Data Anonymous Collection Protocol without Trusted Third Party
-
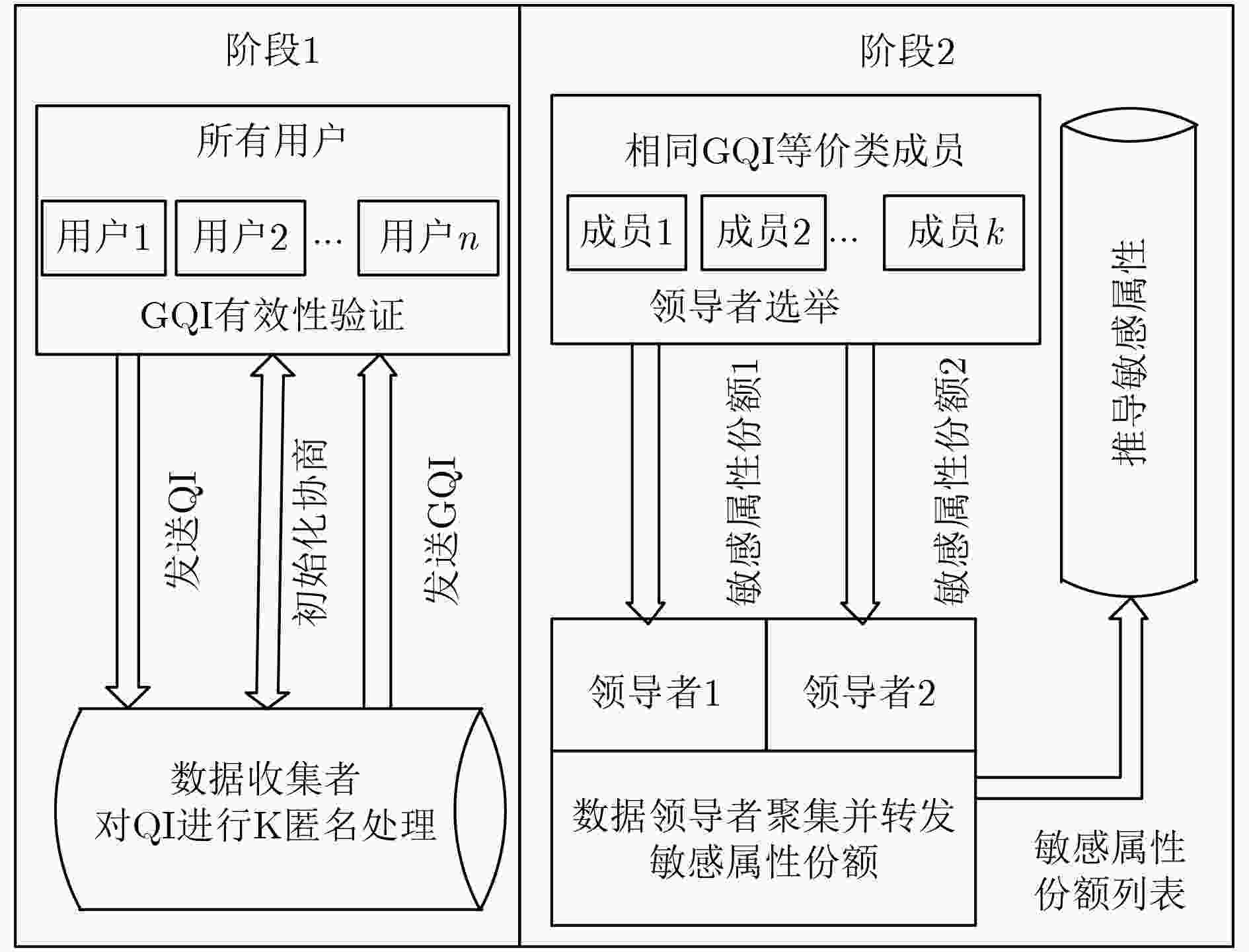
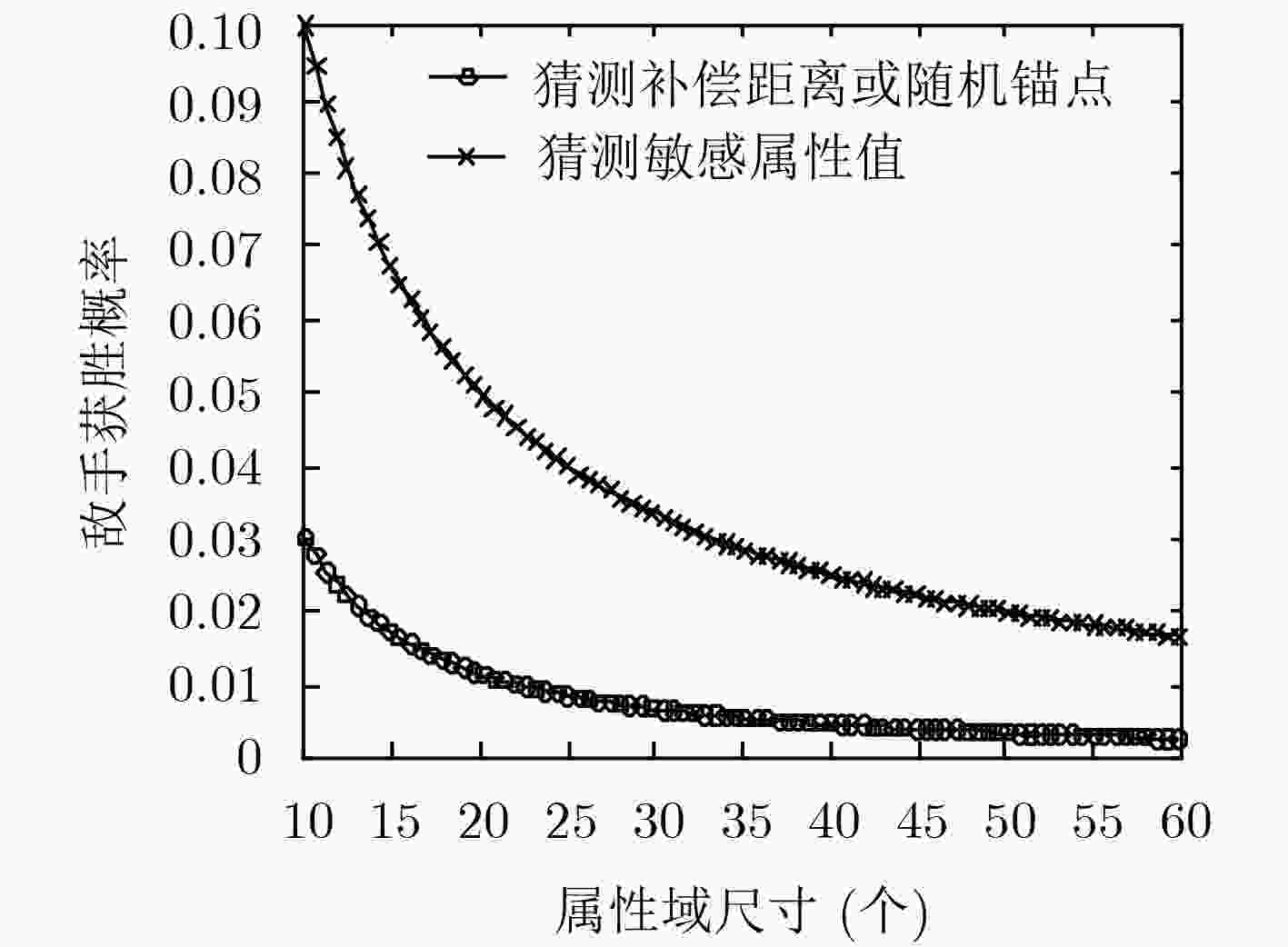
摘要: 针对半诚信的数据收集者对包含敏感属性(SA)数据收集和使用过程中可能造成隐私泄露问题,该文在传统模型中增加实时的数据领导者,并基于改进模型提出一个隐私保护的数据收集协议,确保无可信第三方假设前提下,数据收集者最大化数据效用只能建立在K匿名处理过的数据基础上。数据拥有者分布协作的方式参与协议流程,实现了准标识(QI)匿名化后SA的传输,降低了数据收集者通过QI关联准确SA值的概率,减弱内部标识揭露造成隐私泄露风险;通过树形编码结构将SA的编码值分为随机锚点和补偿距离两份份额,由K匿名形成的等价类成员选举获取两个数据领导者,分别对两份份额进行聚集和转发,解除唯一性的网络标识和SA值的关联,有效防止外部标识揭露造成的隐私泄露;建立符合该协议特性的形式化规则并对协议进行安全分析,证明了协议满足隐私保护需求。Abstract: Semi-honest data collectors may cause privacy leaks during the collection and use of Sensitive Attribute (SA) data. In view of the problem, real-time data leaders are added in the traditional model and a privacy-protected data collection protocol based on the improved model is proposed. Without the assumption of trusted third party, the protocol ensures that data collectors maximization data utility can only be established on the basis of K-anonymized data. Data owners participates in the protocol flow in a distributed and collaborative manner to achieve the transmission of SA after the Quasi-Identifier (QI) is anonymized. This reduces the probability that the data collector uses the QI to associate SA values and weakens the risk of privacy leakage caused by internal identity disclosure. It divides the coded value of the SA into two shares of a random anchor point and a compensation distance through the tree coding structure and the members of the equivalent class formed by K-anonymity elect two data leaders to aggregate and forward the two shares respectively, which releases the association between unique network identification and SA values and prevents leakage of privacy caused by external identification effectively. Formal rules are established that meet the characteristics of the protocol and analyze the protocol to prove that the protocol meets privacy protection requirements.
-
Key words:
- Data privacy /
- Privacy protection /
- K-anonymity /
- Sensitive Attribute (SA) /
- Anonymization
-
表 1 阶段1协议步骤
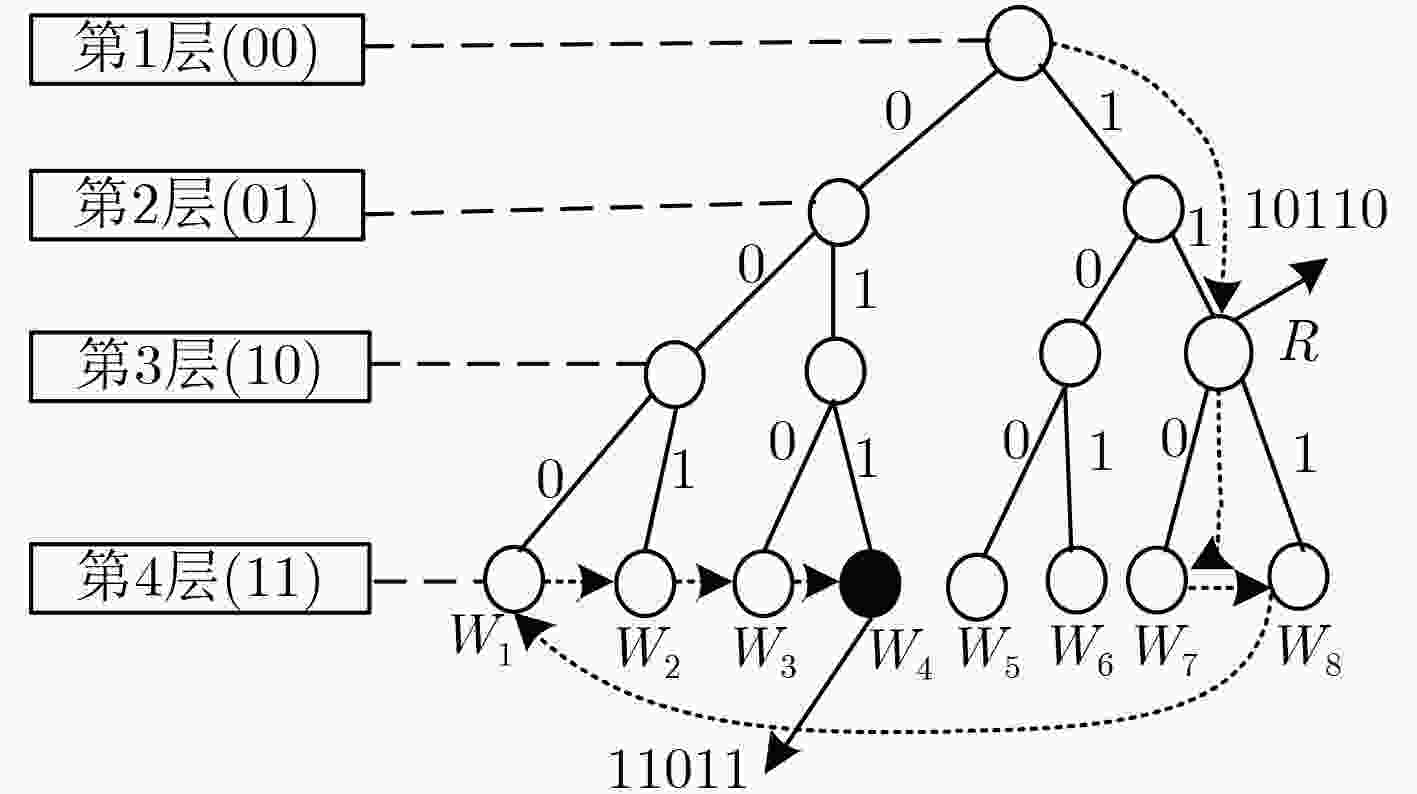
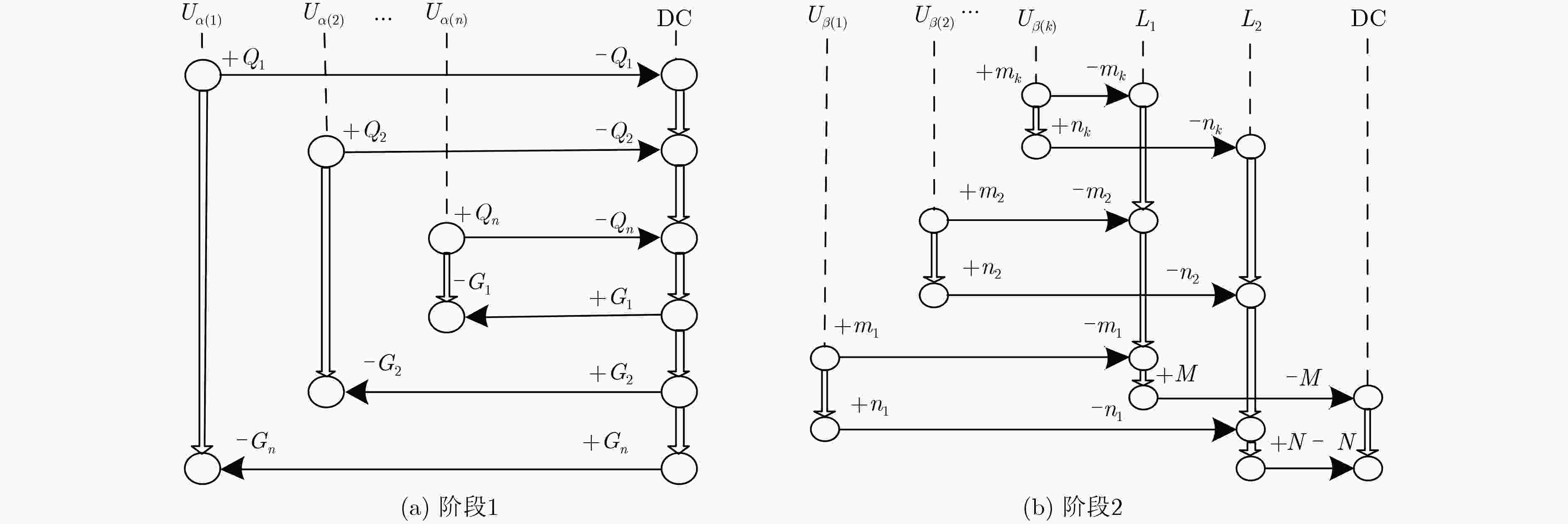
(1) for ${U_i} \in \text{U}$, $1 \le i \le N$ do ${U_i}$发送${Q_i}$给${\rm{DC}}$. (2) ${\rm{DC}}$通过K匿名将$Q$泛化为$G$ for ${G_j} \in \text{G}$, $1 \le j \le M$ do (3) for ${G_j}$中元组对应的${U_k}$, $1 \le k \le K$ do ${\rm{DC}}$向${U_k}$发送${G_j}$ if 每个${U_k}$验证${G_j}$是有效,进入阶段2 else 终止协议 表 2 阶段2协议步骤
(1) for $ {G_j} \in \text{G}$, $ 1 \le j \le M$ do 随机选取领导者$ L_1^j$和$ L_2^j$ for $ {G_j}$中元组对应的$ {{U}_{k}}$, $ 1 \le k \le K$ do 发送$ ({G_j},{R_k})$和$ ({G_j},{D_k})$分别给$ L_1^j$和$ L_2^j$ (2) $ L_1^j$和$ L_2^j$分别聚集$ ({G_j},{R_k})$和$ ({G_j},{D_k})$列表的给$ {\rm{DC}}$ (3) for $ 1 \le i \le N$ do $ {\rm{DC}}$计算$ {W_i}{\rm{ = }}{R_i} \oplus {D_i}$ (4) 搜索$ {W_i}$映射的$ {S_i}$得到数据列表$ (\text{G},\text{S})$ -
曹珍富, 董晓蕾, 周俊, 等. 大数据安全与隐私保护研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(10): 2137–2151. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20160684CAO Zhenfu, DONG Xiaolei, ZHOU Jun, et al. Research advances on big data security and privacy preserving[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(10): 2137–2151. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20160684 包国华, 王生玉, 李运发. 云计算中基于隐私感知的数据安全保护方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017(1): 84–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2017.01.013BAO Guohua, WANG Shengyu, and LI Yunfa. Research on data security protection method based on privacy awareness in cloud computing[J]. Netinfo Security, 2017(1): 84–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2017.01.013 IMRUL K and ADRIANA I. Privacy and security in online social networks: A survey[J]. Online Social Networks and Media, 2017, 4(3): 1–21. doi: 10.1109/ICME.2011.6012166 SWEENEY L. k-Anonymity: A model for protecting privacy[J]. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, 2002, 10(5): 557–570. doi: 10.1142/S0218488502001648 MACHANAVAJJHALA A, GEHRKE J, KIFER D, et al. l-Diversity: Privacy beyond k-anonymity[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering, Atlanta, USA, 2006: 24. LI Ninghui, LI Tiancheng, and VENKATASUBRAMANIAN S. t-Closeness: Privacy beyond k-anonymity and l-diversity[C]. Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Data Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey, 2007: 106–115. DWORK C, KENTHAPADI K, MCSHERRY F, et al. Our data, ourselves: Privacy via distributed noise generation[C]. Proceedings of the 24th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Petersburg, Russia, 2006: 486–503. DWORK C, NAOR M, PITASSI T, et al. Differential privacy under continual observation[C]. Proceedings of the 42nd ACM symposium on Theory of Computing, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 2010: 715–724. CLARKE A and STEELE R. A smartphone-based system for population-scale anonymized public health data collection and Intervention[C]. Proceedings of the 47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, USA, 2014: 2908–2917. ZHONG Sheng, YANG Zhiqiang, and CHEN Tingting. k-anonymous data collection[J]. Information Sciences, 2009, 179(17): 2948–2963. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2009.05.004 XUE Mingqiang, PAPADIMITRIOU P, RAÏSSI C, et al. Distributed privacy preserving data collection[C]. Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications, Hongkong, China, 2011: 93–107. LI Hongtao, GUO Feng, ZHANG Wenyin, et al. (a, k)-Anonymous scheme for privacy-preserving data collection in IoT-based healthcare services systems[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2018, 42(3): 56. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-0896-7 刘琴, 刘旭辉, 胡柏霜, 等. 个人健康记录云管理系统中支持用户撤销的细粒度访问控制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1206–1212. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160621LIU Qin, LIU Xuhui, HU Baishuang, et al. Fine-grained access control with user revocation in cloud-based personal health record system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1206–1212. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160621 LUO Entao, BHUIYAN M Z A, WANG Guojun, et al. Privacy protector: Privacy-protected patient data collection in IoT-based healthcare systems[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(2): 163–168. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700364 龚奇源, 杨明, 罗军舟. 面向关系-事务数据的数据匿名方法[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(11): 2828–2842. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005099GONG Qiyuan, YANG Ming, and LUO Junzhou. Data anonymization approach for microdata with relational and transaction attributes[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(11): 2828–2842. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005099 KIM S and CHUNG Y D. An anonymization protocol for continuous and dynamic privacy-preserving data collection[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 93: 1065–1073. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.09.009 VILLADANGOS J, CORDOBA A, FARINA F, et al. Efficient leader election in complete networks[C]. Proceedings of the 13th Euromicro Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Network-Based Processing, Lugano, Switzerland, 2005: 136–143. 罗恩韬, 王国军. 移动社交网络中一种朋友发现的隐私安全保护策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(9): 2165–2172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151479LUO Entao and WANG Guojun. A novel friends matching privacy preserving strategy in mobile social networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(9): 2165–2172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151479 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
