Sparse ISAR Imaging Exploiting Dictionary Learning
-
摘要: 鉴于稀疏ISAR成像方法的成像质量受到待成像场景的稀疏表示不准确的限制,该文将字典学习(DL)技术引入到ISAR稀疏成像中,以提升目标成像质量。该文给出基于离线DL和在线DL两种ISAR稀疏成像方法。前者通过已有同类目标ISAR图像进行学习,获得更优稀疏表示,后者在成像过程中从现有数据中通过优化获得稀疏表示。仿真和实测ISAR数据成像结果表明,结合离线DL和在线DL的成像方法均可获得比现有方法更优的成像结果,离线DL成像优于在线DL成像,而且前者计算效率优于后者。Abstract: In view of the imaging quality of sparse ISAR imaging methods is limited by the inaccurate sparse representation of the scene to be imaged, the Dictionary Learning (DL) technique is introduced into ISAR sparse imaging to get better sparse representation of the scene. An off-line DL based imaging method and an on-line DL based imaging method are proposed. The off-line DL imaging method can obtain a better sparse representation via a dictionary learned from the available ISAR images. The on-line DL imaging method can obtain the sparse representation from the data currently considered by jointly optimizing the imaging and DL processes. The results of both simulated and real ISAR data show that the on-line DL imaging method and the off-line dictionary imaging method are both able to better sparsely represent the target scene leading to better imaging results. The off-line DL based imaging method works better than the on-line DL based imaging method with respect to both imaging quality and computational efficiency.
-
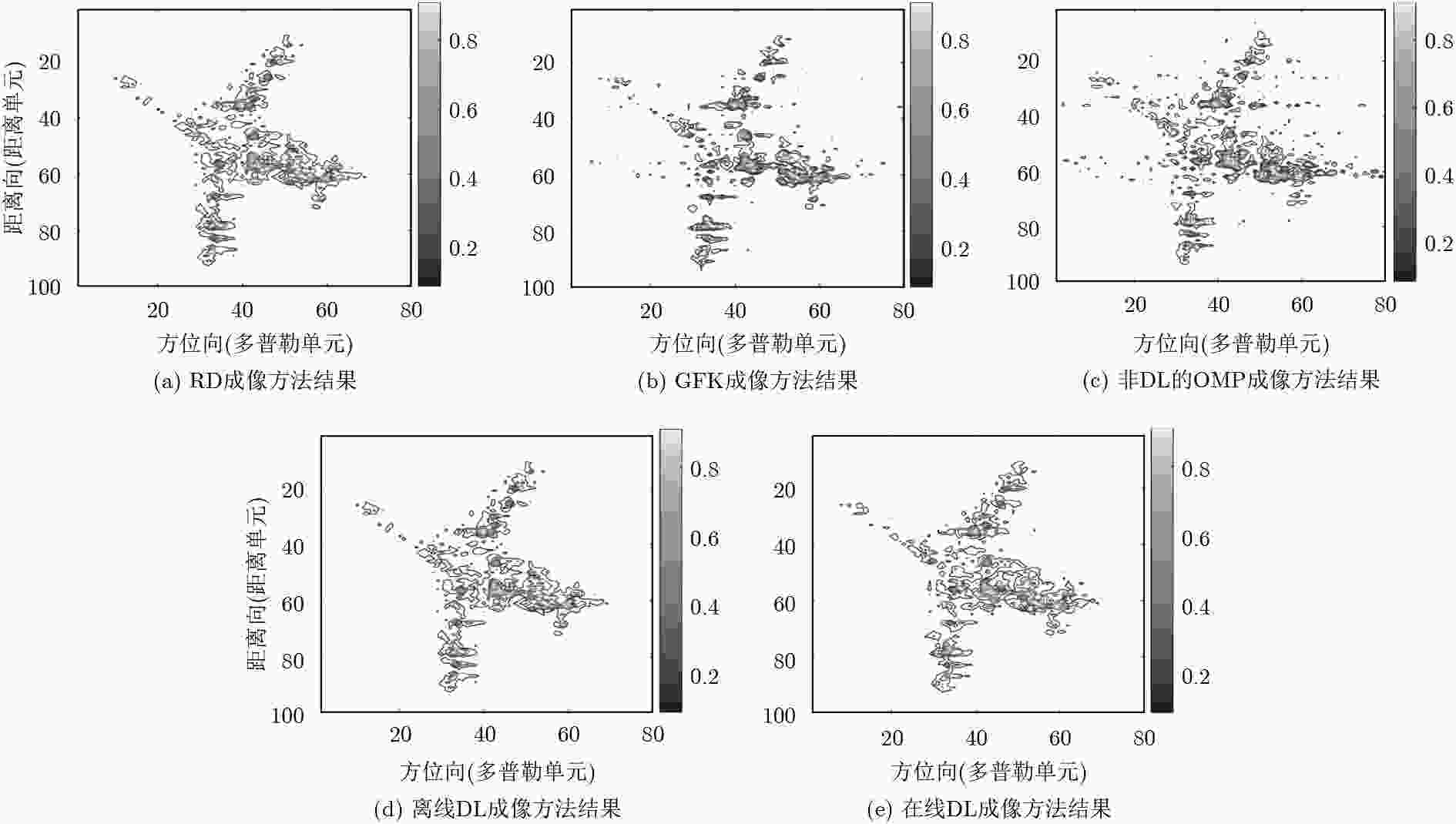
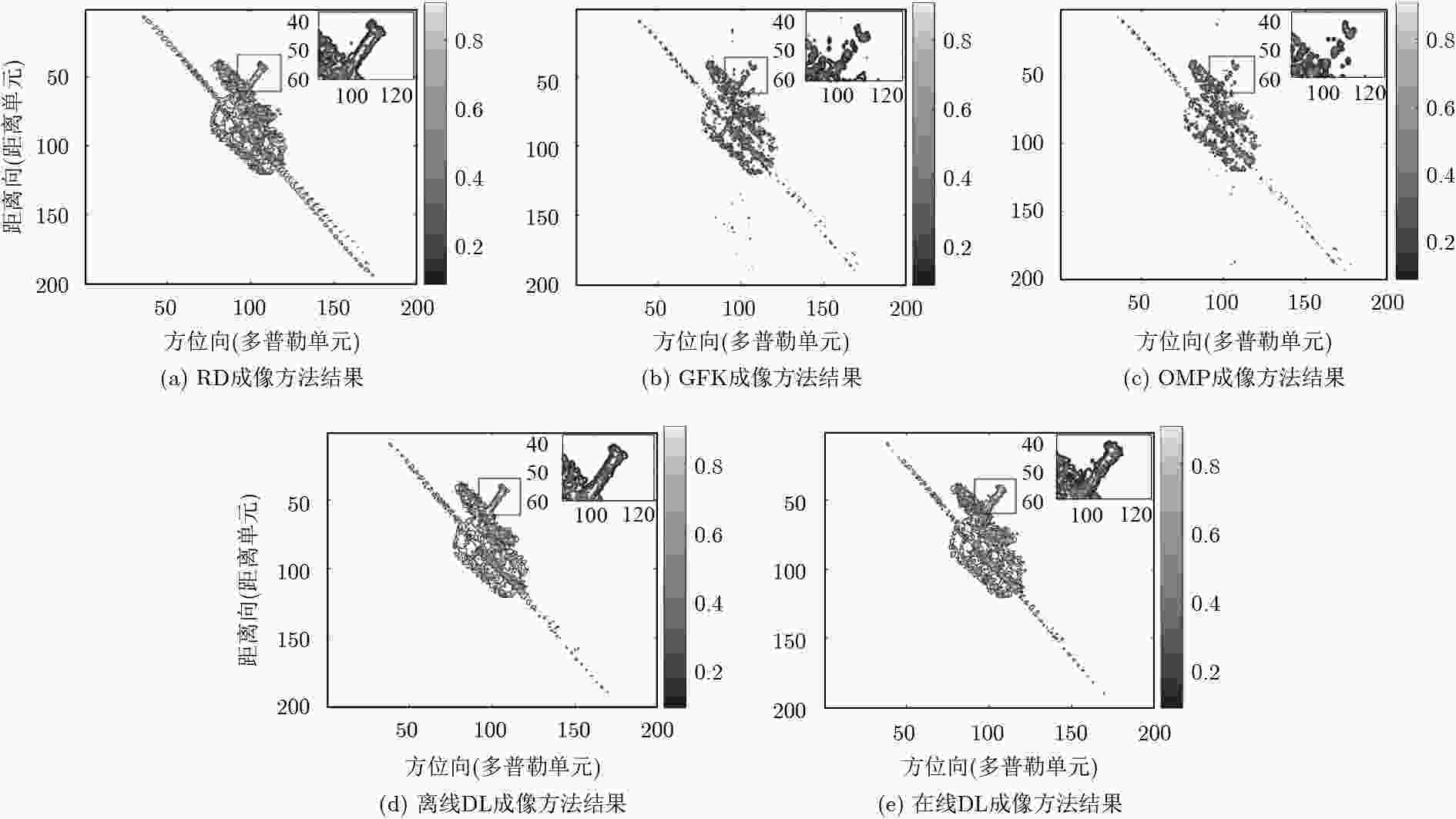
表 1 飞机目标成像性能评价
成像方法 FA MD RRMSE TCR ENT IC 运算时间(s) OMP 89 165 0.1923 57.0203 5.4631 8.0294 116.1757 GKF 86 103 0.2044 55.5930 5.3800 8.1449 1.0058e3 在线DL 74 75 0.1535 57.5629 5.3807 8.2103 52.5790 离线DL 64 70 0.1411 59.0322 5.3685 8.2868 24.8510 表 2 卫星目标成像性能评价
成像方法 FA MD RRMSE TCR ENT IC 运算时间(s) OMP 146 507 0.3736 63.2956 6.4209 9.8099 56.1323 GKF 140 478 0.2550 65.3382 6.3740 10.3843 1.6485e4 在线DL 142 161 0.1765 65.9163 6.6098 9.5039 19.2178 离线DL 122 147 0.1564 67.2506 6.6137 9.6094 4.1543 -
PRICKETT M J and CHEN C C. Principles of inverse synthetic aperture radar /ISAR/ imaging[C]. IEEE Electronics and Aerospace Systems Conference, New York, USA, 1980: 340–345. GENG Minming, TIAN Ye, FANG Jian, et al. Implementation of GPU-based iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm in sparse microwave imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 3863–3866. CETIN M and KARL W C. Feature-enhanced synthetic aperture radar image formation based on nonquadratic regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(4): 623–631. doi: 10.1109/83.913596 汪玲, 朱栋强, 马凯莉, 等. 空间目标卡尔曼滤波稀疏成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(4): 846–852. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170319WANG Ling, ZHU Dongqiang, MA Kaili, et al. Sparse imaging of space targets using Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(4): 846–852. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170319 徐宗本, 吴一戎, 张冰尘, 等. 基于L1/2正则化理论的稀疏雷达成像[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(14): 1306–1319. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00372XU Zongben, WU Yirong, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Sparse radar imaging based on L1/2 regularization theory[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(14): 1306–1319. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00372 HASANKHAN M J, SAMADI S, and ÇETIN M. Sparse representation-based algorithm for joint SAR image formation and autofocus[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2017, 11(4): 589–596. doi: 10.1007/s11760-016-0998-y BI Hui, BI Guoan, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Complex-image-based sparse SAR imaging and its equivalence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5006–5014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2803802 SAMADI S, CETIN M, and MASNADI-SHIRAZI M A. Sparse representation-based synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2011, 5(2): 182–193. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0235 WANG Ling, LOFFELD O, MA Kaili, et al. Sparse ISAR imaging using a greedy kalman filtering approach[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 138: 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.03.002 DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 BARANIUK R and STEEGHS P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2007: 128–133. WANG Lu, ZHAO Lifan, and BI Guoan. Structured sparse representation based ISAR imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2014 15th International Radar Symposium, Gdansk, Poland, 2014: 1–5. YANKELEVSKY Y and ELAD M. Dictionary learning for high dimensional graph signals[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 4669–4673. YANKELEVSKY Y and ELAD M. Structure-aware classification using supervised dictionary learning[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, USA, 2017: 4421–4425. SOĞANLUI A and ÇETIN M. Dictionary learning for sparsity-driven SAR image reconstruction[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Paris, France, 2014: 1693–1697. JIANG Changhui, ZHANG Qiyang, FAN Rui, et al. Super-resolution CT image reconstruction based on dictionary learning and sparse representation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 8799. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27261-z AHARON M, ELAD M, and BRUCKSTEIN A. rmK-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311–4322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199 PATI Y C, REZAIIFAR R, and KRISHNAPRASAD P S. Orthogonal matching pursuit: recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition[C]. Proceedings of the 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 1993: 40–44. WANG Ling and LOFFELD O. ISAR imaging using a null space ℓ1minimizing Kalman filter approach[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Workshop on Compressed Sensing Theory and Its Applications to Radar, Sonar and Remote Sensing, Aachen, Germany, 2016: 232–236. AHARON M and ELAD M. Sparse and redundant modeling of image content using an image-signature-dictionary[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2008, 1(3): 228–247. doi: 10.1137/07070156X ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, YU Yusheng, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 204–208. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562 汪玲, 朱岱寅, 朱兆达. 基于SAR实测数据的舰船成像研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(2): 401–404.WANG Ling, ZHU Daiyin, and ZHU Zhaoda. Study on ship imaging using SAR real data[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(2): 401–404. HU Changyu, WANG Ling, and LOFFELD O. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging exploiting dictionary learning[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 1084–1088. LOFFELD O, ESPETER T, and CONDE M H. From weighted least squares estimation to sparse CS reconstruction[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 3rd International Workshop on Compressed Sensing Theory and Its Applications to Radar, Sonar and Remote Sensing, Pisa, Italy, 2015: 149–153. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
