Underdetermined Wideband DOA Estimation Based on Distributed Compressive Sensing
-
摘要: 为解决基于稀疏阵列的宽带欠定信号到达角(DOA)估计问题,该文提出基于分布式压缩感知(DCS)的宽带DOA估计算法。首先,对稀疏阵列宽带信号处理模型进行理论推导与分析,将宽带信号DOA估计建模成DCS问题;其次,利用经典DCS算法实现稀疏阵列上的宽带欠定信号DOA估计;最后,引入网格失配误差,建立包含网格失配参数的DCS模型,并进行迭代求解,实现对DOA和网格失配参数的联合估计。仿真结果表明,该算法能够实现宽带欠定信号DOA估计,较现有成果而言,在保证测向精度的同时,具备分辨率高、运算速度快的优点。Abstract: In order to realize underdetermined wideband Direction Of Arrival(DOA) estimation based on sparse array, an algorithm on account of Distributed Compressive Sensing(DCS) is proposed. Firstly, wideband signal processing model based on sparse array is deduced and the underdetermined wideband DOA estimation is formulated as a DCS problem. Then, the DCS-Simultaneous Orthogonal Matching Pursuit(DCS-SOMP) algorithm is utilized to solve this problem. Finally, the off-grid problem is considered and a joint DCS model containing off-grid parameters is established. Estimations of DOAs and off-grid parameters are achieved through iterative solution. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is effective and have advantages in resolution and computational complexity.
-
表 1 DCS-SOMP算法
输入:虚拟阵列接收数据${{\text{z}}_h}$,过完备字典集${\text{Φ}_h}\left( \psi \right)$,信号个数$K$。 输出:重构信号${{\text{s}}_h}$,支撑基列标集合$\varOmega$。 初始化:迭代计数$i = 1,{\varOmega_0}=\varnothing ,{\hat {\text{s}}_h} = {\text{0}}$,残差初值${{\text{r}}_{h, 0}} = {{\text{z}}_h}$。 步骤 1 支撑基选择:
$ {g_i} = \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{g \in \left\{ {1, 2, \cdots , G} \right\}} \sum\limits_{h = 1}^H {\frac{{\left| {\left\langle {{{\text{r}}_{h, i - 1}}, {{\text{φ}} _{h, g}}} \right\rangle } \right|}}{{{{\left\| {{{\text{φ}} _{h, g}}} \right\|}_2}}}} ,{\varOmega_i}={\varOmega_{i - 1}} \cup \left\{ {{g_i}} \right\}$;步骤 2 残差更新:${\hat{\text{ s}}_h}={{\text{Φ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}^\dagger {{\text{z}}_h},{{\text{r}}_{h, i}} = {{\text{z}}_h} - {{\text{Φ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}{\hat {\text{s}}_h}$; 步骤 3 条件判断:若$i < K$,则$i = i + 1$跳至步骤1,否则跳至步
骤4;步骤 4 结果结算:$\varOmega={\varOmega_i},{{\text{s}}_h}={{\text{Φ}} _\varOmega}^\dagger {{\text{z}}_h}$。 表 2 DCS-JSOMP算法
输入:虚拟阵列接收数据${{\text{z}}_h}$,过完备字典集${\text{Φ}_h}\left( \text{Ψ} \right)$,网格失配字典${\text{Γ}_h}\left( \text{Ψ} \right)$,信号个数$K$。 输出:重构信号${{\text{s}}_h}$,支撑基列标集合$\varOmega$,网格失配误差${\text{Δ}} $。 初始化:迭代计数$i = 1,{\varOmega_0}=\varnothing,{\hat{\text{ s}}_h} = {\text{0}},\hat{\text{β}}_h={\text{0}}$,残差${{\text{r}}_{h, 0}} = {{\text{z}}_h}$。
步骤 1 支撑基选择:${c_g} = \sum\limits_{h = 1}^H {\frac{{\left| {\left\langle {{{\text{r}}_{h, i - 1}}, {{\text{φ }}_{h, g}}} \right\rangle } \right|}}{{{{\left\| {{{\text{φ}} _{h, g}}} \right\|}_2}}}} ,{d_g} = \sum\limits_{h = 1}^H {\frac{{\left| {\left\langle {{{\text{r}}_{h, i - 1}}, {\text{γ}_{h, g}}} \right\rangle } \right|}}{{{{\left\| {{\text{γ}_{h, g}}} \right\|}_2}}}} ,{g_i} = \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{g \in \left\{ {1, 2, \cdots , G} \right\}} \sqrt {{c_g}^2 + {d_g}^2} ,{\varOmega_i}={\varOmega_{i - 1}} \cup \left\{ {{g_i}} \right\}$;步骤 2 残差更新:${\hat{\text{ s}}_h} = {{\text{Φ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}^\dagger \left( {{{\text{z}}_h} - {{\text{Γ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}{\hat{\text{β}}_h}} \right),{\hat{\text{β}}_h} = {{\text{Γ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}^\dagger \left( {{{\text{z}}_h} - {{\text{Φ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}{{\hat {\text{s}}}_h}} \right),{{\text{r}}_{h, i}} = {{\text{z}}_h} - {{\text{Φ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}{\hat{\text{ s}}_h} - {{\text{Γ}} _{{\varOmega_i}}}{\hat{\text{β}}_h}$; 步骤 3 条件判断:若$i < K$,则$i = i + 1$跳至步骤1,否则跳至步骤4;
步骤 4 结果结算:$\varOmega={\varOmega_i},{{\text{s}}_h} = {{\text{Φ}} _\varOmega}^\dagger \left( {{{\text{z}}_h} - {{\text{Γ}} _\varOmega}{\hat{\text{β}}_h}} \right),{\text{β}_h} = {{\text{Γ}} _\varOmega}^\dagger \left( {{{\text{z}}_h} - {{\text{Φ}} _\varOmega}{{\text{s}}_h}} \right),{\text{Δ}} =\frac{1}{H}\sum\limits_{h = 1}^H {\frac{{{{\text{β}} _h}}}{{{{\text{s}}_h}}}} $。表 3 5种算法单次蒙特卡洛实验用时(s)
算法 信噪比变化 频域快拍次数变化 DCS-SOMP 0.1747 0.1943 DCS-JSOMP 0.3439 0.3784 SS-MUSIC 0.5021 0.5207 WNNSBL 3.3751 3.0231 OGSLIM 0.6068 0.6678 -
SELVA J. Efficient wideband DOA estimation through function evaluation techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(12): 3112–3123. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2824256 DAS A and SEJNOWSKI T J. Narrowband and wideband off-grid direction-of-arrival estimation via sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2018, 43(1): 108–118. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2017.2660278 ZHANG Ailian and XU Wen. A new sparse subspace method for wideband DOA estimation[C]. OCEANS, Aberdeen, UK, 2017: 1–7. LIU Jianyan, LU Yilong, ZHANG Yanmei, et al. DOA estimation with enhanced DOFs by exploiting cyclostationarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(6): 1486–1496. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2645542 SHEN Qing, CUI Wei, LIU Wei, et al. Underdetermined wideband DOA estimation of off-grid sources employing the difference co-array concept[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 130: 299–304. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.07.022 PAL P and VAIDYANATHAN P P. Nested arrays: A novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(8): 4167–4181. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2049264 VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Sparse sensing with co-prime samplers and arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(2): 573–586. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2089682 VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Sparse sensing with coprime arrays[C]. Proceedings of the 2010 Conference Record of the 44th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2010: 1405–1409. doi: 10.1109/acssc.2010.5757766. HAN Keyong and NEHORAI A. Wideband direction of arrival estimation using nested arrays[C]. Proceedings of the 20135th IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, St. Martin, France, 2013: 188–191. doi: 10.1109/camsap.2013.6714039. HAN Keyong and NEHORAI A. Wideband Gaussian source processing using a linear nested array[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(11): 1110–1113. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2281514 SHEN Qing, LIU Wei, CUI Wei, et al. Group sparsity based wideband DOA estimation for co-prime arrays[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE China Summit & International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Xi'an, China, 2014: 252–256. doi: 10.1109/chinasip.2014.6889242. SHEN Qing, LIU Wei, CUI Wei, et al. Low-complexity direction-of-arrival estimation based on wideband co-prime arrays[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2015, 23(9): 1445–1456. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2015.2436214 HE Zhenqing, SHI Zhiping, HUANG Lei, et al. Underdetermined DOA estimation for wideband signals using robust sparse covariance fitting[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(4): 435–439. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2358084 HU Nan, SUN Bing, ZHANG Yi, et al. Underdetermined DOA estimation method for wideband signals using joint nonnegative sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(5): 535–539. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2673850 HU Nan, SUN Bing, WANG Jiajun, et al. Source localization for sparse array using nonnegative sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 127: 37–43. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.02.025 冯明月, 何明浩, 徐璟, 等. 低信噪比条件下宽带欠定信号高精度DOA估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1340–1347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160921FENG Mingyue, HE Minghao, XU Jing, et al. High accuracy DOA estimation under low SNR condition for wideband underdetermined signals[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1340–1347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160921 DUARTE M F, SARVOTHAM S, BARON D, et al. Distributed compressed sensing of jointly sparse signals[C]. Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 39th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2005: 1537–1541. TROPP J A, GILBERT A C, and STRAUSS M J. Simultaneous sparse approximation via greedy pursuit[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Philadelphia, USA, 2005: 721–724. doi: 10.1109/icassp.2005.1416405. TAN Zhao and NEHORAI A. Sparse direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays with off-grid targets[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(1): 26–29. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2289740 -






 下载:
下载:
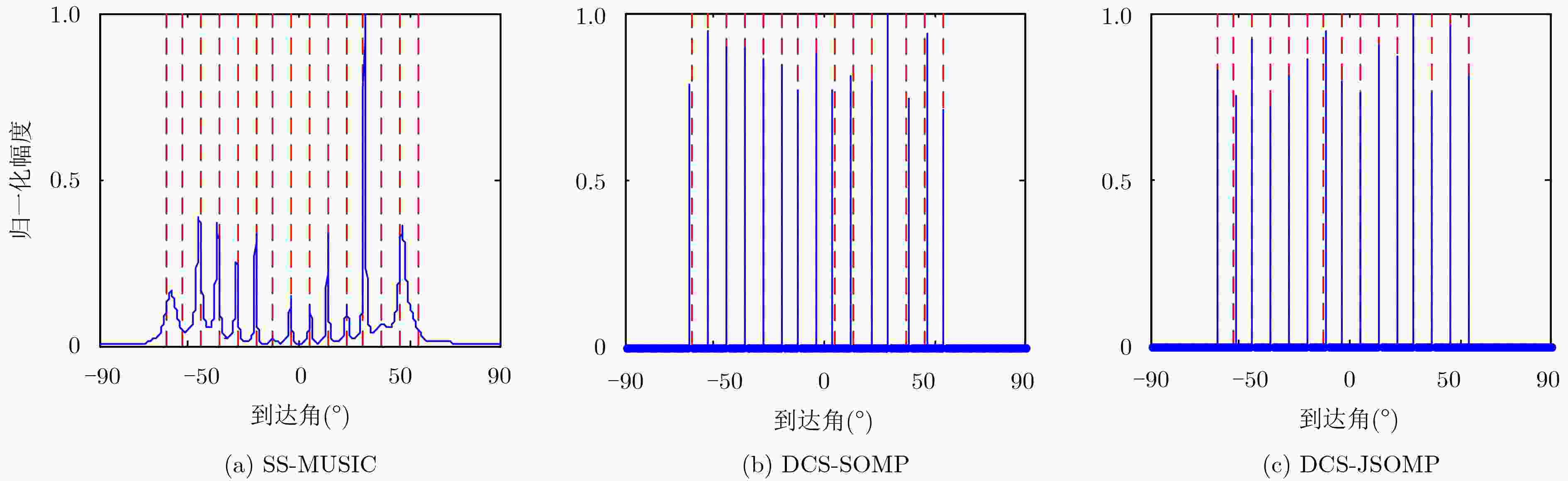
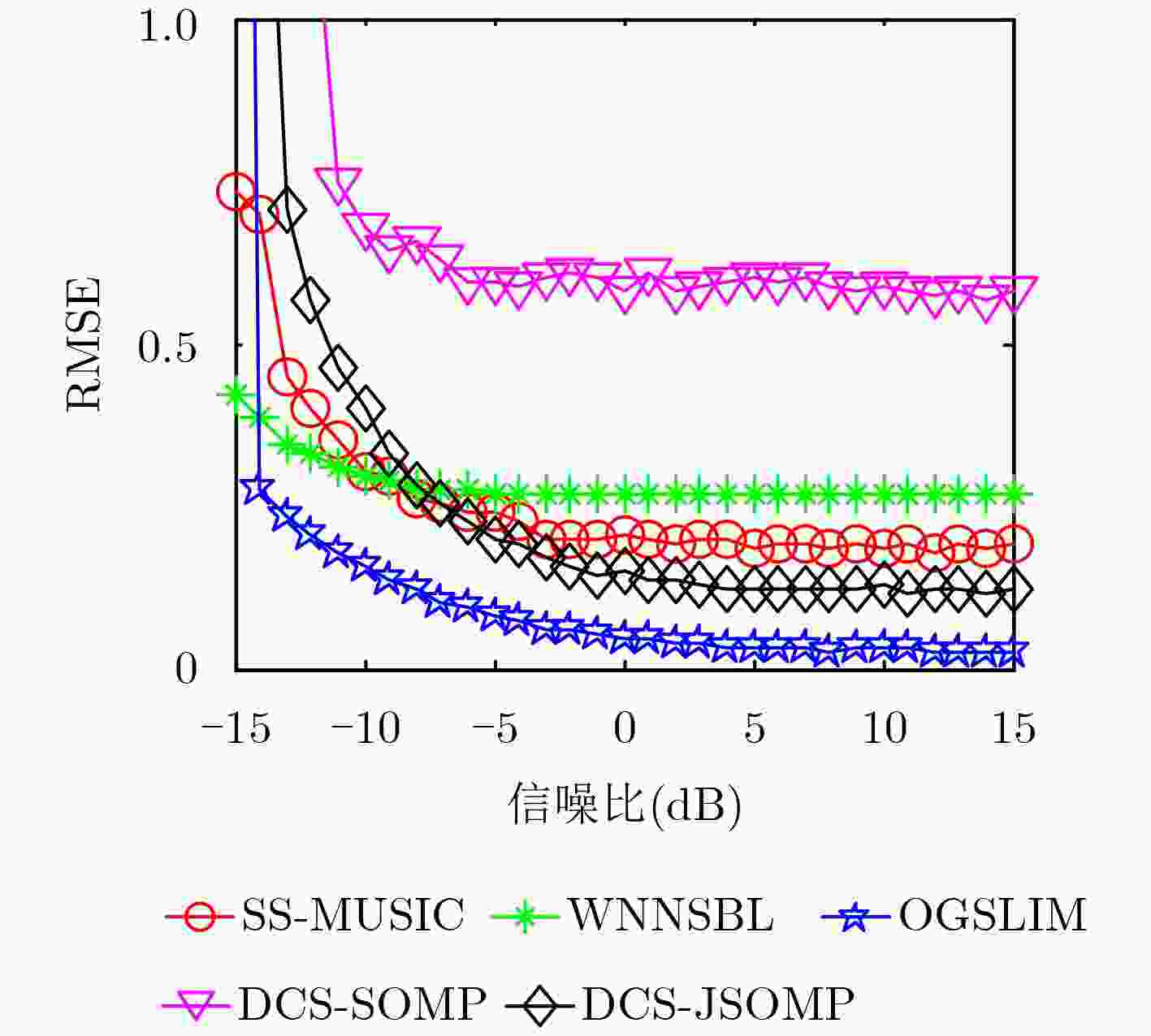
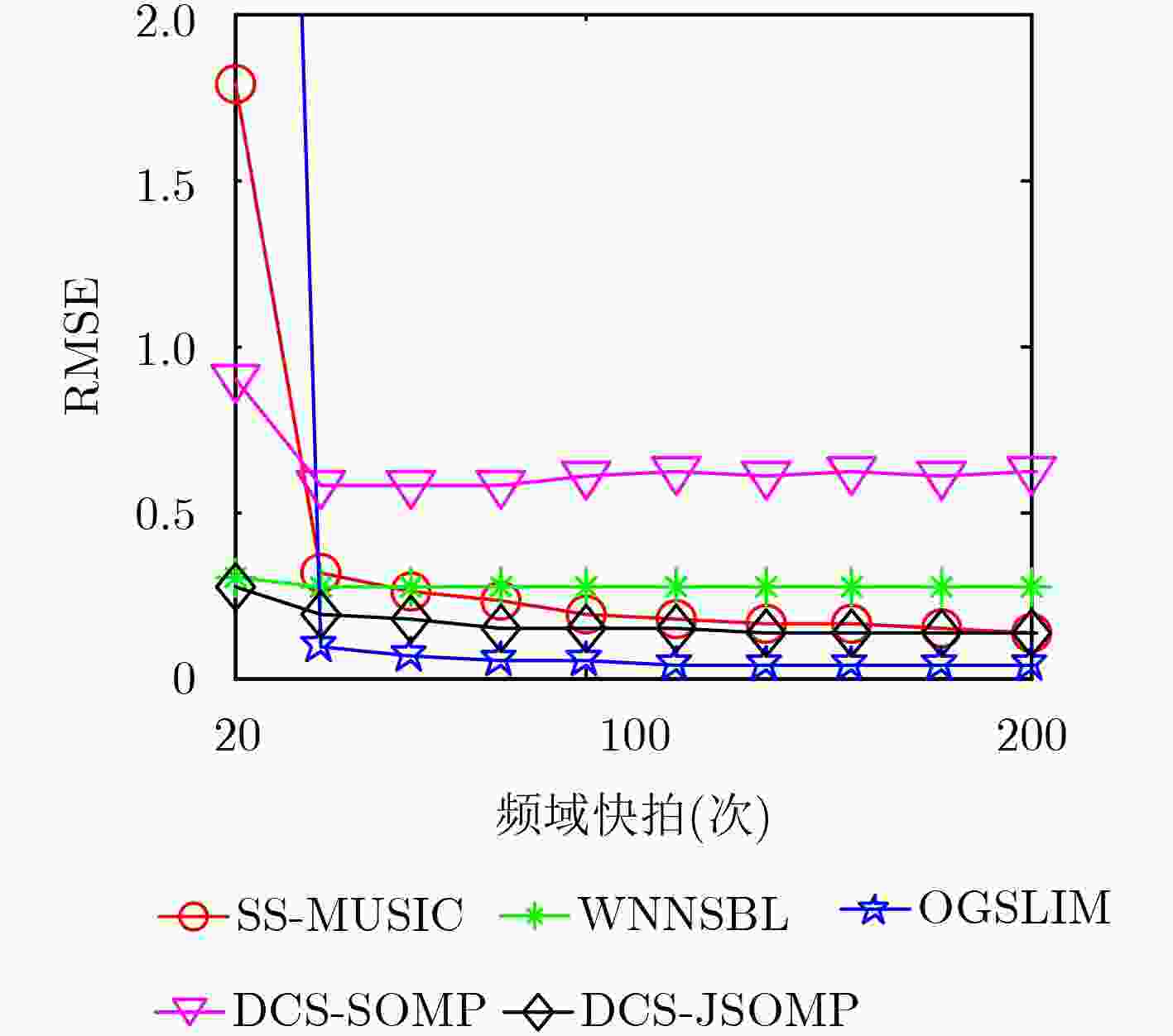
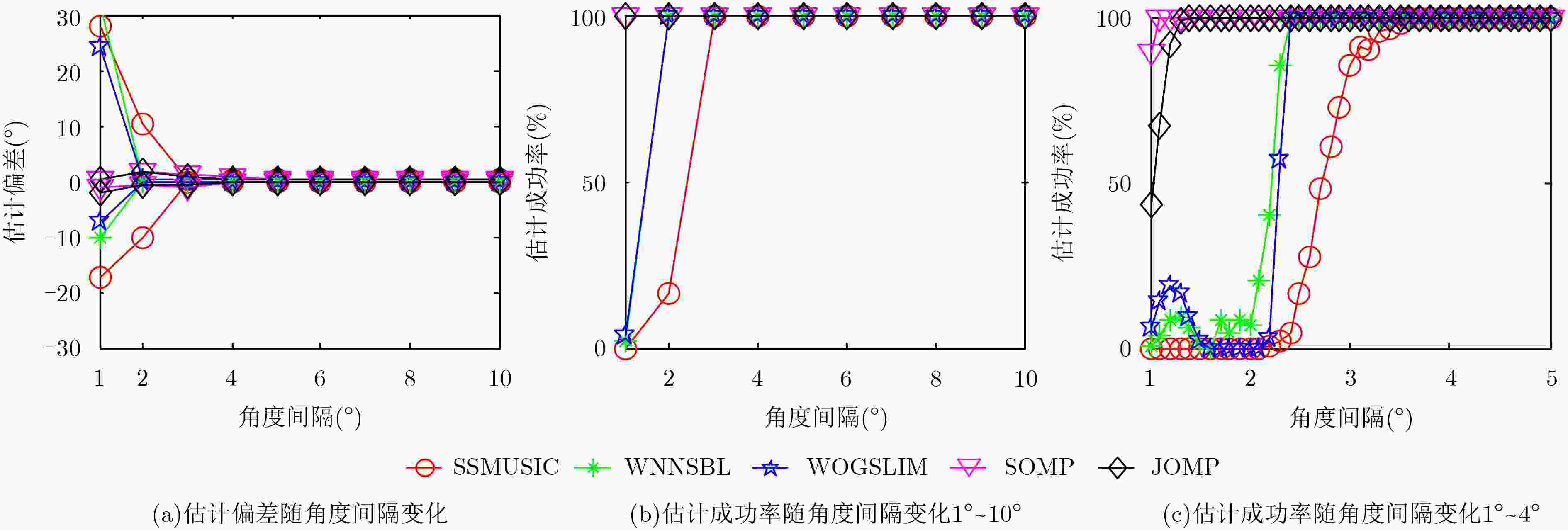


 下载:
下载:
