Compressed Sensing Image Restoration Based on Non-local Low Rank and Weighted Total Variation
-
摘要: 为准确有效地实现自然图像的压缩感知(CS)重构,该文提出一种基于图像非局部低秩(NLR)和加权全变分(WTV)的CS重构算法。该算法考虑图像的非局部自相似性(NSS)和局部光滑特性,对传统的全变分(TV)模型进行改进,只对图像的高频分量设置权重,并用一种差分曲率的边缘检测算子来构造权重系数。此外,算法以改进的TV模型与NLR模型为约束构建优化模型,并分别采用光滑非凸函数和软阈值函数来求解低秩和全变分优化问题,很好地利用了图像的自身性质,保护了图像的细节信息,并提高了算法的抗噪性和适应性。仿真结果表明,与基于NLR的CS算法相比,相同采样率下,该文所提算法的峰值信噪比最高可提高2.49 dB,且抗噪性更强,验证了算法的有效性。Abstract: In order to reconstruct natural image from Compressed Sensing(CS) measurements accurately and effectively, a CS image reconstruction algorithm based on Non-local Low Rank(NLR) and Weighted Total Variation(WTV) is proposed. The proposed algorithm considers the Non-local Self-Similarity(NSS) and local smoothness in the image and improves the traditional TV model, in which only the weights of image’s high-frequency components are set and constructed with a differential curvature edge detection operator. Besides, the optimization model of the proposed algorithm is built with constraints of the improved TV and the non-local low rank model, and a non-convex smooth function and a soft thresholding function are utilized to solve low rank and TV optimization problems respectively. By taking advantage of them, the proposed method makes full use of the property of image, and therefore conserves the details of image and is more robust and adaptable. Experimental results show that, compared with the CS reconstruction algorithm via non-local low rank, at the same sampling rate, the Peak Signal to Noise Ratio(PSNR) of the proposed method increases by 2.49 dB at most and the proposed method is more robust, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 基于非局部低秩和加权全变分的图像压缩感知重构算法(NLR-WTV)
输入: 从原始图像${{u}}$采样得到的压缩感知测量值${{y}}$ 初始化:${{{u}}_0} = {{{Φ}} ^{\rm{T}}}{{y}}$, ${{a}}$, ${{b}}$, ${{c}}$, ${\lambda _1}$, ${\lambda _2}$, ${\mu _1}$, ${\mu _2}$; Outer loop for $k{\rm{ }} = 1, {\rm{ }}2, ·\!·\!·, K$ (1) 根据块匹配法找到图像各相似像素点的位置; (2) 根据式(6)、式(7)和式(8)计算图像的低频分量${{{u}}_{\rm{L}}}$和高频分
量${{{u}}_{\rm{R}}}$;(3) if $k \le {K_{{0}}}$, ${{{w}}_i} = 1$ else 根据式(9)计算${{{w}}_i}$;end if Inner loop for $t{\rm{ }} = 1, {\rm{ }}2, ·\!·\!·, T\;$ (a) 根据式(17)计算${{{L}}_i}^{(k + 1)}$; (b) 根据式(19)计算${{{x}}^{(k + 1)}}$; (c) 分别根据式(21)和式(22)计算图像在低频和高频的梯度
${{{z}}_1}^{(k + 1)}$和${{{z}}_2}^{(k + 1)}$;(d) 根据式(25)计算${{{u}}^{(k + 1)}}$; end for 根据式(14)更新${{a}}$, ${{b}}$和${{c}}$; end for 输出:重构图像${ {{ u} } \!\,\!\! { { {\widehat} }= { {{u} }^{(k + 1)} }$ 表 2 不同算法重构图像的PSNR(dB)和SSIM比较
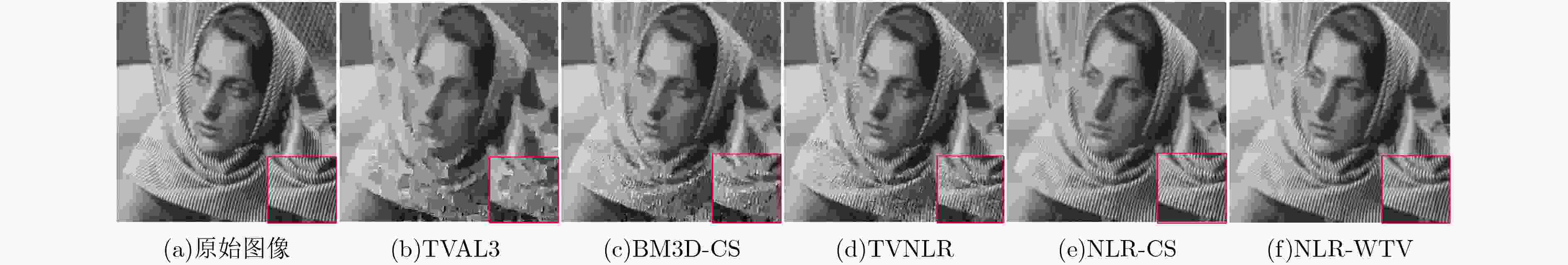
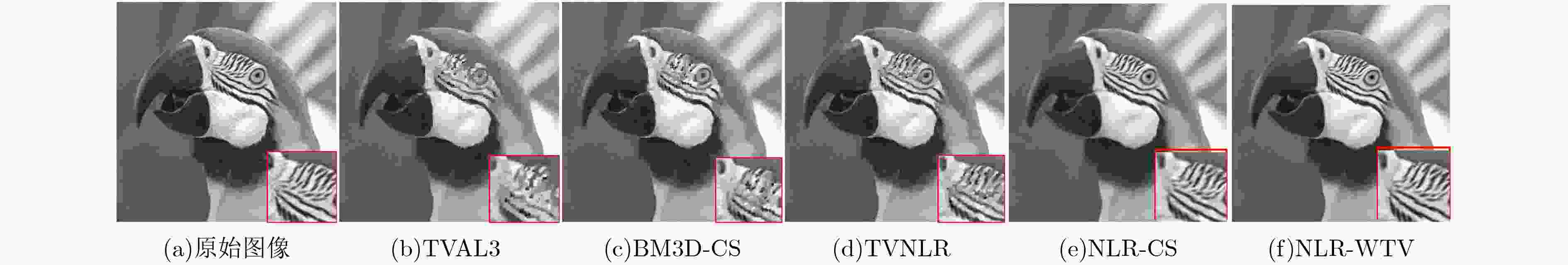
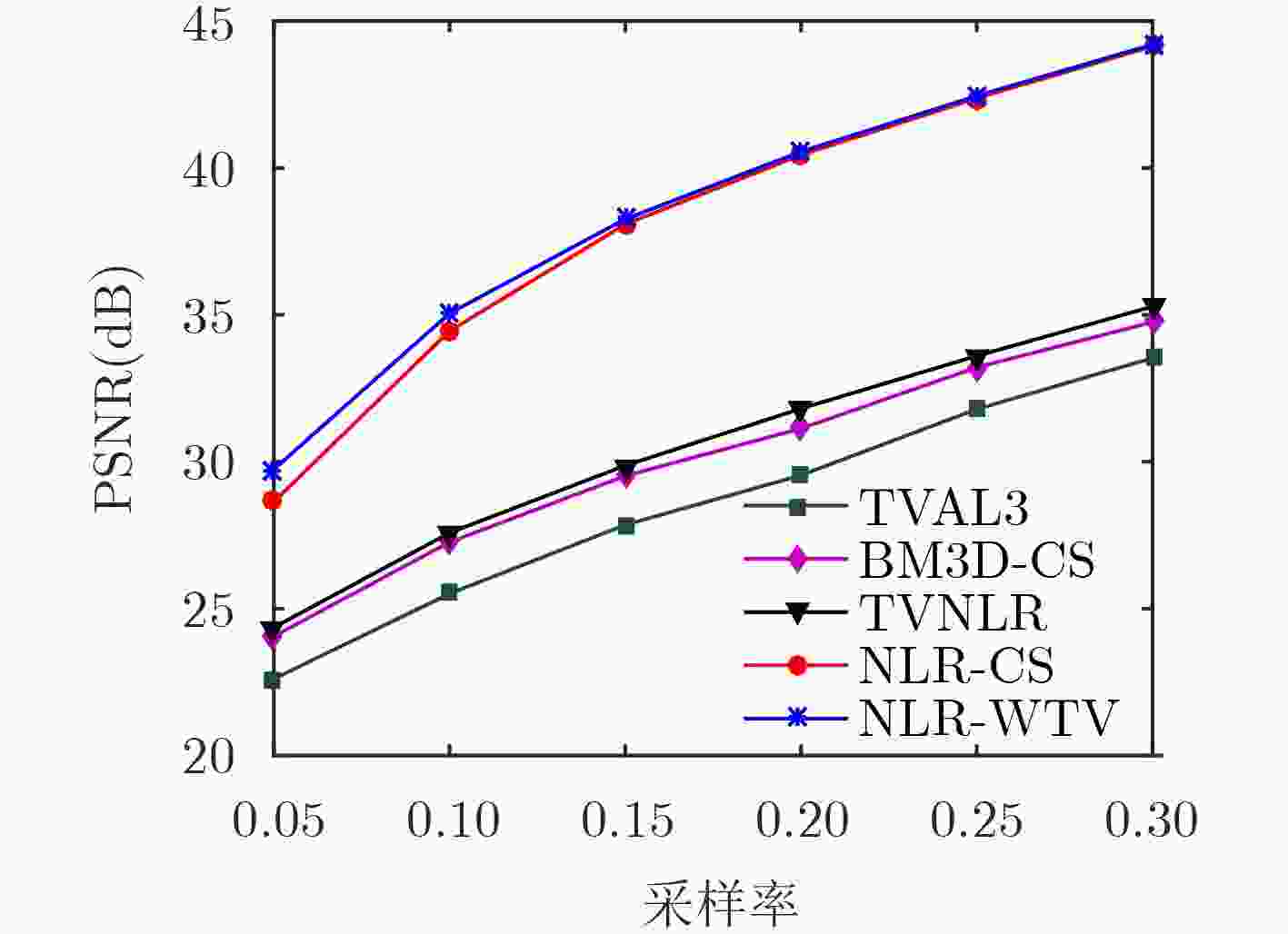
采样率 算法 性能指标 Monarch Barbara Lena Boats Parrots Cameraman 5% TVAL3 PSNR 20.06 19.79 23.08 22.38 22.87 22.89 SSIM 0.508 0.412 0.560 0.543 0.593 0.605 BM3D-CS PSNR 22.73 21.34 24.12 23.31 24.13 23.76 SSIM 0.642 0.523 0.693 0.610 0.692 0.658 TVNLR PSNR 23.02 22.65 25.41 24.79 25.89 24.39 SSIM 0.751 0.568 0.745 0.696 0.800 0.737 NLR-CS PSNR 26.38 27.94 30.64 29.81 31.71 25.38 SSIM 0.848 0.830 0.875 0.830 0.885 0.770 NLR-WTV PSNR 28.21 29.10 30.83 30.14 32.31 27.87 SSIM 0.883 0.862 0.879 0.857 0.891 0.817 表 3 算法测量值含噪的SSIM值比较
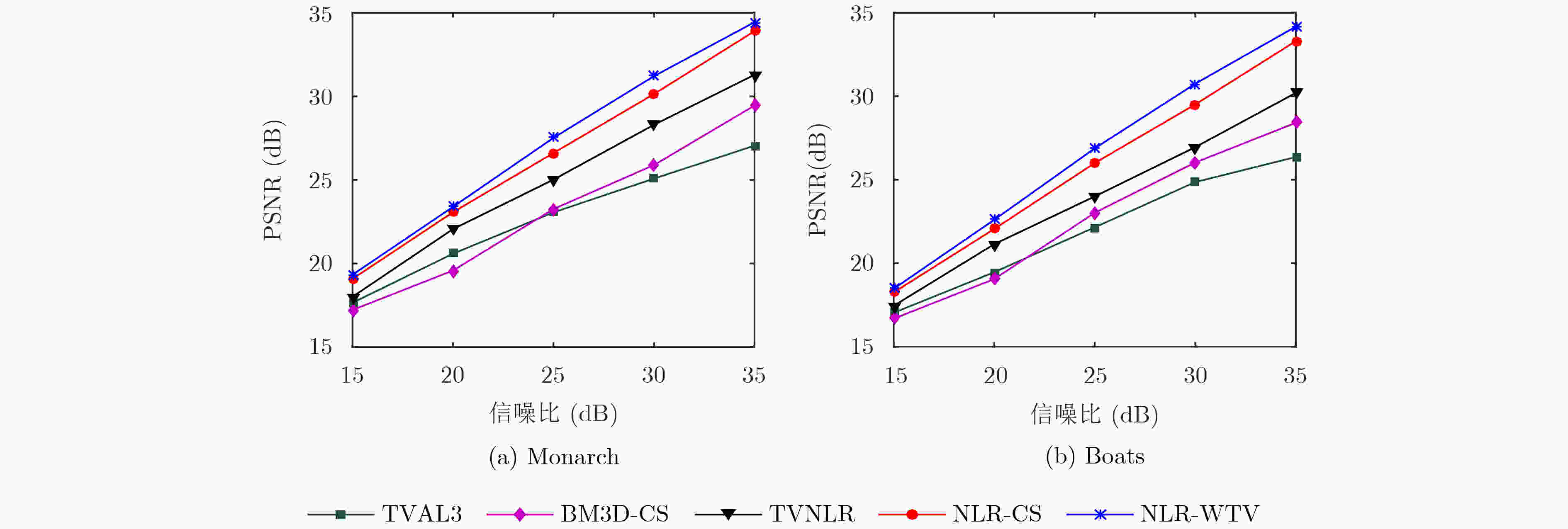
图像 算法 15 20 25 30 35 Monarch NLR-CS 0.374 0.550 0.748 0.874 0.939 NLR-WTV 0.387 0.569 0.761 0.890 0.948 Boats NLR-CS 0.276 0.452 0.672 0.824 0.904 NLR-WTV 0.281 0.466 0.681 0.844 0.927 -
CANDES E J, ROMBERG J, and TAO T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489–509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 石光明, 刘丹华, 高大化, 等. 压缩感知理论及其研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(5): 1070–1081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.05.028SHI Guangming, LIU Danhua, GAO Dahua, et al. Advances in theory and application of compressed sensing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(5): 1070–1081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.05.028 ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Debin, ZHAO Chen, et al. Compressed sensing recovery via collaborative sparsity[C]. 2012 Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, USA, 2012: 287–296. HE Guiqing, XING Siyuan, DONG Dandan, et al. Panchromatic and multi-spectral image fusion method based on two-step sparse representation and wavelet transform[C]. The 9th Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2017: 259–262. RUBINSTEIN R, BRUCKSTEIN A M, and ELAD M. Dictionaries for sparse representation modeling[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(6): 1045–1057. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2010.2040551 HONG Tao and ZHU Zhihui. Online learning sensing matrix and sparsifying dictionary simultaneously for compressive sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 153: 188–196. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.05.021 EGIAZARIAN K, FOI A, and KATKOVNIK V. Compressed sensing image reconstruction via recursive spatially adaptive filtering[C]. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Antonio, USA, 2007: I-549-I-552. BUADES A, COLL B, and MOREL J M. A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one[J]. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 2005, 4(2): 490–530. doi: 10.1137/040616024 LIU Hangfan, XIONG Ruiqin, ZHANG Xinfeng, et al. Nonlocal gradient sparsity regularization for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(9): 1909–1921. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2556498 YU Jun and DONG Shumin. Nonlocal variational method application for image denoising[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xiamen, China, 2017: 1–6. DONG Weisheng, SHI Guangming, LI Xin, et al. Compressive sensing via nonlocal low-rank regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3618–3632. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2329449 宋云, 李雪玉, 沈燕飞, 等. 基于非局部相似块低秩的压缩感知图像重建算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(3): 695–703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.03.029SONG Yun, LI Xueyu, SHEN Yanfei, et al. Compressed sensing image reconstruction based on low rank of non-local similar patches[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(3): 695–703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.03.029 LIU Hangfan, XIONG Ruiqin, LIU Dong, et al. Low rank regularization exploiting intra and inter patch correlation for image denoising[C]. 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing, USA, 2017: 1–4. GU Shuhang, XIE Qi, MENG Deyu, et al. Weighted nuclear norm minimization and its applications to low level vision[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 121(2): 183–208. doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0930-5 RUDIN L I, OSHER S, and FATEMI E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[C]. The 11th Annual International Conference of the Center for Nonlinear Studies on Experimental mathematics: Computational Issues in Nonlinear Science, Los Alamos, USA, 1992: 259–268. LI Chengbo, YIN Wotao, and ZHANG Yin. TVAL3: TV minimization by augmented lagrangian and alternating direction algorithms[EB/OL]. http://www.caam.rice.edu/~optimization/L1/TVAL3/, 2013. CHEN Qiang, MONTESINOS P, SUN Quansen, et al. Adaptive total variation denoising based on difference curvature[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2010, 28(3): 298–306. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2009.04.012 ZHANG Jian, LIU Shaohui, XIONG Ruiqin, et al. Improved total variation based image compressive sensing recovery by nonlocal regularization[C]. 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Beijing, China, 2013: 2836–2839. CANDèS E J, WAKIN M B, and BOYD S P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted ${\ell _1}$ minimization[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2008, 14(5/6): 877–905. doi: 10.1007/s00041-008-9045-xWANG Ting, NAKAMOTO K, ZHANG Heye, et al. Reweighted anisotropic total variation minimization for limited-angle CT reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2017, 64(10): 2742–2760. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2017.2750199 LI Yan. Sparse hyperspectral unmixing combined L1/2 norm and reweighted total variation regularization[C]. The Ninth International Conference on Digital Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 2017: 1042046. BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 ZHANG Mingli, DESROSIERS C, and ZHANG Caiming. Effective compressive sensing via reweighted total variation and weighted nuclear norm regularization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, LA, United States, 2017: 1802–1806. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
