Remote Sensing Image Classification Method Based on Deep Convolution Neural Network and Multi-kernel Learning
-
摘要:
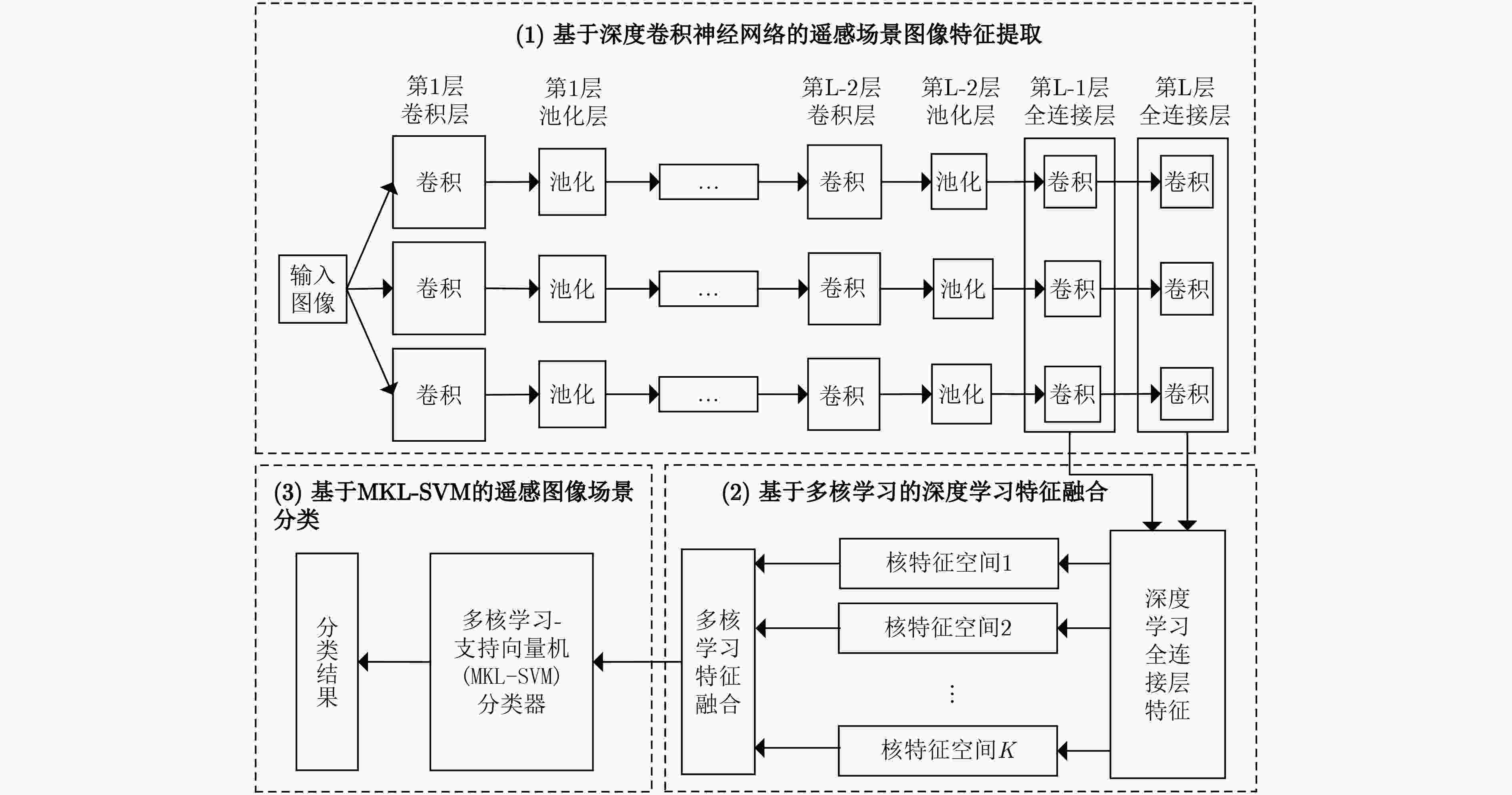
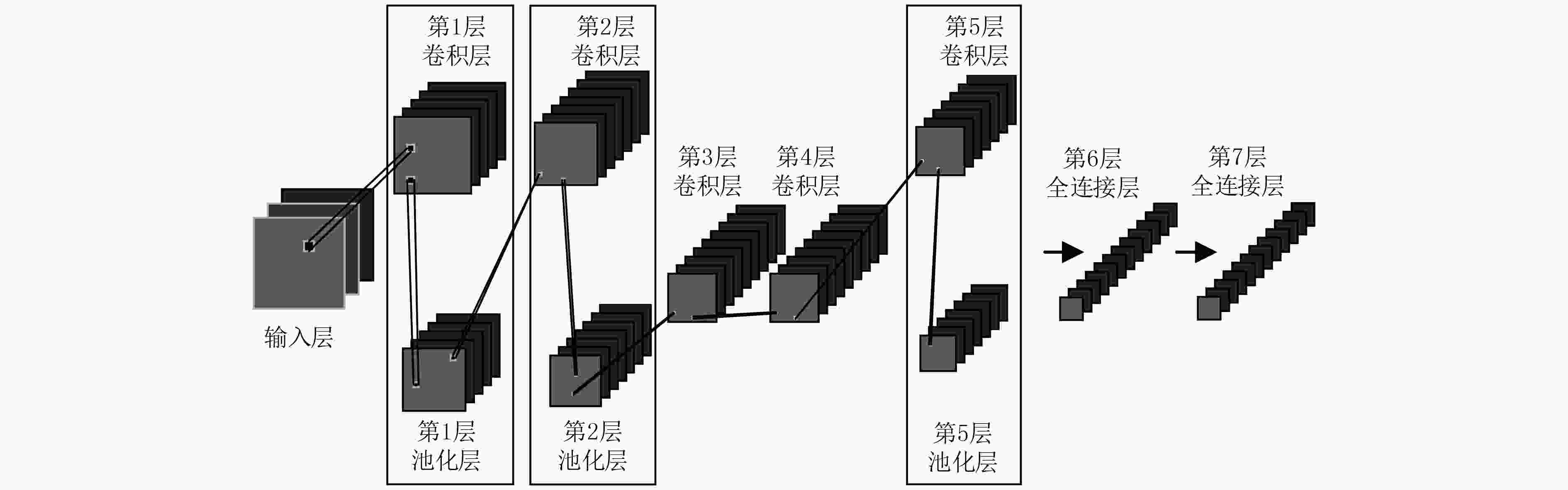
为解决传统遥感图像分类方法特征提取过程复杂、特征表现力不强等问题,该文提出一种基于深度卷积神经网络和多核学习的高分辨率遥感图像分类方法。首先基于深度卷积神经网络对遥感图像数据集进行训练,学习得到两个全连接层的输出将作为遥感图像的两种高层特征;然后采用多核学习理论训练适合这两种高层特征的核函数,并将它们映射到高维空间,实现两种高层特征在高维空间的自适应融合;最后在多核融合特征的基础上,设计一种基于多核学习-支持向量机的遥感图像分类器,对遥感图像进行精确分类。实验结果表明,与目前已有的基于深度学习的遥感图像分类方法相比,该算法在分类准确率、误分类率和Kappa系数等性能指标上均有所提升,在实验测试集上3个指标分别达到了96.43%, 3.57%和96.25%,取得了令人满意的结果。
Abstract:To solve the problems of complex feature extraction process and low characteristic expressiveness of traditional remote sensing image classification methods, a high resolution remote sensing image classification method based on deep convolution neural network and multi-kernel learning is proposed. Firstly, the deep convolution neural network is constructed to train the remote sensing image data set to learn the outputs of two fully connected layers, which are taken as two high-level features of remote sensing images. Then, the multi-kernel learning is used to train the kernel functions for these two high-level features, so that they can be mapped to the high dimensional space, where these two features are fused adaptively. Finally, with the combined features, a remote sensing image classifier based on Multi-Kernel Learning-Support Vector Machine (MKL-SVM) is designed for remote sensing image classification. Experimental results show that compared with the existing deep learning based remote sensing classification methods, the proposed algorithm achieves improved results in terms of classification accuracy, error, and Kappa coefficient. On the experimental test set, the above three indicators reach 96.43%, 3.57%, and 96.25% respectively, and satisfactory results are obtained.
-
表 1 3种算法各分类性能指标值
指标 算法1 算法2 本文算法 Ac 0.8808 0.9337 0.9643 Er 0.1192 0.0663 0.0357 Kappa系数 0.8748 0.9304 0.9625 -
WANG Xin, SHEN Siqiu, NING Chen, et al. Multi-class remote sensing objects recognition based on discriminative sparse representation[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(6): 1381–1394. doi: 10.1364/ao.55.001381 WANG Xin, XIONG Xingnan, NING Chen, et al. Integration of heterogeneous features for remote sensing scene classification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 15–23. doi: 10.1117/1.jrs.12.015023 NING Chen, LIU Wenbo, ZHANG Gong, et al. Enhanced synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition method based on novel features[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(31): 8893–8904. doi: 10.1364/ao.55.008893 冯子勇. 基于深度学习的图像特征学习和分类方法的研究及应用[D]. [博士论文], 华南理工大学, 2016.FENG Ziyong. Research and application of image feature learning and classification methods based on deep learning[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], South China University of Technology, 2016. 林妙真. 基于深度学习的人脸识别研究[D]. [硕士论文], 大连理工大学, 2013.LIN Miaozhen. Research on face recognition based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Dalian University of Technology, 2013. 奚雪峰, 周国栋. 面向自然语言处理的深度学习研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1445–1465. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150682XI Xuefeng and ZHOU Guodong. A survey on learning for natural language processing[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1445–1465. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150682 张建华. 基于深度学习的语音识别应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2015.ZHANG Jianhua. Research into speech recognition application based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2015. 刘大伟, 韩玲, 韩晓勇. 基于深度学习的高分辨率遥感影像分类研究[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(4): 306–314. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0428001LIU Dawei, HAN Ling, and HAN Xiaoyong. High spatial resolution remote sensing image classification based on deep learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(4): 306–314. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0428001 曲景影, 孙显, 高鑫. 基于CNN模型的高分辨率遥感图像目标识别[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2016, 35(8): 45–50. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2016.08.011QU Xianying, SUN Xian, and GAO Xin. Remote sensing image target recognition based on CNN[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2016, 35(8): 45–50. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2016.08.011 周敏, 史振威, 丁火平. 遥感图像飞机目标分类的卷积神经网络方法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2017, 22(5): 702–708. doi: 10.11834/jig.160595ZHOU Min, SHI Zhenwei, and DING Huoping. Aircraft classification in remote-sensing images using convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2017, 22(5): 702–708. doi: 10.11834/jig.160595 黄洁, 姜志国, 张浩鹏, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的遥感图像舰船目标检测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(9): 1841–1848. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0755HUANG Jie, JIANG Zhiguo, ZHANG Haopeng, et al. Ship object detection in remote sensing images using convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2017, 43(9): 1841–1848. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0755 LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 GAO Ligang, CHEN Paiyu, and YU Shimeng. Demonstration of convolution kernel operation on resistive crosspoint array[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2016, 7(7): 870–873. doi: 10.1109/LED.2016.2573140 GIRSHICK R, IANDOLA F, DARRELL T, et al. Deformable part models are convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA, 2015: 437–446. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298641. HINTON G E. How neural networks learn from experience[J]. Scientific American, 1992, 267(3): 145–151. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0992-144 BOUVRIE J. Notes on convolutional neural networks[R]. Massachusetts: Center for biological and computational learning, 2006: 38–44. RUMELHAR T D E, HINTON G E, and WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533–536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. doi: 10.1145/3065386. NING Chen, LIU Wenbo, and WANG Xin. Infrared object recognition based on monogenic features and multiple kernel learning[C]. The 2018 IEEE International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing. Chongqing, China, 2018: 204–208. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
