RGB-D Saliency Detection Based on Optimized ELM and Depth Level
-
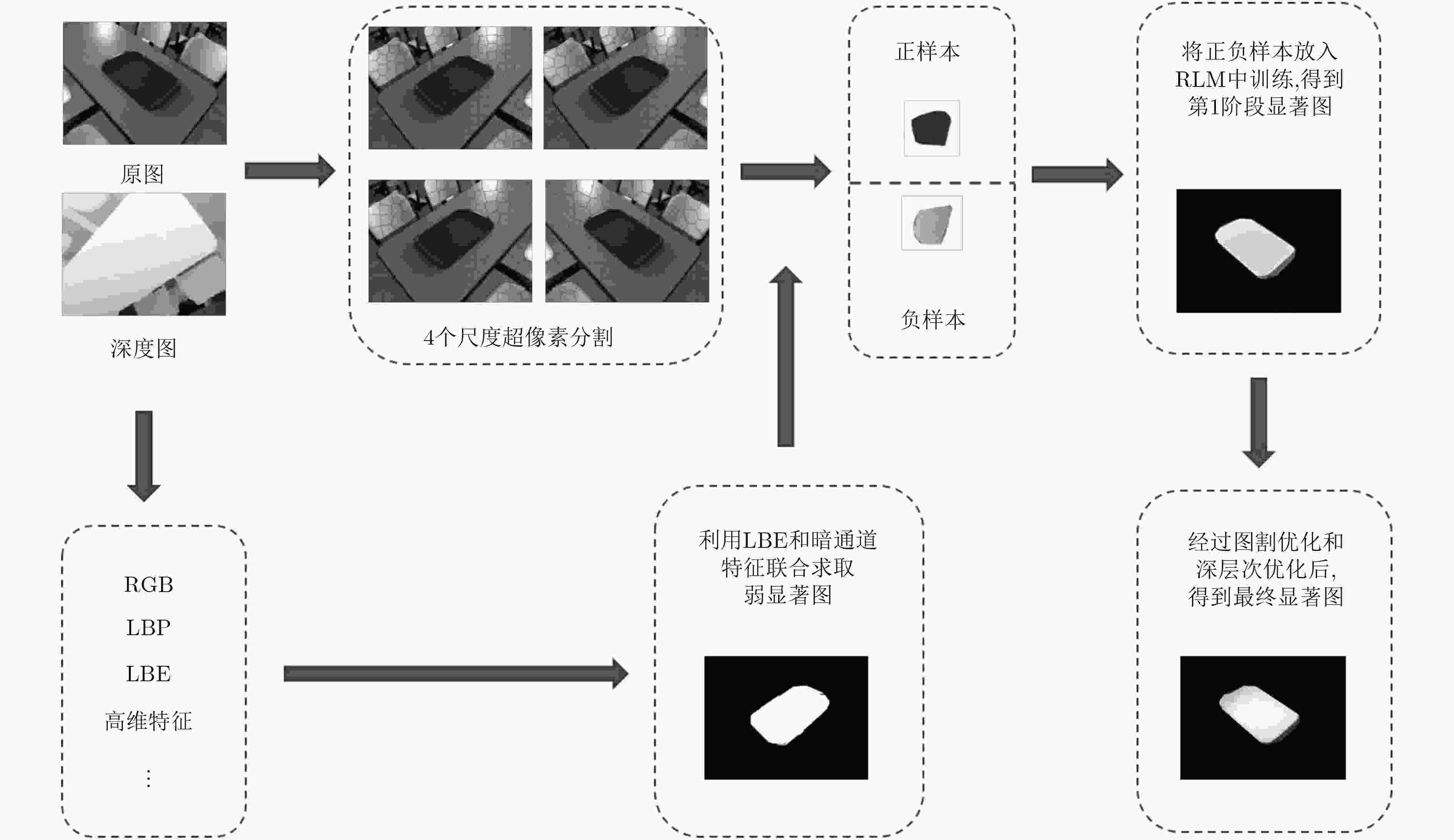
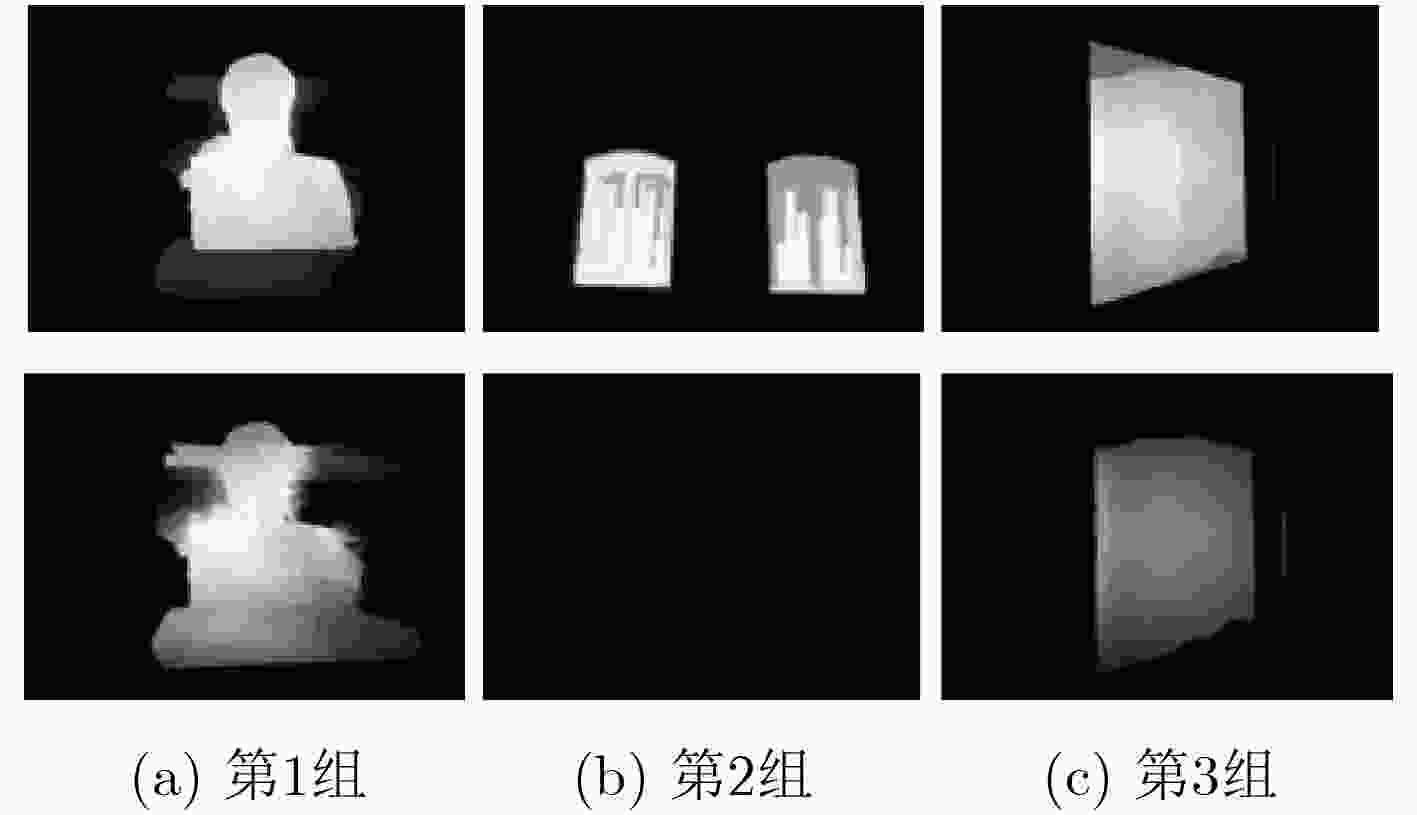
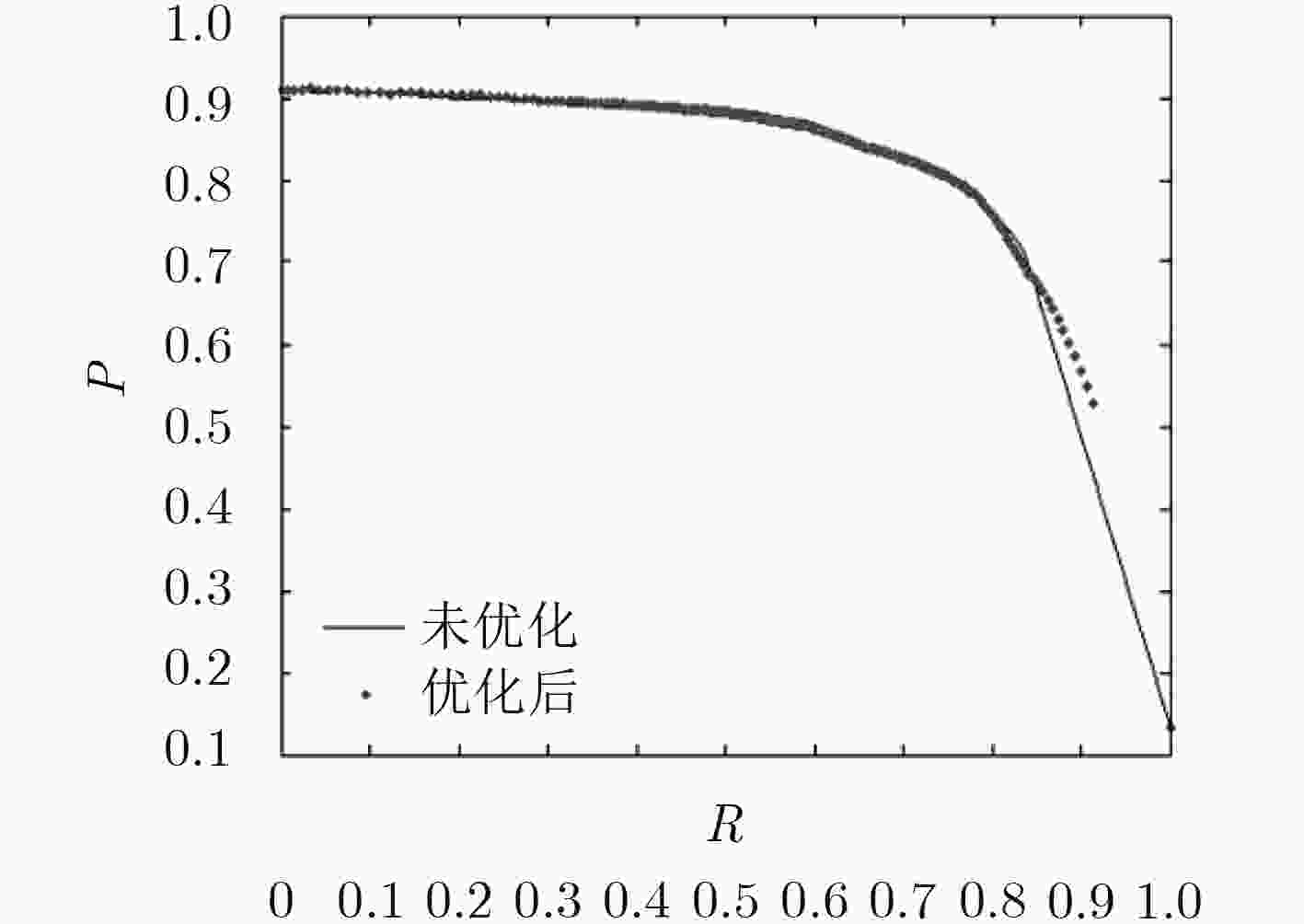
摘要: 目前,相当多的显著目标检测方法均聚焦于2D的图像上,而RGB-D图像所需要的显著检测方法与单纯的2D图像相去甚远,这就需要新的适用于RGB-D的显著检测方法。该文在经典的RGB显著检测方法,即极限学习机的应用的基础上,提出融合了特征提取、前景增强、深度层次检测等多种思路的新的RGB-D显著性检测方法。该文的方法是:第一,运用特征提取的方法,提取RGB图4个超像素尺度的4096维特征;第二,依据特征提取中产生的4个尺度的超像素数量,分别提取RGB图的RGB, LAB, LBP特征以及深度图的LBE特征;第三,根据LBE和暗通道特征两种特征求出粗显著图,并在4个尺度的遍历中不断强化前景、削弱背景;第四,根据粗显著图选取前景与背景种子,放入极限学习机中进行分类,得到第1阶段显著图;第五,运用深度层次检测、图割等方法对第1阶段显著图进行再次优化,得到第2阶段显著图,即最终显著图。
-
关键词:
- RGB-D显著目标检测 /
- 极限学习机 /
- 流程优化 /
- 多特征 /
- 深度层次优化
Abstract: Currently, many saliency-detection methods focus on 2D-image. But, these methods cannot be applied in RGB-D image. Based on this situation, new methods which are suitable for RGB-D image are needed. This paper presents a novel algorithm based on Extreme Learning Machine(ELM), feature-extraction and depth-detection. Firstly, feature-extraction is used for getting a feature, which contains 4-scale superpixels and 4096 dimensions. Secondly, according to the 4-sacle superpixels, the RGB, LAB and LBP feature of RGB image are computed, and LBE feature of depth image. Thirdly, weak salient map with LBE and dark-channel features are computed, and the foreground objects is strengthened in every circle. Fourthly, according to weak salient map, both foreground seeds and background seeds are chosen, and then, put these seeds into ELM to compute the first stage salient map. Finally, depth-detection and graph-cut are used for optimizing the first stage salient map and getting the second stage salient map. -
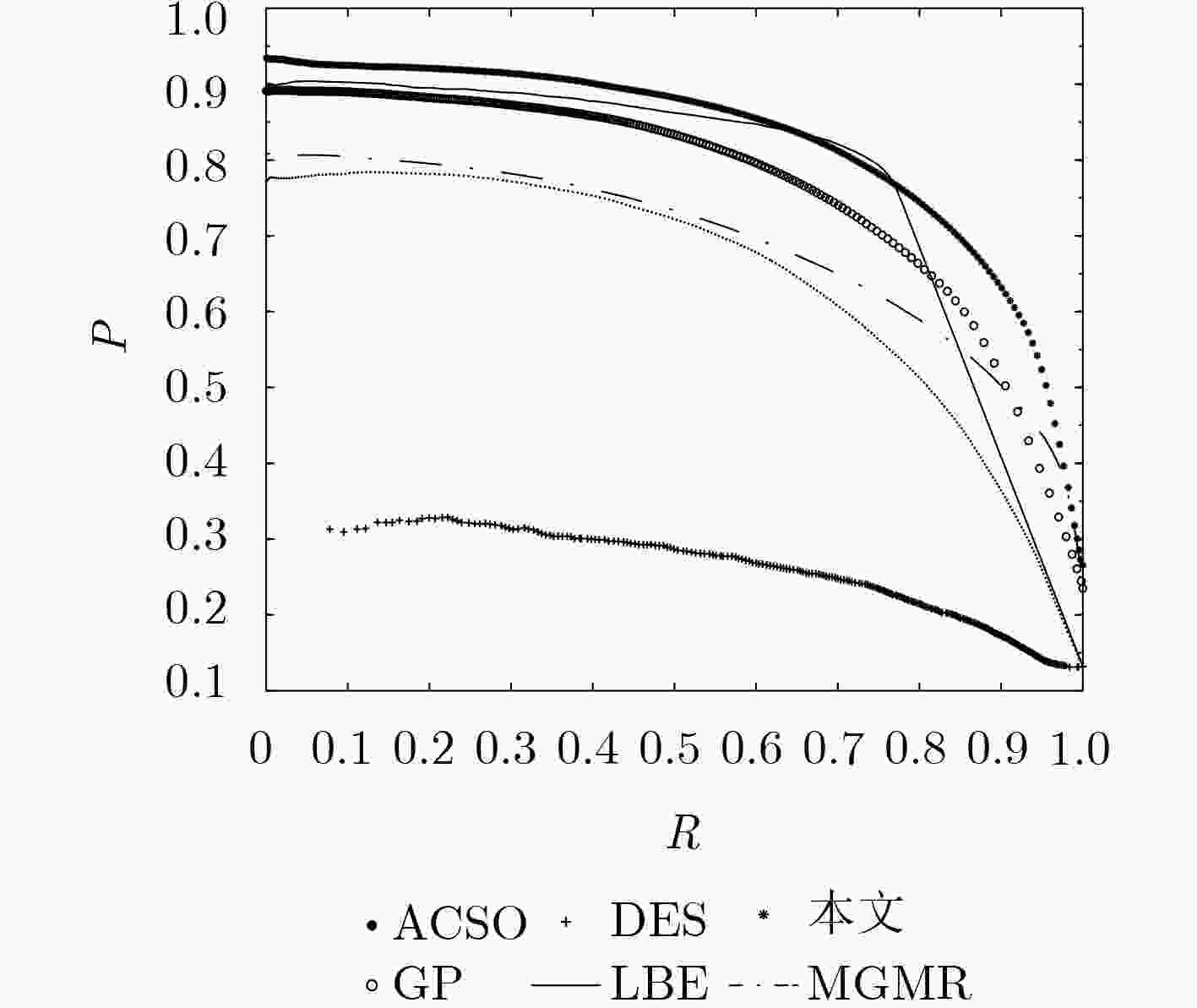
表 1 各算法F-measure值
算法 本文ELM ACSD MGMR GP LBE DES F值 0.7526 0.5857 0.6464 0.7220 0.7408 0.2728 -
GOFERMAN S, ZELNIK-MANOR L, and TAL A. Context-aware saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(10): 1915–1926. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.272 ROTHER C, KOLMOGOROV V, and BLAKE A. "GrabCut": Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 309–314. doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015720 DING Yuanyuan, XIAO Jing, and YU Jingyi. Importance filtering for image retargeting[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, USA, 2011: 89–96. MAHADEVAN V and VASCONCELOS N. Saliency-based discriminant tracking[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 1007–1013. SIAGIAN C and ITTI L. Rapid biologically-inspired scene classification using features shared with visual attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(2): 300–312. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.40 YANG Chuan, ZHANG Lihe, LU Huchuan, et al. Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3166–3173. TONG Na, LU Huchuan, RUAN Xiang, et al. Salient object detection via bootstrap learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1884–1892. PERAZZI F, KRÄHENBÜHL P, PRITCH Y, et al. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 733–740. CHENG Mingming, MITRA N J, HUANG Xiaolei, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569–582. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401 KLEIN D A and FRINTROP S. Center-surround divergence of feature statistics for salient object detection[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2214–2219. PENG Houwei, LI Bing, XIONG Weihua, et al. RGBD Salient Object Detection: A Benchmark and Algorithms[M]. FLEET D, PAJDLA T, SCHIELE B, et al. Computer Vision - ECCV 2014. Cham: Springer, 2014: 92–109. ZHANG Pingping, WANG Dong, LU Huchuan, et al. Learning uncertain convolutional features for accurate saliency detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 212–221. XUE Haoyang, GU Yun, LI Yijun, et al. RGB-D saliency detection via mutual guided manifold ranking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Quebec City, Canada, 2015: 666–670. ZHANG Lu, LIU Jianhua, and LU Huchuan. Saliency detection via extreme learning machine[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 218: 103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.066 LI Guanbin and YU Yizhou. Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features[C]. 2015 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5455–5463. FENG D, BARNES N, YOU Shaodi, et al. Local background enclosure for RGB-D salient object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2343–2350. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. DONAHUE J, JIA Yangqing, VINYALS O, et al. DeCAF: A deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition[C]. The 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 2014: 647–655. RAZAVIAN A S, AZIZPOUR H, SULLIVAN J, et al. CNN features off-the-shelf: An astounding baseline for recognition[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, USA, 2014: 806–813. GUO Jingfang, REN Tongwei, HUANG Lei, et al. Saliency detection on sampled images for tag ranking[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2019, 25(1): 35–47. doi: 10.1007/s00530-017-0546-9 TONG Na, LU Huchuan, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Saliency detection with multi-scale superpixels[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(9): 1035–1039. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2323407 HUANG Guangbin. What are extreme learning machines? Filling the gap between frank Rosenblatt’s dream and john von Neumann’s puzzle[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2015, 7(3): 263–278. doi: 10.1007/s12559-015-9333-0 CAO Weipeng, MING Zhong, WANG Xizhao, et al. Improved bidirectional extreme learning machine based on enhanced random search[J]. Memetic Computing, 2019, 11(1): 19–26. doi: 10.1007/s12293-017-0238-1 ESHTAY M, FARIS H, and OBEID N. Improving extreme learning machine by competitive swarm optimization and its application for medical diagnosis problems[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 104: 134–152. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.024 BOYKOV Y, VEKSLER O, and ZABIH R. Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts[C]. The 7th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 377–384. LIU Shuang, ZHANG Zhong, XIAO Baihua, et al. Ground-based cloud detection using automatic graph cut[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(6): 1342–1346. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2399857 YU Kai, CHEN Xinjian, SHI Fei, et al. A novel 3D graph cut based co-segmentation of lung tumor on PET-CT images with Gaussian mixture models[J]. SPIE, 2016, 9784: 97842V. JU Ran, GE Ling, GENG Wenjing, et al. Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 2014: 1115–1119. CHENG Yupeng, FU Huazhu, WEI Xingxing, et al. Depth enhanced saliency detection method[C]. International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Xiamen, China, 2014. REN Jianqiang, GONG Xiaojin, YU Lu, et al. Exploiting global priors for RGB-D saliency detection[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 25–32. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
