Denoising of MEMS Gyroscope Based on Improved Wavelet Transform
-
摘要:
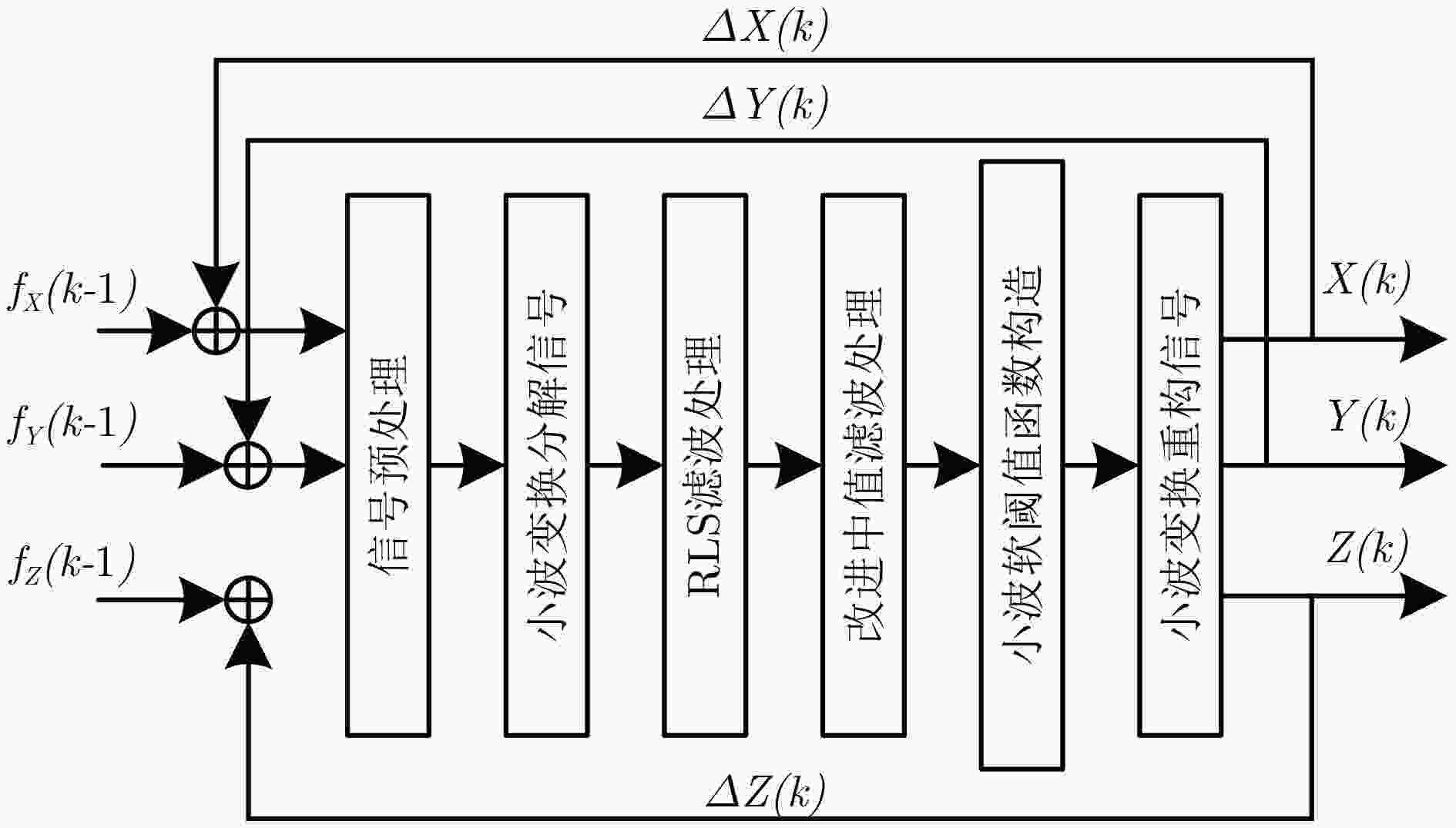
为提高MEMS陀螺仪测量精度,抑制测量噪声对其造成的影响,该文分析了某型号MEMS陀螺仪误差特性,提出基于递归最小二乘法(RLS)多重小波分解重构的强追踪自反馈模型,建立新的软阈值函数。由于模型处理后的数据带有部分奇异值,该文提出了一种改进的中值滤波算法。对于陀螺仪零偏噪声问题,提出零偏不稳定性抑制算法,并对该算法模型进行了详细的描述。将某项目研究中列车姿态测量系统的实验数据应用到该算法模型中。测试实验分为静态、动态两组,其结果均表明:该算法减小了信号中的噪声,有效地抑制了MEMS陀螺仪随机漂移,提高了姿态解算的精度。肯定了该算法对陀螺仪输出信号噪声去除,以及使用精度提升的可行性和有效性。
Abstract:In order to improve the measurement accuracy of Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) gyroscopes, the influence of measurement noise on them is suppressed. The error characteristics of a certain type of MEMS gyroscope are analyzed. A strong tracking self-feedback model based on Recursive Least Square (RLS) multiple wavelet decomposition reconstruction is proposed to establish a new soft threshold function. Since the model processed data has partial singular values, an improved median filtering algorithm is proposed. For the problem of gyro zero-bias noise, a zero-bias stability suppression algorithm is proposed. In this paper, the algorithm model is described in detail, and the experimental data of the train attitude measurement system in a project research are applied to the algorithm model. The test experiments are divided into static and dynamic groups. The results show that the algorithm reduces the noise in the signal, suppresses effectively the random drift of the MEMS gyroscope and improves the accuracy of the attitude calculation. The feasibility and effectiveness of this method are affirmed to remove the signal noise of the gyroscope output and improve the accuracy of the use.
-
Key words:
- MEMS gyroscope /
- Wavelet decomposition /
- Attitude estimation
-
表 1 传感器性能参数
陀螺仪 加速度计 磁力计 测量范围 ±150, ±500, ±1000, ±2000 (°/s) ±2, ±4, ±8, ±16 (g) ±0.6 (mT) 噪声密度 0.01° (/s·$\sqrt {{\rm{Hz}}} $) 110 (μg/$\sqrt {{\rm{Hzrms}}} $) 48 (nv/$\sqrt {{\rm{Hz}}} $) 敏感度 12.5 mv (/°·s) 1000 (mv/g) 0.1 mv (v·μT) 温漂 2% –0.3%/℃ ±0.3% 采样频率 0.1~200 Hz 0.1~20 Hz 0.1~20 Hz ARW (°/h0.5) 1.57 – – RRW (°/h1.5) 600 – – BI (°/h) 224.2 – – 表 2 两种小波变换对陀螺仪数据处理结果
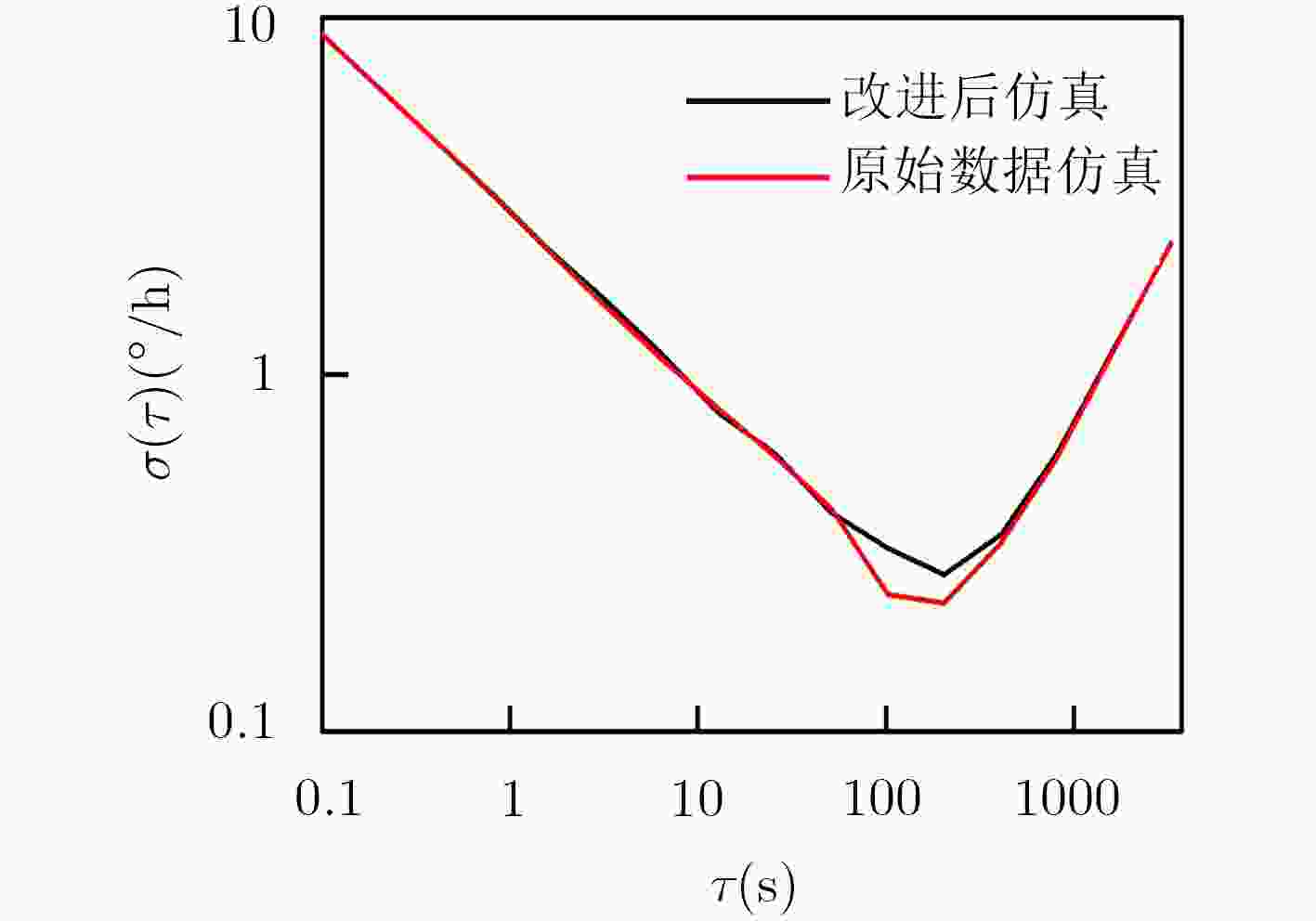
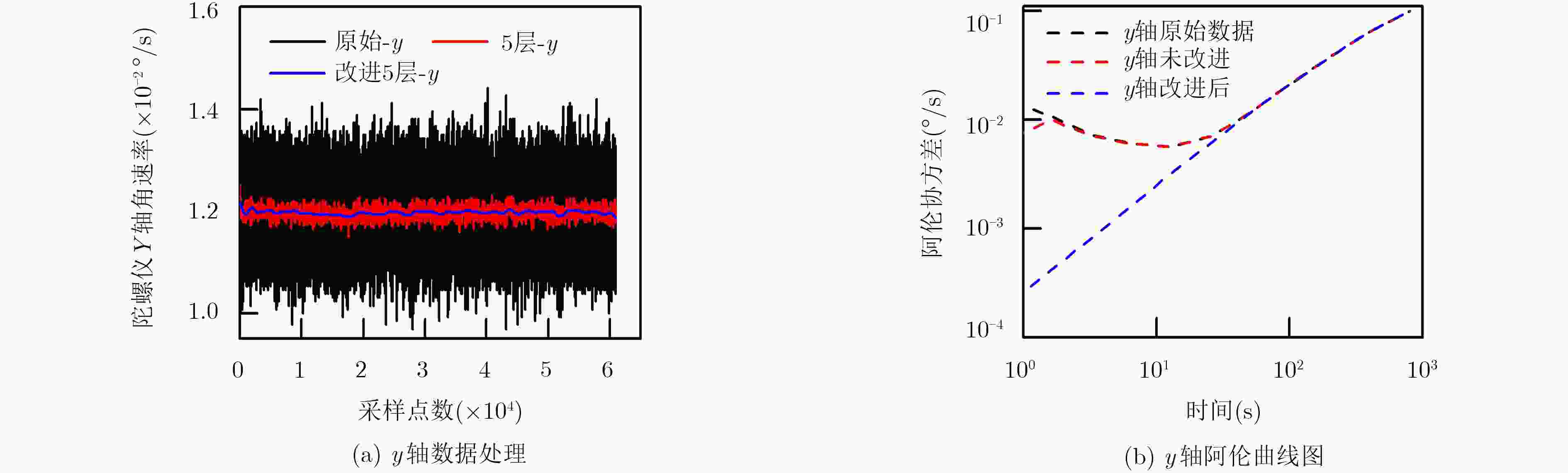
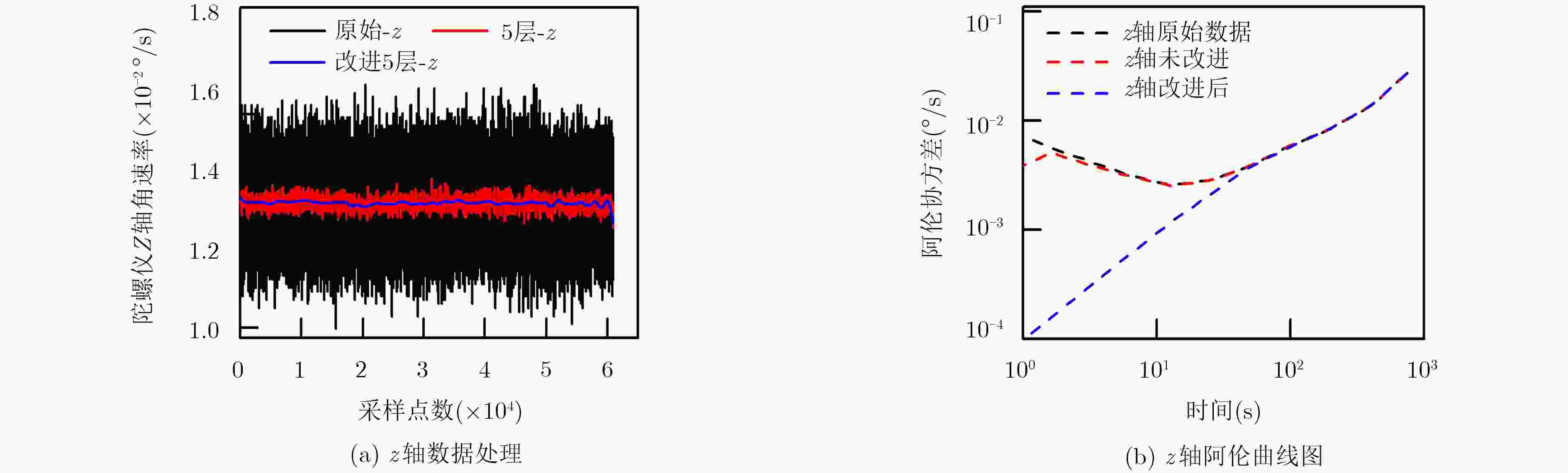
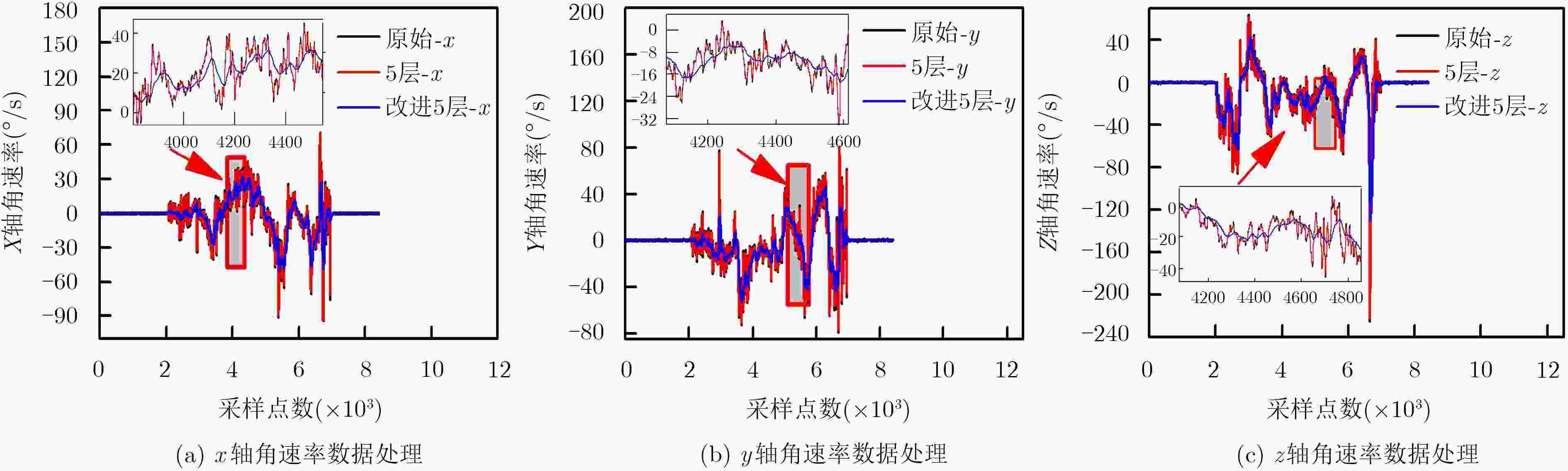
算法 坐标轴 运行时间(s) RMS误差估计 RRW (°/h1.5) ARW (°/h0.5) BI (°/h) RR (°/h) 传统的小波变换 x 26.754976 10.1147 195.2674 0.0301 1.8401 5.3524 y 28.744975 9.2655 260.4219 0.0283 1.7349 4.5069 z 27.645963 9.2012 220.3894 0.0117 1.4410 12.7358 改进的小波变换 x 26.85396 0.1290 68.6507 0 0 3.0727 y 28.64576 0.1249 32.9762 0 0 2.3039 z 27.69872 0.1247 8.6092 0 0 8.7398 表 3 姿态解算的MSE误差估计
坐标轴 MSE误差 算法改进前 算法改进后 z 4.3257×10–4 1.1512×10–7 x 8.7754×10–4 8.5849×10–7 y 1.5196×10–4 8.4663×10–5 表 4 两种算法角速率误差比较数据
算法 坐标轴 MSE (°/s) 运行时间(s) MAE (°/s) ARE (%) 传统的小波变换 x 0.0421 7.614595 0.0554 11.10 y 0.0623 8.130619 0.0796 13.41 z 0.0976 8.647342 0.0842 15.76 改进的小波变换 x 0.0999 8.467372 0.0236 8.86 y 0.0043 7.047250 0.0354 10.87 z 0.0025 8.021335 0.0416 12.52 表 5 两种算法的姿态角误差参数
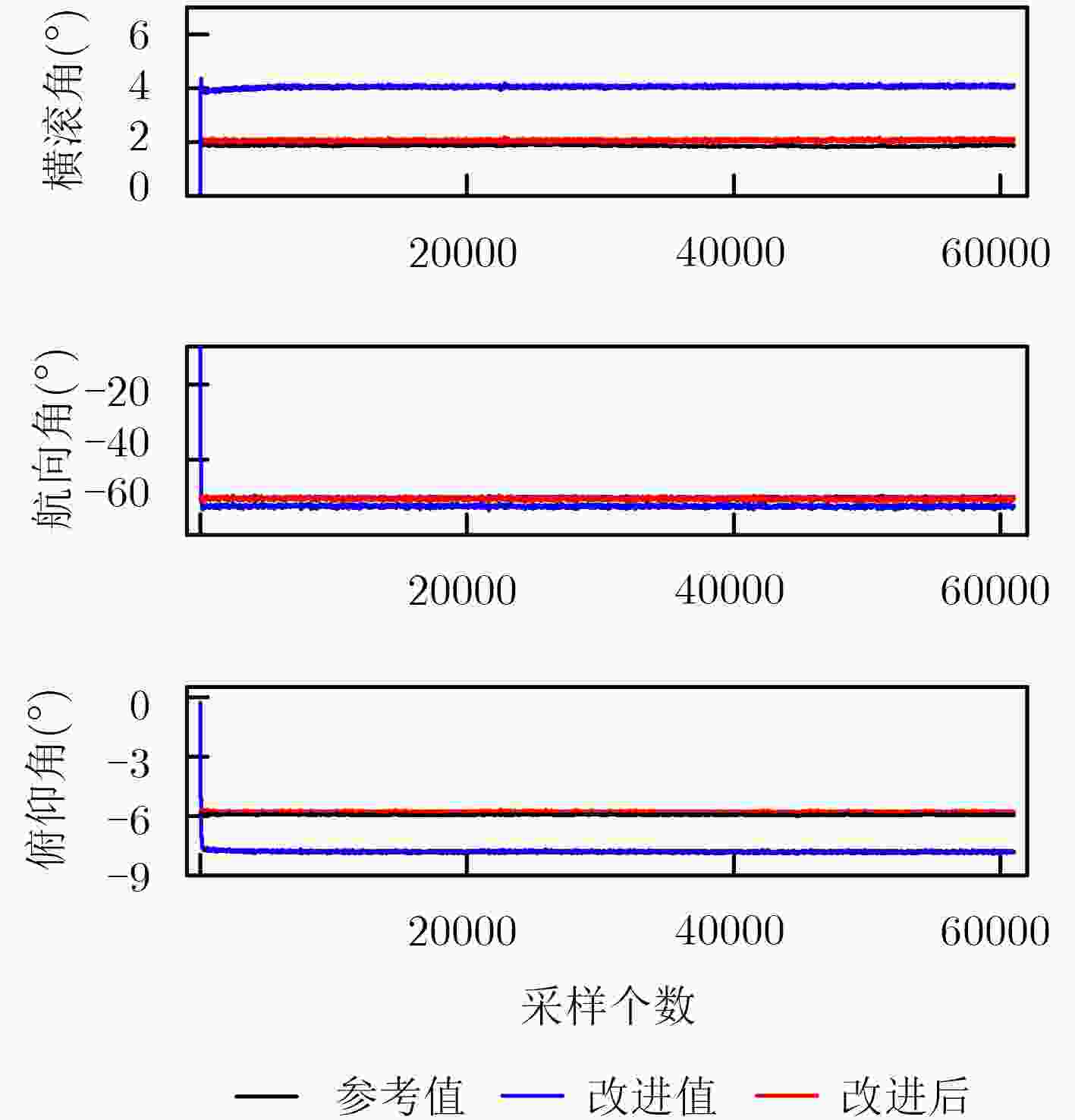
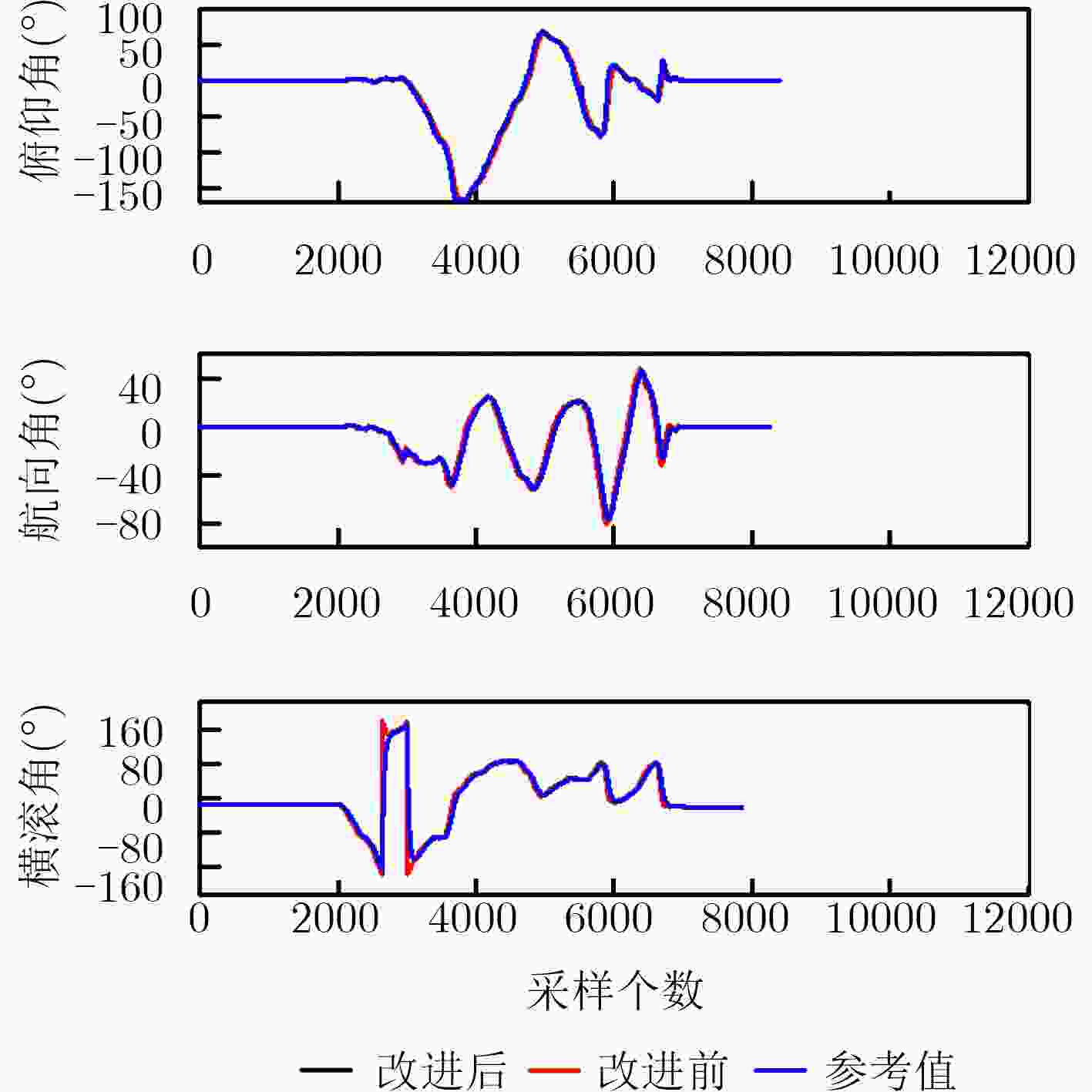
算法 姿态角 MSE (°/s) MAE (°/s) 文献[20]算法 俯仰角 0.4912 0.4524 航向角 0.0028 0.1873 横滚角 0.0020 0.1171 本文算法 俯仰角 0.2928 0.2360 航向角 0.0021 0.1354 横滚角 0.0014 0.0816 -
ZHANG Yanshun, PENG Chuang, MOU Dong, et al. An adaptive filtering approach based on the dynamic variance model for reducing MEMS gyroscope random error[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 3943–3957. doi: 10.3390/s18113943 XING Haifeng, CHEN Zhiyong, YANG Haotian, et al. Self-alignment MEMS IMU method based on the rotation modulation technique on a swing base[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(4): 1178–1200. doi: 10.3390/s18041178 WANG Wei and CHEN Xiyuan. Application of improved 5th-cubature kalman filter in initial strapdown inertial navigation system alignment for large. misalignment angles[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 659–676. doi: 10.3390/s18020659 LI Tao, YUAN Gannan, LI wang, et al. Particle filter with novel nonlinear error model for miniature gyroscope based measurement while drilling navigation[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(3): 371–385. doi: 10.3390/s16030371 GUO Zhanshe, FU Peng, LIU feng, et al. Design and FEM simulation for a novel resonant silicon MEMS gyroscope with temperature compensation function[J]. Microsyste Technologies, 2018, 24(3): 1453–1459. doi: 10.1007/s00542-017-3524-4 JON O, AIFONSO B, IBAN L, et al. Evaluation of experimental GNSS and 10-DOF MEMS IMU measurements for train positioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 6(5): 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2838799 XIAO Dingbang, XIA Dewei, LI Qingsong, et al. A temperature self-calibrating torsional accelerometer with fully differential configurationand integrated reference capacitor[J]. IEEE Sensors, 2015, 6(7): 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICSENS.2015.7370428 IGOR P, BROCK B, CAREY M, et al. Towards self-navigating cars using MEMS IMU: Challengesand opportunities[C]. International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems, Moltrasio, Italy, 2018: 1–4. 金靖, 王峥, 张忠钢, 等. 基于多元线性回归模型的光纤陀螺温度误差建模[J]. 宇航学报, 2008, 29(6): 1921–1916. doi: 10.387/s100-1328JIN Jing, WANG Zheng, ZHANG Zhonggang, et al. Temperature errors modeling for fiber optic gyroscope using multiple linear regression models[J]. Journal of Aerospace, 2008, 29(6): 1921–1916. doi: 10.387/s100-1328 DING Jicheng, ZHANG Qian, HUANG Weiquan, et al. Laser gyroscope temperature compensat-i on using modified RBFNN[J]. Sensors, 2014, 14(10): 18711–18727. doi: 10.3390/s141018711 YUAN Guangmin, YUAN Weizheng, LIANG Xue, et al. Dynamic performance comparison of two kalman filters for rate signal direct modeling and differencing modeling for combining a MEMS gyroscope array to improve accuracy[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(11): 27590–27610. doi: 10.3390/s151127590 ZHA Feng, XU Jiangning, LI JingshuHe, et al. IUKF neural network modeling for FOG temperature drift[J]. Beijing Institute of Aerospace Information, 2013, 24(5): 838–844. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2013.00097 ZHI S, JACQUES G, MICHAEL J, et al. Low cost two dimension navigation using an augmented Kalman filter/Fast Orthogonal Search module for the integration of reduced inertial sensor system and global positioning[J]. Elsevier, 2011, 19(6): 1111–1132. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2011.01.001 REN Honglian and PETER K. Investiga-tion of attitude tracking using an integrated inertial and magnetic navigation system for hand-held surgical instruments[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2012, 17(2): 210–217. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2010.2095504 CHEN Xiyuan, XU Yuan, LI Qinghua, et al. Application of adaptive extended kalman smoothing on INS/WSN integration system for mobile robot indoors[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2013, 10(10): 1–8. doi: 10.1155/2013/130508 CHU Hairong, SUN Tingting, ZHANG Baiqiang, et al. Rapid transfer alignment of MEMS SINS based on adaptive incremental kalman filter[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(1): 152–166. doi: 10.3390/s17010152 FENG Yibo, LI Xisheng, and ZHANG Xiaojuan. An adaptive compensation algorithm for temperature drift of micro-electro-mechanical systems gyroscopes using a strong tracking kalman filter[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(5): 11222–11238. doi: 10.3390/s150511222 BIRSEL A and BILLUR B. Leg motion classification with artificial neural networks using wavelet-based features of gyroscope signals[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(2): 1721–1743. doi: 10.3390/s110201721 李杰, 曲芸, 刘俊, 等. 模平方小波阈值在MEMS陀螺仪在信号降噪总的应用[J]. 中国惯性术学报, 2008, 16(4): 236–239. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2008.02.03LI Jie, QU Yun, LIU Jun, et al. Application of modular square wavelet threshold for denoising MEMS-based gyros signal[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2008, 16(4): 236–239. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2008.02.03 刘菲, 任章, 李青东. 基于小波方差的MEMS IMU随机误差模型间接估计方法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2016, 24(1): 77–82. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2016.01.014LIU Fei, REN Zhang, and LI Qingdong. Indirect estimation method for random error models of MEMS IMU based on wavelet variance[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2016, 24(1): 77–82. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2016.01.014 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
