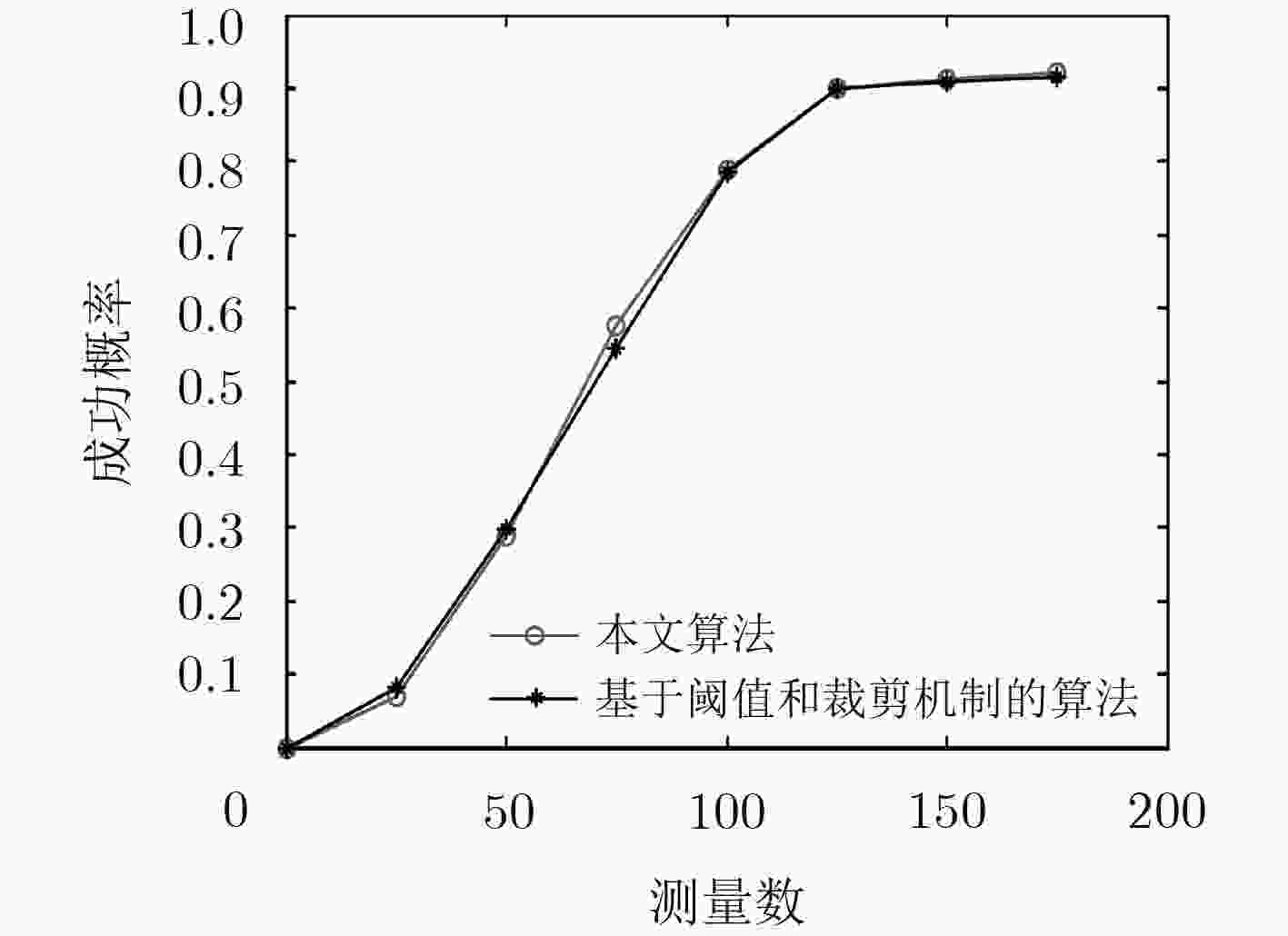
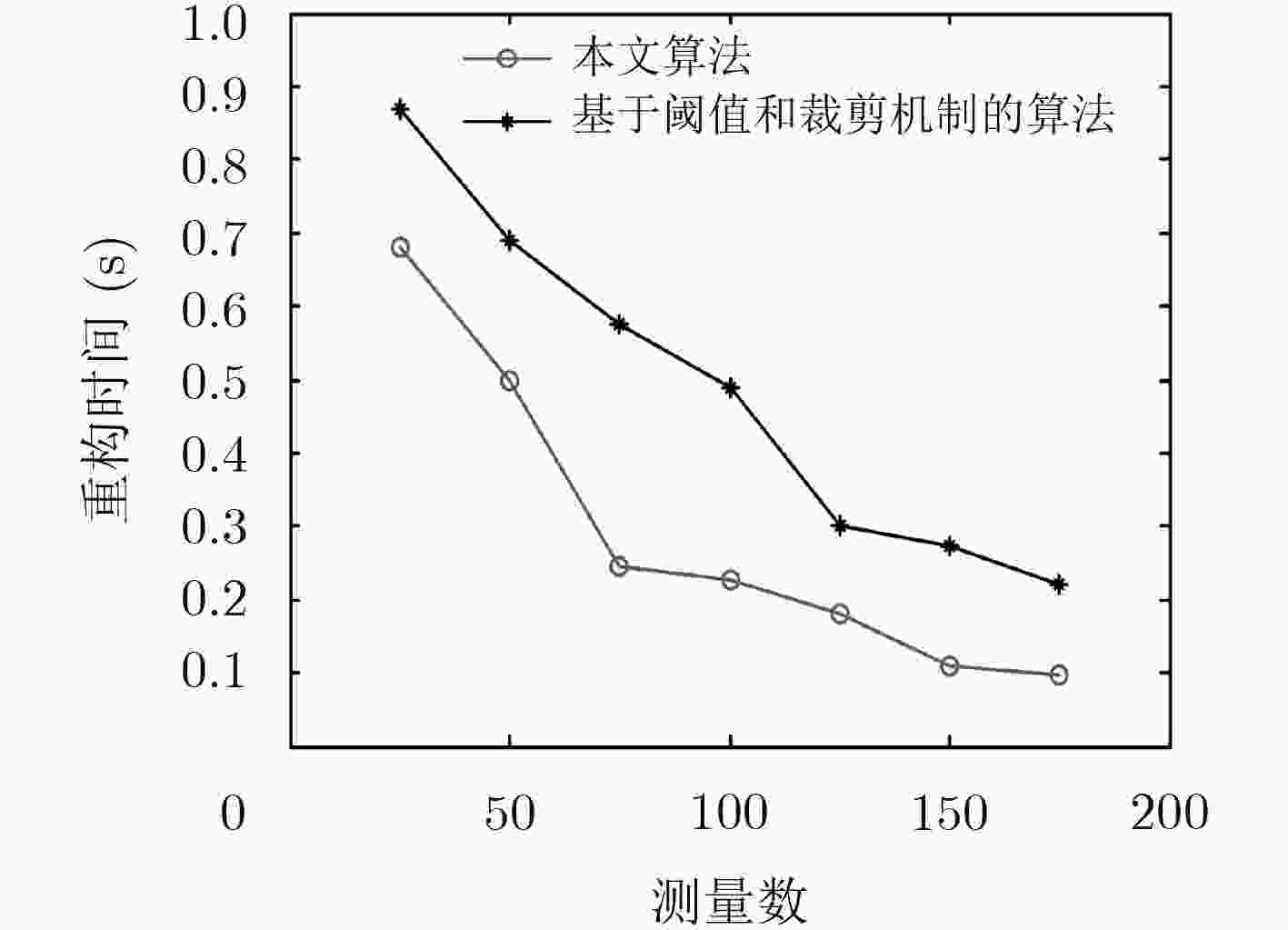
摘要: 针对目前国内矿井目标定位精度低和定位实时性差的现况,该文提出一种基于分布式压缩感知原理构造指纹数据库的方法,该方法在离线阶段只需采集少量巷道中的指纹信息(参考节点ID信息、基于电磁波到达时间(TOA)的距离测量值和实际距离值),便可高概率重构矿井目标指纹数据库指纹信息,从而达到减少数据采集工作量和提高工作效率的目的。后续在线阶段,只需获得某时刻参考节点ID信息和目标节点被参考节点测得的实时TOA距离测量值,根据模式匹配方法可获得该时刻目标节点距离参考节点的待估距离值,保证了定位精度和定位实时性。在此基础上,提出一种改进的压缩采样修正匹配追踪算法(CoSaMMP)进行指纹信息重构,该算法利用折半法增大裁剪力度从而有效缩短重构数据时间。仿真结果表明所提算法的可行性及有效性。
-
关键词:
- 分布式压缩感知 /
- 指纹数据库 /
- 压缩采样修正匹配追踪 /
- TOA测距
Abstract: A method of establishing a fingerprint database, which is based on distributed compressed sensing, is proposed to improve the low positioning accuracy and poor real-time positioning that exist in the current mine target positioning in China. Using the method, the fingerprint information of mine target fingerprint database can be reconstructed with high probability by collecting only a few fingerprint information (reference node IDs, Time Of Arrival (TOA) measurements based on electromagnetic wave and actual distance values) in the roadway in the off-line stage. Therefore, the data collection workload can be reduced and the work efficiency can be improved as well. In the subsequent on-line stage, according to the pattern matching method, the estimated distance between the target node and the reference nodes at the certain time can be obtained only by getting the reference node IDs and the real-time TOA measurements measured by the reference nodes at a certain moment, which guarantees the positioning accuracy and positioning real-time performance. Based on this method, an improved Compressive Sampling Modifying Matching Pursuit (CoSaMMP) algorithm is proposed to reconstruct the fingerprint information. The algorithm can effectively shorten the reconstruction time by using the folding method to increase the cutting force. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is feasible and effective. -
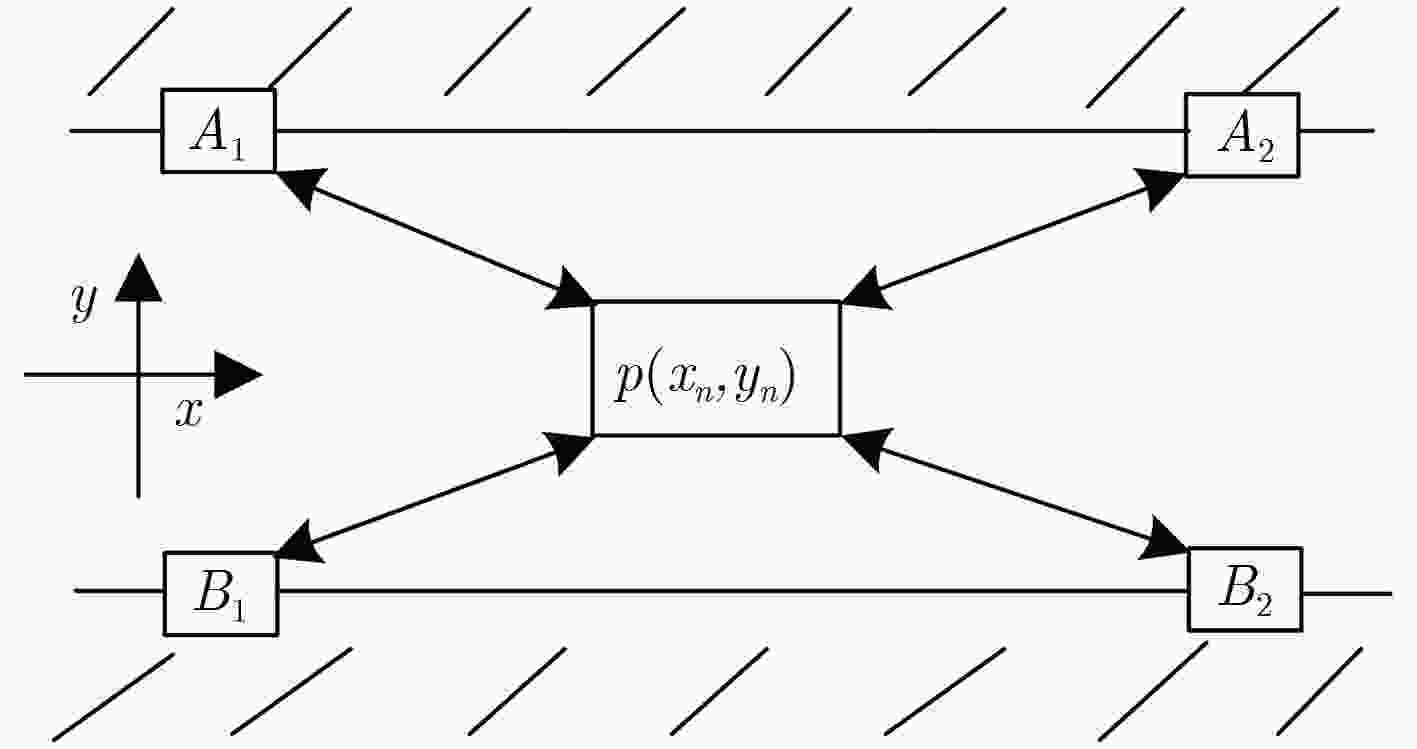
表 1 指纹数据库指纹信号
指纹信号 指纹数据 1 ${A_1}$,${A_1}$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${A_1}$($N$个${A_1}$) 2 ${A_2}$,${A_2}$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${A_2}$($N$个${A_2}$) 3 ${B_1}$,${B_1}$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${B_1}$($N$个${B_1}$) 4 ${B_2}$,${B_2}$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${B_2}$($N$个${B_2}$) 5 ${d_{11}}(p)$,${d_{21}}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${d_{N1}}(p)$ 6 ${d_{12}}(p)$,${d_{22}}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${d_{N2}}(p)$ 7 ${d_{13}}(p)$,${d_{23}}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${d_{N3}}(p)$ 8 ${d_{14}}(p)$,${d_{24}}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,${d_{N4}}(p)$ 9 $d\,'\!\!_{11}(p)$,$d\,'\!\!_{21}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,$d\,'\!\!_{N1}(p)$ 10 $d\,'\!\!_{12}(p)$,$d\,'\!\!_{22}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,$d\,'\!\!_{N2}(p)$ 11 $d\,'\!\!_{13}(p)$,$d\,'\!\!_{23}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,$d\,'\!\!_{N3}(p)$ 12 $d\,'\!\!_{14}(p)$,$d\,'\!\!_{24}(p)$,$ ·\!·\!· $,$d\,'\!\!_{N4}(p)$ 表 2 各算法的时间复杂度
算法 时间复杂度(M<N) SVR-Kriging $O\left( {{N^3}} \right)$ CoSaMP O(MN) CoSaMMP $\le$O(MN) ICoSaMMP(本文算法) $\le$O(MN) 表 3 本文算法各信号平均误差
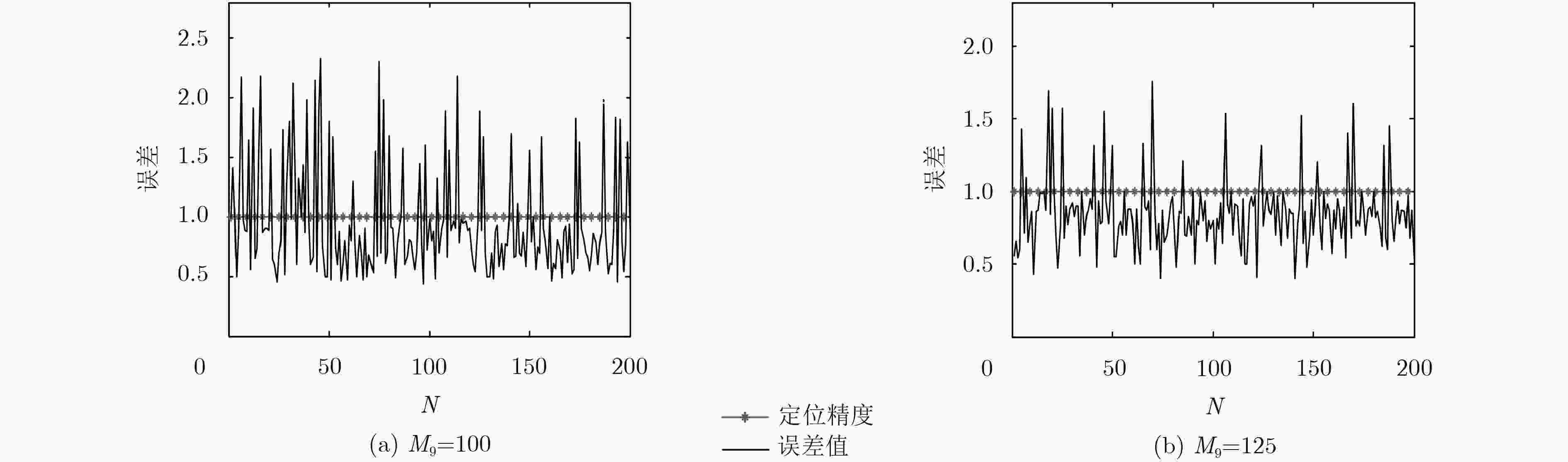
采样数 l = 9 l = 10 l = 11 l = 12 Ml = 100 0.98 1.06 0.90 0.96 Ml = 125 0.85 0.76 0.92 0.86 表 4 误差对比
定位算法 本文算法 SVR-Kriging算法 采样数 Ml = 100 Ml = 125 Ml = 100 最大误差 2.37 1.85 1.90 最小误差 0.43 0.32 0.39 平均误差 0.98 0.85 0.92 -
孙继平. 2016年版《煤矿安全规程》监控与通信条款解析[J]. 工矿自动化, 2016, 42(5): 1–8. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.2016.05.001SUN Jiping. Explanations for part of monitoring and communication of Coal Mine Safety Regulations of 2016 Edition[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2016, 42(5): 1–8. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.2016.05.001 邓兵, 孙正波, 杨乐, 等. 存在站址误差时的线性校正TDOA定位算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 44(4): 106–111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.04.019DENG Bing, SUN Zhengbo, YANG Le, et al. TDOA localization with linear-correction in the presence of sensor position errors[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2017, 44(4): 106–111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.04.019 田强, 冯大政, 杨凡, 等. 基于线性校正的TOA联合同步与定位算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 245–249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.01TIAN Qiang, FENG Dazheng, YANG Fan, et al. Joint TOA-based synchronization and localization via linear-correction technique[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 245–249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.01 徐琨, 刘宏立, 马子骥, 等. 容忍多径效应的无线传感网络测距算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(10): 2461–2468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.10.014XU Kun, LIU Hongli, MA Ziji, et al. Multipath-tolerant ranging algorithm in underground tunnel for wireless sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(10): 2461–2468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.10.014 CHEN Hongyang, LIU Bin, HUANG Pei, et al. Mobility-assisted node localization based on TOA measurements without time synchronization in wireless sensor networks[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2012, 17(1): 90–99. doi: 10.1007/s11036-010-0281-3 WANG Gang and CHEN Hongyang. An importance sampling method for TDOA-based source localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2011, 10(5): 1560–1568. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.030311.101011 李论, 张著洪, 丁恩杰, 等. 基于RSSI的煤矿巷道高精度定位算法研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(1): 183–191, 200. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000632LI Lun, ZHANG Zhuhong, DING Enjie, et al. Precision positioning algorithm in coal mine tunnel based on RSSI[J]. Journal of China University of Mining &Technology, 2017, 46(1): 183–191, 200. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000632 郝丽娜, 张秀均, 郁万里, 等. 基于RSS手指模的煤矿井下WLAN定位方法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2012, 31(9): 46–49. doi: 10.13873/j.1000-97872012.09.020HAO Lina, ZHANG Xiujun, YU Wanli, et al. Underground coal mine WLAN localization algorithm based on RSS fingerprinting[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2012, 31(9): 46–49. doi: 10.13873/j.1000-97872012.09.020 孙继平, 李晨鑫. 基于卡尔曼滤波和指纹定位的矿井TOA定位方法[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(6): 1127–1133. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000117SUN Jiping and LI Chenxin. Mine time of arrival positioning method based on Kalman filtering and fingerprint positioning[J]. Journal of China University of Mining &Technology, 2014, 43(6): 1127–1133. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000117 王红军, 周宇, 王伦文. 基于SVR-Kriging插值的矿井工人二维指纹定位数据库构建算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(11): 2571–2578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170058WANG Hongjun, ZHOU Yu, and WANG Lunwen. Establishment algorithm of two dimensional fingerprint database for mine workers based on SVR-Kriging interpolation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(11): 2571–2578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170058 DUARTE M F, SARVOTHAM S, BARON D, et al. Distributed compressed sensing of jointly sparse signals[C]. Conference Record of the Thirty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2005: 1537–1541. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2005.1600024. CANDES E J and TAO T. Decoding by linear programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(12): 4203–4215. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.858979 徐勇. 分布式压缩感知的算法及其应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国地质大学, 2015: 2–47.XU Yong. The research on algorithms of distributed compressed sensing and their applications[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], China University of Geosciences, 2015: 2–47. GUO Jiateng, JIANG Jizhou, WU Lixin, et al. 3D modeling for mine roadway from laser scanning point cloud[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 4452–4455. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730160. 徐志明, 田子建, 王文清, 等. 基于压缩感知的区域离散化矿井目标定位方法[J]. 工矿自动化, 2018, 44(8): 67–70. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.2018020005XU Zhiming, TIAN Zijian, WANG Wenqing, et al. Region discretization mine target positioning method based on compressed sensing[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2018, 44(8): 67–70. doi: 10.13272/j.issn.1671-251x.2018020005 甘伟, 许录平, 张华, 等. 一种贪婪自适应压缩感知重构[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 39(3): 50–57, 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2012.03.008GAN Wei, XU Luping, ZHANG Hua, et al. Greedy adaptive recovery algorithm for compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2012, 39(3): 50–57, 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2012.03.008 WANG Qun and LIU Zhiwen. A robust and efficient algorithm for distributed compressed sensing[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2011, 37(6): 916–926. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2011.09.008 NEEDELL D and TROPP J A. CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 26(3): 301–321. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2008.07.002 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
