Bayesian Network Structure Learning Based on Improved Whale Optimization Strategy
-
摘要: 针对当前贝叶斯网络结构学习算法易陷入局部最优和寻优效率低的问题,该文提出一种基于改进鲸鱼优化策略的贝叶斯网络结构学习算法。该算法首先提出一种新的方法建立较优的初始种群,然后利用不产生非法结构的交叉变异算子构建适用于贝叶斯网络结构学习的改进捕食行为,同时采用动态调节参数增强算法个体寻优的能力,通过适应度排序更新种群,最终获得最优的贝叶斯网络结构。仿真结果表明,该算法具有全局收敛性,寻优效率高,精确率高于其它同类优化算法。Abstract: A Bayesian network structure learning algorithm based on improved whale optimization strategy is proposed to solve the problem that the current Bayesian network structure learning algorithm is easily trapped in local optimal and is of low optimization efficiency. The improved algorithm proposes first a new method to establish a better initial population, and then it uses the cross mutation operator that does not produce the illegal structure to construct an improved predation behavior suitable for Bayesian network structure learning. At the same time, it adopts the dynamic parameter tuning strategy to enhance the individual search ability. The population is updated followed by the fitness order so that the optimal Bayesian network structure is obtained. Simulation results demonstrate that the algorithm has global convergence, high efficiency and higher accuracy than other similar optimization algorithms.
-
表 1 贝叶斯网络的标准评价量
评价量 物理意义 TP (True Positive,真正例) 得到的网络结构与标准网络结构相同的边的数量 TN (True Negative,真负例) 得到的网络结构与标准结构相同无边情况的数量 FP (False Positive,假正例) 得到的网络结构与标准结构相比增加的边的数量 FN (False Negative,假负例) 得到的网络结构与标准结构相比丢失的边的数量 Pre (Precision,精确率) 真正类别占正类别的比例 Sen (Sensitivity,敏感度) 真正类别占所有类别的比例 Score 网络结构的BIC得分 t 网络结构的执行时间 表 2 不同算法在ASIA网络中的对比
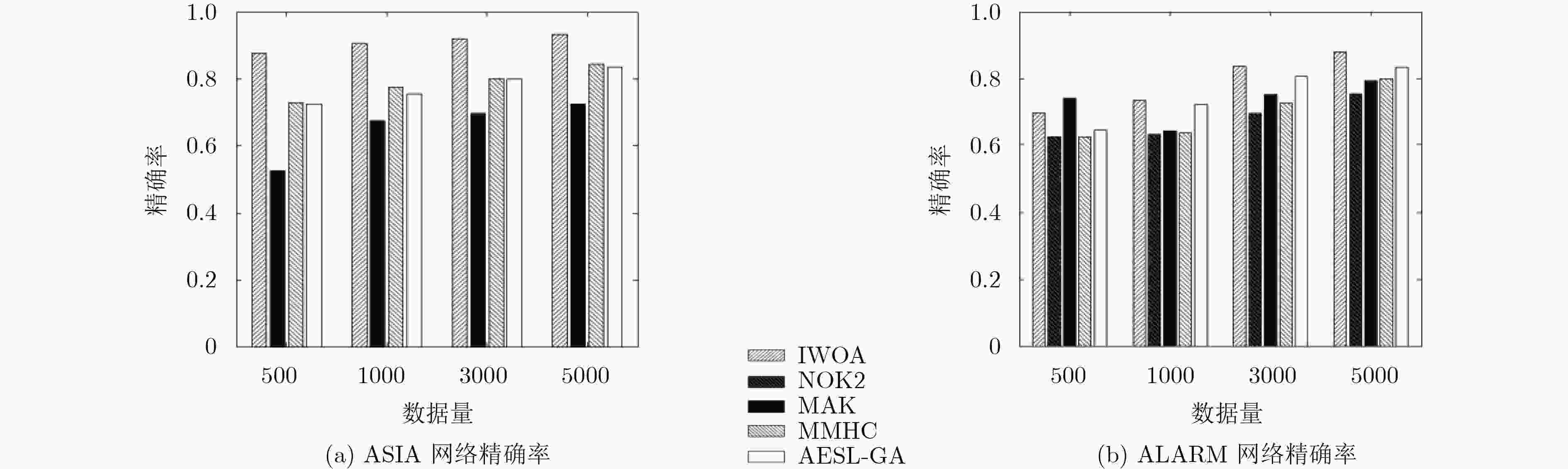
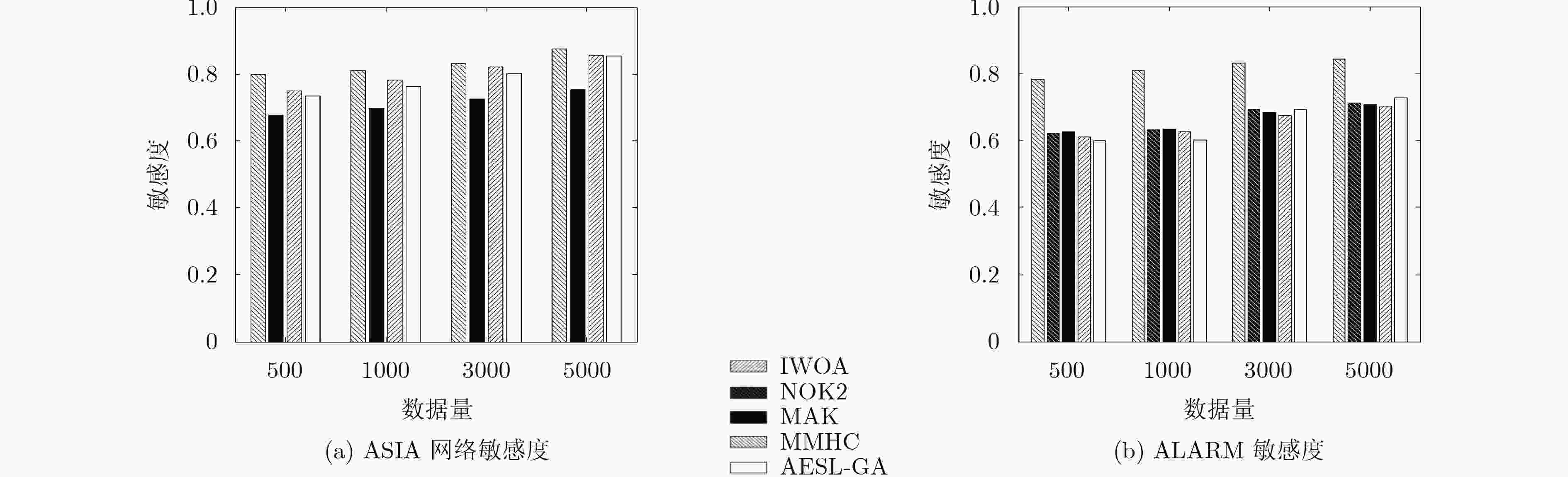
数据量 算法 TP TN FP FN t(s) Score 500 IWOA 7.0 47.3 0.2 0.9 6.09 –1153.8$ \pm $2.13 MAK 4.2 44.6 3.8 3.4 3.62 –1170.5$ \pm $4.46 MMHC 6.7 47.2 1.1 1.2 3.54 –1157.1$ \pm $6.79 AESL-GA 6.5 46.3 1.7 1.5 4.21 –1165.5$ \pm $9.12 1000 IWOA 7.2 47.6 0 0.8 6.28 –2314.8$ \pm $3.52 MAK 4.6 45.0 3.4 3.2 3.70 –2317.5$ \pm $7.47 MMHC 6.9 45.7 0.9 0.8 4.58 –2315.6$ \pm $6.45 AESL-GA 6.4 46.4 1.5 1.6 6.02 –2317.2$ \pm $2.24 3000 IWOA 7.4 47.8 0 0.6 7.81 –6711.8$ \pm $5.77 MAK 5.0 46.2 3.4 3.0 4.32 –6723.9$ \pm $5.84 MMHC 7.0 46.9 0.7 0.6 6.27 –6713.3$ \pm $6.46 AESL-GA 6.9 47.1 1.2 0.9 8.63 –6719.5$ \pm $7.31 5000 IWOA 7.6 47.9 0 0.4 9.00 –11201.0$ \pm $11.42 MAK 5.0 46.6 3.4 3.0 5.31 –11212.9$ \pm $12.35 MMHC 7.2 47.5 0.5 0.6 9.01 –11208.9$ \pm $15.57 AESL-GA 7.1 47.7 1.0 0.8 9.56 –11210.4$ \pm $14.63 表 3 不同算法在ALARM网络中的对比
数据量 算法 TP TN FP FN t(s) Score 500 IWOA 37.2 1271.6 8.4 1.4 205.72 –5575.61$ \pm $7.28 NOK2 31.8 1269.5 10.1 5.6 35.91 –5374.76$ \pm $18.05 MAK 32.2 1261.4 20.5 7.2 314.16 –5580.04$ \pm $10.02 MMHC 27.6 1244.1 15.3 20.2 2647.78 –5598.67$ \pm $20.33 AESL-GA 33.3 1274.7 11.3 12.7 2647.78 –5472.37$ \pm $15.35 1000 IWOA 37.6 1274.2 7.8 1.0 223.87 –10752.25$ \pm $5.35 NOK2 32.2 1270.3 9.8 5.4 37.64 –10538.84$ \pm $20.20 MAK 33.4 1265.2 19.8 5.8 356.10 –10771.08$ \pm $12.36 MMHC 30.2 1250.4 10.8 15.2 3637.85 –10824.35$ \pm $15.89 AESL-GA 35.4 1275.2 10.0 9.2 3637.85 –10964.18$ \pm $8.23 3000 IWOA 39.5 1279.5 5.6 0.4 476.02 –28340.28$ \pm $13.89 NOK2 35.6 1271.9 7.2 4.0 57.35 –29043.43$ \pm $14.74 MAK 36.4 1283.4 14.2 4.4 505.57 –29308.01$ \pm $14.20 MMHC 32.6 1253.5 10.2 12.3 3963.62 –28939.91$ \pm $17.12 AESL-GA 37.0 1277.1 6.9 7.0 3963.62 –29248.78$ \pm $19.30 5000 IWOA 40.8 1280.6 5.2 0.2 856.10 –47893.12$ \pm $17.66 NOK2 36.2 1273.4 6.5 3.3 69.67 –48126.57$ \pm $19.58 MAK 37.7 1270.9 10.7 3.7 948.41 –48259.15$ \pm $20.45 MMHC 35.1 1277.8 7.5 8.0 5613.55 –48677.04$ \pm $19.52 AESL-GA 38.3 1278.7 6.3 4.2 5613.55 –48148.56$ \pm $24.79 -
CONTALDI C, VAFAEE F, and NELSON P C. Bayesian network hybrid learning using an elite-guided genetic algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2018. doi: 10.1007/s10462-018-9615-5 刘广怡, 李鸥, 宋涛, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络的无线传感网高效数据传输方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1362–1367. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151027LIU Guangyi, LI Ou, SONG Tao, et al. Energy-efficiency data transmission method in WSN based on Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1362–1367. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151027 邓歆, 孟洛明. 基于贝叶斯网络的通信网告警相关性和故障诊断模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(5): 1182–1186.DENG Xin and MENG Luoming. Bayesian networks based alarm correlation and fault diagnosis in communication networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(5): 1182–1186. CHICKERING D M. Learning Bayesian Networks is NP-complete[M]. FISHER D and LENZ H J. Learning from Data. New York: Springer, 1996: 121–130. SCANAGATTA M, CORANI G, DE CAMPOS C P, et al. Approximate structure learning for large Bayesian networks[J]. Machine Learning, 2018, 107(8/10): 1209–1227. doi: 10.1007/s10994-018-5701-9 DENNIS D M K, WILLIAMS M R, and SIGMAN M E. Investigative probabilistic inferences of smokeless powder manufacturers utilizing a Bayesian network[J]. Forensic Chemistry, 2017, 3: 41–51. doi: 10.1016/j.forc.2016.12.001 LIU Hui, ZHOU Shuigeng, LAM W, et al. A new hybrid method for learning Bayesian networks: separation and reunion[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 121: 185–197. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.01.029 TSAMARDINOS I, BROWN L E, and ALIFERIS C F. The max-min hill-climbing Bayesian network structure learning algorithm[J]. Machine Learning, 2006, 65(1): 31–78. doi: 10.1007/s10994-006-6889-7 刘浩然, 孙美婷, 李雷, 等. 基于蚁群节点寻优的贝叶斯网络结构算法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(1): 143–150. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2017.01.019LIU Haoran, SUN Meiting, LI Lei, et al. Study on Bayesian network structure learning algorithm based on ant colony node order optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(1): 143–150. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2017.01.019 刘彬, 王海羽, 孙美婷, 等. 一种通过节点序寻优进行贝叶斯网络结构学习的算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1234–1241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170675LIU Bin, WANG Haiyu, SUN Meiting, et al. Learning Bayesian network structure from node ordering searching optimal[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1234–1241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170675 MIRJALILI S and LEWIS A. The whale optimization algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 95: 51–67. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 MENG Qingfei, CHEN Yuehui, WANG Dong, et al. Learning bayesian networks structure based part mutual information for reconstructing gene regulatory networks[C]. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Liverpool, UK, 2017: 647–654. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-63312-1_57. DE CAMPOS C P, SCANAGATTA M, CORANI G, et al. Entropy-based pruning for learning bayesian networks using BIC[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 260: 42–50. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2018.04.002 ZAKHAROV V K and RODIONOV T V. Naturalness of the class of Lebesgue-Borel-Hausdorff measurable functions[J]. Mathematical Notes, 2014, 95(3/4): 500–508. doi: 10.1134/S0001434614030225 FANG Wei, SUN Jun, CHEN Huanhuan, et al. A decentralized quantum-inspired particle swarm optimization algorithm with cellular structured population[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 330: 19–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.055 陈志敏, 田梦楚, 吴盘龙, 等. 基于蝙蝠算法的粒子滤波法研究[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(5): 050502. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.050502CHEN Zhimin, TIAN Mengchu, WU Panlong, et al. Intelligent particle filter based on bat algorithm[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(5): 050502. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.050502 ADABOR E S, ACQUAAH-MENSAH G K, and ODURO F T. SAGA: A hybrid search algorithm for Bayesian network structure learning of transcriptional regulatory networks[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2015, 53: 27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.08.010 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
