Computing Offloading and Resource Optimization in Ultra-dense Networks with Mobile Edge Computation
-
摘要:
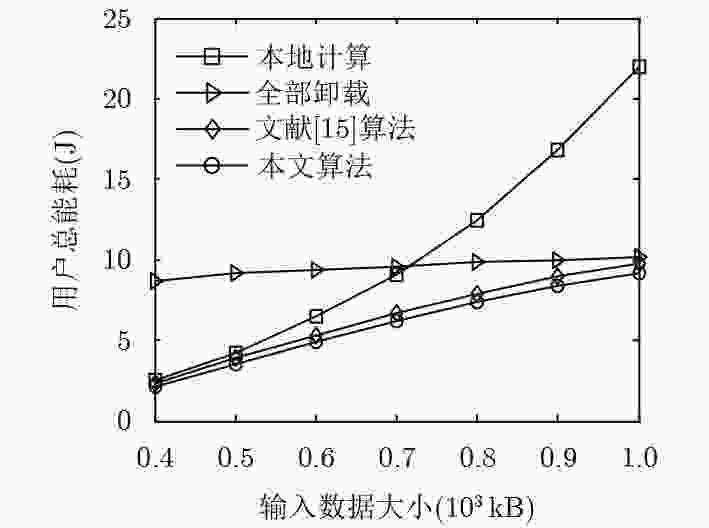
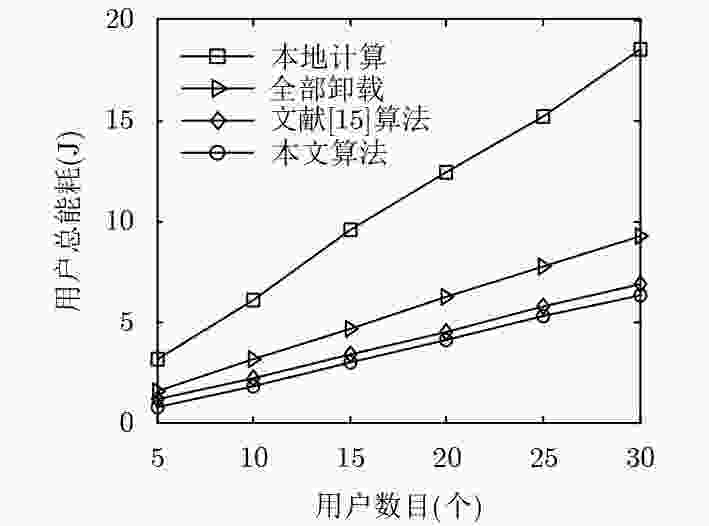
移动边缘计算(MEC)通过在无线网络边缘为用户提供计算能力,来提高用户的体验质量。然而,MEC的计算卸载仍面临着许多问题。该文针对超密集组网(UDN)的MEC场景下的计算卸载,考虑系统总能耗,提出卸载决策和资源分配的联合优化问题。首先采用坐标下降法制定了卸载决定的优化方案。同时,在满足用户时延约束下采用基于改进的匈牙利算法和贪婪算法来进行子信道分配。然后,将能耗最小化问题转化为功率最小化问题,并将其转化为一个凸优化问题得到用户最优的发送功率。仿真结果表明,所提出的卸载方案可以在满足用户不同时延的要求下最小化系统能耗,有效地提升了系统性能。
Abstract:Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) improves the quality of users experience by providing users with computing capabilities at the edge of the wireless network. However, computing offloading in MEC still faces some problems. In this paper, a joint optimization problem of offloading decision and resource allocation is proposed for the computation offloading problem in Ultra-Dense Networks (UDN) with MEC. To solve this problem, firstly, the coordinate descent method is used to formulate the optimization scheme for the offloading decision. Meanwhile, the improved Hungarian algorithm and greedy algorithm are used to allocate the channels to meet the user’s delay requirements. Finally, the problem of minimizing energy consumption is converted into a problem of minimizing power. Then it is converted into a convex optimization problem to get the user’s optimal transmission power. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme can minimize the energy consumption of the system while satisfying the users’ different delay requirements, and improve effectively the performance of the system.
-
表 1 任务卸载和资源分配算法
输入:用户数$N$,${t_n} = {\rm{(}}{w_n},{d_n}{\rm{,}}T_n^{\ {\rm{max}}}{\rm{)}}$,${f^c}$,初始卸载决定${{{A}}^0}$。 初始化:$l \leftarrow 0$, Repeat $l \leftarrow l + 1$ for $n = 1{\rm{ : }}N$ 根据式(13)得到${{{A}}^{l - 1}}{\rm{(}}n{\rm{)}}$; 采用改进的匈牙利算法和贪婪算法得到子信道分配矩阵${{{C}}_{{N_c} \times K}}$; 根据凸优化问题P3采用内点法求解得到每个子信道上最优的发
送功率$p_n^k$;根据式(12)计算$Q_n^l$; end $q_l^* \leftarrow {\rm{ma}}{{\rm{x}}_{n = 1, \cdots ,N}}Q_n^l$和$n_l^* \leftarrow {\rm{arg ma}}{{\rm{x}}_{n = 1, \cdots ,N}}Q_n^l$; 更新${{{A}}^l} \leftarrow {{{A}}^{l - 1}}\left( {n_l^*} \right)$; Until $q_l^* \le 0$; 输出:卸载决定矩阵${{{A}}^{\rm{*}}}$,信道分配矩阵${{C}}_{{N_c} \times K}^{\rm{*}}$,功率分配矩阵${{{P}}^{\rm{*}}}$。 表 2 仿真参数
参数 取值 子信道带宽$B$ 0.2 MHz 子信道个数 20 用户最大发送功率${P_{\max }}$ 23 dBm 空闲时电路功率消耗${P^i}$ 10 mW 背景噪声功率${\omega _0}$ –100 dBm 用户的计算能力$f_n^l$ 0.1~1 GHz/周期 计算任务的大小${d_n}$ 400~1200 kB 需要的CPU周期${w_n}$ 0.2~1 GHz 用户容忍最大时延$T_n^{\ \max }$ 1~4 s MEC的计算能力${f^c}$ 4 GHz/周期 -
WANG Shiqiang, ZAFER M, and LEUNG K K. Online placement of multi-component applications in edge computing environments[J]. IEEE Access, 2017(5): 2514–2533. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2665971 MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHANG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: the communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201 PAN Jianli and MCELHANNON J. Future edge cloud and edge computing for internet of things applications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(1): 439–449. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2767608 YANG Bin, MAO Guoqiang, DING Ming, et al. Dense small cell networks: from noise-limited to dense interference-limited[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(5): 4262–4277. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2794452 GE Xiaohu, TU Song, MAO Guoqiang, et al. 5G ultra-dense cellular networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2016, 23(1): 72–79. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2016.7422408 YANG Lichao, ZHANG Heli, LI Ming, et al. Mobile edge computing empowered energy efficient task offloading in 5G[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 6398–6409. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2799620 ZHANG Jiao, HU Xiping, NING Zhaolong, et al. Energy-latency tradeoff for energy-aware offloading in mobile edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(4): 2633–2645. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2786343 LIU Jianhui and ZHANG Qi. Offloading schemes in mobile edge computing for ultra-reliable low latency communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 12825–12837. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2800032 MAO Yuyi, ZHANG Jun, SONG S H, et al. Stochastic joint radio and computational resource management for multi-user mobile-edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(9): 5994–6009. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2717986 TI N T and LE Longbao. Computation offloading leveraging computing resources from edge cloud and mobile peers[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. ZHAO Pengtao, TIAN Hui, QIN Cheng, et al. Energy-saving offloading by jointly allocating radio and computational resources for mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2017(5): 11255–11268. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2710056 ZHANG Jing, XIA Weiwei, YAN Feng, et al. Joint computation offloading and resource allocation optimization in heterogeneous networks with mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 19324–19337. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2819690 GUO Jun, ZHANG Heli, YANG Lichao, et al. Decentralized computation offloading in mobile edge computing empowered small-cell networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Singapore, Singapore, 2017: 1–6. RANADHEERA S, MAGHSUDI S, and HOSSAIN E. Computation offloading and activation of mobile edge computing servers: a minority game[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(5): 688–691. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2810292 WANG Chenmeng, YU F R, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Joint computation offloading and interference management in wireless cellular networks with mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(8): 7432–7445. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2672701 DINH T Q, TANG Jianhua, LA Q D, et al. Offloading in mobile edge computing: task allocation and computational frequency scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(8): 3571–3584. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2699660 RAM S S, VEERAVALLI V V, and NEDIC A. Distributed non-autonomous power control through distributed convex optimization[C]. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2009, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009: 3001–3005. LIU Peng, LI Jiandong, LI Hongyan, et al. Convex optimisation-based joint channel and power allocation scheme for orthogonal frequency division multiple access networks[J]. IET Communications, 2015, 9(1): 28–32. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2014.0409 3GPP organizational parthners. Evolved universal terrestrial radio access (E-UTRA); Further advancements for E-UTRA physical layer aspects (Release 9), document TS 36.814, 3GPP[OL]. http://www.3gpp.org/ftp/,2012. -





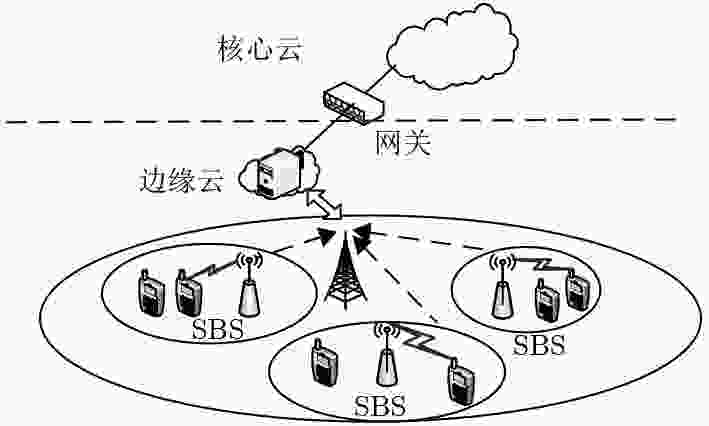
 下载:
下载:
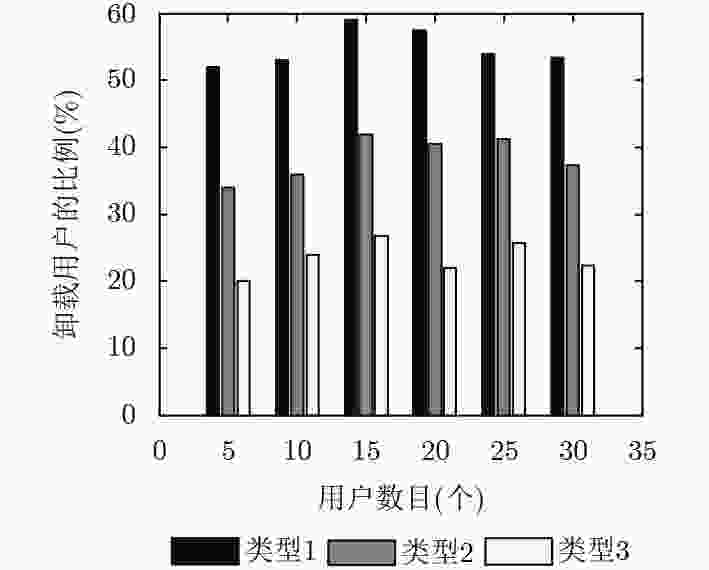
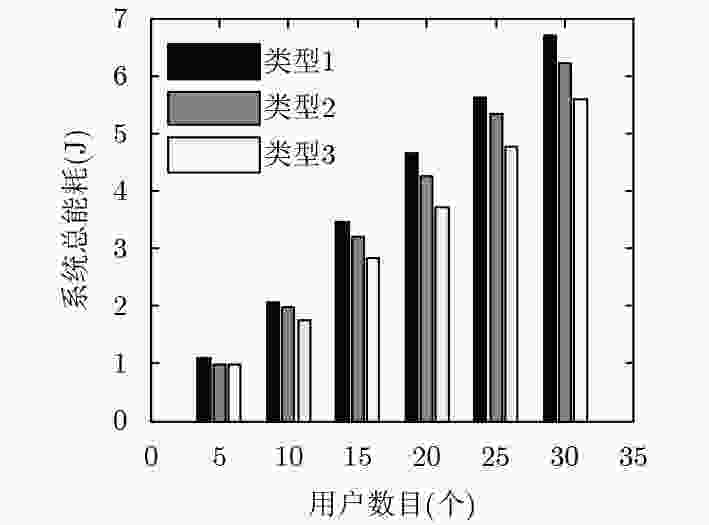
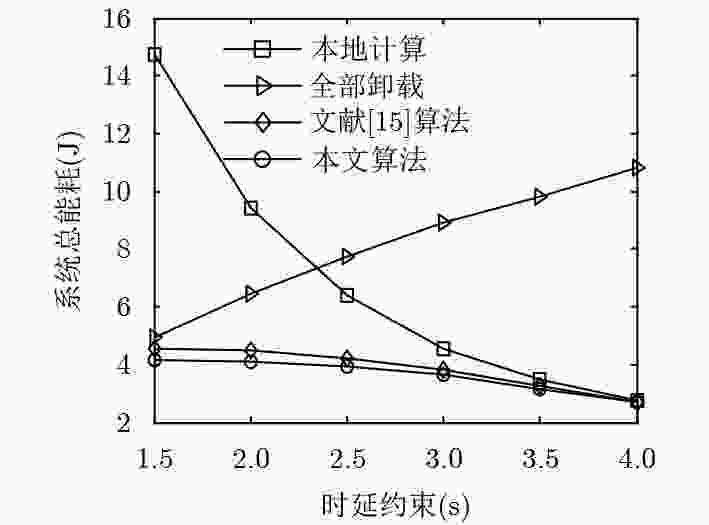


 下载:
下载:
