Integral Attack on Reduced-round Simeck Algorithm
-
摘要: 该文对轻量级分组密码算法Simeck在积分攻击下的安全性进行了研究。通过向前解密扩展已有的积分区分器,构造了16轮Simeck48和20轮Simeck64算法的高阶积分区分器,并在新区分器的基础上,利用等价子密钥技术和部分和技术,结合中间相遇策略和密钥扩展算法的性质,实现了24轮Simeck48和29轮Simeck64算法的积分攻击。攻击24轮Simeck48的数据复杂度为246,时间复杂度为295,存储复杂度为282.52;攻击29轮Simeck64的数据复杂度为263,时间复杂度为2127.3,存储复杂度为2109.02。与Simeck算法已有积分攻击的结果相比,该文对Simeck48和Simeck64积分攻击的轮数分别提高了3轮和5轮。Abstract: The security of lightweight block cipher Simeck against integral attack is evaluated in this paper. First, a 16-round and a 20-round high-order integral distinguisher of Simeck48 and Simeck64 are constructed by decrypting the existed integral distinguisher forward. Then, combined with the meet-in-the-middle strategy and subkey relationship, the integral attacks on 24-round Simeck48 and 29-round Simeck64 are first proposed utilizing the equivalent-subkey and partial-sum technologies based on the new integral distinguishers. The data, time and memory complexity of attacking 24-round Simeck48 are 246, 295 and 282.52 while the data, time and memory complexity of attacking 29-round Simeck64 are 263, 2127.3 and 2109.02. These new attacks improve greatly the results of the previous integral attack on Simeck. Compared with the known results of the integral attack on Simeck, the number of rounds of the integral attacks on Simeck48 and Simeck64 is increased by 3-round and 5-round, respectively.
-
Key words:
- Cryptanalysis /
- Lightweight block cipher /
- Integral attack /
- Simeck algorithm
-
表 1 符号说明
符号 说明 Simeck2n(4n) 分组为2n,密钥为4n的Simeck算法 ${{L} _i}$ 第i轮左半部分输入nbit ${L_i}\left( j \right)$ ${{L} _i}$第j bit ${{R} _i}$ 第i轮右半部分输入nbit ${R_i}\left( j \right)$ ${{R} _i}$第j bit ${K} $ 主密钥${K} = ({{K} _3},{{K} _2},{{K} _1},{{K} _0})$ ${\rm{r}}{{\rm{k}}_i}$ 第i轮nbit的轮子密钥 $ \oplus $ 异或运算 $\& $,$ \odot $ 与运算 $ < < < r$, $ > > > r$ 循环左移、右移rbit 表 2 Simeck算法的参数
算法 分组长度 密钥长度 字长 轮数 Simeck 32 64 16 32 48 96 24 36 64 128 32 44 表 3 Simeck48的主要攻击结果
算法 攻击方法 攻击轮数 数据复杂度 存储复杂度 时间复杂度 成功概率 参考文献 Simeck48(96) 差分攻击 20 ${O} ({2^{46}})$ – 275 1 文献[2] Simeck48(96) 差分攻击 26 ${O} ({2^{47}})$ – 262 1 文献[4] Simeck48(96) 差分攻击 28 ${O} ({2^{46}})$ – 268.3 0.468 文献[5] Simeck48(96) 线性攻击 19 ${O} ({2^{45}})$ – 294 1 文献[3] Simeck48(96) 不可能差分 24 ${O} ({2^{48}})$ ${O} ({2^{74}})$ 294.7 1 文献[2] Simeck48(96) 零相关攻击 24 ${O} ({2^{48}})$ ${O} ({2^{65.06}})$ 291.6 1 文献[6] Simeck48(96) 积分攻击 21 ${O} ({2^{34}})$ ${O} ({2^{66}})$ 295 1 文献[7] Simeck48(96) 积分攻击 24 ${O} ({2^{46}})$ ${O} ({2^{82.52}})$ 295 1 本文 表 4 Simeck64的主要攻击结果
算法 攻击方法 攻击轮数 数据复杂度 存储复杂度 时间复杂度 成功概率 参考文献 Simeck64(128) 差分攻击 26 ${O} ({2^{63}})$ – 2121 1 文献[2] Simeck64(128) 差分攻击 33 ${O} ({2^{63}})$ ${O} ({2^{63}})$ 296 1 文献[4] Simeck64(128) 差分攻击 35 ${O} ({2^{63}})$ – 2116.3 0.555 文献[5] Simeck64(128) 线性攻击 27 ${O} ({2^{61}})$ – 2120.5 0.477 文献[3] Simeck64(128) 不可能差分 25 ${O} ({2^{64}})$ ${O} ({2^{79}})$ 2126.6 1 文献[2] Simeck64(128) 零相关攻击 28 ${O} ({2^{64}})$ ${O} ({2^{97.67}})$ 2123.06 1 文献[6] Simeck64(128) 积分攻击 24 ${O} ({2^{35}})$ ${O} ({2^{90.46}})$ 2127 1 文献[7] Simeck64(128) 积分攻击 29 ${O} ({2^{63}})$ ${O} ({2^{109.02}})$ ${2^{127.3}}$ 1 本文 -
BEAULIEU R, SHORS D, SMITH J, et al. The SIMON and SPECK families of lightweight block ciphers[EB/OL]. http://eprint.iacr.org/2013/404, 2013. YANG Gangqiang, ZHU Bo, SUDER V, et al. The Simeck family of lightweight block ciphers[C]. Proceedings of the 17th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems 2015, Saint-Malo, France, 2015: 307–329. BAGHERI N. Linear cryptanalysis of reduced-round Simeck variants[C]. The 16th International Conference on Cryptology in India, Bangalore, India, 2015: 140–152. KÖLBL S and ROY A. A brief comparison of Simon and Simeck[C]. The 5th International Workshop on Lightweight Cryptography for Security and Privacy, Aksaray, Turkey, 2016: 69–88. BLONDEAU C, BOGDANOV A and WANG M. On the (In)equivalence of impossible differential and zero-correlation distinguishers for Feistel- and Skipjack-type ciphers[C]. The 12-th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2014: 271–288. ZHANG Kai, GUAN Jie, HU Bin, et al. Security evaluation on Simeck against zero-correlation linear cryptanalysis[J]. IET Information Security, 2018, 12(1): 87–93. doi: 10.1049/iet-ifs.2016.0503 ZHANG Kai, GUAN Jie, HU Bin, et al. Integral cryptanalysis on Simeck[C]. The Sixth International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Dalian, China, 2016: 216–222. DAEMEN J, KNUDSEN L R, and RIJMEN V. The block cipher square[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Haifa, Israel, 1997: 149–165. LUCKS S. The saturation attack—A bait for Twofish[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Yokohama, Japan, 2001: 1–15. BIRYUKOV A and SHAMIR A. Structural cryptanalysis of SASAS[C]. International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques: Advances in Cryptology, Innsbruck, Austria, 2001: 395–405. KNUDSEN L and WAGNER D. Integral cryptanalysis[C]. The 9th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Leuven, Belgium, 2002: 112–127. ZHANG Wentao, SU Bozhan, WU Wenling, et al. Extending higher-order integral: An efficient unified algorithm of constructing integral distinguishers for block ciphers[C]. The 10th International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Singapore, 2012: 117–134. ISOBE T and SHIBUTANI K. Generic key recovery attack on Feistel scheme[C]. The 19th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Bengaluru, India, 2013: 464–485. FERGUSON N, KELSEY J, LUCKS S, et al. Improved cryptanalysis of Rijndael[C]. The 7th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, New York, USA, 2000: 213–230. YI Wentan, WU Baofeng, CHEN Shaozhen, et al. Improved integral and zero-correlation linear cryptanalysis of CLEFIA block cipher[C]. The 12th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Beijing, China, 2016: 33–46. FUNABIKI Y, TODO Y, ISOBE T, et al. Improved integral attack on HIGHT[C]. The 22nd Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Auckland, New Zealand, 2017: 363–383. -





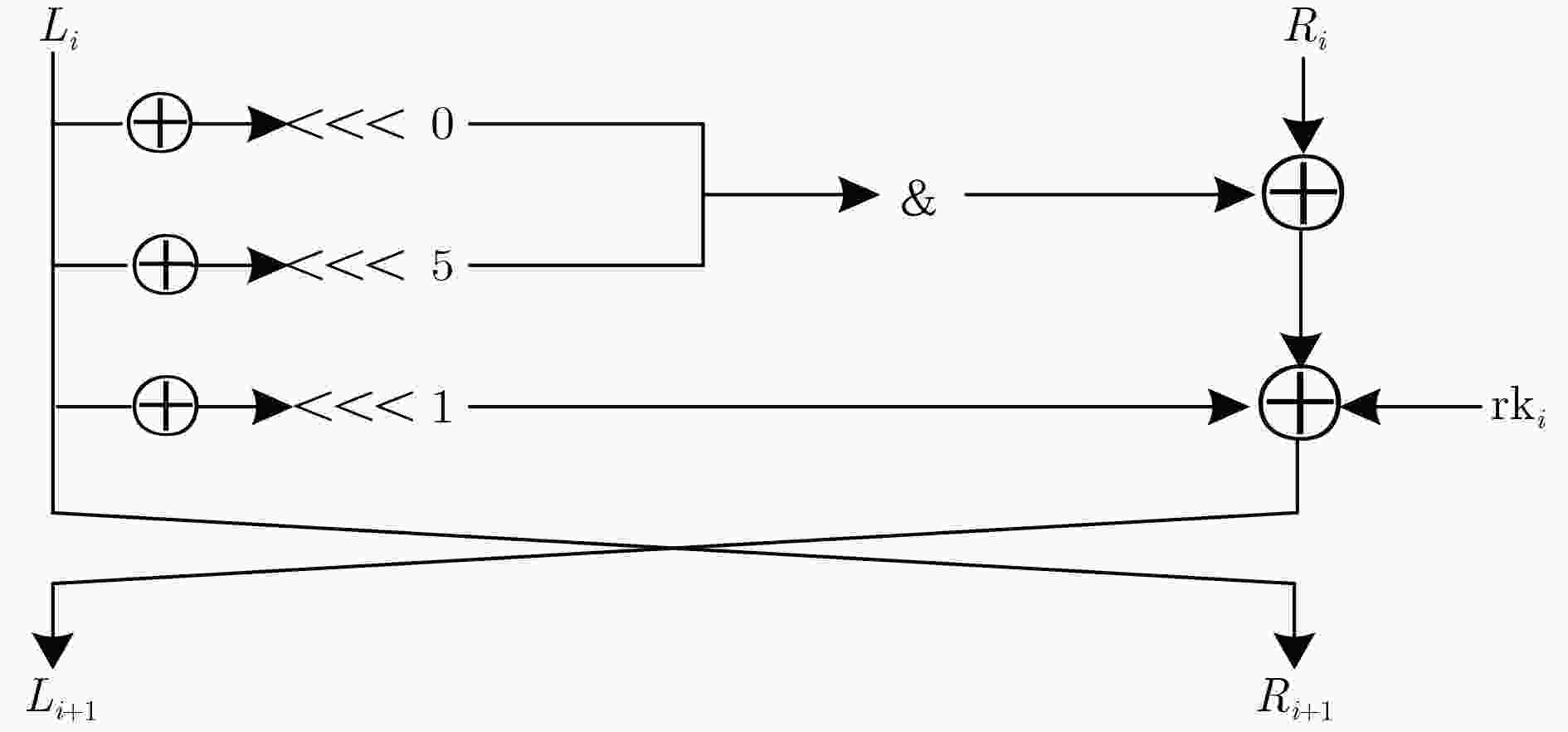
 下载:
下载:
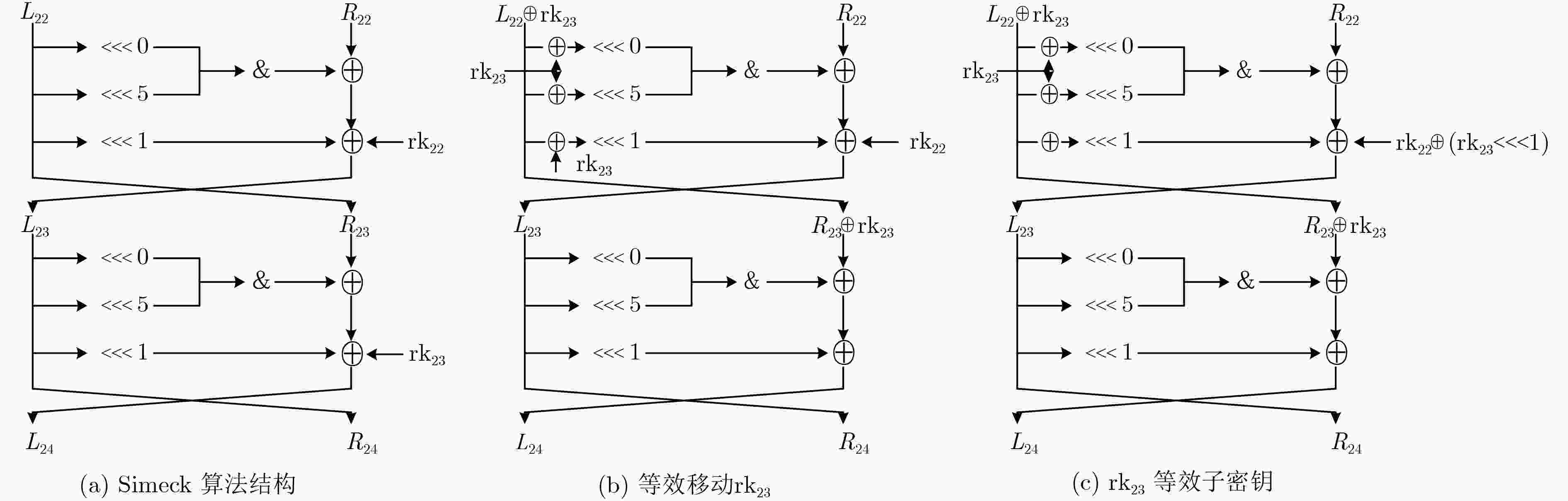
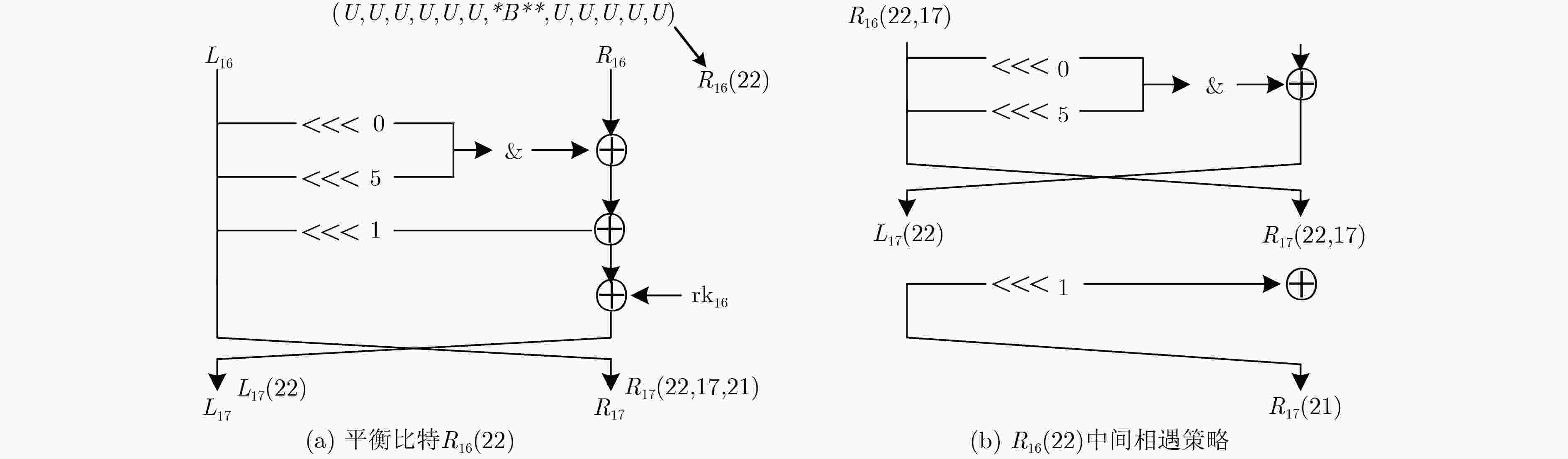
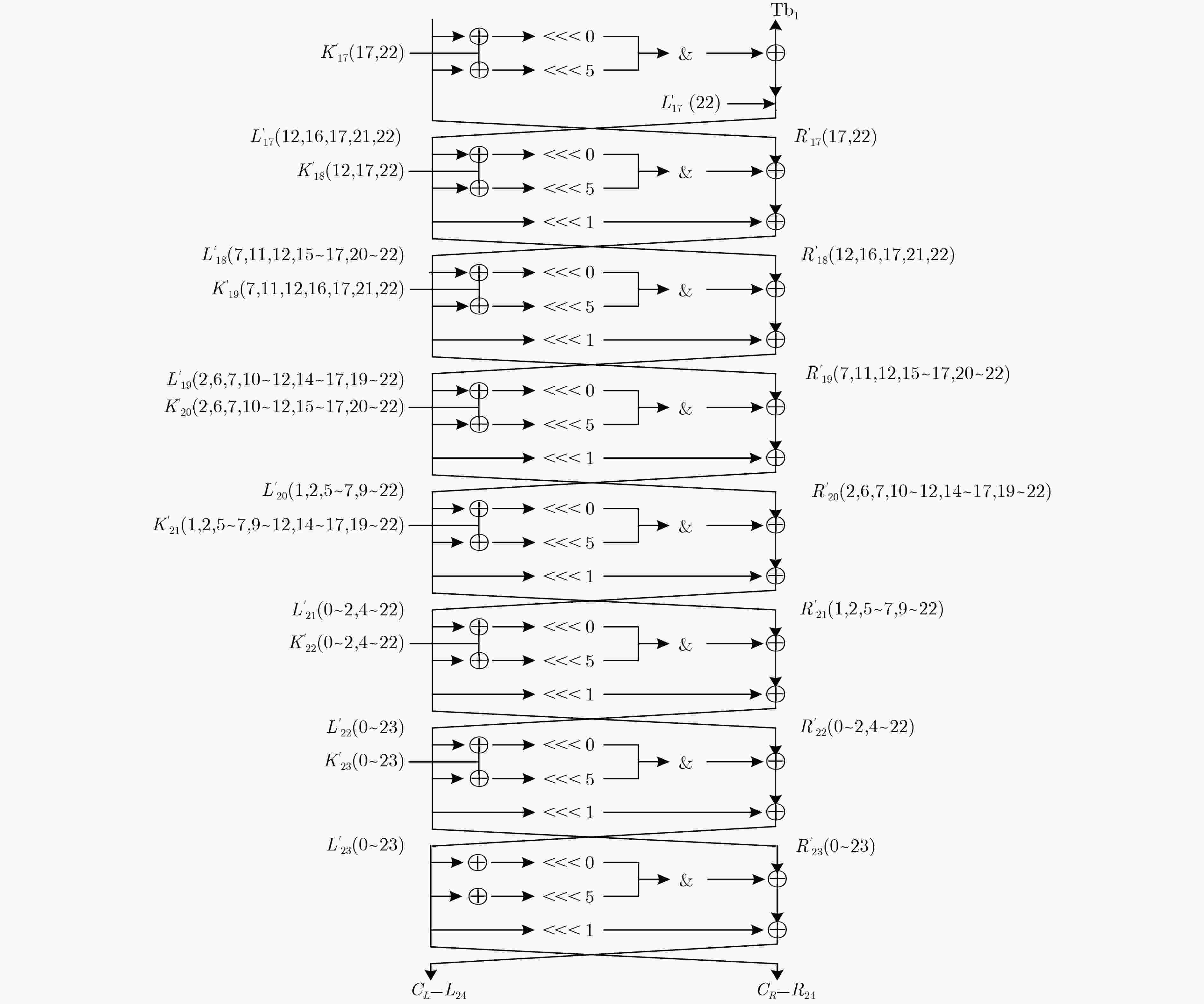


 下载:
下载:
