Velocity Estimation of Moving Targets Based on Least Square Fitting of High-resolution SAR Echo Sequences
-
摘要:
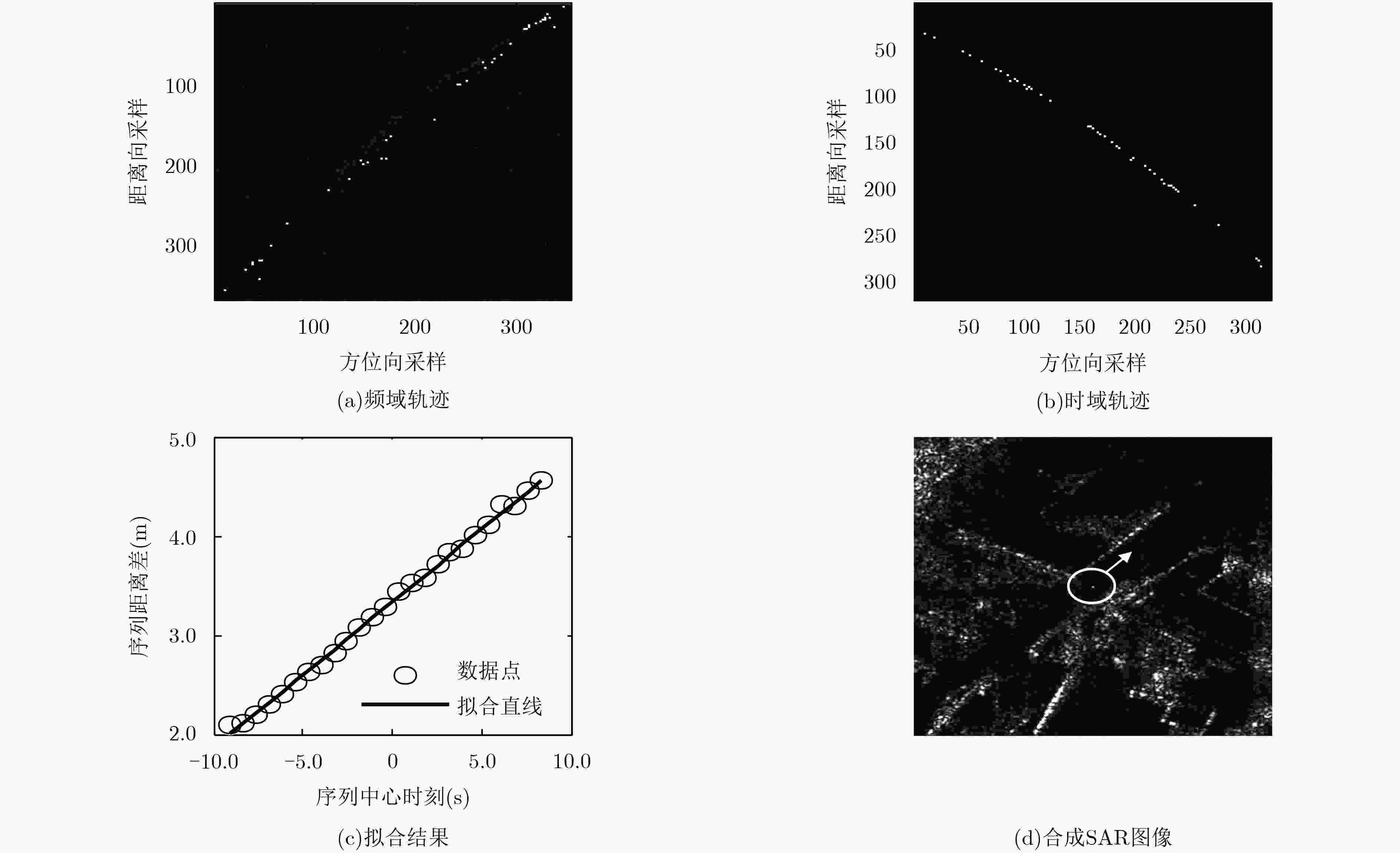
运动目标速度估计是机载单天线高分辨率合成孔径雷达(SAR)实现运动目标成像和定位的关键环节。针对现有方法运算量大、易受距离徙动干扰等缺点,该文提出一种基于回波序列最小二乘拟合的速度估计方法。利用该方法,首先通过包络相关提取相邻回波序列的距离变化量,然后对其做最小二乘线性拟合,目标的距离向速度和方位向速度可由拟合系数计算得到。与传统方法相比,该方法不仅计算量小,而且无须先做距离徙动校正(RCMC)。该文给出了新方法的数学模型和参数选取原则,分析了该方法的估计精度、计算量和适用条件,并通过仿真和实际数据处理验证了该方法的有效性。
Abstract:Velocity estimation of moving targets is a key part of ground moving target imaging and positioning in airborne single-antenna high-resolution SAR system. In order to solute the defects of traditional algorithms, such as high computation brought by searching and interpolation and low reliability caused by range cell migration, a novel method based on least square fitting of echo sequence is proposed. Range changes between adjacent echo sequences are extracted using envelope correlation, and coefficients of range change equation are obtained by least square linear fitting, from which radial velocity and along-track velocity can be derived. Compared with the traditional algorithms, the new method has less computation and can work without RCMC. The mathematical model is presented and the principle of parameter selection is provided, and accuracy, computation and applicable conditions of the algorithm are analyzed. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is validated by simulation and real data.
-
表 1 雷达仿真参数
参数名称 参数值 距离向点数 2048 方位向点数 32768 中心频率(GHz) 15.6 距离向采样率(GHz) 1 信号带宽(MHz) 700 信号脉宽(μs) 2 飞机地速(m/s) 80 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1440 中心斜距(km) 15 目标1距离向速度(m/s) 3 目标1方位向速度(m/s) –20 目标2距离向速度(m/s) –10 目标2方位向速度(m/s) –10 表 2 匀速运动目标距离向速度估计结果
目标编号 Hough变换速度估计结果 (m/s) Hough变换估计相对误差(%) 本文算法速度估计结果(m/s) 本文算法估计相对误差(%) 目标1 3.34 11.50 3.06 2.25 目标2 –10.17 1.75 –9.92 0.80 表 3 匀速运动目标方位向速度估计结果
目标编号 MD速度估计结果(m/s) MD估计相对误差(%) 本文算法速度估计结果(m/s) 本文算法估计相对误差(%) 目标1 –20.50 2.54 –20.71 3.58 目标2 –9.98 0.16 –10.06 0.60 表 4 算法运算时间(s)
目标编号 Hough变换执行时间 MD执行时间 本文算法执行时间 目标1 2.96 32.26 0.50 目标2 3.44 24.78 0.34 表 5 加速运动目标距离向速度估计结果
目标编号 Hough变换速度估计结果 (m/s) Hough变换估计相对误差(%) 本文算法速度估计结果(m/s) 本文算法估计相对误差(%) 目标3 –13.50 35.00 –9.93 0.70 表 7 加速运动目标方位调频率估计结果
目标编号 MD速度估计结果(Hz/s) MD估计相对误差(%) 本文算法速度估计结果(Hz/s) 本文算法估计相对误差(%) 目标3 444.67 313.3 108.08 0.46 表 6 加速运动目标方位向速度估计结果
目标编号 MD 速度估计结果(m/s) MD估计相对误差(%) 本文算法速度估计结果(m/s) 本文算法估计相对误差(%) 目标3 –173.24 1632.40 –45.49 354.90 表 8 清除地杂波频谱后的速度估计结果
波束角(°) 距离向速度估计结果(m/s) 距离向速度估计相对误差(%) 方位向速度估计结果(m/s) 方位向速度估计相对误差(%) 1 2.93 2.33 –21.83 9.15 3 3.27 9.00 –23.90 19.50 5 4.01 33.67 –24.93 24.65 表 9 不同信噪比下的速度估计结果
信噪比(dB) 距离向速度估计结果(m/s) 距离向速度估计相对误差(%) 方位向速度估计结果(m/s) 方位向速度估计相对误差(%) 0 –9.92 0.80 –10.06 0.60 –20 –9.93 0.70 –9.68 3.20 –30 –9.74 2.60 –14.30 43.00 表 10 实测数据参数
参数名称 参数值 距离向点数 733 方位向点数 32768 中心频率(GHz) 15.6 距离向采样率(GHz) 1 信号带宽(MHz) 700 信号脉宽(μs) 60 飞机地速(m/s) 78 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 1400 中心斜距(km) 33 -
RANEY R K. Synthetic aperture imaging radar and moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1971, AES-7(3): 499–505. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1971.310292 LI Yake, WANG Yanfei, and LIU Chang. Detect and autofocus the moving target by its range walk in time domain[C]. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 2011: 1-5. doi: 10.1109/WCSP.2011.6096755. 王智睿, 张旭东, 许稼. 基于Radon变换的SAR地面运动目标径向速度估计[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 55(8): 860–865. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2015.08.008WANG Zhirui, ZHANG Xudong, and XU Jia. Radial velocity estimation based on Radon transforms for SAR images of moving ground targets[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2015, 55(8): 860–865. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2015.08.008 SAMCZYNSKI P and KULPA K S. Coherent MapDrift technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3): 1505–1517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2032241 李亚超, 周峰, 邢孟道, 等. 一种直升机的舰船Dechirp实测数据SAR成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(8): 1794–1798. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.01535LI Yachao, ZHOU Feng, XING Mengdao, et al. An effective method for ship dechirp data imaging in helicopter SAR system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(8): 1794–1798. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.01535 HUANG Penghui, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. A fast SAR imaging method for ground moving target using a second-order WVD transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 1940–1956. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2490582 ZHOU F, WU R, XING M, et al. Approach for single channel SAR ground moving target imaging and motion parameter estimation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2007, 1(1): 59–66. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20060040 YANG Jiefang, ZHANG Yunhua, and KANG Xueyan. A Doppler ambiguity tolerated algorithm for airborne SAR ground moving target imaging and motion parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(12): 2398–2402. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2478799 KIRSCHT M. Detection and velocity estimation of moving objects in a sequence of single-look SAR images[C]. Proceedings of 1996 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Lincoln, USA, 1996: 333–335. 盛蔚, 毛士艺. 一种合成孔径雷达对地面运动目标成像和精确定位的算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2004, 26(4): 598–606.SHENG Wei and MAO Shiyi. An effective method for ground moving target imaging and location in SAR system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2004, 26(4): 598–606. WANG Zhirui, XIA Xianggen, XU Jia, et al. Ground moving target imaging based on 2-D velocity search in high resolution SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 68–72. GU Dandan, LIANG Zichang, WU Yajun, et al. Efficient motion compensation of moving targets in SAR imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2017 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium, Suzhou, China, 2017: 1–2. SHI Hongyin, YANG Xiaoyan, ZHOU Qiuxiao, et al. SAR slow moving target imaging based on over-sampling smooth algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(4): 876–882. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.06.005 SU Jia, TAO Haihong, WANG Ling, et al. Coherently integrated cubic function based Doppler parameters estimation for moving-target imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2017 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium, Suzhou, China, 2017: 1–2. LI Dong, ZHAN Muyang, SU Jia, et al. Performances analysis of coherently integrated CPF for LFM signal under low SNR and its application to ground moving target imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6402–6419. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2727508 WANG Hanyun and JIANG Yicheng. Real-time parameter estimation for SAR moving target based on WVD slice and FrFT[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(1): 47–49. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.1740 LI Zhongyu, WU Junjie, LIU Zhutian, et al. An optimal 2-D spectrum matching method for SAR ground moving target imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5961–5974. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2829166 DELISLE G Y and WU Haiqing. Moving target imaging and trajectory computation using ISAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 887–899. doi: 10.1109/7.303757 STRUTZ T. Data Fitting and Uncertainty: A Practical Introduction to Weighted Least Squares and Beyond[M]. Wiesbaden, Vieweg + Teubner, 2011: 89–91. 王琦, 王岩飞. 利用短时FFT的距离-多普勒域SAR运动目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2006, 28(4): 628–631.WANG Qi and WANG Yanfei. Moving target detection with short time FFT for SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2006, 28(4): 628–631. -





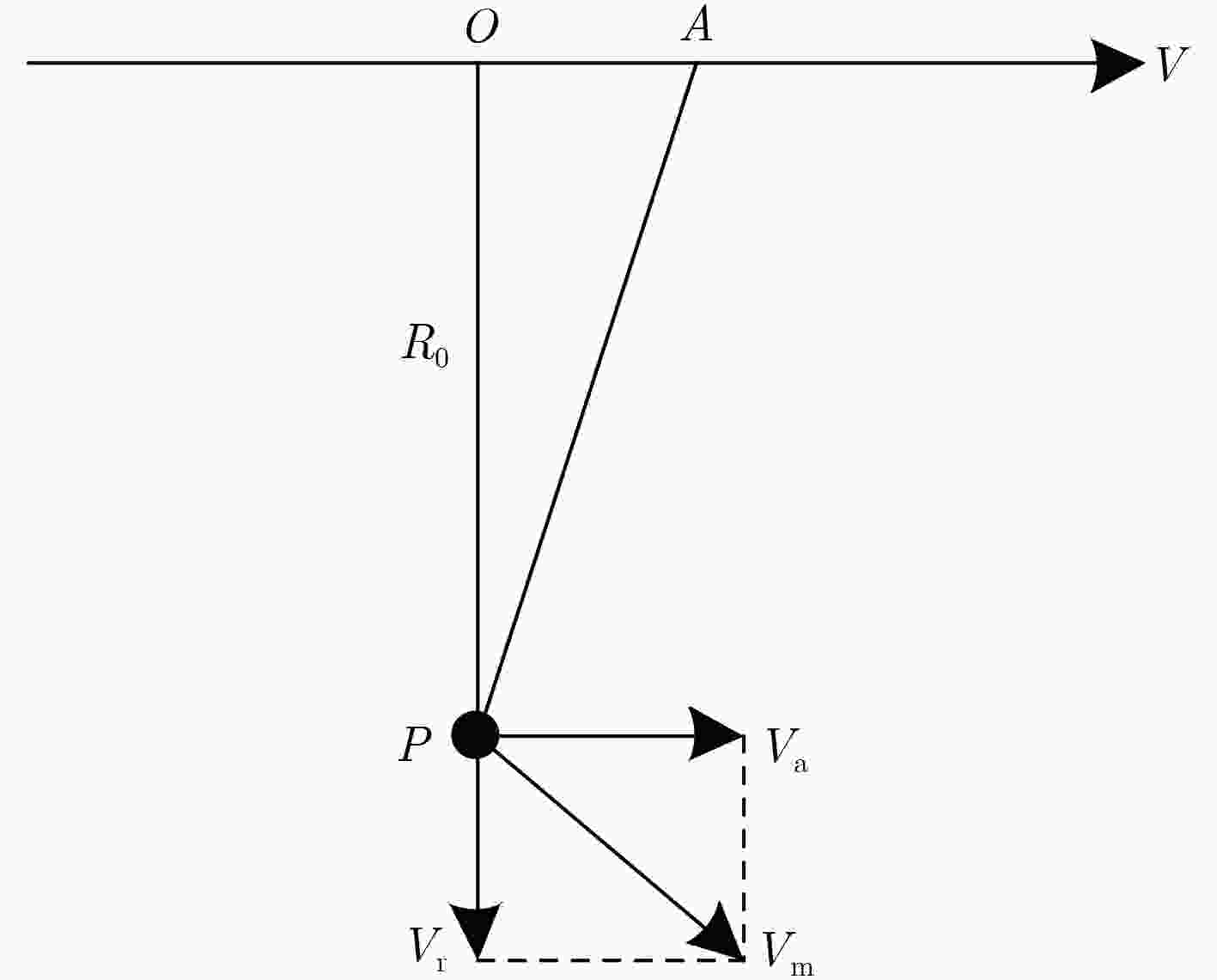
 下载:
下载:
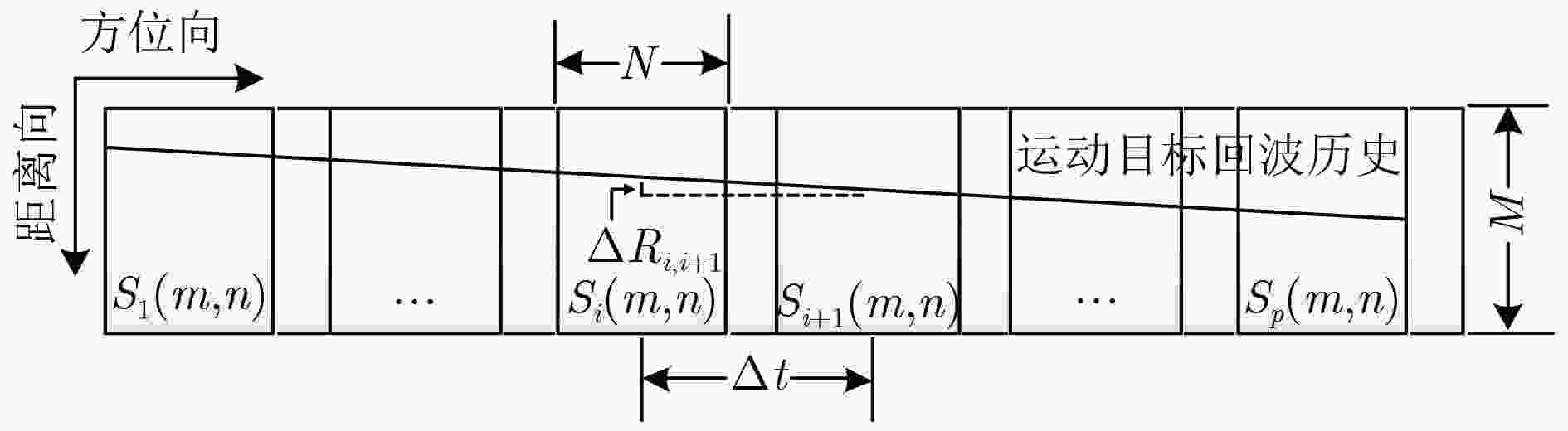
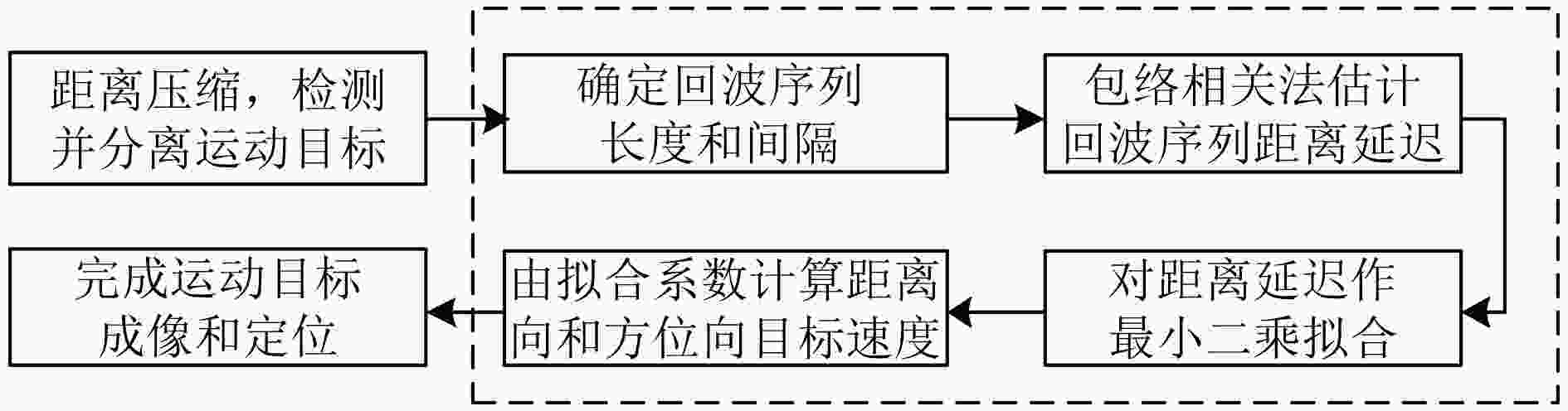
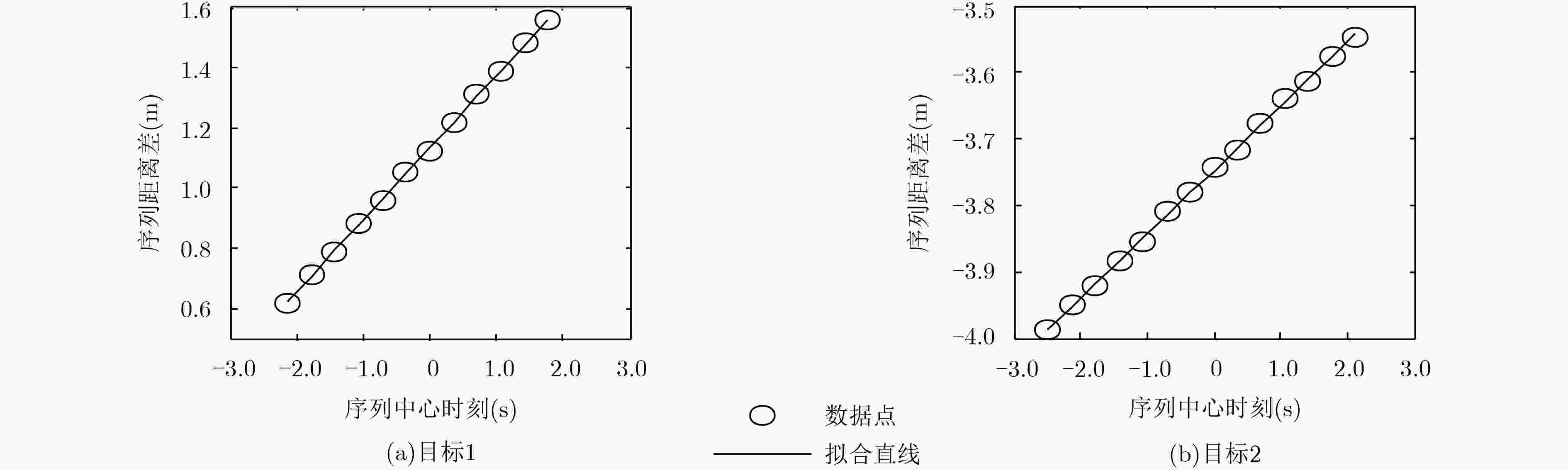


 下载:
下载:
