Evil Waveform Evaluating Method for New GNSS Signals
-
摘要:
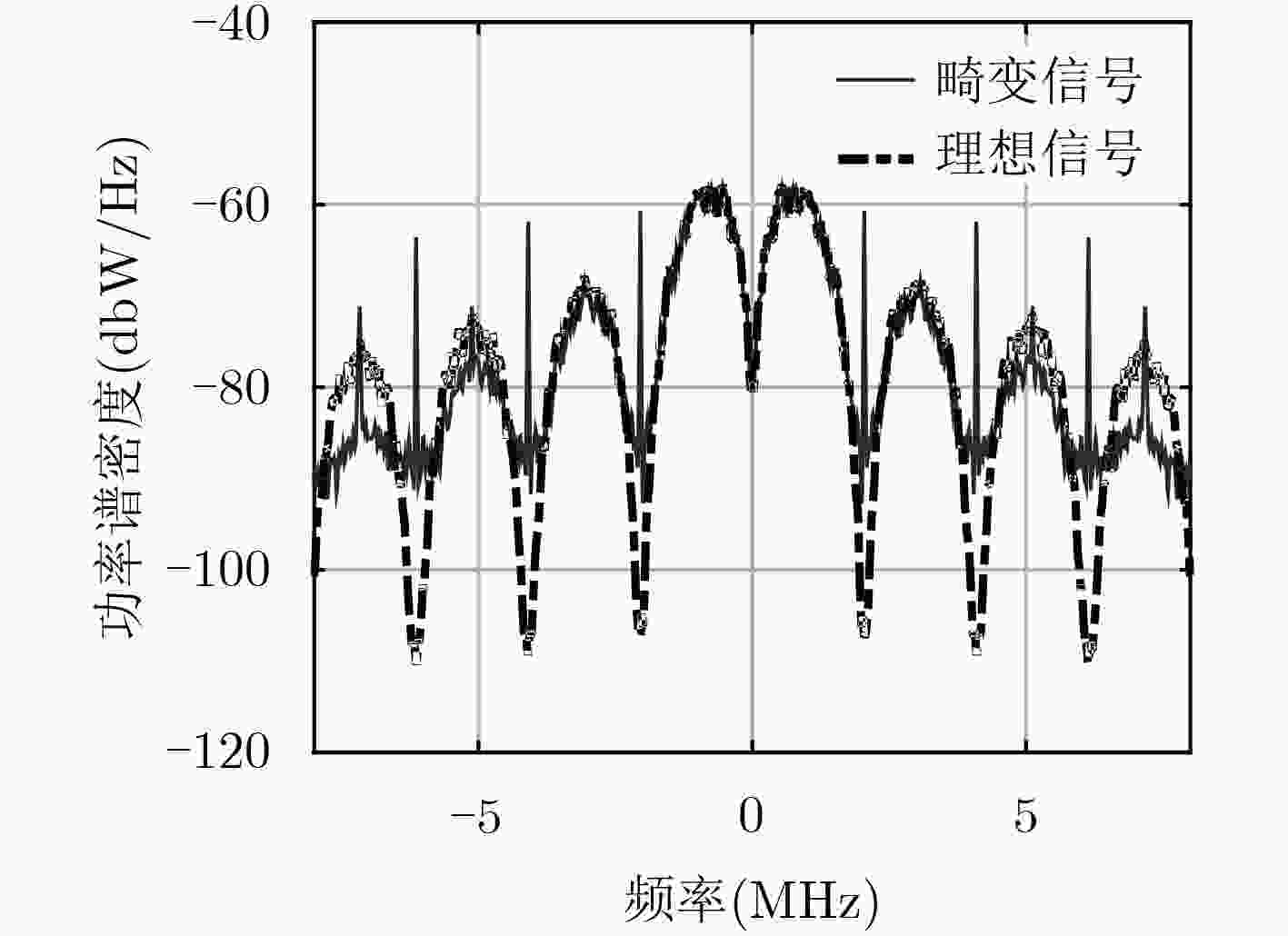
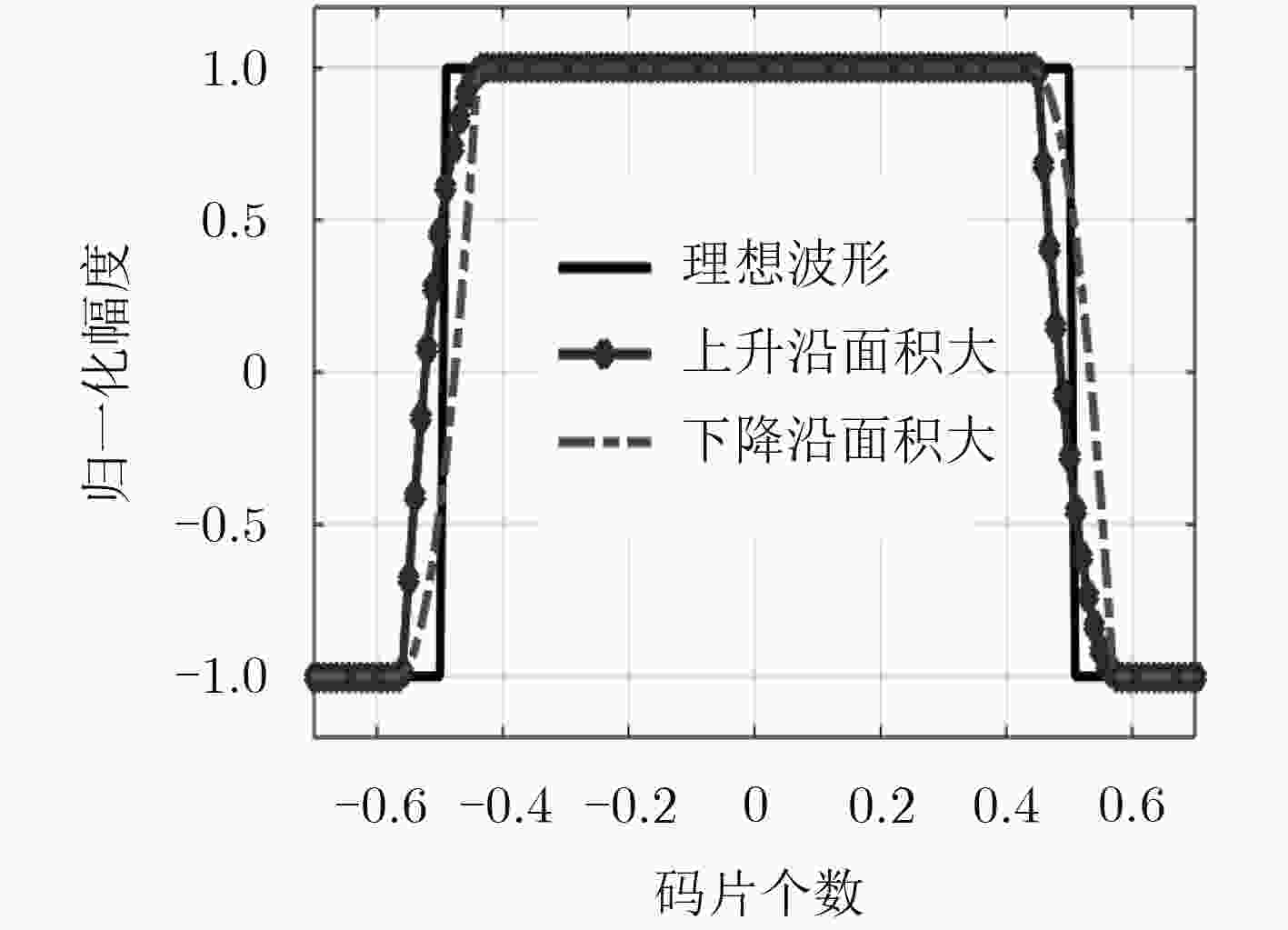
全球卫星导航系统(GNSS)导航信号的波形特性将会影响导航信号质量,而信号质量优劣则直接决定了整个GNSS的服务性能极限。传统的波形畸变评估方法主要针对传统相移键控(PSK)调制信号的波形幅度和宽度开展研究,而忽视了波形不对称对跟踪误差和测距误差带来的影响。该文在国际民航组织(ICAO)所采用的传统测距码波形分析模型TMA/TMB/TMC基础上,给出了适用于各种新型二进制偏置载波(BOC)调制的波形畸变分析扩展模型。接着提出能够精细分析波形上升下降沿对称特性(WRaFES)分析模型,并从时域波形、相关函数、S曲线过零点偏差3个方面,深入仿真分析了WRaFES模型的性能特点。最后,以北斗试验卫星M1-S B1Cd信号为例,给出了基于WRaFES模型及相关曲线特性的实测分析结果。研究表明:该方法能够精确分析导航信号波形不对称性及对用户带来的影响,研究成果可为新型卫星导航信号评估提供一种新方法和新思路,同时还可为GNSS用户接收机相关器间隔参数的合理选取提供建议和技术支撑。
Abstract:The waveform characteristics of the navigation signals of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs) will be of vital importance for signal quality, which plays an imperative and direct role in achieving high performance of GNSS services. These traditional methods for evaluating evil waveforms mainly deal with the amplitude and width of simple modulated signals such as Phase Shift Keying (PSK) signals. However, no research is done on the influences of waveform asymmetry on tracking errors and ranging errors. Based on the traditional thread models, such as Thread Model A (TMA), Thread Model B (TMB) and Thread Model C (TMC), adopted by International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), this paper provides a new extended general thread model suitable for new Binary Offset Carrier (BOC) modulated signals. Then a new evil waveform analysis method, Waveform Rising and Falling Edge Symmetry (WRaFES) Method, is proposed. The effects of WRaFES model are analyzed in detail in terms of time domain, correlation peak and S curve bias. Finally, by taking the B1Cd signal of the first modernized BeiDou navigation satellite System (BDS) experimental satellite named M1-S as an example, tested results of WRaFES model and correlation curves are shown in detail. Results show that the proposed methods could be able to analyze the asymmetry of signal deformation and its impact on ranging performance with high accuracy. The research brings about a new reference for new satellite navigation signal evaluation and signal system optimized design. In addition, it can provide valuable suggestions and technical supports for GNSS users to choose reasonable receivers’ correlator spacing.
-
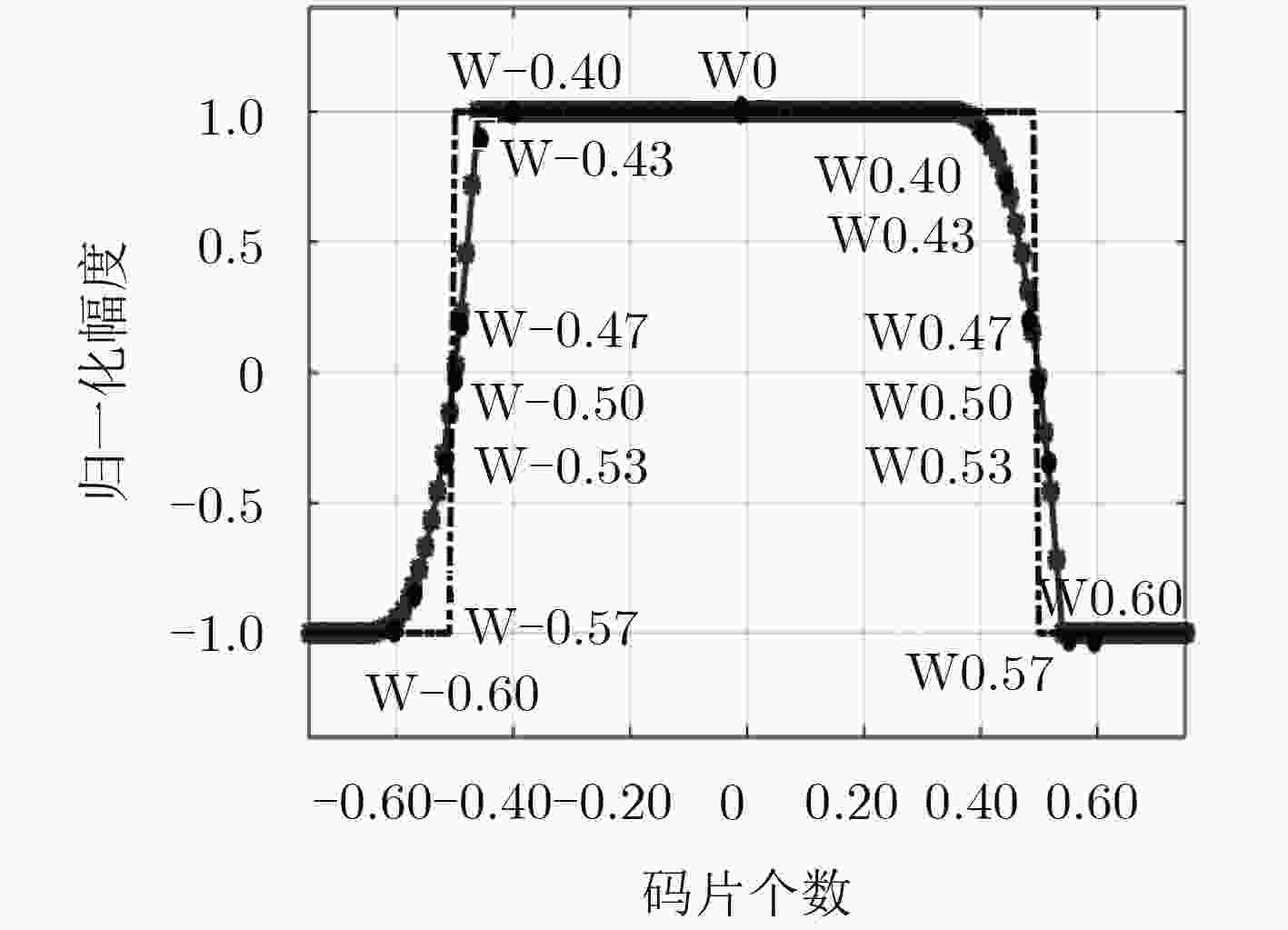
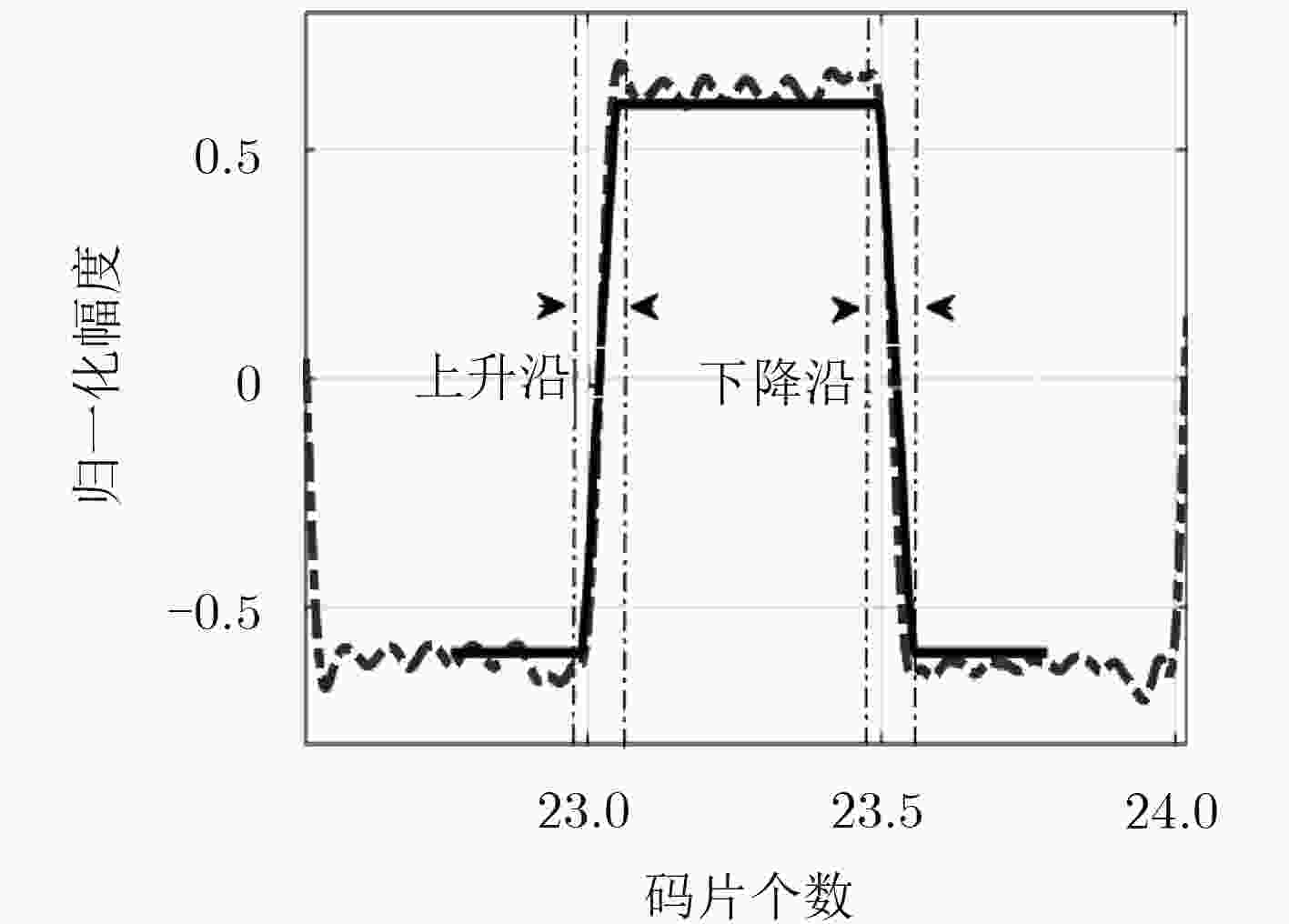
表 1 WRaFES参数列表
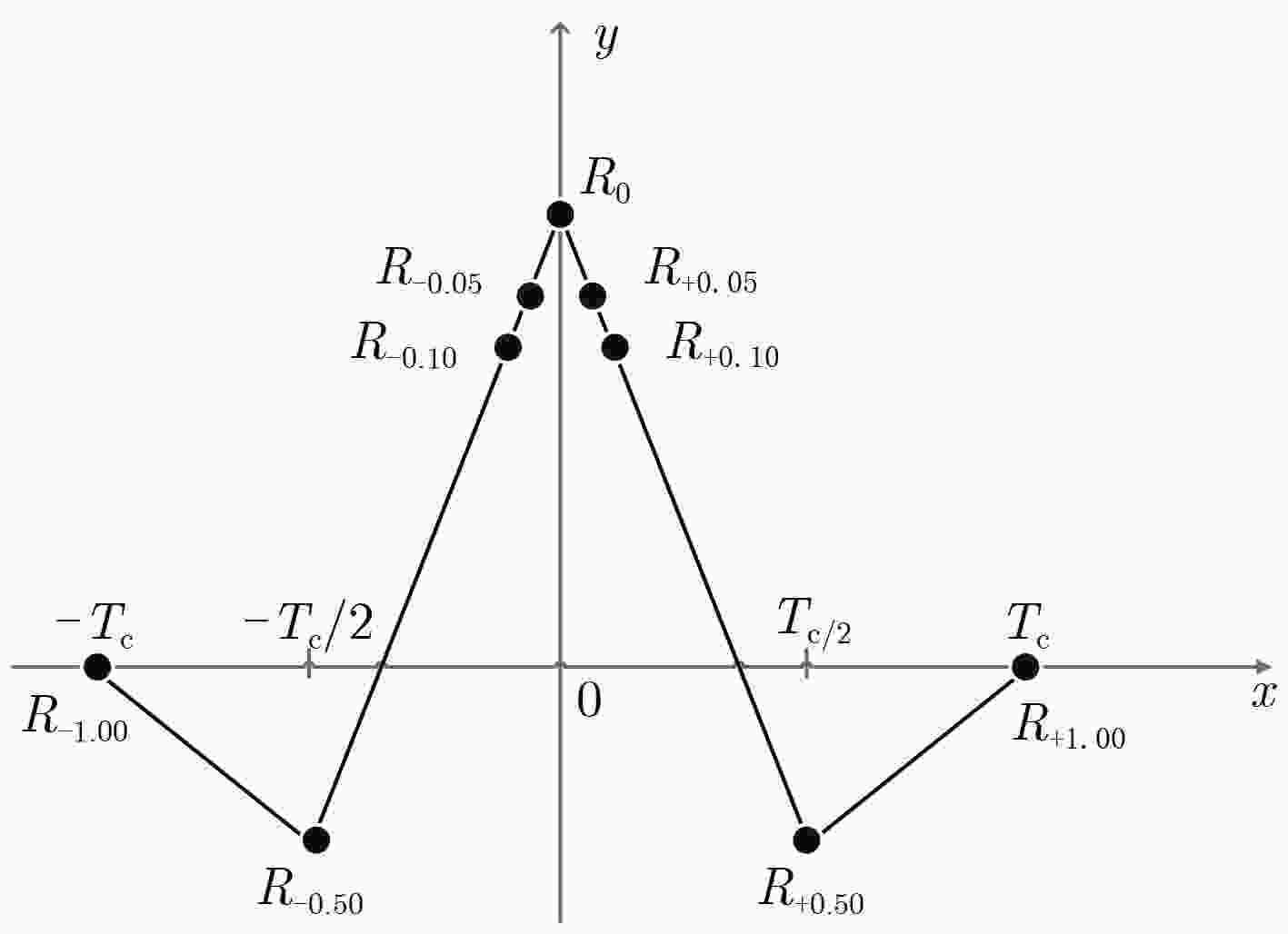
$\Delta \Delta $测试参数 对称性面积比参数: $M1 = \frac{{({W_{ - 0.50}} - {W_{0.50}}) - ({W_{ - 0.47}} - {W_{0.47}})}}{{{W_0}}}$$M2 = \frac{{({W_{ - 0.53}} - {W_{0.53}}) - ({W_{ - 0.50}} - {W_{0.50}})}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M24 = 20 \times \lg \left[ {\displaystyle\frac{{\displaystyle\int_{t = - 0.60{T_{\rm c}}}^{t = - 0.40{T_{\rm c}}} {s(t){\rm dt}} }}{{\displaystyle\int_{t = 0.40{T_{\rm c}}}^{t = 0.60{T_{\rm c}}} {s(t){\rm dt}} }}} \right]$ 对称性评价参数: 非对称性评价参数: $M3 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.40}} - {W_{0.40}})}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M4 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.43}} - {W_{0.43}})}}{{{W_0}}}$
$M5 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.47}} - {W_{0.47}})}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M6 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.50}} - {W_{0.50}})}}{{{W_0}}}$
$M7 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.53}} - {W_{0.53}})}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M8 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.57}} - {W_{0.57}})}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M9 = \displaystyle\frac{{({W_{ - 0.60}} - {W_{0.60}})}}{{{W_0}}}$$M10 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{ - 0.40}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M11 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.40}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M12 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{ - 0.43}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M13 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.43}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M14 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{ - 0.47}}}}{{{W_0}}}$
$M15 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.47}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M16 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{-0.50}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M17 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.50}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M18 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{-0.53}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M19 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.53}}}}{{{W_0}}}$
$M20 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{-0.57}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M21 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.57}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M22 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{-0.60}}}}{{{W_0}}}$ $M23 = \displaystyle\frac{{{W_{0.60}}}}{{{W_0}}}$表 2 相关特性参数均值和方差
参数 ${P_1}$ ${P_2}$ ${P_3}$ ${P_4}$ ${P_5}$ ${P_6}$ ${P_7}$ 均值 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.85 方差 $\frac{{0.6}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{2.4}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{0.6}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{1.2}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{2.0}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{2.0}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{2.775}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ 参数 ${P_8}$ ${P_9}$ ${P_{10}}$ ${P_{11}}$ ${P_{12}}$ ${P_{13}}$ ${P_{14}}$ 均值 0.85 0.70 0.70 –0.50 –0.50 0 0 方差 $\frac{{2.775}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{0.51}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{0.51}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{0.75}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{0.75}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{1.0}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ $\frac{{1.0}}{{2T\,(C/{N_0})}}$ 表 3 BDS M1-S B1CdWRaFES 参数统计结果
参数 M1 M2 M5 M6 M7 M24 M14 M15 M16 M17 M18 M19 均值 0.0132 0.0149 0.0118 0.0014 0.0162 0.0091 0.5775 0.5893 0.0010 0.0003 0.5766 0.5928 标准差 0.1233 0.1396 0.1568 0.1292 0.1708 1.6188 0.0942 0.1359 0.0896 0.0942 0.1223 0.1571 参数 M3 M4 M8 M9 M10 M11 M12 M13 M20 M21 M22 M23 均值 0.0008 0.0110 0.0339 0.0247 1.0391 1.0383 0.9369 0.9481 0.9321 0.9659 1.0425 1.0673 标准差 0.2455 0.1999 0.2571 0.3510 0.1557 0.2294 0.1089 0.1809 0.1941 0.2557 0.2759 0.3286 表 4 BDS M1-S B1Cd实测相关特性参数统计结果
参数 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 均值 0.0148 –0.0002 –0.0022 0.0114 0.0099 –0.0048 0.8663 标准差 0.0352 0.0488 0.0369 0.0369 0.0526 0.0745 0.0076 参数 P8 P9 P10 P11 P12 P13 P14 均值 0.8698 0.7160 0.7060 –0.5013 –0.5099 0.0151 0.0211 标准差 0.0079 0.0121 0.0136 0.0593 0.0636 0.0576 0.0728 -
陈昌川, 周杨, 张天骐. TDDM-BOC信号组合码序列及信息序列盲估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2760–2766. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160042CHEN Changchuan, ZHOU Yang, and ZHANG Tianqi. Blind estimation of the combination code sequence and information sequence for TDDM-BOC signal[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2760–2766. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160042 EDGAR C, CZOPEK F, and BARKER L B. A cooperative anomaly resolution on PRN-19[C]. Proceedings of 1999 Institute of Navigation GPS, Nashville, Tennessee, USA, 1999: 2269–2271. 贺成艳, 郭际, 卢晓春, 等. GNSS导航信号常见畸变产生机理及对测距性能影响分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(7): 1611–1620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.07.22HE Chengyan, GUO Ji, LU Xiaochun, et al. Generation mechanisms of GNSS navigation signal distortions and influence on ranging performance[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(7): 1611–1620. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.07.22 PHELTS R E. Multicorrelator techniques for robust mitigation of threats to GPS signal quality[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Stanford University, 2001: 1–345. FONTANELLA D, PAONNI M, and EISSFELLER B. A novel evil waveforms threat model for new generation GNSS signals: theoretical analysis and performance[C]. Proceedings of the 20105th ESA Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing, Noordwijk, Netherlands, 2010: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/NAVITEC.2010.5708037. MISRA P and ENGE P. Global Positioning System: Signals, Measurements, and Performance[M]. 2nd ed. Lincoln, MA, Ganga-Jamuna Press, 2006: 1125–1134. JAHROMI A J, BROUMANDAN A, DANESHMAND S, et al. Galileo signal authenticity verification using signal quality monitoring methods[C]. Proceedings of 2016 International Conference on Localization and GNSS, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ICL-GNSS.2016.7533684. 贺成艳. GNSS空间信号质量评估方法研究及测距性能影响分析[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2013: 1–205.HE Chengyan. Research on evaluation methods of GNSS signal quality and the influence of GNSS signal on ranging performance[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013: 1–205. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
