Efficient Workload Balance Technology on Many-core Crypto Processor
-
摘要:
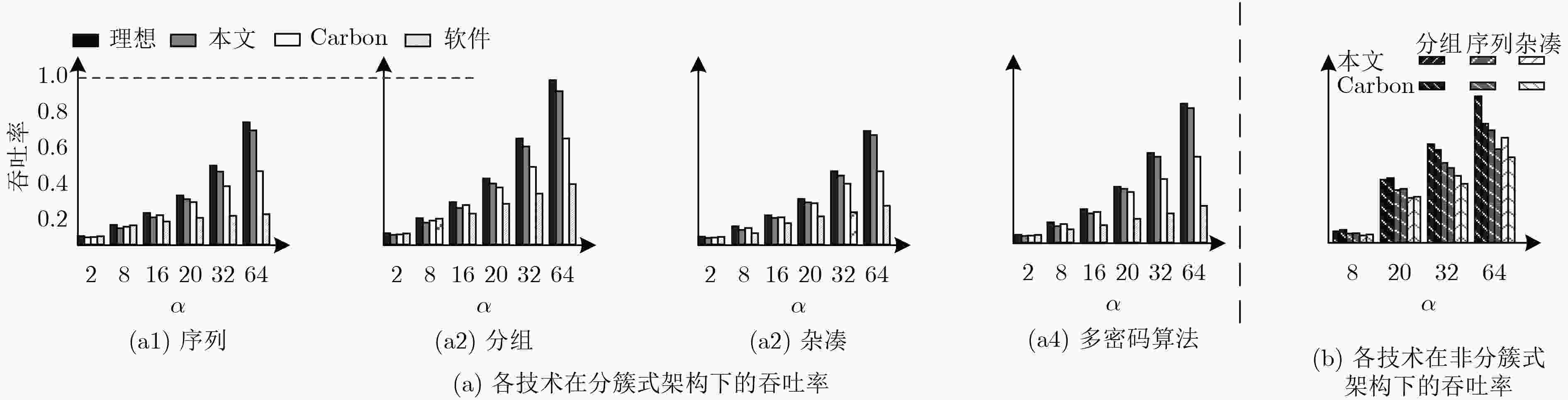
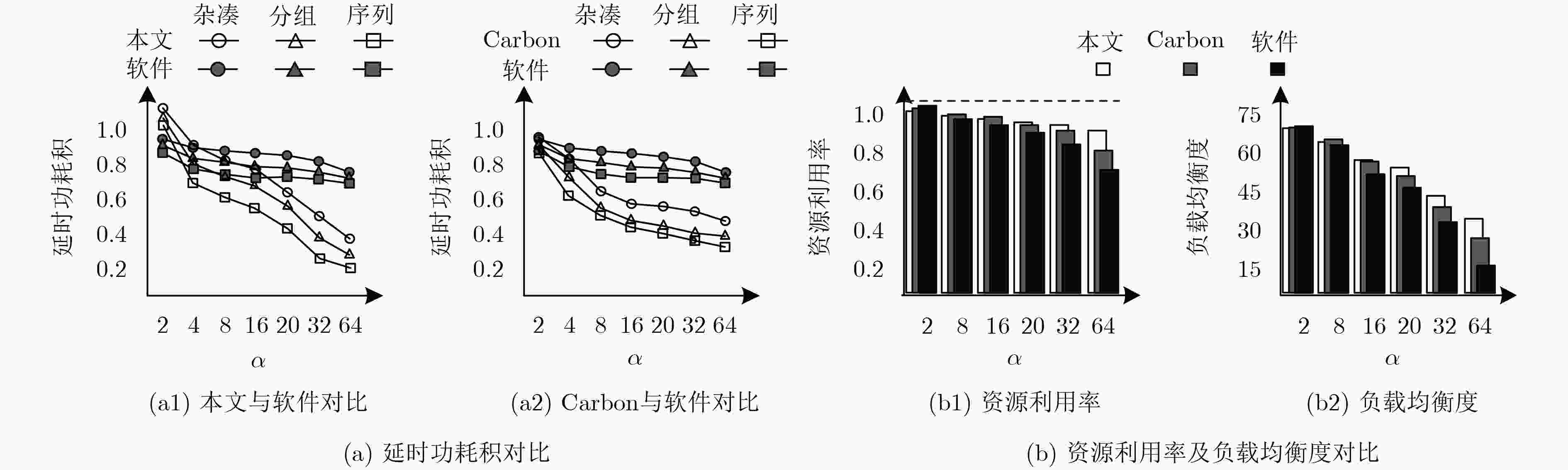
工作负载分配不均是制约众核密码平台资源利用率提高的重要因素,动态负载分配可提高平台资源利用率,但具有一定开销;所以更高的负载均衡频率并不一定带来更高的负载均衡增益。因此,该文建立了关于负载均衡增益率与负载均衡频率的数学模型。基于模型,提出一种面向众核密码平台的无冲突负载均衡策略和一种基于硬件作业队列的“可扩展-可移植”负载均衡引擎——“簇间微网络-簇内环阵列”。实验证明:在性能、延时功耗积、资源利用率和负载均衡度方面,该文设计的负载均衡引擎与基于“作业窃取”的软件技术相比平均优化约4.06倍、7.17倍、23.01%和2.15倍;与基于“作业窃取”的硬件技术相比约优化1.75倍、2.45倍、10.2%、和1.41倍;与理想硬件技术相比,密码算法吞吐率平均只降低了约5.67%(最低3%)。实验结果表明该文技术具有良好的可扩展性和可移植性。
Abstract:Imbalanced workload distribution results in low resource utilization of many-core crypto-platform. Dynamic workload allocation can improve the resource utilization with some overhead. Therefore, a higher frequency of workload balancing is not equivalent to higher gains. This paper establishes a mathematical model for gain rate and frequency of workload balancing. Based on this model, a collision-free workload balancing policy is proposed for many-core crypto systems, and a hierarchical "expandable-portable" engine is put forward, which consists of "Inter-cluster micro-network and intra-cluster ring-array" adopting hardware job queue technology. Experiment results show that the proposed workload-balancing engine is 4.06, 7.17, 23.01% and 2.15 times higher than the software technology based on " job stealing” in terms of performance, delay power consumption, resource utilization and workload balance; 1.75, 2.45, 10.2%, and 1.41 times better compared with the hardware technology based on "job stealing". By contrast with the ideal hardware technology, the average throughput of encryption algorithms is only decreased by 5.67% (the lowest 3%). The experiment also proves the scalability and portability of the proposed technique.
-
表 1 无冲突负载均衡算法
Require:${L_{{\rm{td}}}},{N_{{\rm{cl}}}},{L_{{\rm{dt}}}},{T_{{\rm{cp}}}},{\rm{Thpu}}{{\rm{t}}_{{\rm{SM}}}},{\rm{Thpu}}{{\rm{t}}_{{\rm{Nt}}}},{S_{\rm{c}}}$//簇间均衡操作集合 1 Assign ${\rm{Balance\_c}} \leftarrow {\rm{True,}}{{{N}}_2} \leftarrow {\rm{Num}}[{S_{\rm{c}}}],{n_2} \leftarrow 0,{t_2} \leftarrow {T_{{\rm{op}}}}$
${t_3} \leftarrow ({L_{{\rm{td}}}} + {L_{{\rm{dt}}}})/{\rm{Thpu}}{{\rm{t}}_{{\rm{SM}}}},{t_4} \leftarrow ({L_{{\rm{td}}}} + {L_{{\rm{dt}}}})/{\rm{Thpu}}{{\rm{t}}_{Nt}}$2 while new ${\rm{job[}}k{\rm{][}}i{\rm{] = = True}}$ do//更新负载情况 3 ${t_{\rm{1}}} \leftarrow {L_{{\rm{tdki}}}} \cdot {N_{{\rm{clki}}}} \cdot {L_{{\rm{dtki}}}};{\rm{Addc}}[k] \leftarrow {\rm{Addc}}[k] + {t_1};$ 4 end while 5 while ${\rm{Balance\_c}} = = {\rm{True}}$ do//簇间负载均衡 6 for $k \leftarrow 0$ to ${N_2}$ do 7 for $w \leftarrow 0$ to ${N_2}$ do 8 if $w \ne k$ then 9 if ${\rm{Thpu}}{{\rm{t}}_{{\rm{SM}}}} \ge {\rm{Thpu}}{{\rm{t}}_{Nt}}$ then 10 if ${\rm{Addp[}}k{\rm{] - Addp[}}w{\rm{] - }}{t_{\rm{1}}}{\rm{ > }}{t_{2}}{\rm{ + }}{t_{\rm{4}}}$ then//式(13) 11 ${\rm{Balancep\_Request[}}w{\rm{][}}k{]} \leftarrow {\rm{True;}}$ 12 ${\rm{Balancec\_Request[}}w{]} = {\rm{Balancec\_Request[}}w{]} + 1;$ 13 end if 14 else then 15 if ${\rm{Addp[}}k{\rm{] - Addp[}}w{\rm{] - }}{t_{\rm{1}}} > {t_2} + {t_3}$ then//式(13) 16 ${\rm{Balancep\_Request[}}w{\rm{][}}k{]} \leftarrow {\rm{True;}}$ 17 ${\rm{Balancec\_Request[}}w{]} = {\rm{Balancec\_Request[}}w{]} + 1;$ 18 end if 19 end else 20 end for 21 if ${\rm{Balancec\_Request[}}w{]} > 1$ then 22 ${\rm{choose }}\ p{\rm{[}}{{\rm{n}}_{2}}{\rm{];}}{n_2} \leftarrow {(}{n_{2}}{\rm{ + 1)mol}}{N_{2}};$ 23 end if 24 end for 25 end while 表 2 仿真参数
参数 值 核心数目 4~64 本地缓存大小 8 kB 共享缓存大小 16 MB 簇内互连方式 二向环 簇间互连方式 2D-mesh 共享访问延时/本地访问延时 3 表 3 测试基准说明
测试基准 算法分类 算法特征
(bit)作业数目 平均作业
大小(kB)测试基准 算法分类 算法特征
(bit)作业数目 平均作业
大小(kB)备注 DES 分组 64 1024 54.4 A5 序列 1 1024 41.1 算法特征表示分组/杂凑算法的处理位宽或者序列算法的输出位宽 AES 分组 128 1024 46.3 ZUC 序列 32 1024 50.4 SM4 分组 512 1024 32.2 RC4 序列 8 1024 47.3 SHA256 杂凑 512 1024 44.6 RSA 公钥 — 1024 40.3 SM3 杂凑 512 1024 38.8 SM2 公钥 — 1024 22.8 SHA-1 杂凑 512 1024 33.2 -
KIM C and HUH J. Exploring the design space of fair scheduling supports for asymmetric multicore systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2018, 67(8): 1136–1152. doi: 10.1109/TC.2018.2796077 KIM K W, CHO Y, EO J, et al. System-wide time versus density tradeoff in real-time multicore fluid scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2018, 67(7): 1007–1022. doi: 10.1109/TC.2018.2793919 LEE J, NICOPOULOS C, LEE H G, et al. IsoNet: Hardware-based job queue management for many core architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 2013, 21(6): 1080–1093. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2012.2202699 KUMAR S, HUGHES C J and NGUYEN A. Carbon: Architectural support for fine-grained parallelism on chip multiprocessors[C]. International Symposium on Computer Architecture, California, USA, 2007: 162–173. CHEN J, JUANG P, KO K, et al. Hardware-modulated parallelism in chip multiprocessors[J]. ACM Sigarch Computer Architecture News, 2005, 33(4): 54–63. doi: 10.1145/1105734.1105742 LEE J, NICOPOULOS C, LEE Y, et al. Hardware-based job queue management for manycore architectures and OpenMP environments[J]. IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium, 2011, 21(6): 407–418. doi: 10.1109/IPDPS.2011.47 刘宗斌, 马原, 荆继武, 等. SM3哈希算法的硬件实现与研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2011, 59(9): 191–193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2011.09.059LIU Zongbin, MA Yuan, JING Jiwu, et al. Implementation of SM3 hash function on FPGA[J]. Information Network Security, 2011, 59(9): 191–193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2011.09.059 徐金甫, 杨宇航. SM4算法在粗粒度阵列平台的并行化映射[J]. 电子技术应用, 2017, 43(4): 39–42.XU Jinfu and YANG Yuhang. Parallel mapping of SM4 algorithm on coarse-grained array platform[J]. Electronic Technology Application, 2017, 43(4): 39–42. DUBEY P. Recognition, mining and synthesis moves computers to the era of tera[J]. Technology@Intel Magazine, 2005, 9(2): 1–10. RATTNER J. Cool codes for hot chips: A quantitative basis for multi-core design[C]. Hot Chips 18 Symposium IEEE, Cupertino, USA, 2016: 1–28. AN H, TAURA K, and SPOTTER D. A tool for spotting scheduler-caused delays in task parallel runtime systems[C]. IEEE International Conference on CLUSTER Computing, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 114–125. KWOK Y K and AHMAD I. Static scheduling algorithms for allocating directed task graphs to multiprocessors[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 1999, 31(4): 406–471. doi: 10.1145/344588.344618 TITHI J J, MATANI D, MENGHANI G, et al. Avoiding locks and atomic instructions in shared-memory parallel BFS using optimistic parallelization[C]. Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops & Phd Forum IEEE, Cambridge, UK, 2013: 1628–1637. MOON S W, REXFORD J, and SHIN K G. Scalable hardware priority queue architectures for high-speed packet switches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2000, 49(11): 1215–1227. doi: 10.1109/RTTAS.1997.601359 CHEN Quan, ZHENG Long, and GUO Minyi. Adaptive Demand-aware Work-stealing in Multi-programmed Multi-core Architectures[J]. Concurrency and Computation: practice & Experience, 2016, 28(2): 455–471. doi: 10.1002.cpe.3619 -





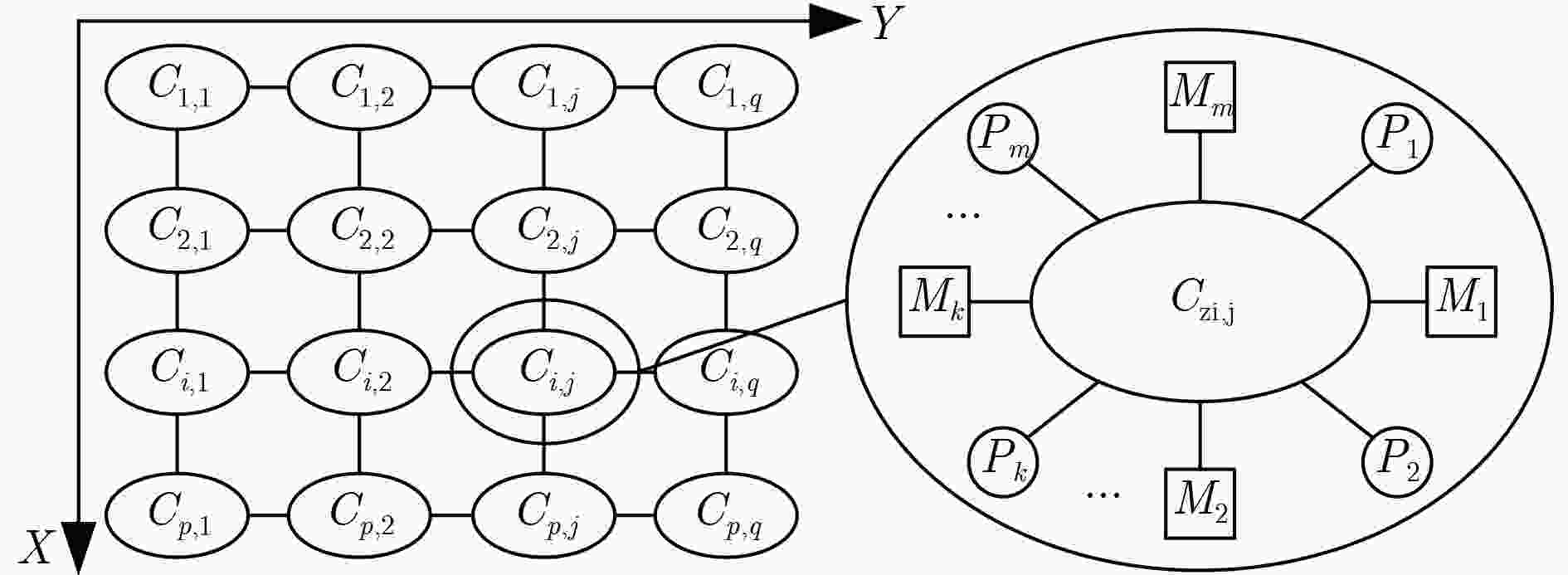
 下载:
下载:
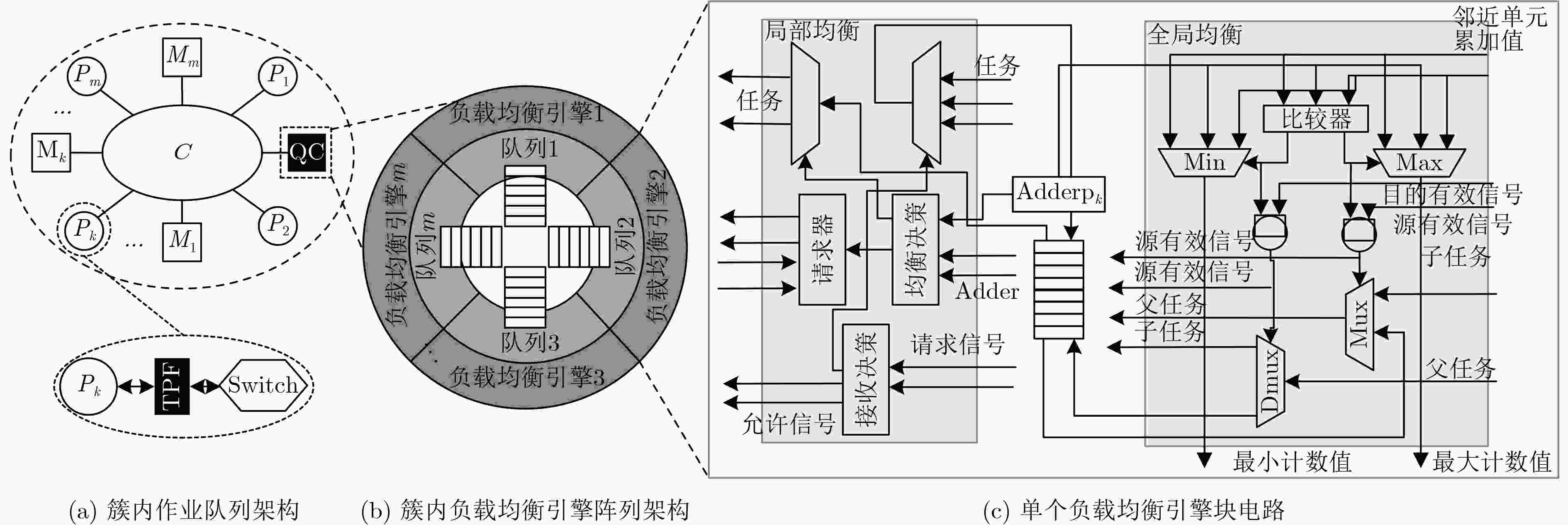
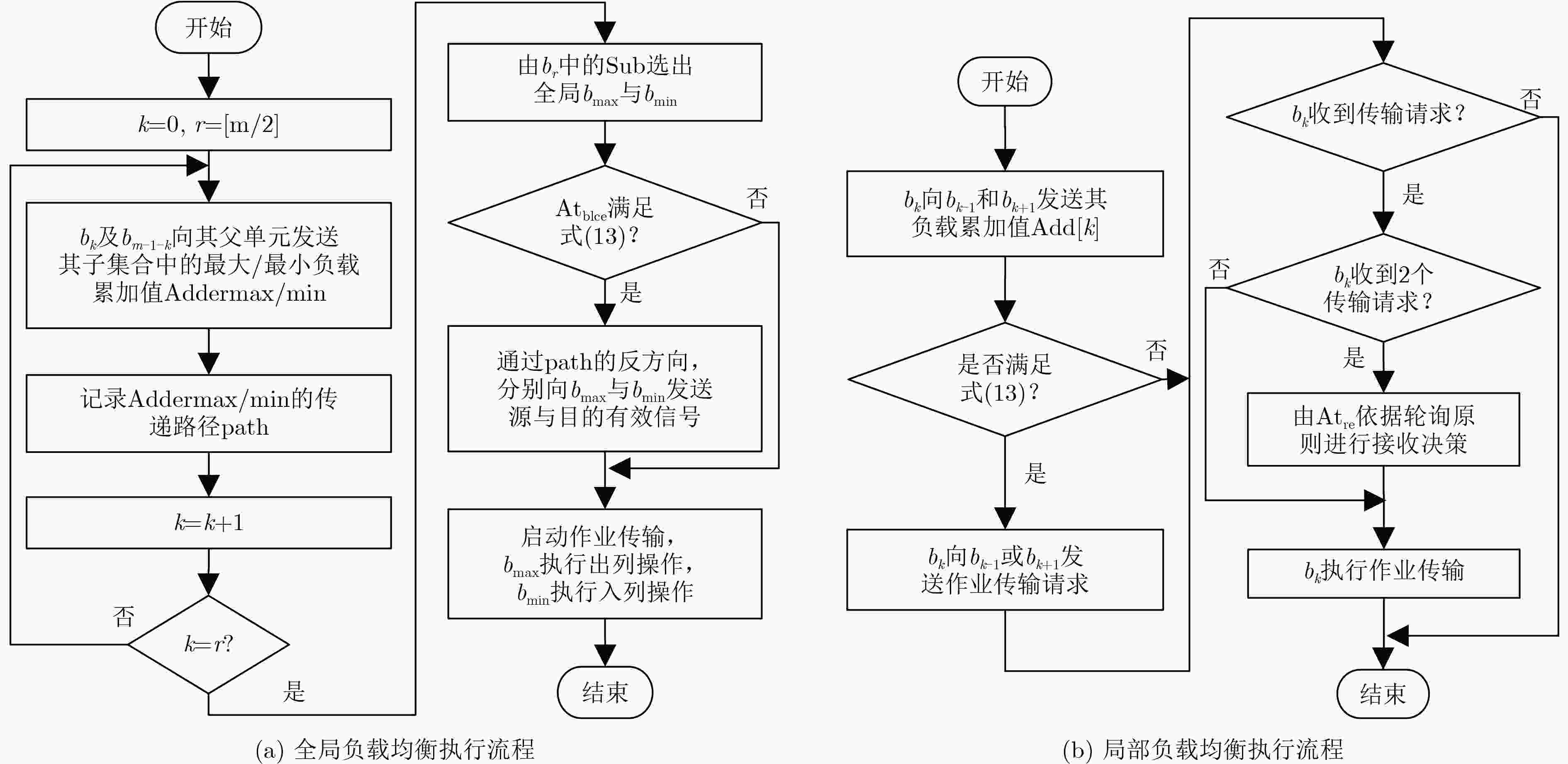
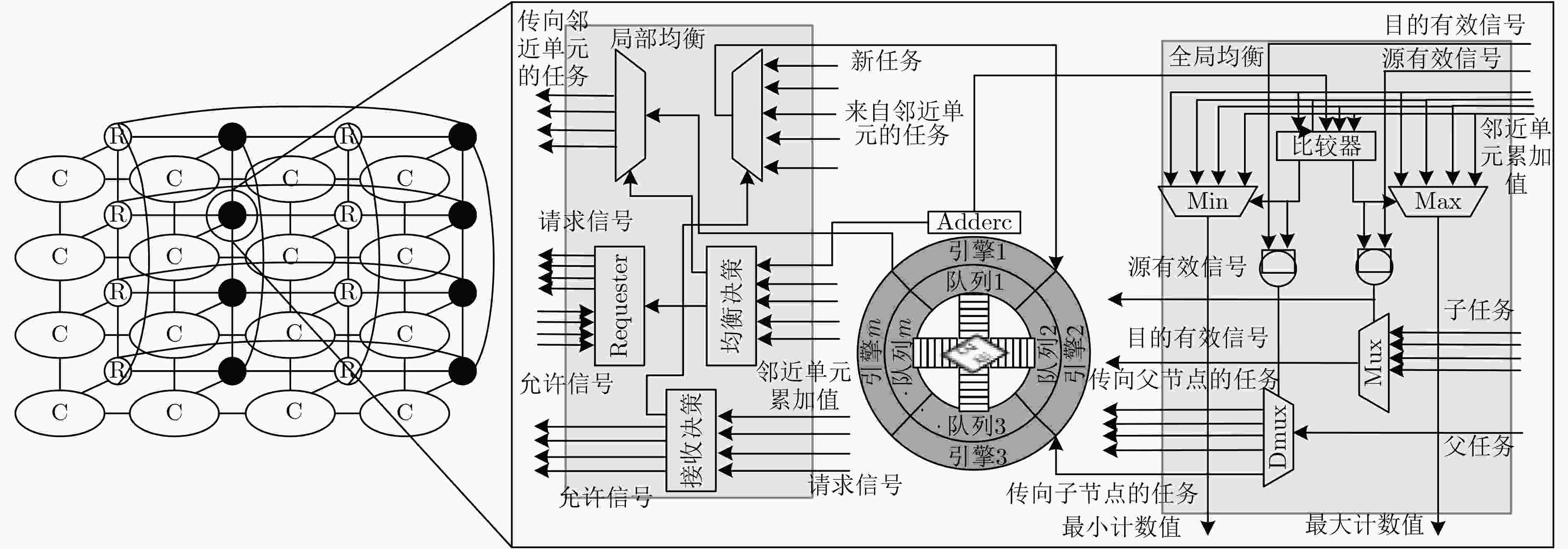


 下载:
下载:
