Person Re-identification Based on Attribute Hierarchy Recognition
-
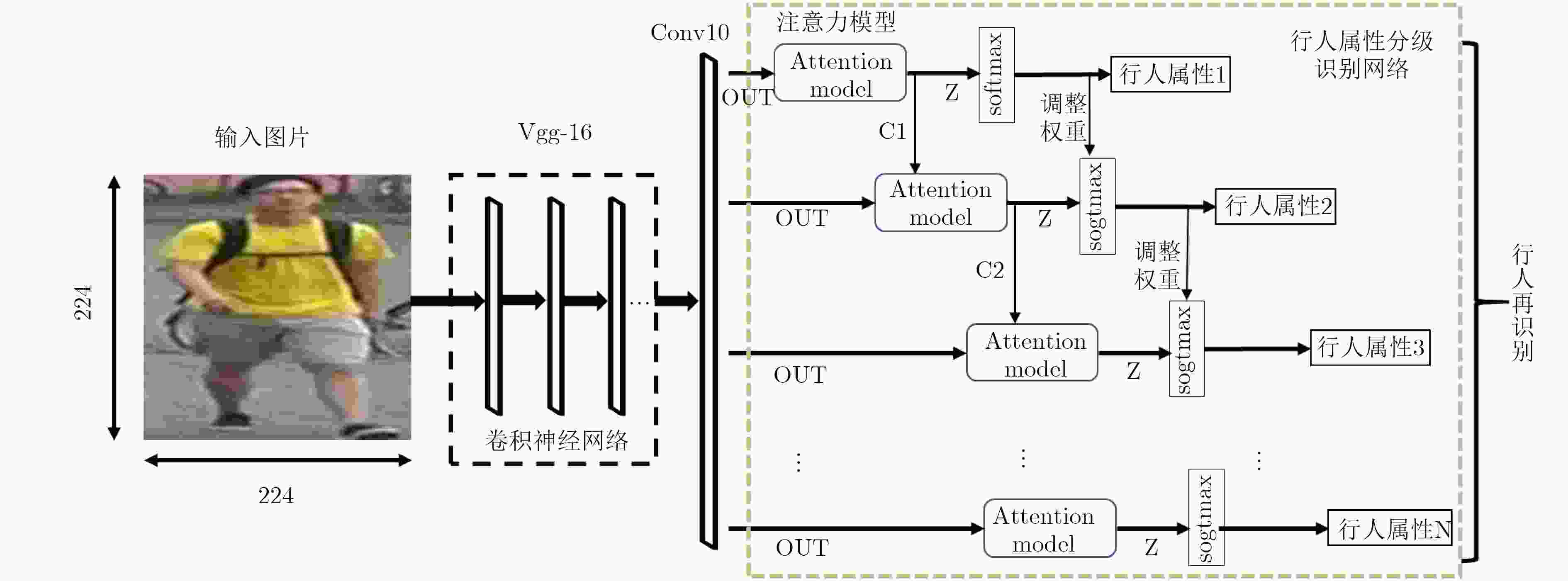
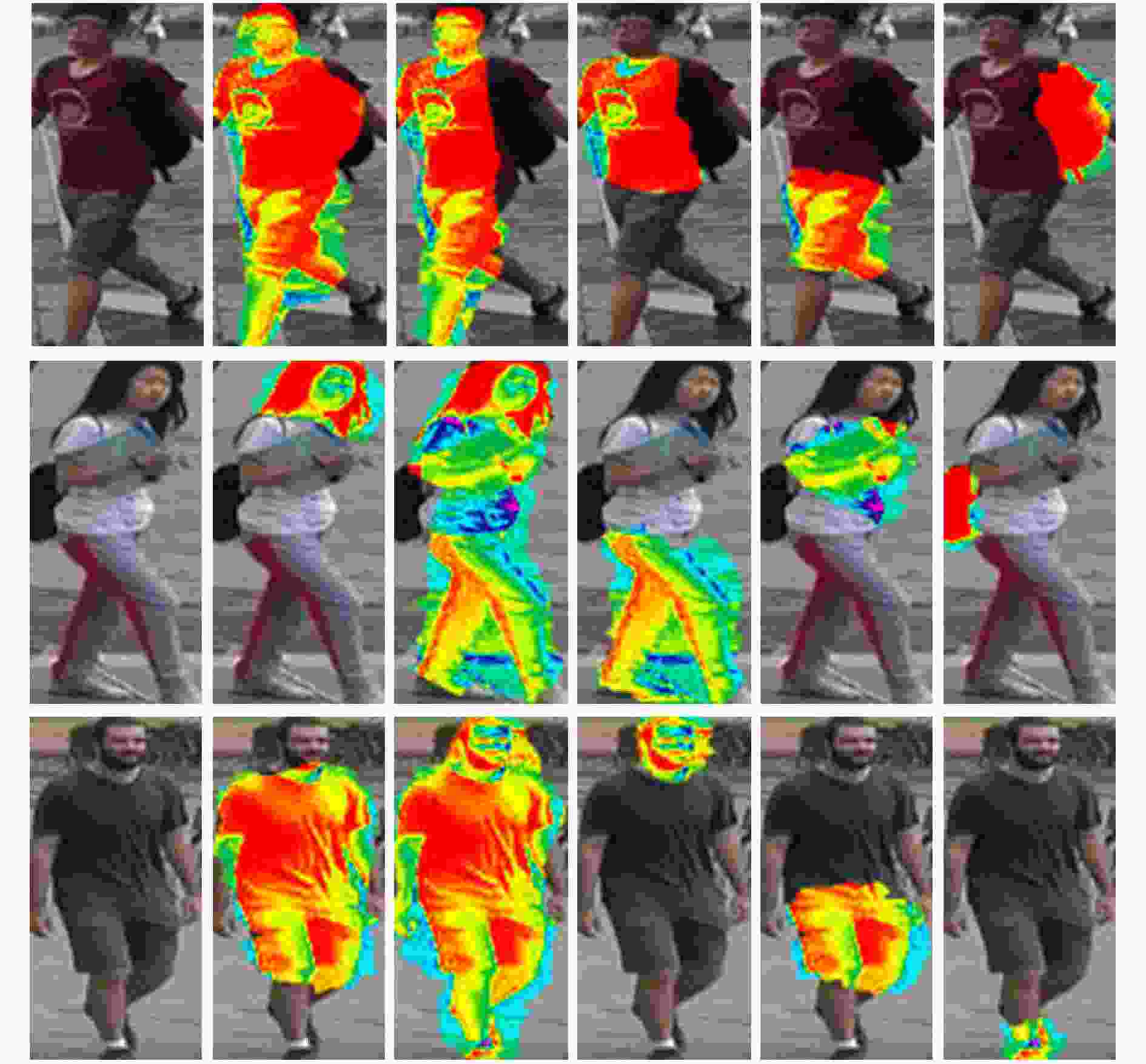
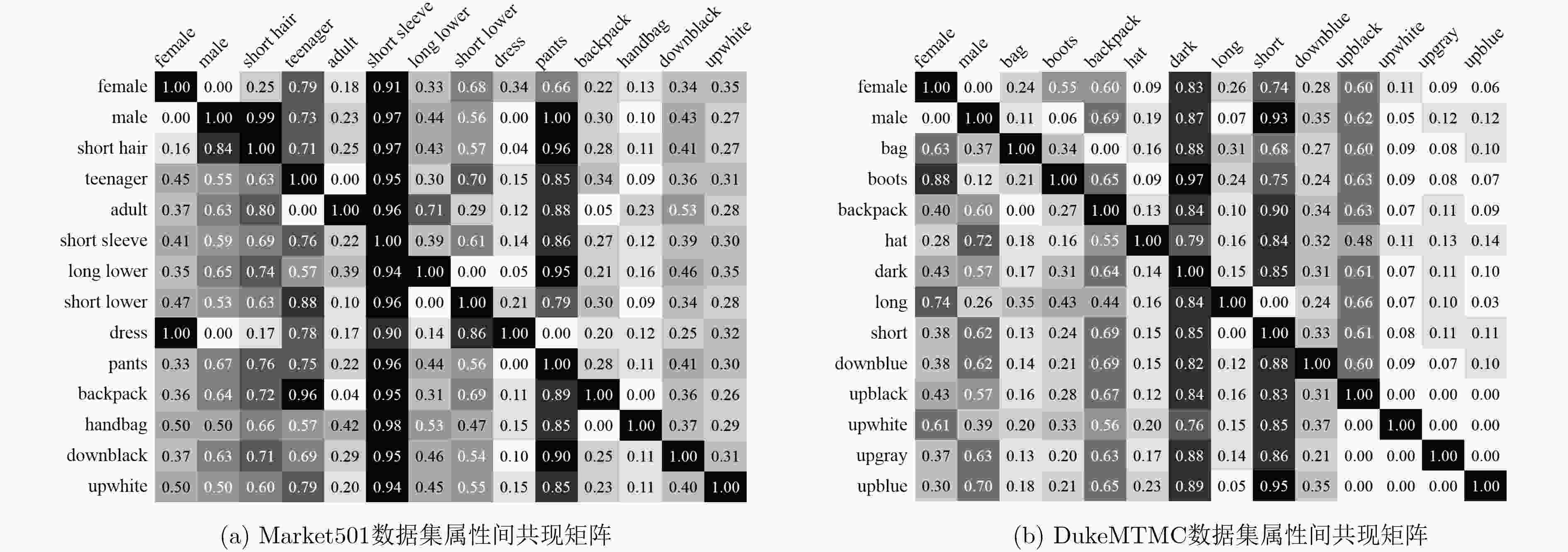
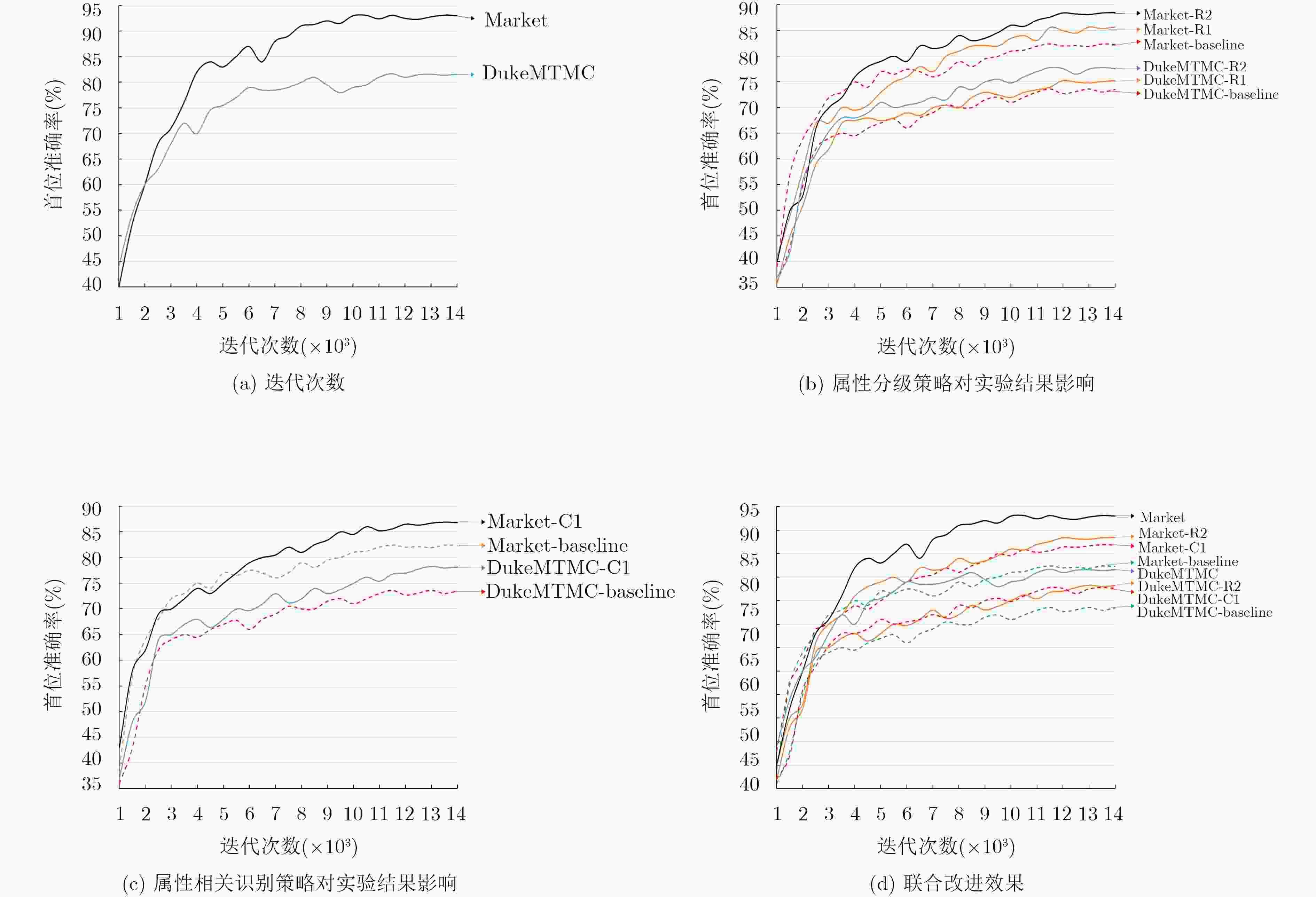
摘要: 为了提高行人再识别算法的识别效果,该文提出一种基于注意力模型的行人属性分级识别神经网络模型,相对于现有算法,该模型有以下3大优点:一是在网络的特征提取部分,设计用于识别行人属性的注意力模型,提取行人属性信息和显著性程度;二是在网络的特征识别部分,针对行人属性的显著性程度和包含的信息量大小,利用注意力模型对属性进行分级识别;三是分析属性之间的相关性,根据上一级的识别结果,调整下一级的识别策略,从而提高小目标属性的识别准确率,进而提高行人再识别的准确率。实验结果表明,该文提出的模型相较于现有方法,有效提高了行人再识别的首位准确率,其中,Market1501数据集上,首位准确率达到了93.1%,在DukeMTMC数据集上,首位准确率达到了81.7%。Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy rate of person re-identification, a pedestrian attribute hierarchy recognition neural network is proposed based on attention model. Compared with the existing algorithms, the model has the following three advantages. Firstly, the attention model is used in this paper to identify the pedestrian attributes, and to extract of pedestrian attribute information and degree of significance. Secondly, the attention model in used in this paper to classify the attributes according to the significance of the pedestrian attributes and the amount of informationcontained. Thirdly, this paper analyzes the correlation between attributes, and adjusts the next level identification strategy according to the recognition results of the upper level. It can improve the recognition accuracy of small target attributes, and the accuracy of pedestrian recognition is improved. The experimental results show that the proposed model can effectively improve the first accuracy rate (rank-1) of person re-identification compared with the existing methods. On the Market1501 dataset, the first accuracy rate is 93.1%, and the first accuracy rate is 81.7% on the DukeMTMC dataset.
-
Key words:
- Person re-identification /
- Attention model /
- Deep learning /
- Saliency /
- Hierarchy
-
表 1 Market1501数据集中的属性类别
属性类(G) 属性 数量(k) Gender male, female 2 Age child, teenager, adult, old 4 Hair length long, short 2 Length of lower-body clothing long, short 2 Type of lower-body clothing pants, dress 2 Wearing hat yes, no 2 Carrying bag yes, no 2 Carrying backpack yes, no 2 Carrying handbag yes, no 2 Color of upper-body clothing black, white, red, purple,yellow, gray, blue, green 8 Color of lower-body clothing black, white, pink, purple,yellow, gray, blue, green, brown 9 表 2 Market1501数据集各属性识别准确率(%)
行人属性 gender age hair L.slv L.low S.cloth B.pack H.bag bag hat C.up C.low mean 基础网络 82.18 85.32 80.12 92.48 71.58 85.67 79.57 81.54 79.66 70.56 91.23 87.81 82.31 本文算法 90.27 88.15 91.54 93.55 87.25 90.48 89.77 87.65 84.67 87.39 92.44 93.48 89.72 表 3 DukeMTMC数据集各属性识别准确率(%)
行人属性 gender hat boots L.up B.pack H.bag bag C.shoes C.up C.low mean 基础网络 82.47 75.48 76.14 73.58 71.58 69.42 78.31 68.54 62.17 51.24 70.89 本文算法 83.59 87.24 84.56 76.33 77.11 75.32 83.78 72.19 74.88 62.18 77.72 表 4 Market1501数据集行人再识别结果(%)
-
FARENZENA M, BAZZANI L, PERINA A, et al. Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2360–2367. 曾明勇, 吴泽民, 田畅, 等. 基于外观统计特征融合的人体目标再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(8): 1844–1851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01389ZENG Mingyong, WU Zemin, TIAN Chang, et al. Fusing appearance statistical features for person re-identification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(8): 1844–1851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01389 陈鸿昶, 陈雷, 李邵梅, 等. 基于显著度融合的自适应分块行人再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(11): 2652–2660. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170162CHEN Hongchang, CHEN Lei, LI Shaomei, et al. Person re-identification of adaptive blocks based on saliency fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(11): 2652–2660. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170162 KÖSTINGER M, HIRZER M, WOHLHART P, et al. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2288–2295. LI Wei, ZHAO Rui, XIAO Tong, et al. DeepReID: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 152–159. LIU Hao, FENG Jiashi, QI Meibin, et al. End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3492–3506. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2700762 MATSUKAWA T and SUZUKI E. Person re-identification using CNN features learned from combination of attributes[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 2428–2433. LI Wei, ZHU Xiatian, and GONG Shaogang. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018, 2285–2294. LIN Yutian, ZHENG Liang, ZHENG Zhedong, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07220, 2017. XU K, BA J, KIROS R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention[C]. 2015 International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA, 2015: 2048–2057. LIAO Shengcai, HU Yang, ZHU Xiangyu, et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2197–2206. CHEN Dapeng, YUAN Zejian, CHEN Badong, et al. Similarity learning with spatial constraints for person re-identification[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1268–1277. ZHANG Li, XIANG Tao, and GONG Shaogang. Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1239–1248. VARIOR R R, HALOI M, and WANG Gang. Gated Siamese convolutional neural network architecture for human re-identification[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 791–808. LI Dangwei, CHEN Xiaotang, ZHANG Zhang, et al. Learning deep context-aware features over body and latent parts for person re-identification[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7398–7407. SU Chi, LI Jianing, ZHANG Shiliang, et al. Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3980–3989. LI Wei, ZHU Xiatian, and GONG Shaogang. Person re-identification by deep joint learning of multi-loss classification[C]. The 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 2194–2200. WANG Hanxiao, GONG Shaogang, and XIANG Tao. Highly efficient regression for scalable person re-identification[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.01341, 2016. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. ZHENG Zhedong, ZHENG Liang, and YANG Yi. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3774–3782. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
