Adaptive Fading Memory Based Bluetooth Sequence Matching Localization Algorithm
-
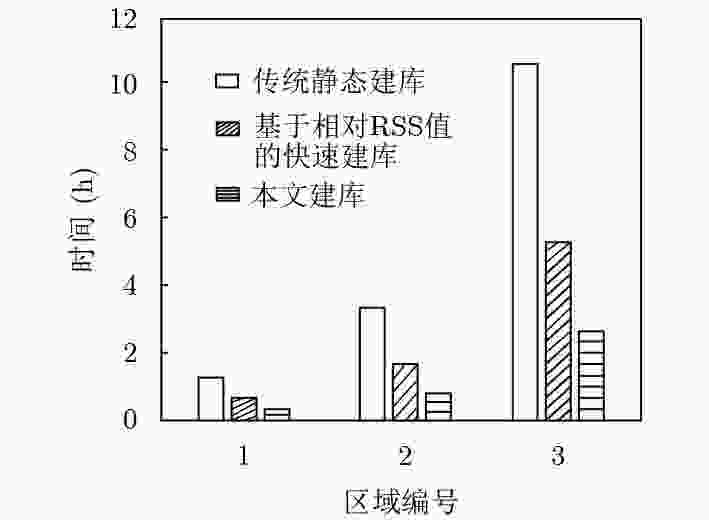
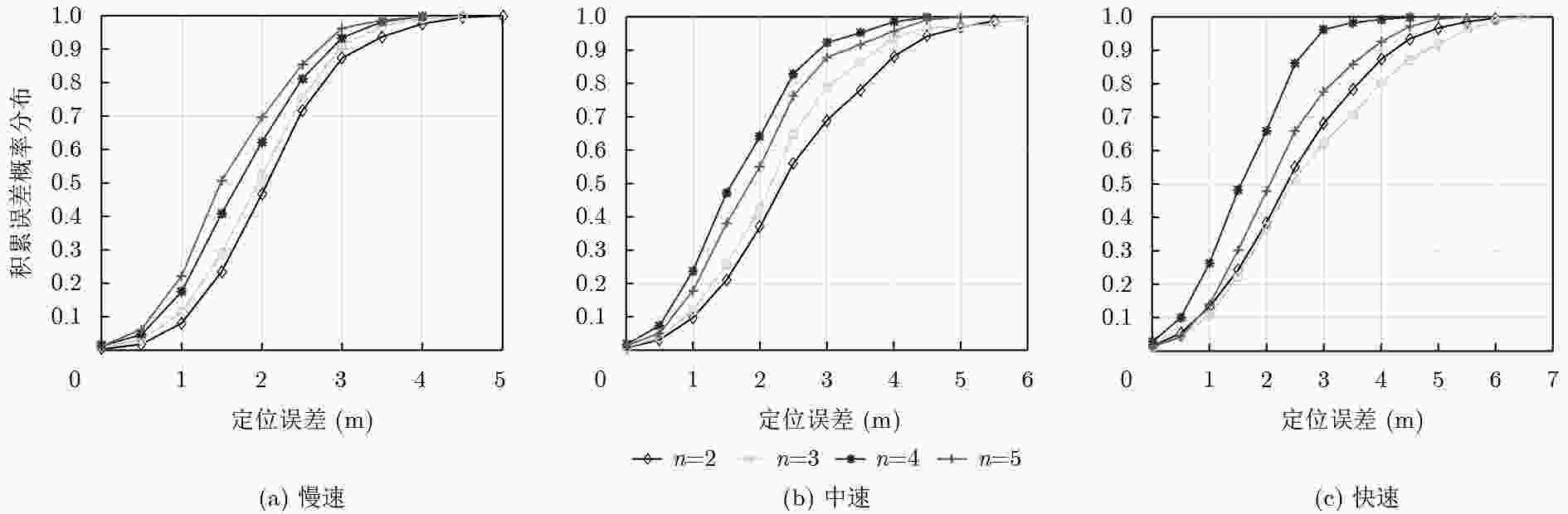
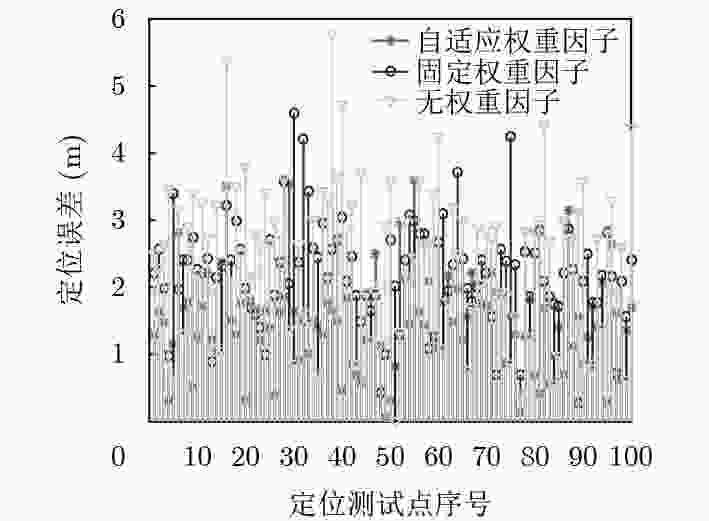
摘要: 针对传统指纹定位算法建库耗时长和定位精度低的问题,该文提出一种基于自适应渐消记忆的蓝牙序列匹配定位算法。首先,利用行人航迹推算(PDR)和最近邻算法(NNA)对运动序列进行位置标定和接收信号强度(RSS)映射;然后,根据邻近位置的相关性,采用序列递归搜索算法构建指纹序列数据库;最后,通过自适应渐消记忆算法,并结合初始序列匹配度实现位置估计。实验结果表明,该算法在室内环境下能够获得较低的建库时间开销以及较高的定位精度。Abstract: The traditional fingerprinting localization algorithm has high construct time overhead and low positioning accuracy. Because of this problem, an adaptive fading memory based bluetooth sequence matching localization algorithm is proposed. Firsly, Pedestrian Dead Reckoning(PDR) and Nearest Neighbor Algorithm(NNA) are applied to performing position calibration and Received Signal Strength(RSS) mapping of Motion Sequences. Secoudly, according to the relevance of neighboring locations, a sequence recursive search method is used to construct fingerprint sequence database. Finally, an adaptive fading memory algorithm and initial sequence matching degree are considered to realize the position estimation of target. The experimental results show that this algorithm is able to consume low construct time overhead and achieve high indoor localization precision.
-
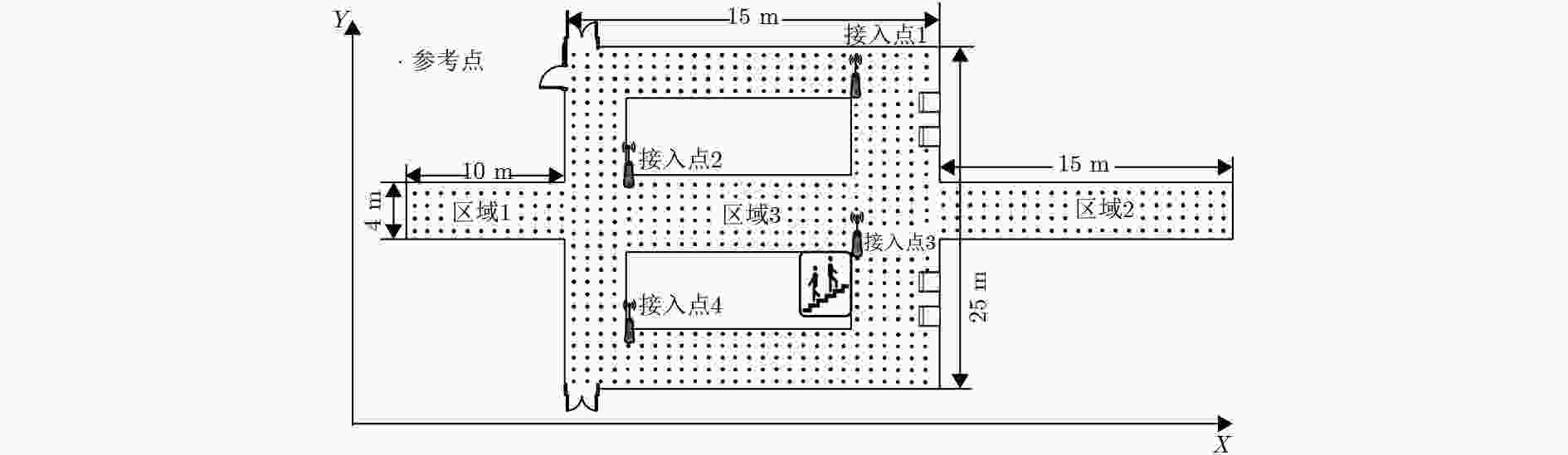
表 1 序列递归搜索算法伪代码
算法:序列递归搜索 输入:局部邻近性矩阵${\text{M}}$;初始数据库${\text{D}}$;指纹序列维度$n$。 输出:指纹序列集${\text{R}}$。 (1) 创建集合${\text{R}}$存储所有指纹序列,集合${\text{Q}}$存储临时指纹序列; (2) for ${\text{D}}$中的每一个指纹点$s$; (3) 将$s$添加到${\text{Q}}$中; (4) 自定义变量$p$; (5) $p = n$; (6) do (7) $p = p - 1$; (8) 利用${\text{M}}$寻找与${\text{Q}}$中序列终点邻近的所有位置点; (9) for 每一个邻近位置点$q$ (10) 将$q$添加到${\text{Q}}$中,更新指纹序列; (11) end for (12) until $p = 0$; (13) for Q中每一条序列${\text{u}}$ (14) if u中存在相同指纹点或对应信号存在$v$值 (15) 将${\text{u}}$从${\text{Q}}$中剔除; (16) else 在${\text{Q}}$中保留${\text{u}}$; (17) end for (18) 将${\text{Q}}$中的所有指纹序列添加到${\text{R}}$中; (19) 将${\text{Q}}$置为空; (20) end for 表 2 不同环境下4种算法的定位误差
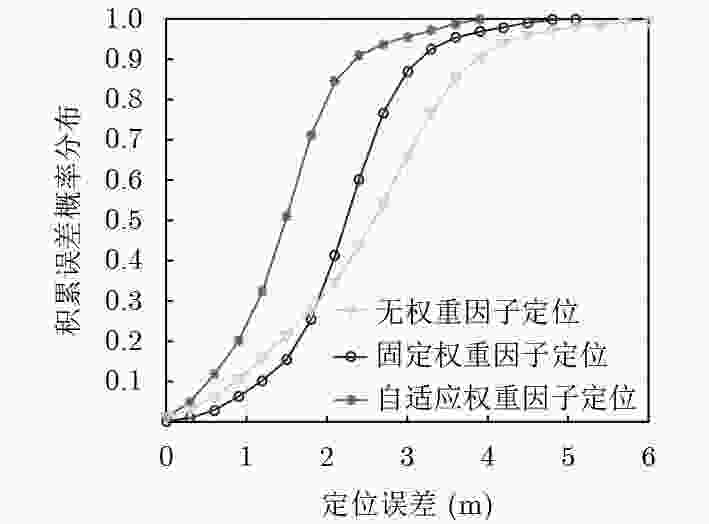
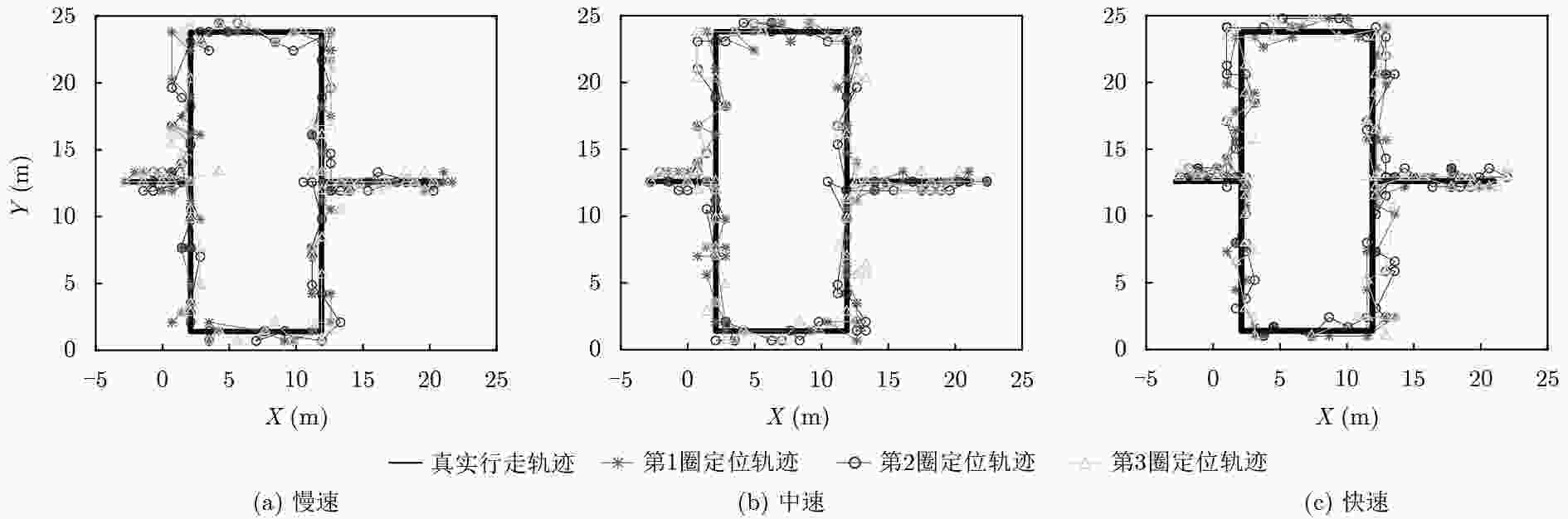
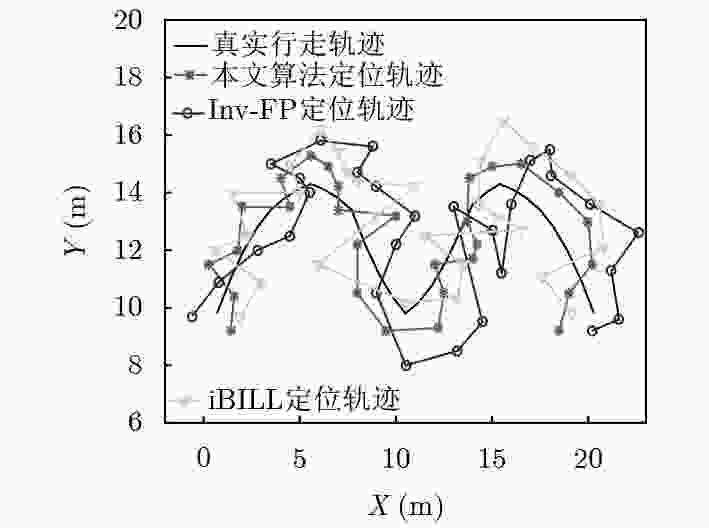
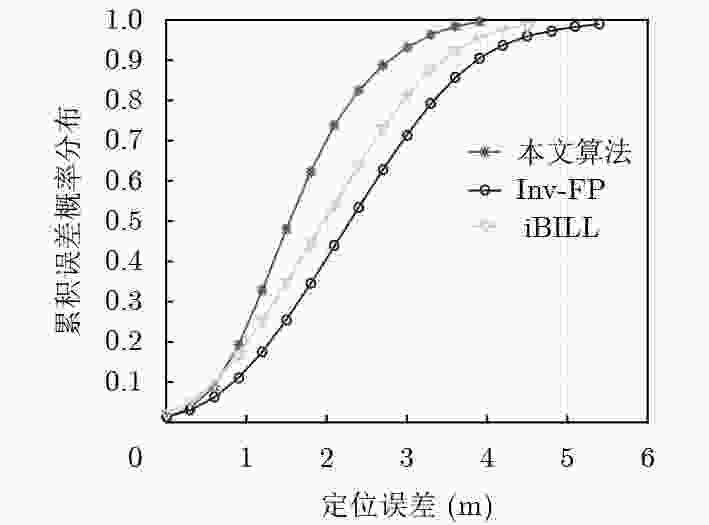
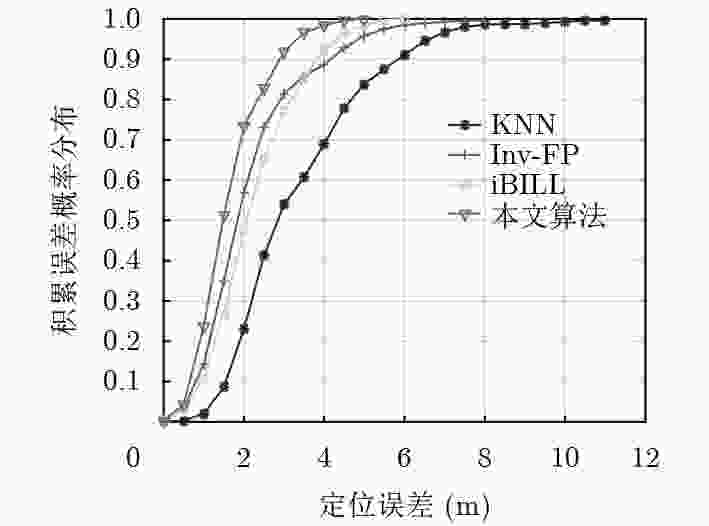
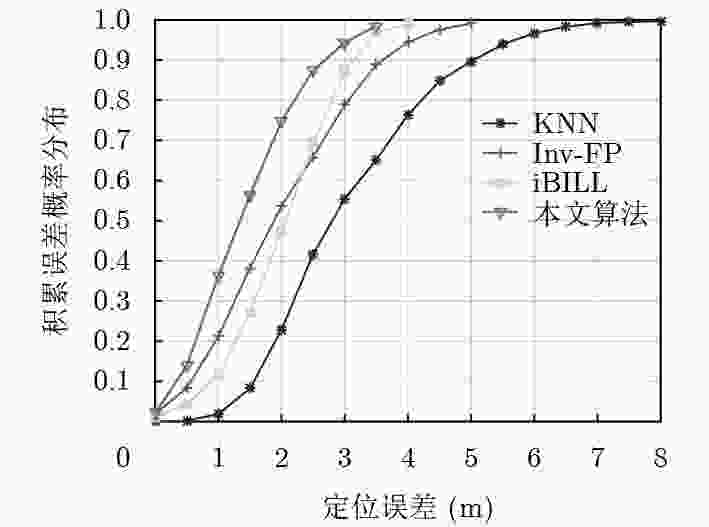
实验环境 算法类型 平均误差(m) 67%误差(m) 90%误差(m) 空旷大厅和走廊环境 KNN 3.46 4.03 5.91 Inv-FP 2.24 2.40 4.23 iBILL 2.33 2.62 3.94 本文算法 1.72 1.93 2.92 室内复杂
办公环境KNN 3.12 3.81 5.23 Inv-FP 2.11 2.59 3.61 iBILL 2.03 2.51 3.24 本文算法 1.54 1.82 2.77 -
VU T H N, RYU K H, and PARK N. A method for predicting future location of mobile user for location-based services system[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2009, 57(1): 91–105. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2008.07.009 GEZICI S, TIAN Zhi, GIANNAKIS G B, et al. Localization via ultra-wideband radios: a look at positioning aspects for future sensor networks[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2005, 22(4): 70–84. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2005.1458289 WANG Yixin, YE Qiang, CHENG Jie, et al. RSSI-based Bluetooth indoor localization[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 11th International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks, Shenzhen, China, 2015: 165–171. doi: 10.1109/MSN.2015.14. WILLEMSEN T, KELLER F, and STERNBERG H. Concept for building a MEMS based indoor localization system[C]. Proceedings of 2014 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Busan, South Korea, 2014: 1–10. doi: 10.1109/IPIN.2014.7275461. YANG Bo, LEI Yiqun, and YAN Bei. Distributed multi-human location algorithm using naive Bayes classifier for a binary pyroelectric infrared sensor tracking system[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(1): 216–223. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2477540 KUNG H Y, CHAISIT S, and PHUONG N T M. Optimization of an RFID location identification scheme based on the neural network[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2015, 28(4): 625–644. doi: 10.1002/dac.2692 JEON W S and JEONG D G. Enhanced channel access for connection state of Bluetooth low energy networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(9): 8469–8481. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2675915 周牧, 王斌, 田增山, 等. 室内BLE/MEMS跨楼层融合定位算法[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(5): 2017076. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017076ZHOU Mu, WANG Bin, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Indoor BLE and MEMS based multi-floor fusion positioning algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(5): 2017076. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017076 LIN C P, TANG S H, LIN C H, et al. An improved modeling of TDR signal propagation for measuring complex dielectric permittivity[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2015, 26(6): 827–834. doi: 10.1007/s12583-015-0599-7 王艳丽, 杨如民, 余成波, 等. 相关性匹配蓝牙信标位置指纹库的室内定位[J]. 电讯技术, 2017, 57(2): 145–150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2017.02.004WANG Yanli, YANG Rumin, YU Chengbo, et al. Indoor localization of Bluetooth beacon position fingerprint based on correlation Algorithm[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2017, 57(2): 145–150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2017.02.004 XU Xiaolong, TANG Yu, WANG Xinheng, et al. Variance-based fingerprint distance adjustment algorithm for indoor localization[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 26(6): 1191–1201. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2015.00130 CHEN Kongyang, WANG Chen, YIN Zhimeng, et al. Slide: towards fast and accurate mobile fingerprinting for Wi-Fi indoor positioning systems[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(3): 1213–1223. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2778082 JUN J, HE Liang, GU Yu, et al. Low-overhead WiFi fingerprinting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(3): 590–603. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2737426 AN J H and CHOI L. Inverse fingerprinting: Server side indoor localization with Bluetooth low energy[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, Valencia, Spain, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2016.7794891. WU Xudong, SHEN Ruofei, FU Luoyi, et al. iBILL: Using iBeacon and inertial sensors for accurate indoor localization in large open areas[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 14589–14599. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2726088 庞业勇, 王少军, 彭宇, 等. 一种在线时间序列预测的核自适应滤波器向量处理器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(1): 53–62. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150157PANG Yeyong, WANG Shaojun, PENG Yu, et al. A kernel adaptive filter vector processor for online time series prediction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 53–62. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150157 冯少江, 徐泽宇, 石明全, 等. 基于改进扩展卡尔曼滤波的姿态解算算法研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2017, 44(9): 227–229, 249. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.09.042FENG Shaojiang, XU Zeyu, SHI Mingquan, et al. Research on attitude algorithm based on improved extended caiman filter[J]. Computer Science, 2017, 44(9): 227–229, 249. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2017.09.042 谷阳, 宋千, 李杨寰, 等. 基于惯性鞋载传感器的人员自主定位粒子滤波方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(2): 484–488. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140362GU Yang, SONG Qian, LI Yanghuan, et al. A particle filter method for pedestrian navigation using foot-mounted inertial sensors[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(2): 484–488. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140362 PEVNY T, BAS P, and FRIDRICH J. Steganalysis by subtractive pixel adjacency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2010, 5(2): 215–224. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2010.2045842 JINDALERTUDOMDEE J, HAYASHIDA M, ZHAO Yang, et al. Enumeration method for tree-like chemical compounds with benzene rings and naphthalene rings by breadth-first search order[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2016, 17: 113. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-0962-4 XIAO Ying and YIN Fuliang. Blind equalization based on RLS algorithm using adaptive forgetting factor for underwater acoustic channel[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2014, 28(3): 401–408. doi: 10.1007/s13344-014-0032-5 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
