Energy Efficiency Routing Strategy with Lightpath Impairment Awareness in Service-Oriented Elastic Optical Networks
-
摘要:
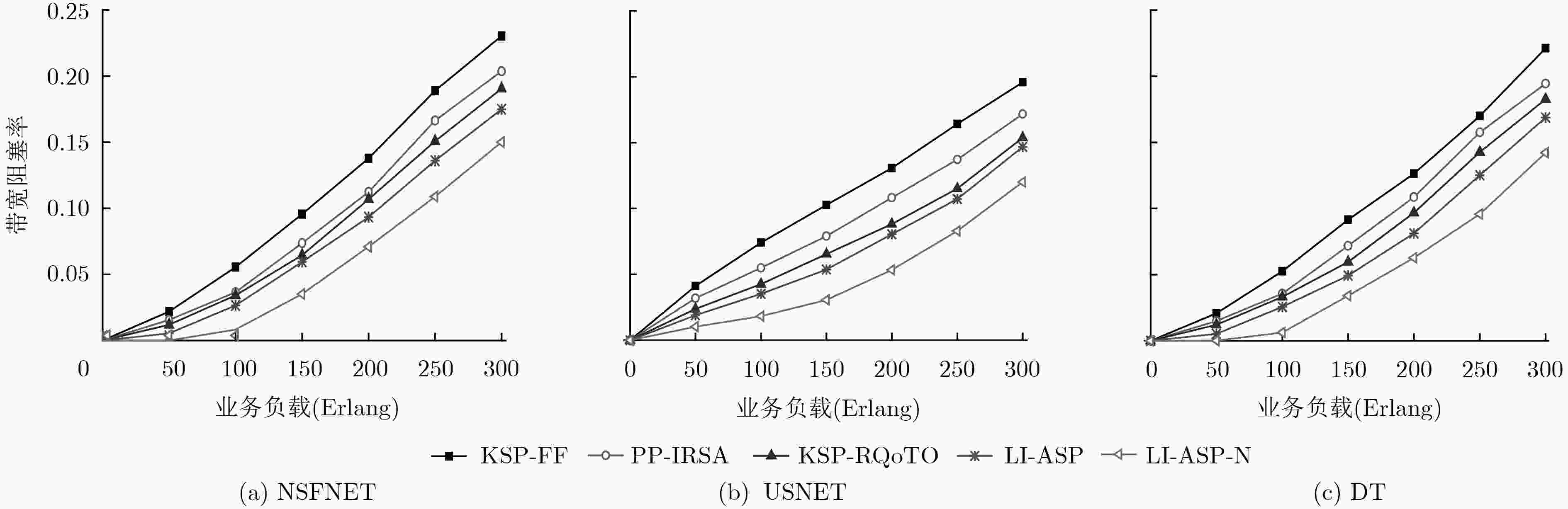
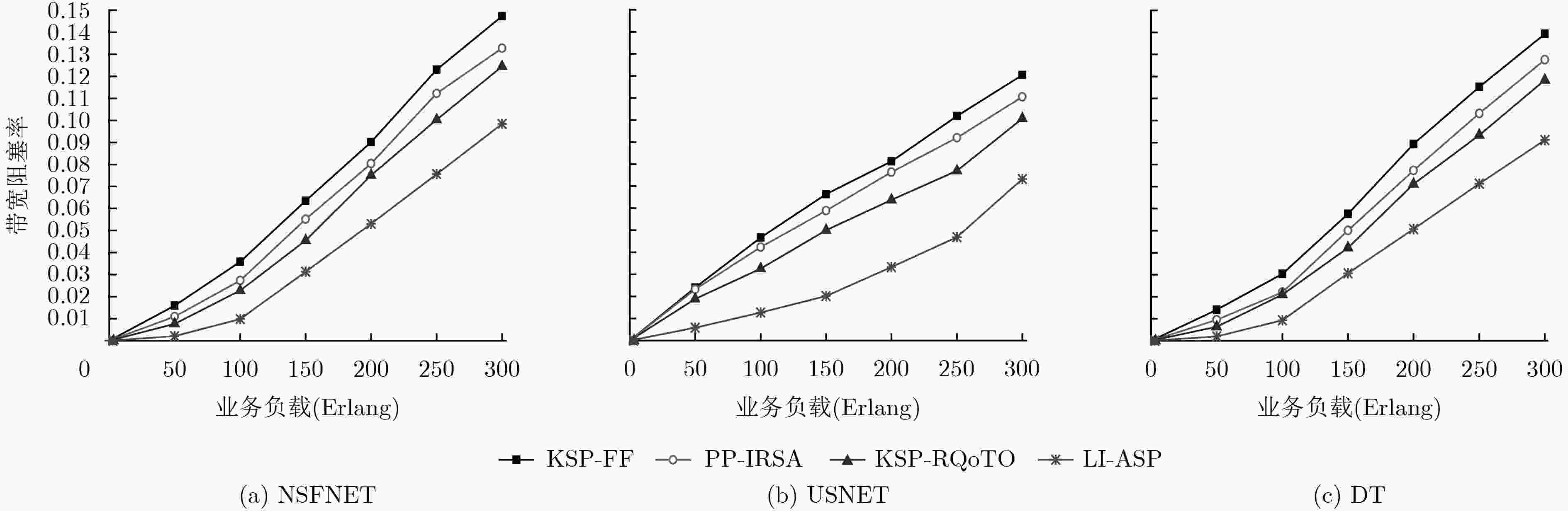
针对弹性光网络中物理损伤导致业务频谱利用率低和传输能耗高问题,该文提出一种面向业务的链路损伤感知频谱分区(LI-ASP)能效路由策略。在LI-ASP策略中,为降低不同信道间非线性损伤,基于负载均衡设计一个综合考虑链路频谱状态和传输损伤的路径权重公式,根据调制方式的频谱效率和最大传输距离构造分层辅助图,从最高调制等级开始,为高质量业务选择K条边分离的最大权重传输路径;为低质量业务选择K条边分离的最短能效路径。然后,LI-ASP策略根据业务速率比值对频谱分区,采用首次命中(FF)和尾端命中(LF)联合频谱分配方式,减少不同传输速率业务间的交叉相位调制。仿真结果表明,该文所提LI-ASP策略在有效降低带宽阻塞率的同时,减少了业务传输能耗。
Abstract:To address the problems of low spectrum utilization and high energy consumption caused by physical impairment in elastic optical networks, a service differentiated energy efficiency routing strategy with Link Impairment-Aware Spectrum Partition (LI-ASP) is proposed. For reducing the nonlinear impairment between different channels, a path weight formula jointly considering the link spectrum state and transmission impairment is designed to balance the load. A modulation level-layered auxiliary graph is constructed according to traffic’s spectrum efficiency and maximum transmission distance. Starting from the highest modulation in the auxiliary graph, the K link-disjoined maximum weight paths are selected for high quality requests, and the K link-disjoined shortest energy efficiency paths are selected for low quality requests. Then, LI-ASP strategy divides spectrum partition according to requests rate ratio. The First-Fit (FF) and Last-Fit (LF) spectrum allocation policies are used to reduce cross-phase modulation between the requests with different rates. The simulation results show that the proposed LI-ASP strategy can reduce the bandwidth blocking probability and energy consumption effectively.
-
表 1 不同调制方式下子载波传输速率、能耗、最大传输距离及信噪比阈值
调制方式 调制等级m 传输速率(Gb/s) 能耗功率(W) 最大传输距离(km) 信噪比阈值(dB) BPSK 1 12.5 112.374 4000 6.8 QPSK 2 25.0 133.416 2000 9.8 8QAM 3 37.5 154.457 1000 13.7 16QAM 4 50.0 175.489 500 16.5 32QAM 5 62.5 196.539 250 19.7 表 2 LI-ASP能效路由策略步骤
输入 光网络拓扑${{G}}\left( {{{V}}, {{E}}, {{S}}} \right)$,节点集${{V}} = \left\{ {{v_i}|i = 1, 2, ·\!·\!· , |{{V}}|} \right\}$,链路集${{E}} = \left\{ {{e_{ij}}|i, j \in {{V}}, i \ne j} \right\}$,链路频隙集${{S}} = \left\{ {{s_i}|i = 1, 2, ·\!·\!· , |{{S}}|} \right\}$,
业务集${{R}} = \left\{ {{r_i}|i = 1, 2, ·\!·\!· , |{{R}}|} \right\}$表示,令$k = 1$,$m = M$,业务请求${r_i}\left( {s, d, {\rm{fs}}\_n, Q} \right)$,s为源节点,d为目的节点,${\rm{fs}}\_n$为业务请求
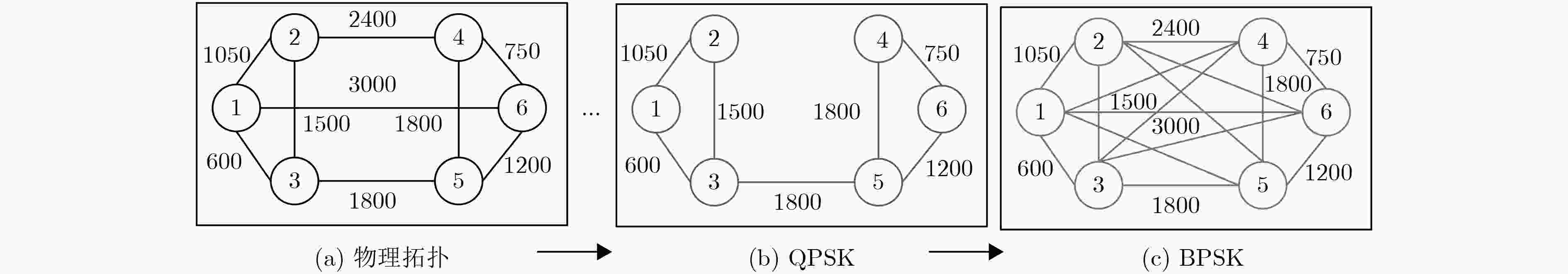
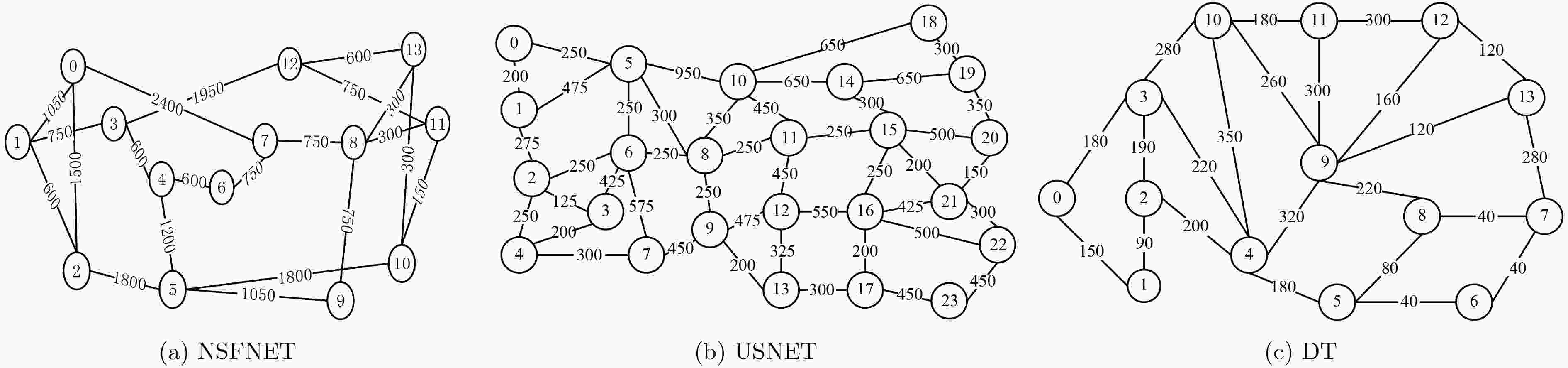
频隙数目,Q=1表示高质量业务;Q=0为低质量业务。使用Dijkstra算法计算所有源目的节点间的K条最短路径KSP集合(预处理),
M层调制等级辅助图(预处理)。输出 业务${r_i}$的传输路径${p_k}$和分配的第1个、最后频隙索引值${f_ {\rm{ts}}}$和${f_ {\rm{te}}}$。 步骤 1 业务${r_i}\left( {s, d, {\rm{fs}}\_n, Q} \right)$到达,从频谱效率最高调制等级m=M分层辅助图开始为业务选择传输路径; 步骤 2 判断Q是否为1,若为1,为高质量业务,算法转步骤3;否则,为低质量业务,转算法步骤4; 步骤 3 根据式(8)计算源和目的节点间K条满足跳数阈值Hop的最大权重路径${{{P}}^H}\{{p_1}, {p_2}, ·\!·\!· , {p_K}\}$,转步骤5; 步骤 4 根据业务源节点和目的节点选择存放在KSP中的K条最短路径,根据能耗模型计算路径能耗,按照能耗大小升序排列K条路径
${{{P}}^L}\{ {p_1}, {p_2}, ·\!·\!· , {p_K}\}$;步骤 5 计算当前调制等级下业务${r_i}$传输所需的频隙数目,从路径集合中选择第${p_k}$条路径,$k = 1, 2, ·\!·\!· , K$,计算该路径上可用频谱块Block
$\{ {b_1}, {b_2}, ·\!·\!· , {b_j}\} $,若可用频谱块集合非空,转算法步骤8;否则转算法步骤6;步骤 6 若$m < 1$,当前传输路径无可用调制方式,转步骤7;否则降低调制等级,$m = m - 1$,转步骤2; 步骤 7 若$k > K$,业务${r_i}$被阻塞,释放网络中已传输业务占用的频谱资源,更新光网络G的频谱资源;否则,$k = k + 1$,$m = M$,转算
法步骤5;步骤 8 根据业务请求频隙数目${\rm{fs}}\_n$,分别计算采用FF和LF频谱分区分配策略需要占用候选路径上各链路相邻信道数目和的值,选择占
用相邻信道数目和值较小的FF或LF频谱分配方式;步骤 9 根据物理损伤模型计算该路径上业务的传输误比特率${\rm{BER}}_{{r_i}}^k$,若${\rm{BER}}_{{r_i}}^k$小于业务误码率阈值,转算法步骤10;否则,$m = m - 1$,
转算法步骤5;步骤 10 判断传输路径${p_k}$是否造成网络中其他正传输业务阻塞,若是,记录阻塞的业务BT$\{ {\rm{rb}}_1, {\rm{rb}}_2, ·\!·\!· , {\rm{rb}}_i\} $,调用LI-ASP能效路由策略重
配置被阻塞的业务BT$\{ {\rm{rb}}_1, {\rm{rb}}_2, ·\!·\!· , {\rm{rb}}_i\} $;否则,转算法步骤12;步骤 11 若业务重配置成功,转算法步骤12;否则,$m = m - 1$,转算法步骤5; 步骤 12 业务${r_i}$成功传输,记录传输路径${p_k}$,记录分配的第1个频隙索引值${f_ {\rm{ts}}}$和最后频隙索引值${f_ {\rm{te}}}$。 表 3 物理损伤参数设置
参数 值 参数 值 G(W/THz) 0.015 L(km) 80 $\alpha $(dB/km) 0.22 v(THz) 193 nsp 1.8 ${\beta _2}$(ps2/km) –21.7 h(J/s) $6.626 \times {10^{ - 34}}$ $\gamma $(W·km)–1 1.32 ${\rm{BER}}_t^h$ ${10^{ - 12}}$ ${\rm{BER}}_t^l$ ${10^{ - 9}}$ -
熊余, 刘川菠, 孙鹏. 考虑业务服务质量的光线路终端节能算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报, 2017, 29(2): 208–215. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2017.02.011XIONG Yu, LIU Chuanbo, and SUN Peng. Energy saving algorithm for optical line terminal considering quality of service[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017, 29(2): 208–215. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2017.02.011 刘焕淋, 熊翠连, 陈勇. 频谱效率优先的任播路由冲突感知的弹性光网络资源重配置[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1697–1703. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161093LIU Huanlin, XIONG Cuilian, and CHEN Yong. Collision-aware reconfiguration resource based on spectrum efficiency first for anycast routing in elastic optical networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1697–1703. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161093 LIU Huanlin, LÜ Lei, CHEN Yong, et al. Fragmentation-avoiding spectrum assignment strategy based on spectrum partition for elastic optical networks[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2017, 9(5): 1–13. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2017.2739750 鲍宁海, 刘翔, 张治中, 等. WDM节能光网络中的抗毁保护算法研究[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报, 2012, 24(3): 278–282. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2015.03.002BAO Ninghai, LIU Xiang, ZHANG Zhizhong, et al. Survival protection algorithm in WDM energy-efficient optical network[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2012, 24(3): 278–282. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2015.03.002 TAN Yanxia, GU Rentao, and JI Yuefeng. Energy-efficient routing, modulation and spectrum allocation in elastic optical networks[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2017, 36(2017): 297–305. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2017.05.001 YANG Song and KUIPERS F. Impairment-aware routing in translucent spectrum-sliced elastic optical path networks[C]. European Conference on Networks and Optical Communications, Vilanova, Spain, 2012: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/NOC.2012.6249946. AGRELL E, ZHAO Juzi, LI Yan, et al. Traffic-grooming-and multipath-routing-enabled impairment-aware elastic optical networks[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2016, 8(2): 58–70. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.8.000058 ZHAO Juzi, WYMEERSCH H, and AGRELL E. Nonlinear impairment-aware static resource allocation in elastic optical networks[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2015, 33(22): 4554–4564. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2474130 REN Rongrong, HOU Weigang, GUO Lei, et al. Spectrum and energy-efficient survivable routing algorithm in elastic optical network[J]. Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(20): 8795–8806. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.06.088 KLEKAMP A, DISCHLER R, and BUCHALI F. Transmission reach of optical-OFDM superchannels with 10-600 Gb/s for transparent bit-rate adaptive networks[C]. European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, Geneva, Switzerland, 2011: 1–3. doi: 10.1364/ECOC.2011.Tu.3.K.2. ZHAO Jijun, WANG Wenyan, LI Wei, et al. A novel partition-plane impairment aware routing and spectrum assignment algorithm in mixed line rates elastic optical networks[J]. Photonic Network Communications, 2017, 33(1): 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11107-015-0601-4 ABKENAR F S, RAHBAR A G, EBRAHIMZADEH A. Providing Quality of Service (QoS) for data traffic in Elastic Optical Networks (EONs)[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2016, 41(3): 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s13369-015-1886-4 GUO Lei, WU Ying, HOU Weigang, et al. Green grooming in spectrum-sliced elastic optical path networks[J]. Photonic Network Communications, 2016, 32(1): 115–125. doi: 10.1007/s11107-015-0580-5 LIU Huanlin, ZHOU Bangtao, and CHEN Yong. Spectrum allocation based on spectrum integration and re-routing for elastic optical networks[J]. IET Optoelectronics, 2016, 10(5): 179–183. doi: 10.1049/iet-opt.2015.0136 TANAKA T, INUI T, KADOHATA A, et al. Multiperiod IP-over-elastic network reconfiguration with adaptive bandwidth resizing and modulation[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2016, 8(7): A180–A190. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.8.00A180 -





 下载:
下载:
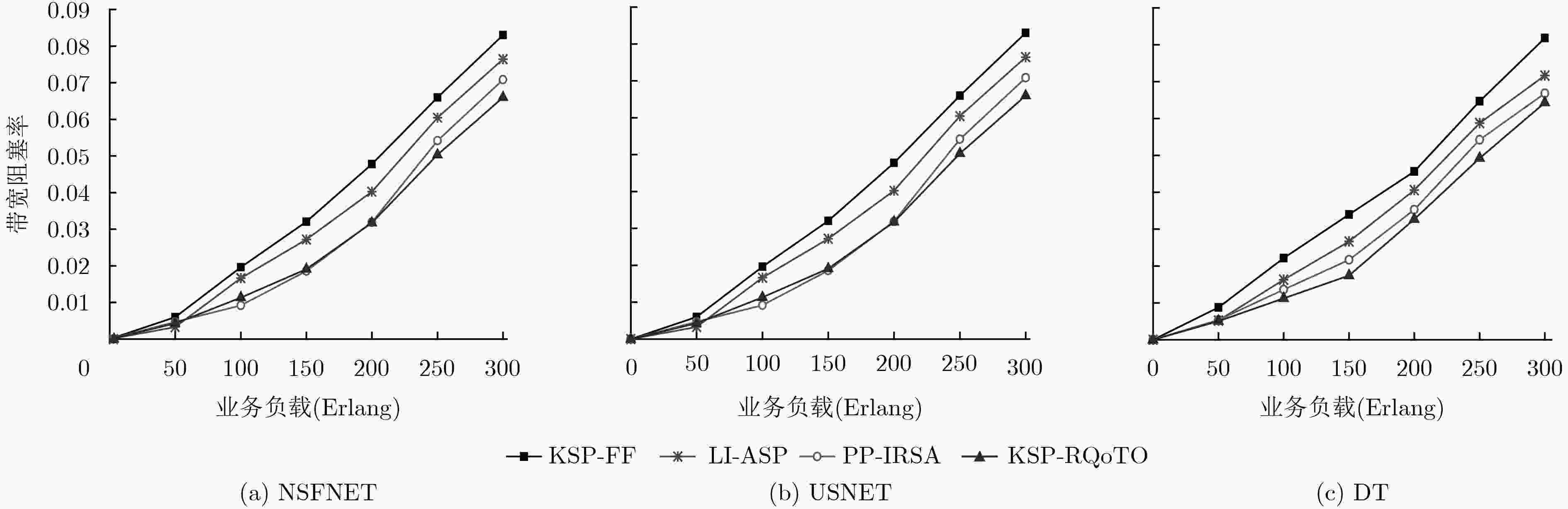
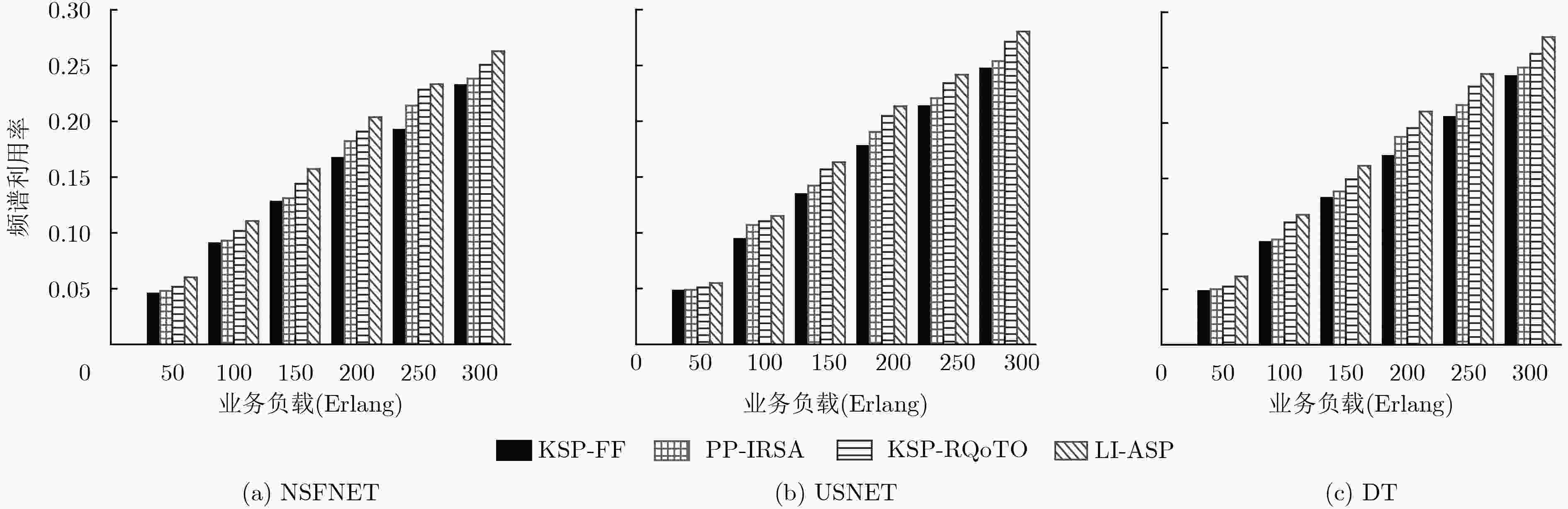
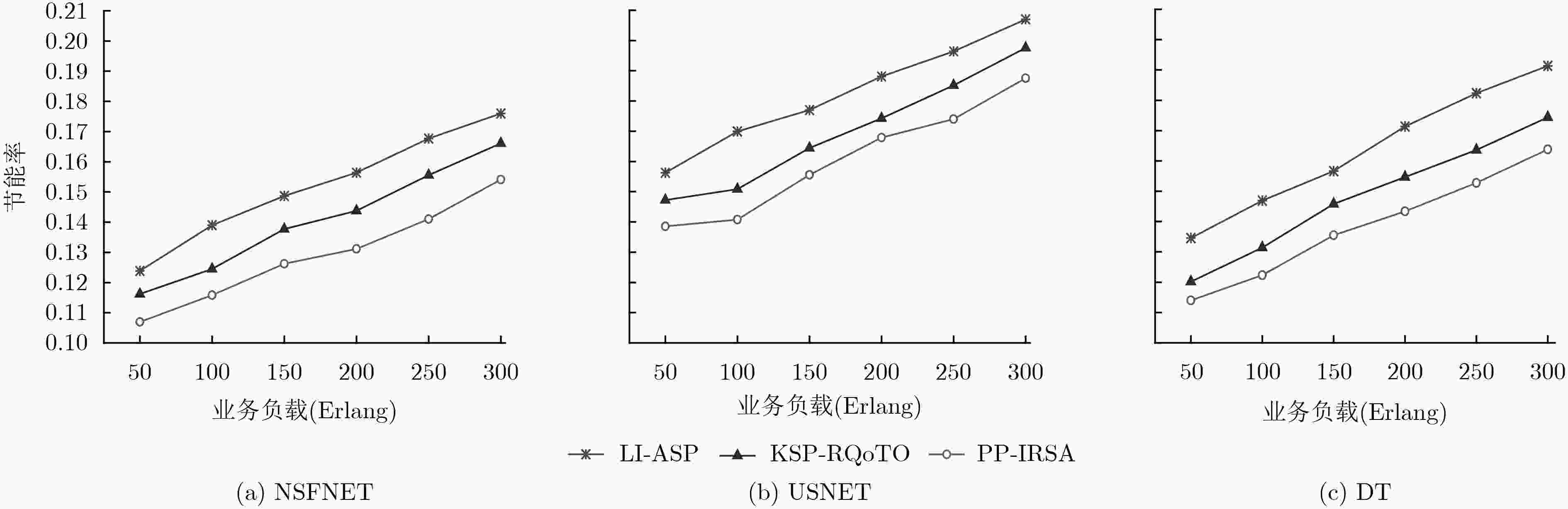


 下载:
下载:
