Semantic Summarization of Reconstructed Abstract Meaning Representation Graph Structure Based on Integer Linear Pragramming
-
摘要: 针对利用抽象语义(AMR)图来预测摘要子图存在的语义结构不完整问题,该文提出一种基于整数线性规划(ILP)重构AMR图结构的语义摘要算法。首先将数据预处理生成一个AMR总图;然后基于统计特征从AMR总图中抽取出摘要子图重要节点信息;最后利用ILP的方法来对摘要子图中节点关系进行重构,利用完整的摘要子图恢复生成语义摘要。实验结果表明,相比其他语义摘要方法,所提方法的ROUGE值和Smatch值都有显著提高,最多分别提高了9%和14%,该方法有利于提高语义摘要的质量。Abstract: In order to solve the incomplete semantic structure problem that occurs in the process of using the Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR) graph to predict the summary subgraph, a semantic summarization algorithm is proposed based on Integer Linear Programming (ILP) reconstructed AMR graph structure. Firstly, the text data are preprocessed to generate an AMR total graph. Then the important node information of the summary subgraph is extracted from the AMR total graph based on the statistical features. Finally, the ILP method is applied to reconstructing the node relationships in the summary subgraph, which is further utilized to generate a semantic summarization. The experimental results show that compared with other semantic summarization methods, the ROUGE index and Smatch index of the proposed algorithm are significantly improved, up to 9% and 14% respectively. This method improves significantly the quality of semantic summarization.
-
表 1 摘要子图节点和边预测正确率(%)
P R F1 节点 71.4 82.5 76.5 边 45.6 60.1 51.9 表 2 不同语义摘要算法的性能对比
算法 ROUGE-1 ROUGE-2 ROUGE-W Smatch 外部语义资源 20.4 5.6 14.3 17.8 语义聚类 21.2 6.0 15.2 19.1 潜在语义分析 22.8 6.8 14.9 20.5 TextRank算法 25.7 8.1 16.8 24.6 PAS语义图 26.5 9.6 18.6 28.9 本文方法 29.3 10.4 19.6 32.1 表 3 使用ILP和未使用ILP摘要质量对比
ROUGE-1 ROUGE-2 ROUGE-W Smatch 未使用ILP 29.1 9.8 18.7 29.7 使用ILP 29.3 10.4 19.6 32.1 结果提升 0.2 0.6 0.9 2.4 表 4 与深度学习算法的性能对比
方法 ROUGE-1 ROUGE-2 ROUGE-W Smatch 本文方法 29.3 10.4 19.6 32.1 深度学习 33.4 13.6 24.8 26.7 -
LYNN H M, CHOI C, and KIM P. An improved method of automatic text summarization for web contents using lexical chain with semantic-related terms[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(12): 4013–4023. doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2612-9 SHETTY K and KALLIMANI J S. Automatic extractive text summarization using K-means clustering[C]. International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, 2017: 1–9. YU Shanshan, SU Jindian, LI Pengfei, et al. Towards high performance text mining: A TextRank-based method for automatic text summarization[J]. International Journal of Grid and High Performance Computing (IJGHPC) , 2016, 8(2): 58–75. doi: 10.4018/IJGHPC.2016040104 NGUYEN-HOANG T A, NGUYEN K, and TRAN Q V. TSGVi: A graph-based summarization system for Vietnamese documents[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2012, 3(4): 305–313. doi: 10.1007/s12652-012-0143-x KHAN A, SALIM N, FARMAN H, et al. Abstractive text summarization based on improved semantic graph approach[J]. International Journal of Parallel Programming, 2018: 1–25. doi: 10.1007/s10766-018-0560-3 BANARESU L, BONIAL C, CAI S, et al. Abstract meaning representation for sembanking[C]. Proceedings of the 7th Linguistic Annotation Workshop and Interoperability with Discourse, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2013: 178–186. LIU Fei, FLANIGAN J, THOMSON S, et al. Toward abstractive summarization using semantic representations[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Denver, USA, 2015: 1077–1086. SONG Linfeng, PENG Xiaochang, ZHANG Yue, et al. AMR-to-text generation with synchronous node replacement grammar[C]. Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 7–13. KONSTAS I, IYER S, YATSKAR M, et al. Neural AMR: Sequence-to-sequence models for parsing and generation[C]. Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 146–157. 明拓思宇, 陈鸿昶, 黄瑞阳, 等. 一种基于加权AMR图的语义子图预测摘要算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2018, 44(10): 292–297. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0050770MING Tuosiyu, CHEN Hongchang, HUANG Ruiyang, et al. A semantic subgraph predictive summary algorithm based on improved AMR graph[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 44(10): 292–297. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0050770 COLLINS M. Discriminative training methods for hidden markov models: Theory and experiments with perceptron algorithms[C]. Proceedings of the ACL-02 conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Philadelphia, USA, 2002, 10: 1–8. HERMANN K M, KOČISKÝ T, GREFENSTETTE E, et al. Teaching machines to read and comprehend[C]. Proceeding NIPS’15 Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015, 1: 1693–1701. LIN Chinyew. ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries[C]. Text Summarization Branches Out: Proceedings of the ACL-04 Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 2004, 10: 74–81. CAI Shu and KNIGHT K. Smatch: An evaluation metric for semantic feature structures[C]. Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2013, 2: 748–752. SEE A, LIU P J, and MANNING C D. Get to the point: Summarization with pointer-generator networks[C]. Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, 2017, 1: 1073–1083. TAN Jiwei, WAN Xiaojun, and XIAO Jianguo. Abstractive document summarization with a graph-based attentional neural model[C]. Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, 2017, 1: 1171–1181. -






 下载:
下载:
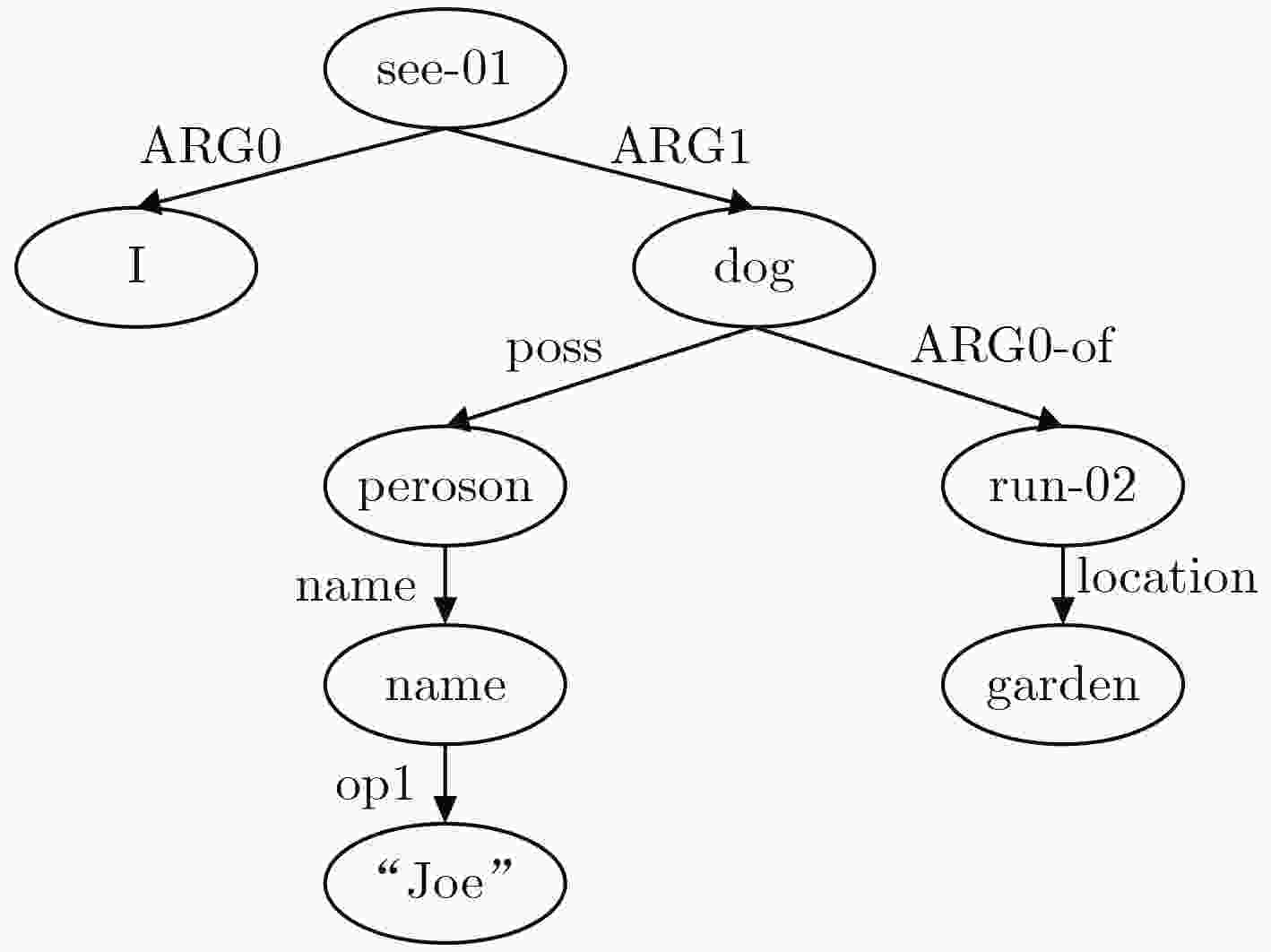
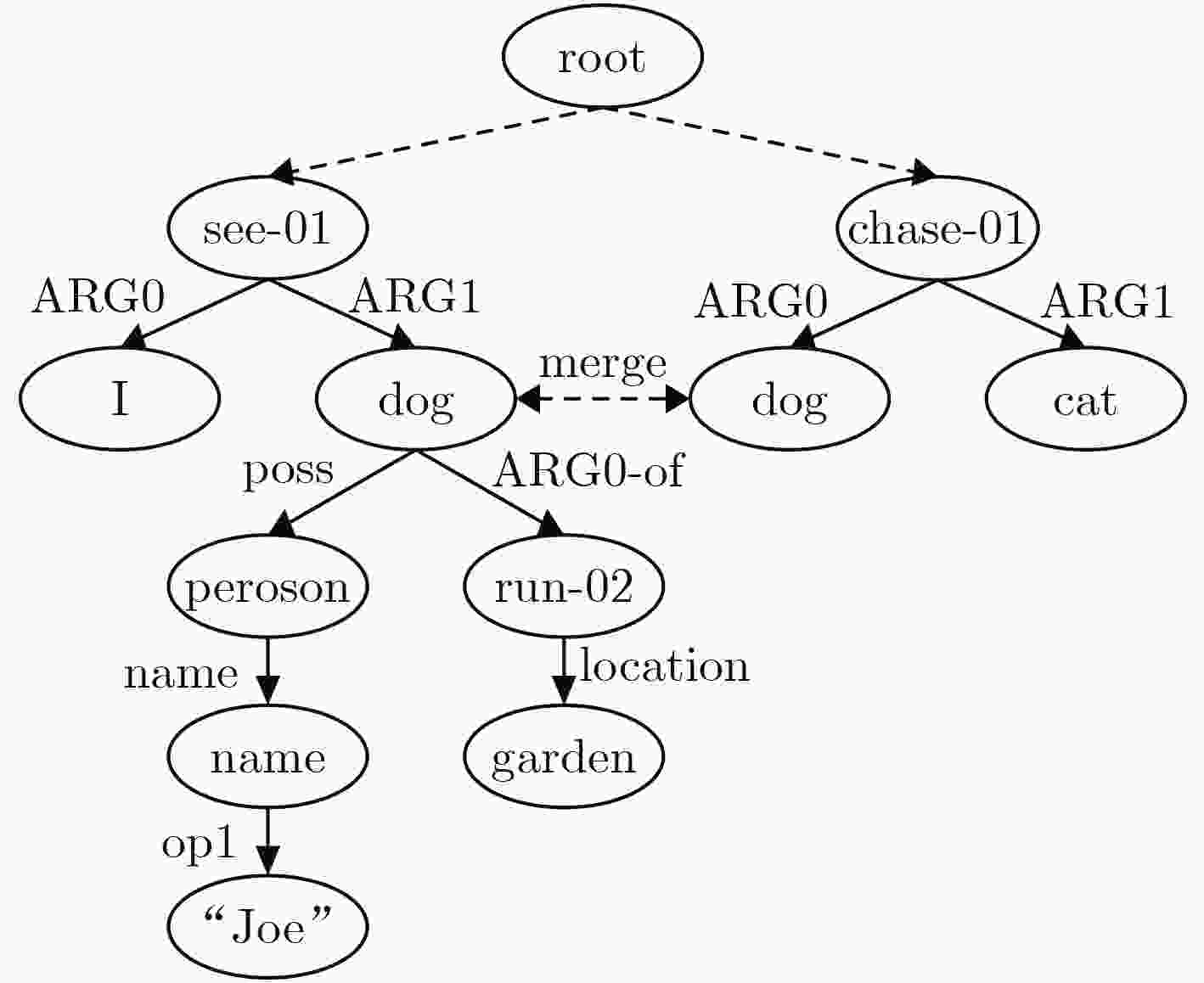
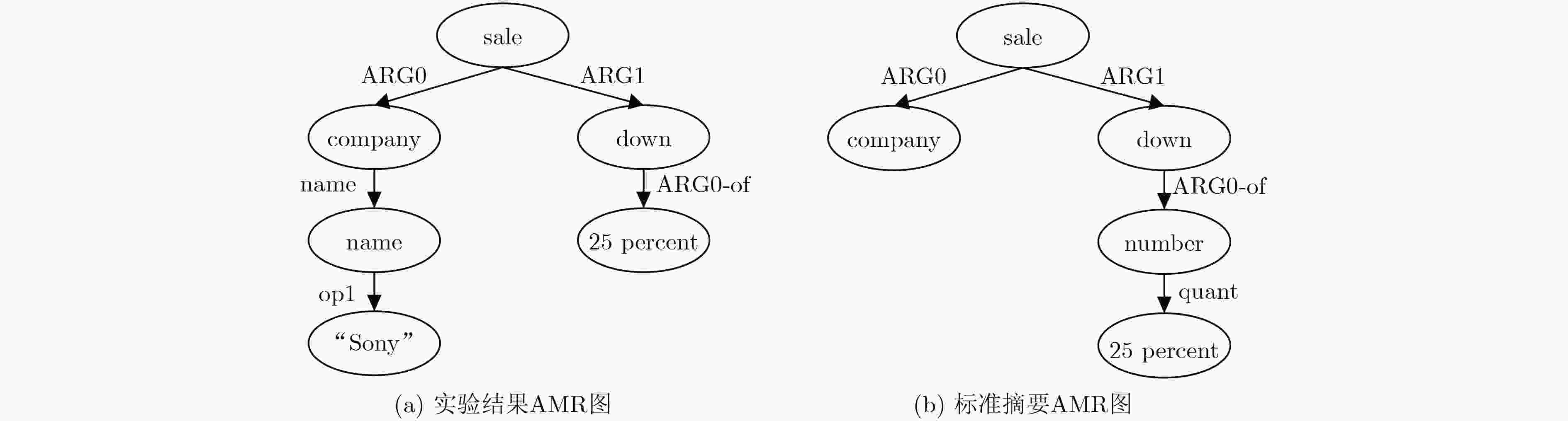
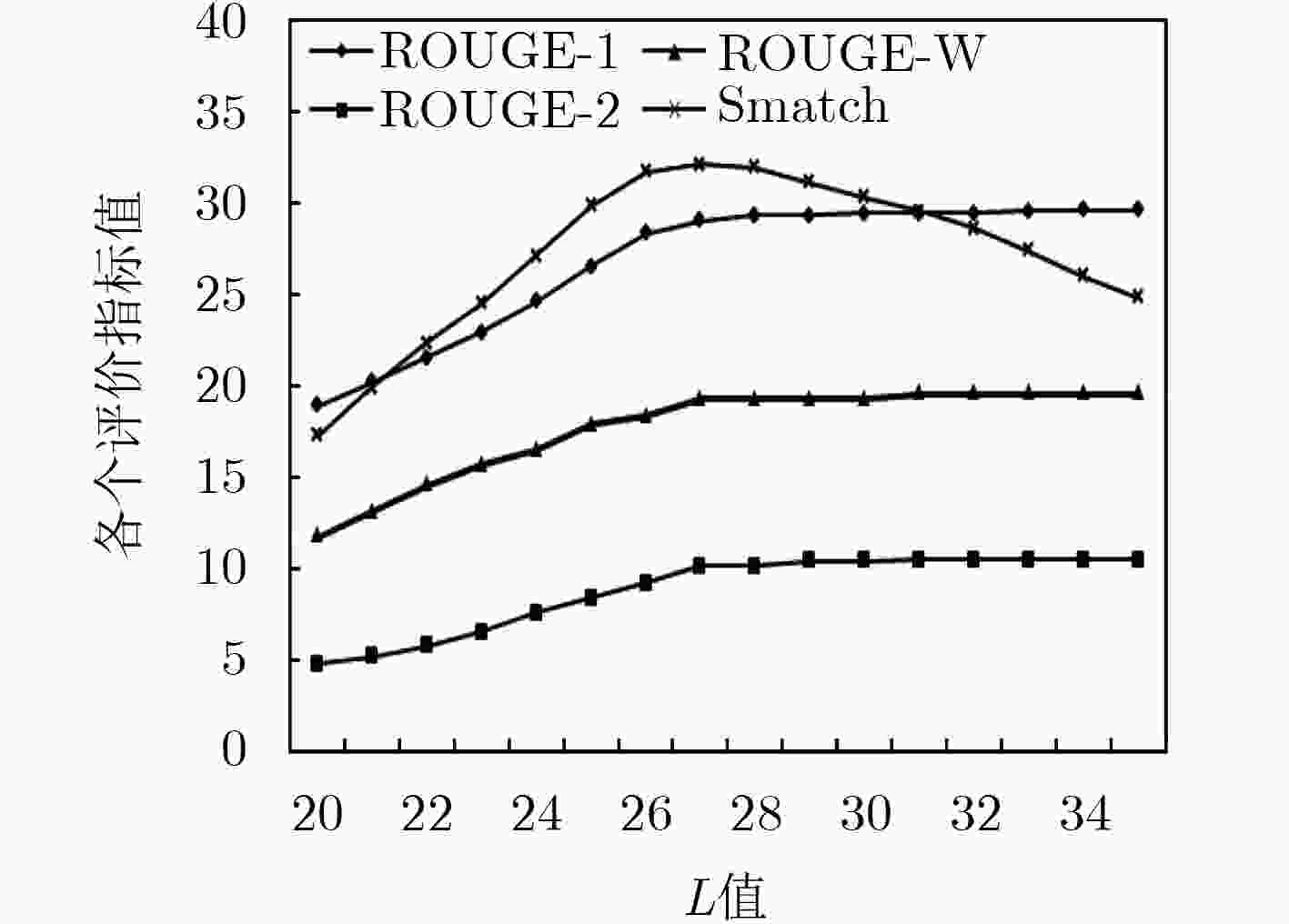


 下载:
下载:
