Geographical Location Recognition of IP Based on Network Structure Features
-
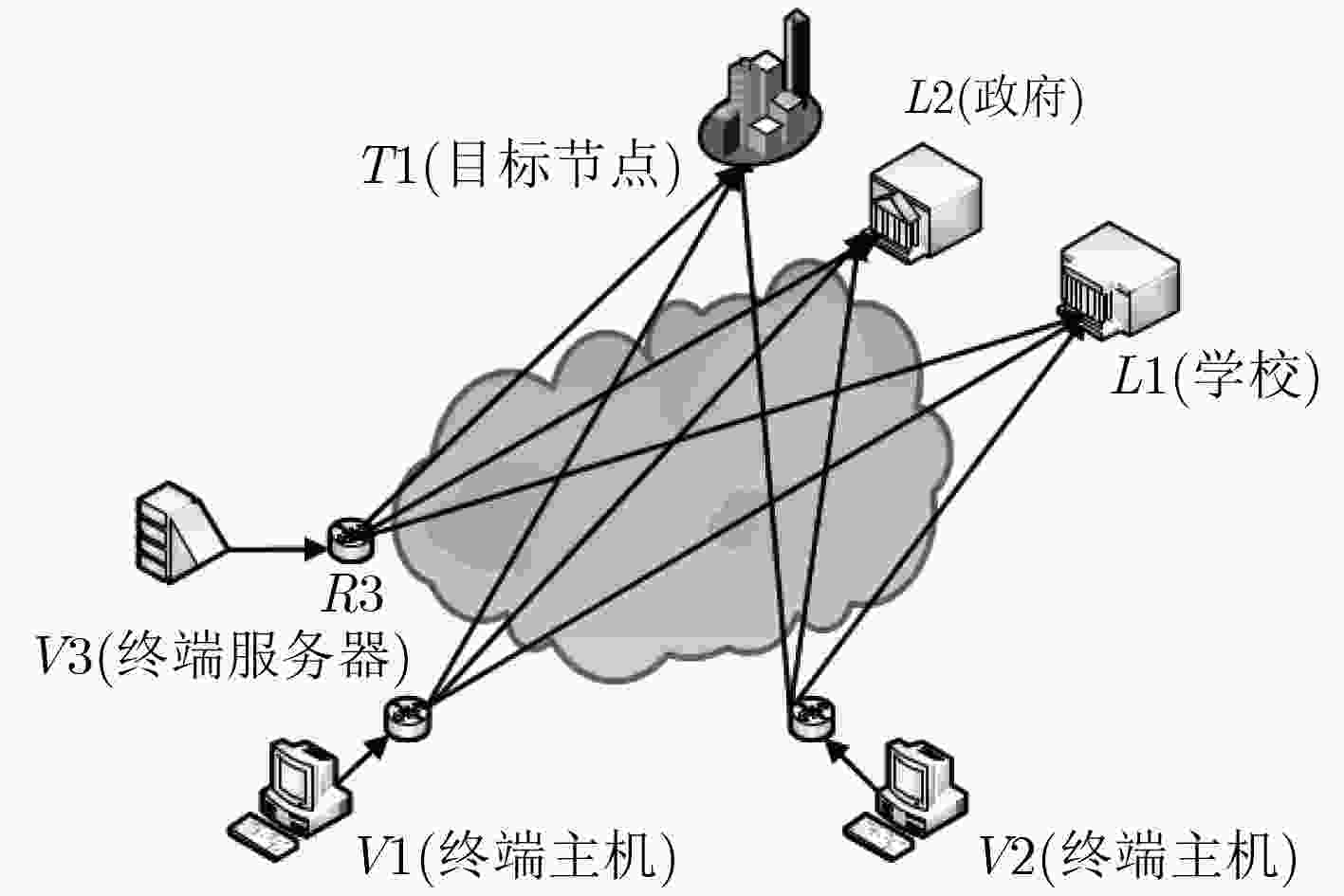
摘要: 现有IP定位技术通过查询IP注册信息数据库或利用测量得到的时延等信息确定IP具体位置,在实际中由于受各种因素的影响,对网络中的大部分IP都无法得到准确、合理的定位结果。为此,该文提出一种基于网络结构特征的IP所属区域识别方法。该方法通过探测节点向待定位的IP发送Traceroute探测包获得两者之间的网络结构特征,并比较待定位节点和已知地理位置节点之间的网络结构特征确定待定位节点所属区域。测试结果表明该文方法和现有的数据库查询的正确率相比有部分提升。Abstract: The existing IP location technology determines the location of IP by querying IP to register information databases or using time-delay information. In fact, due to the influence of various factors, most of the IP in the network can not get accurate and reasonable positioning results. For this reason, a region recognition method of IP is proposed based on network structure features. This method obtains the network topology information between the two nodes by sending the Traceroute detection packet from the detection nodes to the IPs that need to be located Comparing the network structure features between the nodes to be located and the known geographical nodes determines where the nodes located. The actual test shows that this method can achieve better results.
-
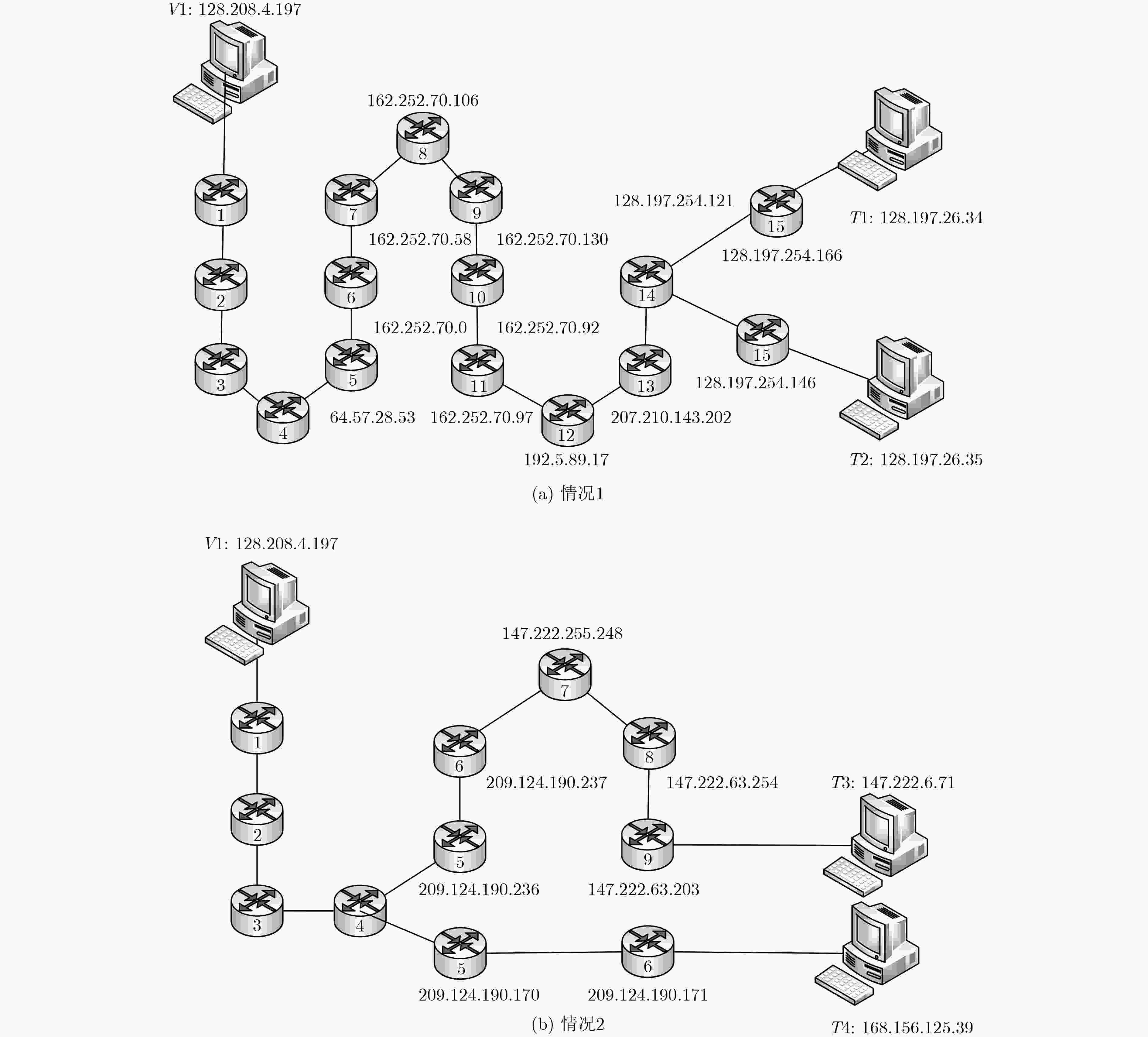
表 1 情况1:华盛顿大学探测波士顿中可能是同一C网的IP对路径信息(可达)
IP 11跳 12跳 13跳 14跳 15跳 16跳 128.197.26.34 162.252.70.97 192.5.89.17 207.210.143.202 128.197.254.121 128.197.254.166 128.197.26.34 128.197.26.35 162.252.70.97 192.5.89.17 207.210.143.202 128.197.254.121 128.197.254.146 128.197.26.35 表 2 情况2:华盛顿大学探测华盛顿州中非同一C网的IP对路径信息(可达)
IP 5跳 6跳 7跳 8跳 9跳 10跳 147.222.6.71 209.124.190.236 209.124.190.237 147.222.255.248 147.222.63.254 147.222.63.203 147.222.6.71 168.156.125.39 209.124.190.170 209.124.190.171 168.156.125.39 表 3 情况1的最小单位网络结构特征
IP 11跳 12跳 13跳 14跳 15跳 16跳 128.197.26.34 162.252.70.* 192.5.89.* 207.210.143.* 128.197.254.* 128.197.254.* 128.197.26.34 128.197.26.35 162.252.70.* 192.5.89.* 207.210.143.* 128.197.254.* 128.197.254.* 128.197.26.35 表 4 情况2的最小单位网络结构特征
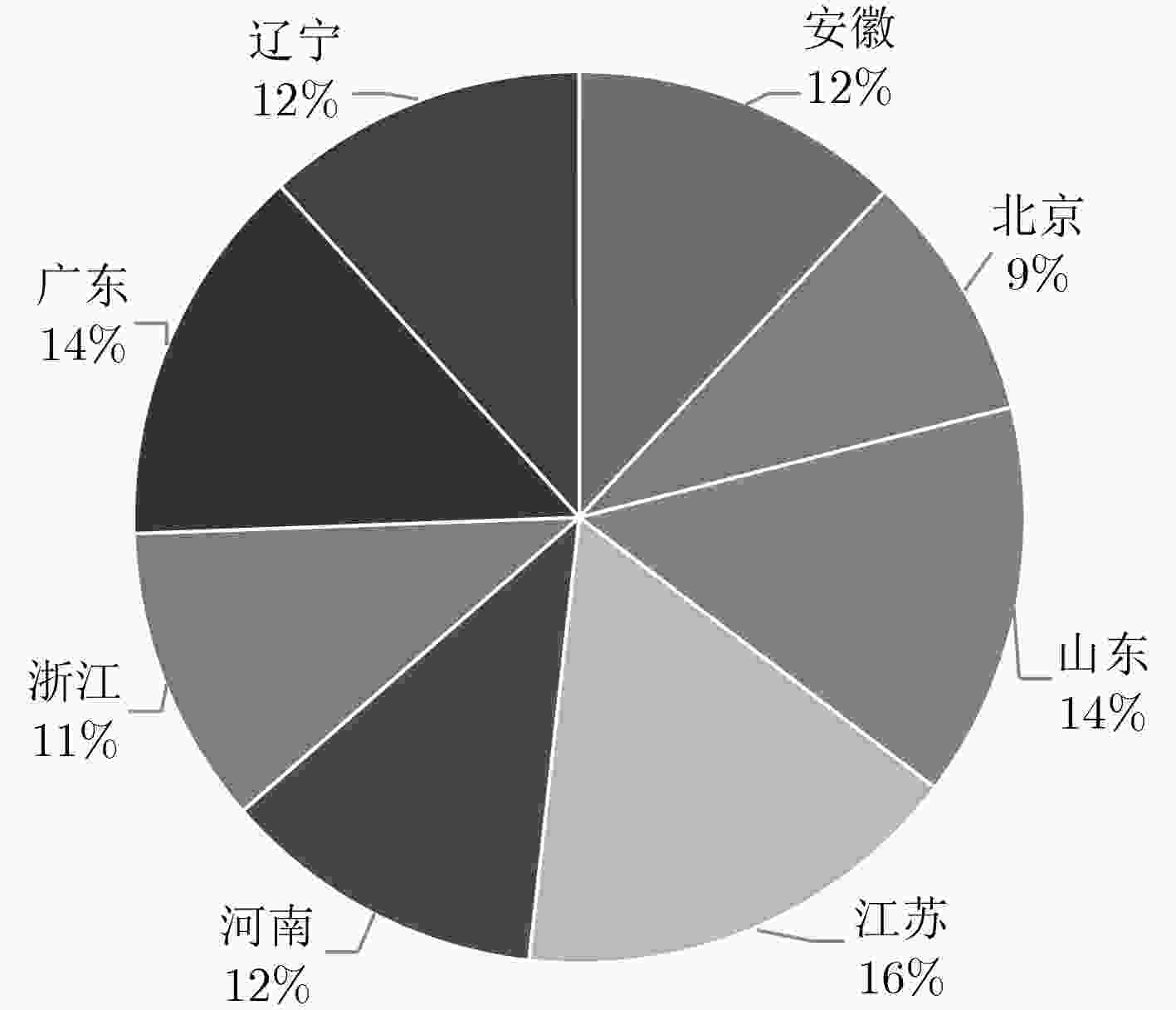
IP 5跳 6跳 7跳 8跳 9跳 10跳 147.222.6.71 209.124.190.* 209.124.190.* 147.222.255.* 147.222.63.* 147.222.63.* 147.222.6.71 168.156.125.39 209.124.190.* 209.124.190.* 168.156.125.39 表 5 中国高校IP分布情况
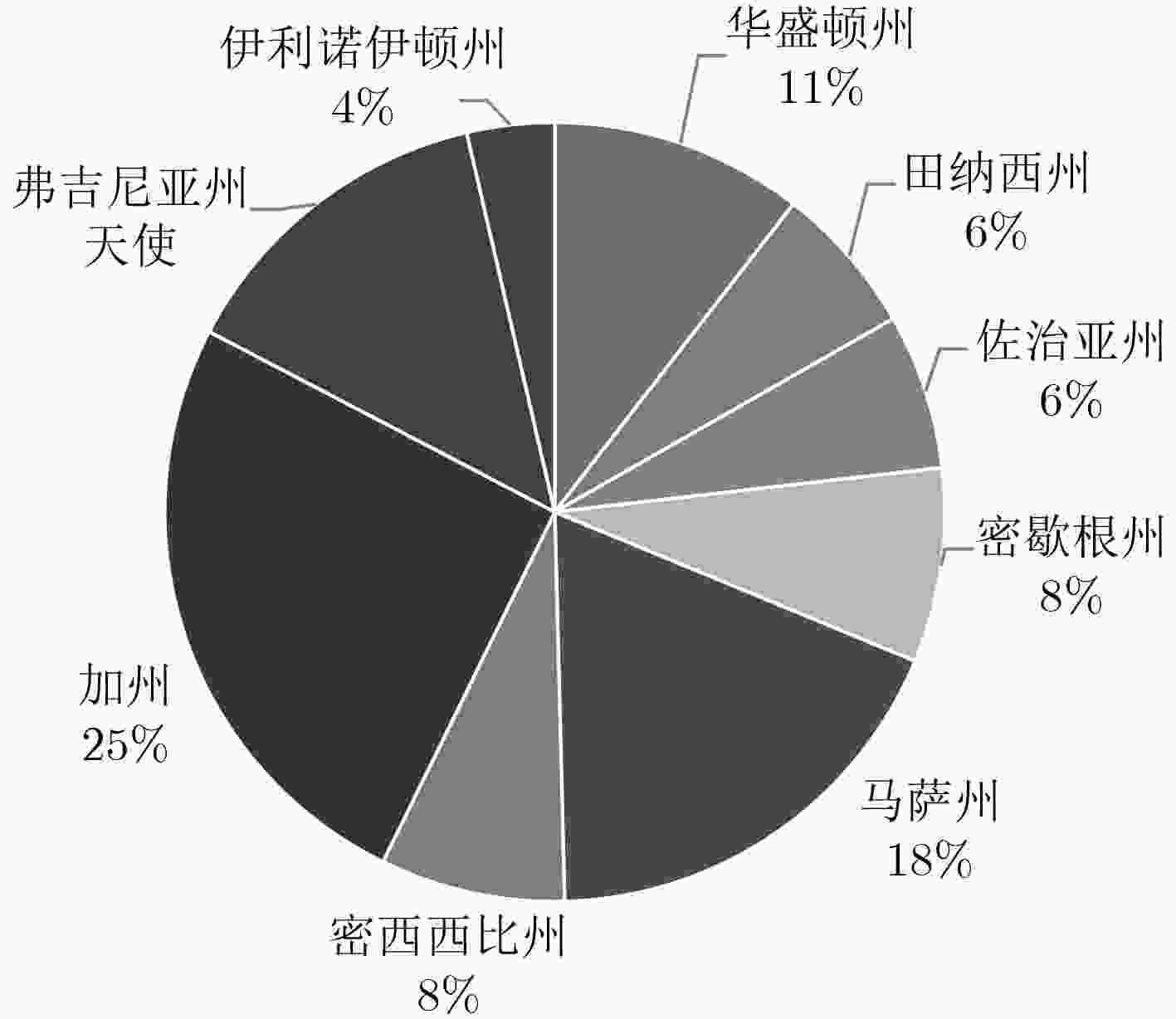
省份 安徽 北京 山东 江苏 河南 浙江 广东 辽宁 总计 数目 113 88 135 155 111 102 131 110 945 表 6 美国高校IP分布情况
州 华盛顿 田纳西 佐治亚 密歇根 马萨 密西西比 加州 弗吉尼亚 伊利 总计 数目 52 31 32 40 91 38 126 68 18 496 -
张少波, BHUIYAN M Z A, 刘琴, 等. 移动社交网络中基于代理转发机制的轨迹隐私保护方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(9): 2158–2164. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151136ZHANG Shaobo, BHUIYAN M Z A, LIU Qin, et al. The method of trajectory privacy preserving based on agent forwarding mechanism in mobile social networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(9): 2158–2164. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151136 王荣荣. 基于位置的社交网络隐私安全研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华东师范大学, 2016. 15-31.WANG Rongrong. Research on location based social network privacy security [D]. [Master dissertation], East China Normal University, 2016. 15-31. 李晴, 叶阿勇, 许力. 社交网络中基于定位欺骗的隐私攻击研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2017, 1(5): 51–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2017.05.008LI Jing, YE Ayong, and XU Li. Research on privacy attack based on location cheating in social network[J]. Information Network Security, 2017, 1(5): 51–56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2017.05.008 MUIR J A and OORSCHOT P C V. Internet geolocation: Evasion and counterevasion[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2009, 42(1): 1–23. doi: 10.1145/1592451.1592455 PADANABHAN V N and SUBRAMANIAN L. An investigation of geographic mapping techniques for internet hosts[J]. ACM Sigcomm Computer Communication Review, 2001, 31(4): 173–185. doi: 10.1145/964723.383073 GUEYE B, ZIVIANI A, CROVELLA M, et al. Constraint-based geolocation of internet hosts[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2006, 14(6): 1219–1232. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2006.886332 ZHOU Haifeng, TAN Liansheng, et al. Traffic matrix estimation: Advanced—Tomogravity method based on a precise gravity model[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2015, 28(10): 1709–1728. doi: 10.1002/dac.2787 朱畅华, 裴昌幸, 李建东, 等. 基于线性规划的Internet端到端时延的估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2004, 26(3): 446–452.ZHU Changhua, PEI Changxing, LI Jiandong, et al. Linear programming based estimation of internet end-to-end delay[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2004, 26(3): 446–452. KATZBASSET E, JOHN J P, KRISHNAMURTHY A, et al. Towards IP geolocation using delay and topology measurements[C]. ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement 2006, Rio De Janeriro, Brazil, 2006: 71–84. ERIKSSON B, BARFORD P, SOMMERS J, et al. A learning-based approach for IP geolocation[C]. Passive and Active Measurement, International Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 2010: 171–180. CHEN Jingning, LIU Fenlin, WANG Tianpeng, et al. Towards region-level IP geolocation based on the path feature[C]. International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology IEEE, PyeongChang, South Korea, 2015: 468–471. REN Lianxing. Method for IP geolocation based on Path Similarity[C]. International Conference on Wireless Communication and Sensor Networks. Boston, USA, 2017: 315–319. CHUN B, CULLER D, ROSCOE T, et al. PlanetLab: an overlay tested for broad-coverage services[J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2003, 33(3): 3–12. doi: 10.1145/956993.956995 谢钧, 俞璐, 金凤林. 基于排队时延和丢包率的拥塞控制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(9): 2058–2064. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01228XIE Jun, YU Lu, and JIN Fenglin. Congestion control based on queuing delay and packet Loss probability[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(9): 2058–2064. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01228 SHAVITT Y and ZILBERMAN N. Geolocation Databases Study[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(10): 2044–2056. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2011.111214 赵帆, 罗向阳, 刘粉林. 网络空间测绘技术研究[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2016, 2(9): 1–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-109x.2016.00097ZHAO Fan, LUO Xiangyang, and LIU Fenlin. Research on cyberspace surveying and mapping technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2016, 2(9): 1–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-109x.2016.00097 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
