The Incentive Model for Mobile Crowd Sensing Oriented to Differences in Mission Costs
-
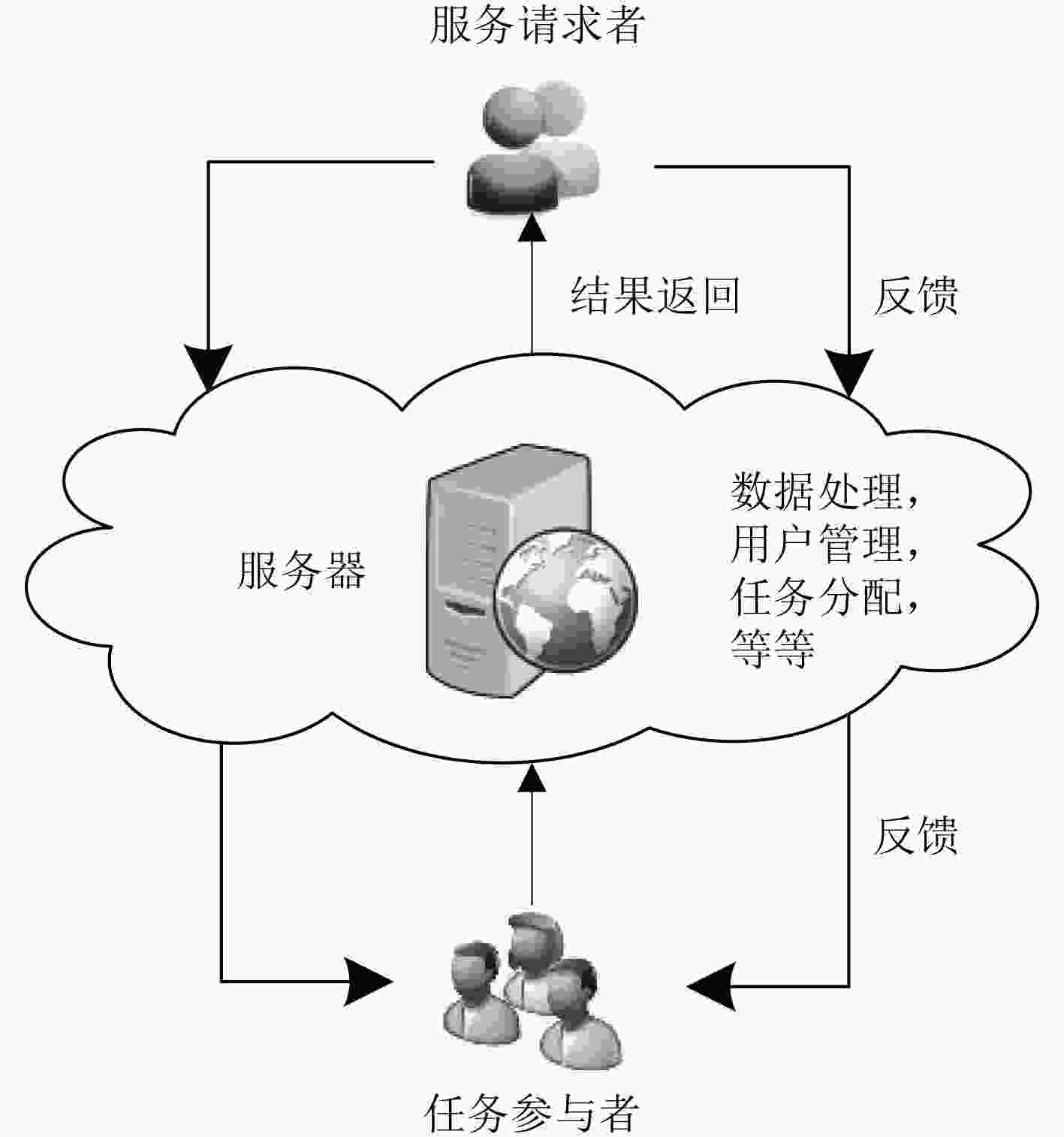
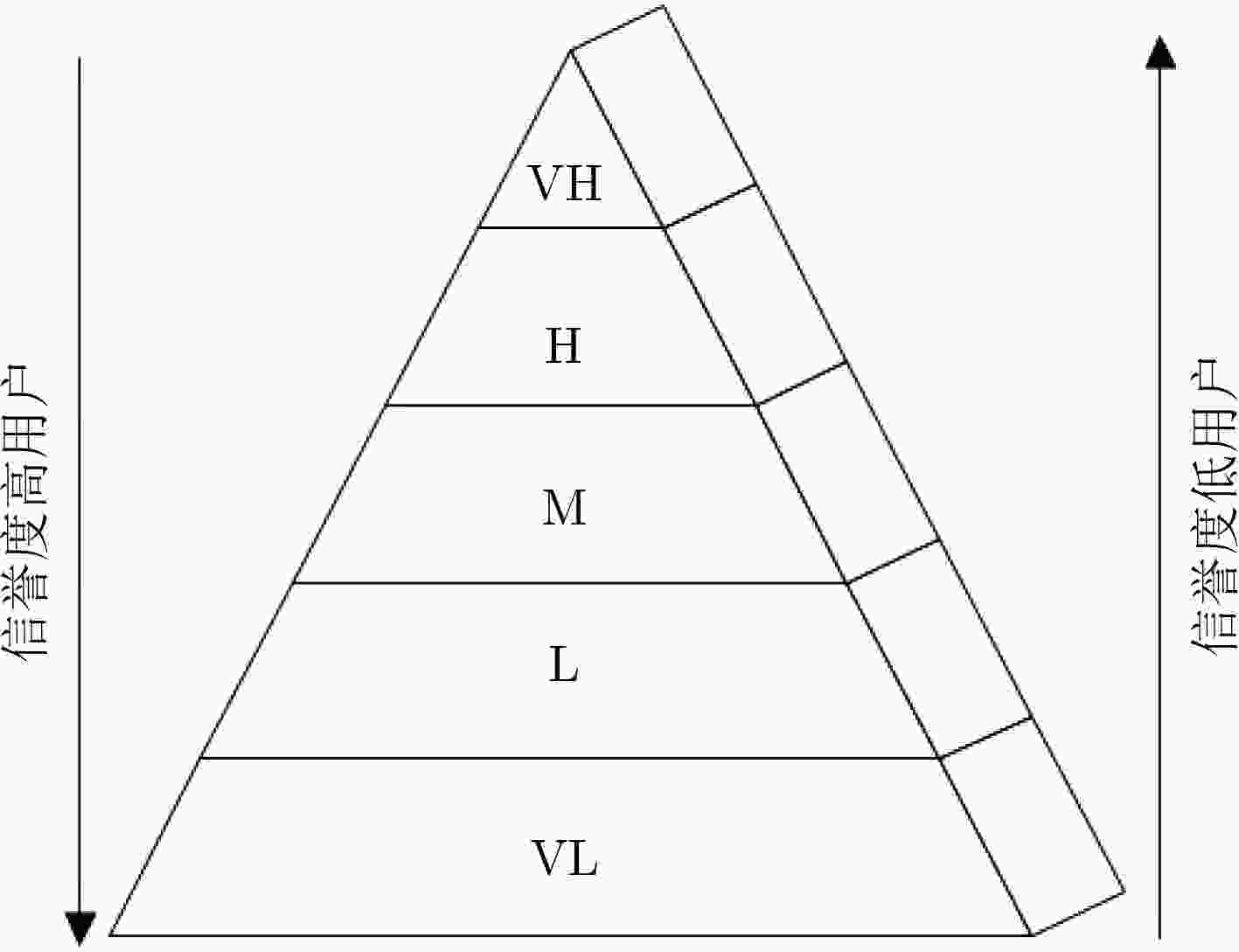
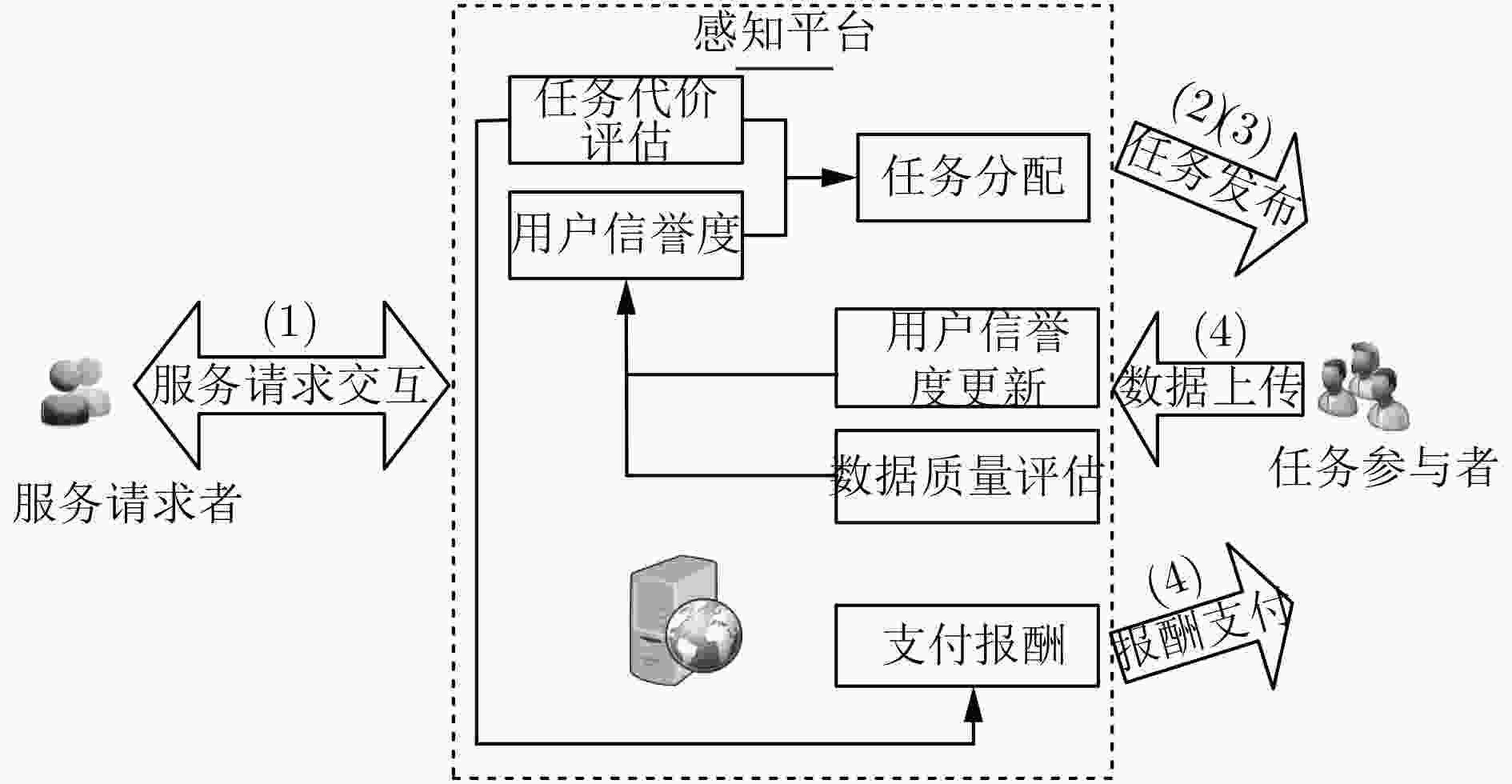
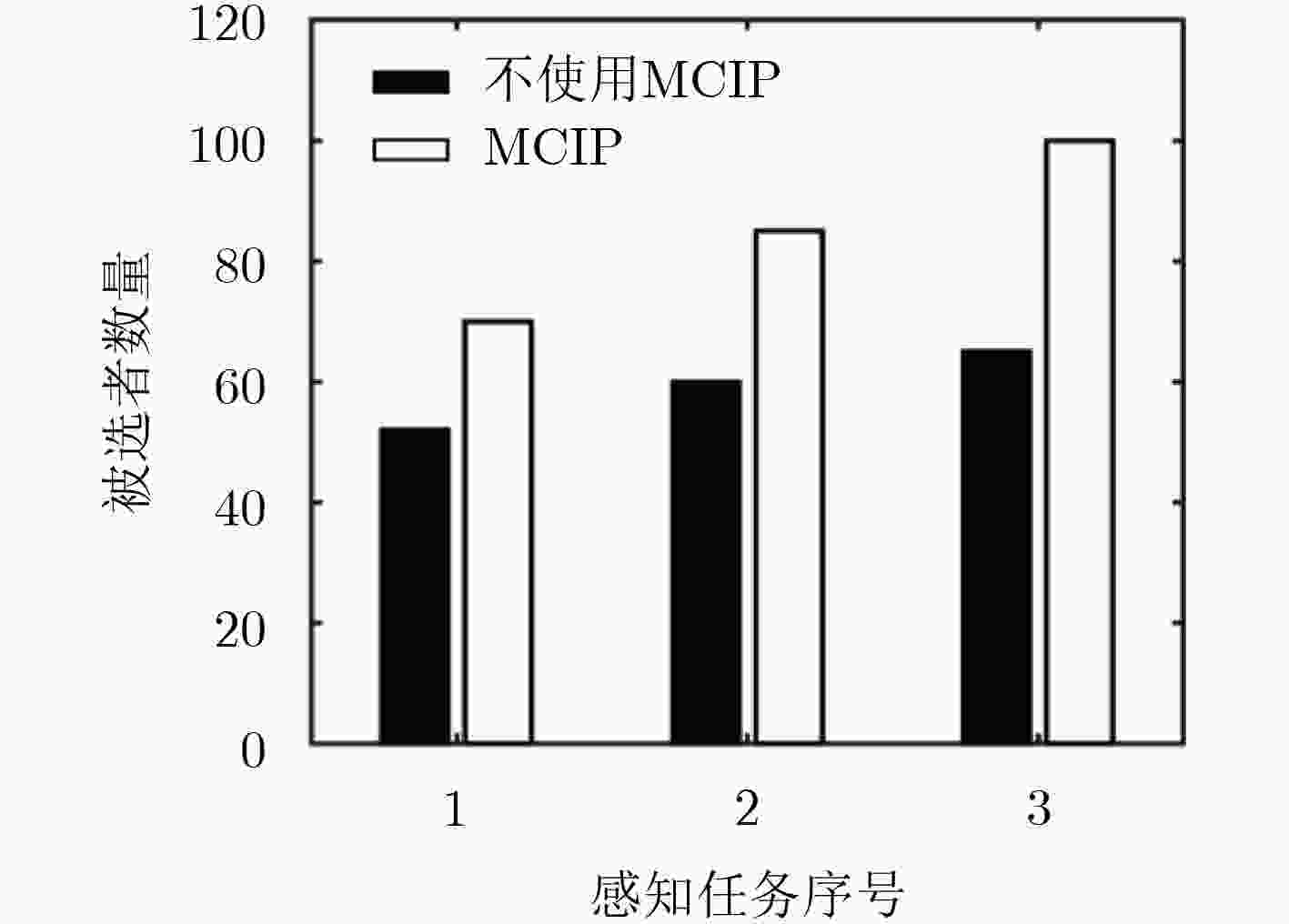
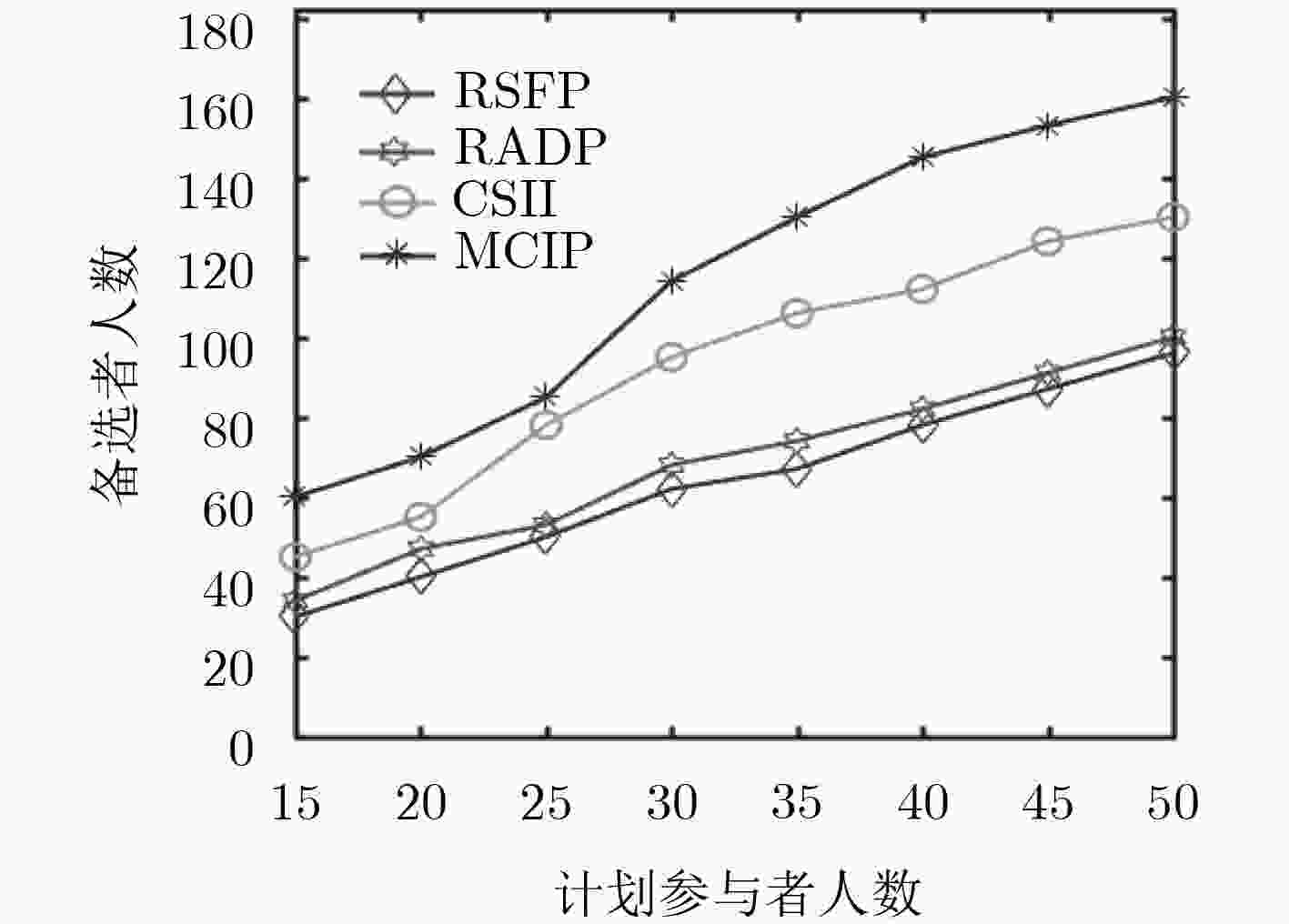
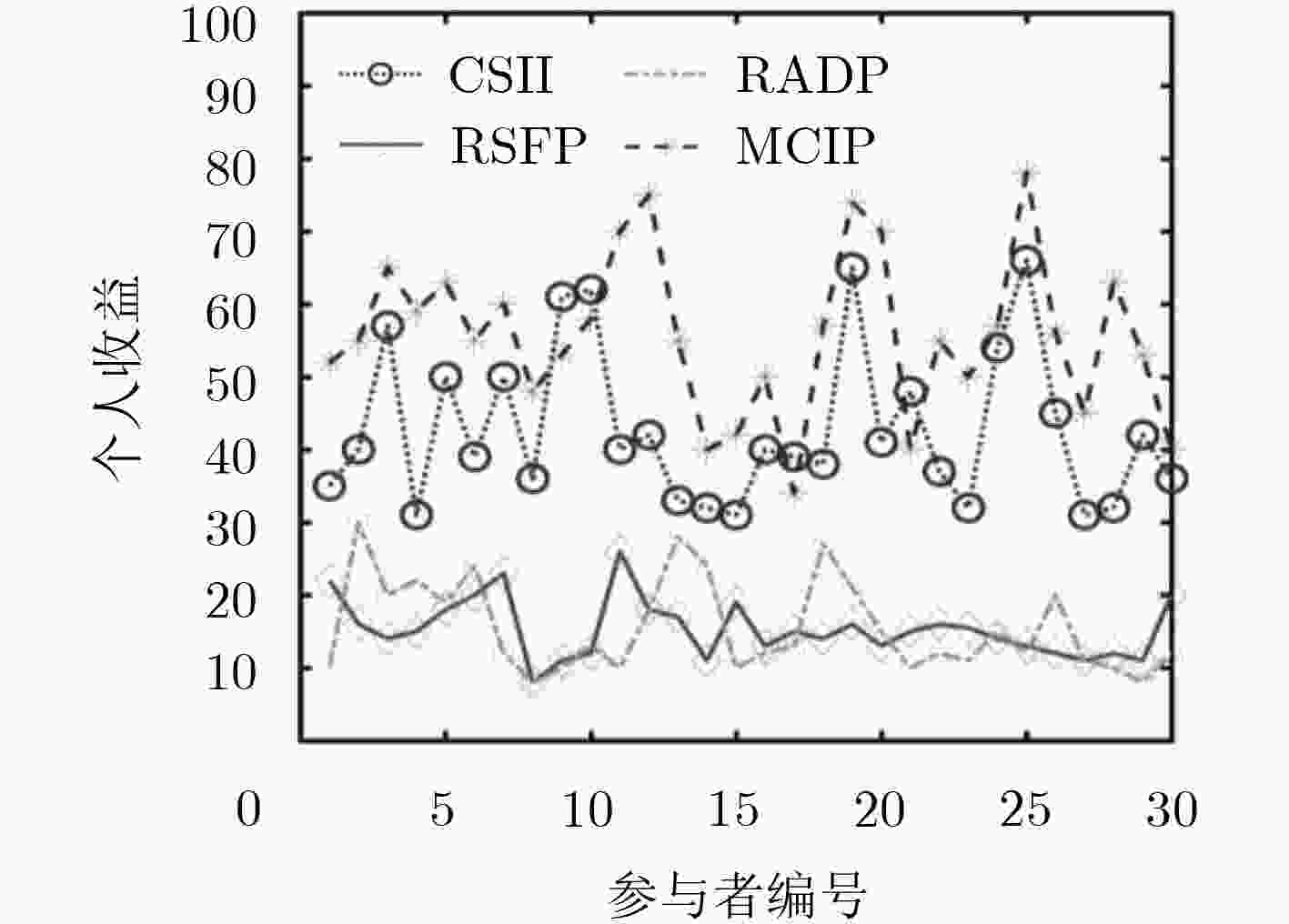
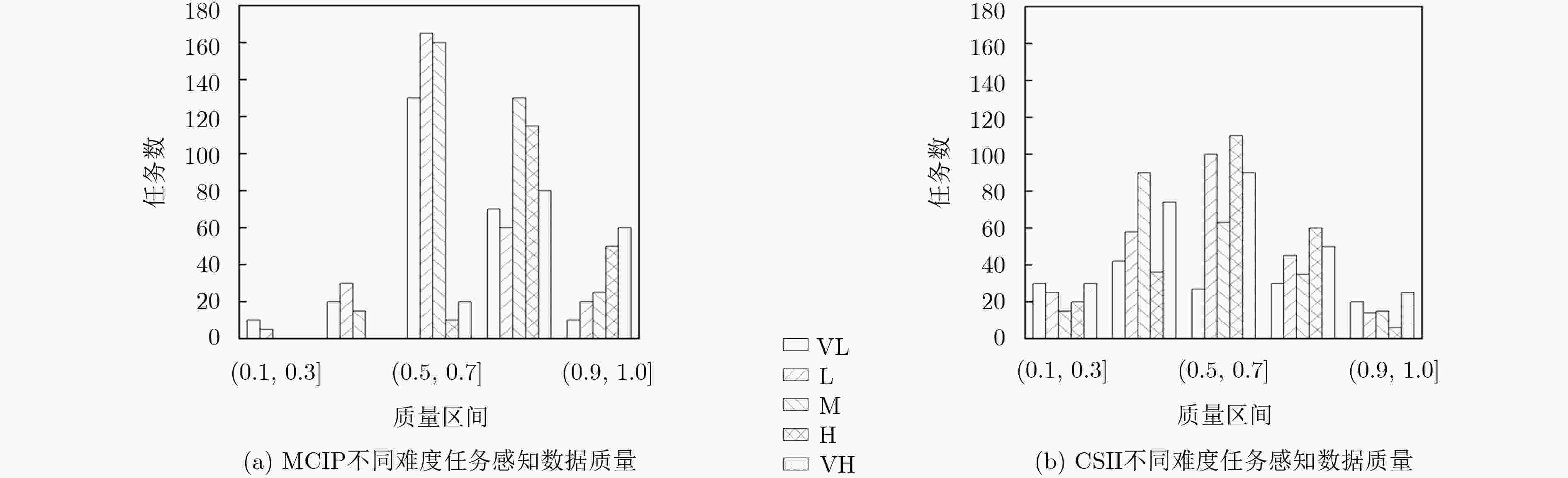
摘要: 针对感知任务参与者数量不足和提供数据质量不高的问题,该文提出一种面向任务代价差异的移动群智感知激励模型。首先,利用模糊推理方法分析数据量、环境条件及设备消耗对任务代价的影响,将感知任务按照代价差异划分为不同等级,同时为请求者制定预算并给予参与者合适的报酬。其次,通过信誉度评估和参与者优选将感知任务分配给更合适的参与者完成感知任务并上传感知数据。最后,对参与者上传感知数据评估,更新参与者信誉度,并根据参与者完成感知任务的代价等级支付相应报酬。基于真实数据集的仿真实验结果表明,该模型能够利用各个模块间的相互影响,有效招募更多的用户参与感知任务并促进参与者上传高质量的感知数据。Abstract: To solve the problem of insufficient number of participants and poor data quality in the sensing mission, a mobile crowd sensing incentive model for mission cost difference is proposed. First of all, the fuzzy reasoning method is used to analyze the impact of data quantity, environmental conditions and equipment consumption on mission cost, and the sensing mission is divided into different levels on the basis of cost difference. Meanwhile, the method is used to prepare a budget for the requester and give the participant an appropriate reward. Then, the sensing mission is assigned to more appropriate participants to complete the sensing mission and upload the sensing data through credibility assessment and participants’ preference. Finally, the sensing data uploaded by participants is evaluated, and the credibility of participants is updated. Besides, the participants are paid according to the cost level of perceived missions. The simulation experiments based on the real data set show that the model can recruit more users to participate in the sensing mission effectively and promote participants to upload high-quality sensing data by using the mutual influence between different modules.
-
Key words:
- Mobile crowd sensing /
- Incentive scheme /
- Differences in mission costs /
- Reputation
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
参数名称 参数值 感知区域(m×m) 250×400 用户数量 182 移动设备感知范围(m) 30 感知任务数量 100 表 2 感知任务信息
感知任务集ID 任务开始时刻 任务结束时刻 允许感知时间(min) 1 01:00:00 01:15:00 15 2 01:30:00 02:00:00 30 3 02:05:00 02:30:00 25 4 02:10:00 02:30:00 20 -
YANG Hongming, DENG Youjun, QIU Jing, et al. Electric vehicle route selection and charging navigation strategy based on crowd sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(5): 2214–2226. doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2682960 CARDONE G, CIRRI A, CORRADI A, et al. The participact mobile crowd sensing living lab: The testbed for smart cities[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(10): 78–85. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.691740 DETERDING S, DAN D, KHALED R, et al. From game design elements to gamefulness: defining " gameification”[C]. Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, Tampere, Finland, 2011: 9–15. KAWAJIRI R, SHIMOSAKA M, and KAHIMA H. Steered crowd sensing: Incentive design towards quality-oriented piace-centric crowd sensing[C]. ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive & Ubiquitous Computing, Seattle, USA, 2014: 691–701. JAIMES L G, VERGARA-LAURENS I J, and RAIJ A. A survey of incentive techniques for mobile crowd sensing[J]. IEEE Internet Things Journal, 2015, 2(5): 370–380. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2015.2409151 CHESSA S, CORRADI A, FOSCHINI L, et al. Empowering mobile crowdsensing through social and ad hoc networking[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(7): 108–114. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7509387 YANG Guang, HE Shibo, SHI Zhiguo, et al. Promoting cooperation by the social incentive mechanism in mobile crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(3): 86–92. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600690CM LEE J S and HOH B. Dynamic pricing incentive for participatory sensing[J]. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 2010, 6(6): 693–708. doi: 10.1016/j.pmcj.2010.08.006 LUO Shuyun, SUN Yongmei, JI Yuefeng, et al. Stackelberg game based incentive mechanisms for multiple collaborative tasks in mobile crowd sensing[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2016, 21(3): 506–522. doi: 10.1007/s11036-015-0659-3 KRONTIRIS I and ALBERS A. Monetary incentives in participatory sensing using multi-attributive auctions[J]. International Journal of Parallel, Emergent and Distributed Systems, 2012, 27(4): 317–336. doi: 10.1080/17445760.2012.686170 WEN Yutian, SHI Jinyu, ZHANG Qi, et al. Quality-driven auction based incentive mechanism for mobile crowd sending[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(9): 4203–4214. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2363842 ZHAO Dong, LI Xiangyang, and MA Huadong. Budget-feasible online incentive mechanisms for crowdsourcing tasks truthfully[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2016, 24(2): 647–661. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2014.2379281 POURYAZDAN M, KANTARIC B, SOYATA T, et al. Anchor-assisted and vote-based trustworthiness assurance in smart city crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 529–541. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2519820 POURYAZDAN M, KANTARIC B, SOYATA T, et al. Quantifying user reputation scores, data trustworthiness, and user incentives in mobile crowd-sending[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 1382–1397. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2660461 吴垚, 曾菊儒, 彭辉, 等. 群智感知激励机制研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(8): 2025–2047. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005049WU Yao, ZENG Juru, PENG Hui, et al. Survey on incentive mechanisms for crowd sending[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(8): 2025–2047. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005049 ZHENG Yu, XIE Xing, and MA Meiying. GeoLife: A colaborative social networking service among user, location and trajectory[J]. IEEE Data Engineering Billetin, 2010, 33(2): 32–40. doi: 10.1.1.165.4216 南文倩, 郭斌, 陈荟慧, 等. 基于跨空间多元交互的群智感知动态激励模型[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(12): 2412–2425. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01872NAN Wenqian, GUO Bin, CHEN Huihui, et al. Multitask-oriented participant selection in mobile crowd sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Computer, 2015, 38(12): 2412–2425. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01872 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
