A Fast Random-valued Impulse Noise Detection Algorithm Based on Deep Belief Network
-
摘要:
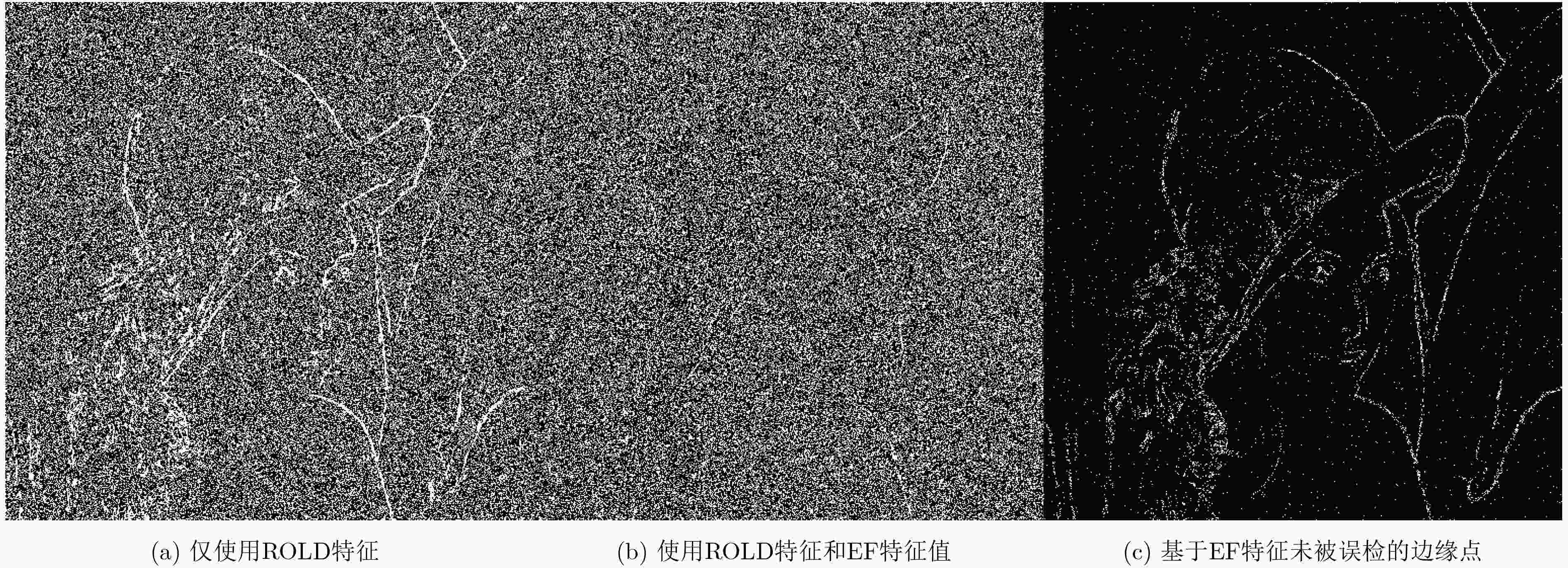
为提高现有随机脉冲噪声(RVIN)检测算法的检测准确率和执行效率,该文试图从构建描述能力更强的特征矢量和训练非线性映射更为准确的预测模型两个方面入手,实现一种基于训练策略的快速RVIN检测算法。一方面,提取多个不同阶的对数绝对差值排序统计值并结合一个能够反映图像边缘特性的统计值作为刻画图块中心像素点是否为噪声的特征矢量。在计算量增加极少的情况下,显著提升了特征矢量的描述能力。另一方面,基于深度置信网络(DBN)训练RVIN预测模型(RVIN检测器)将特征矢量映射为噪声类型标签,实现了比浅层预测模型更为准确的映射。大量实验数据表明:与现有的RVIN检测算法相比,所提算法在检测准确率和执行效率两个方面都更有优势。
Abstract:To improve the detection accuracy and execution efficiency of the existing Random-Valued Impulse Noise (RVIN) detectors, a fast training-based RVIN detection algorithm is implemented by constructing a more descriptive feature vector and training a detection model with more accurate nonlinear mapping. On the one hand, multiple Rank-Ordered Logarithmic absolute Deviation (ROLD) statistics are extracted and combined with a statistical value reflecting the edge characteristics in the form of feature vector to describe how RVIN-like the center pixel of a patch is. The description ability of the feature vector is improved significantly while the computational complexity is just increased in small amount. On the other hand, an RVIN prediction model (RVIN detector) is obtained by training a Deep Belief Network (DBN) to map the feature vectors to noise labels, which is more accurate than the shallow prediction model. Extensive experimental results show that, compared with the existing RVIN detectors, the proposed one has better performance in terms of detection accuracy and execution efficiency.
-
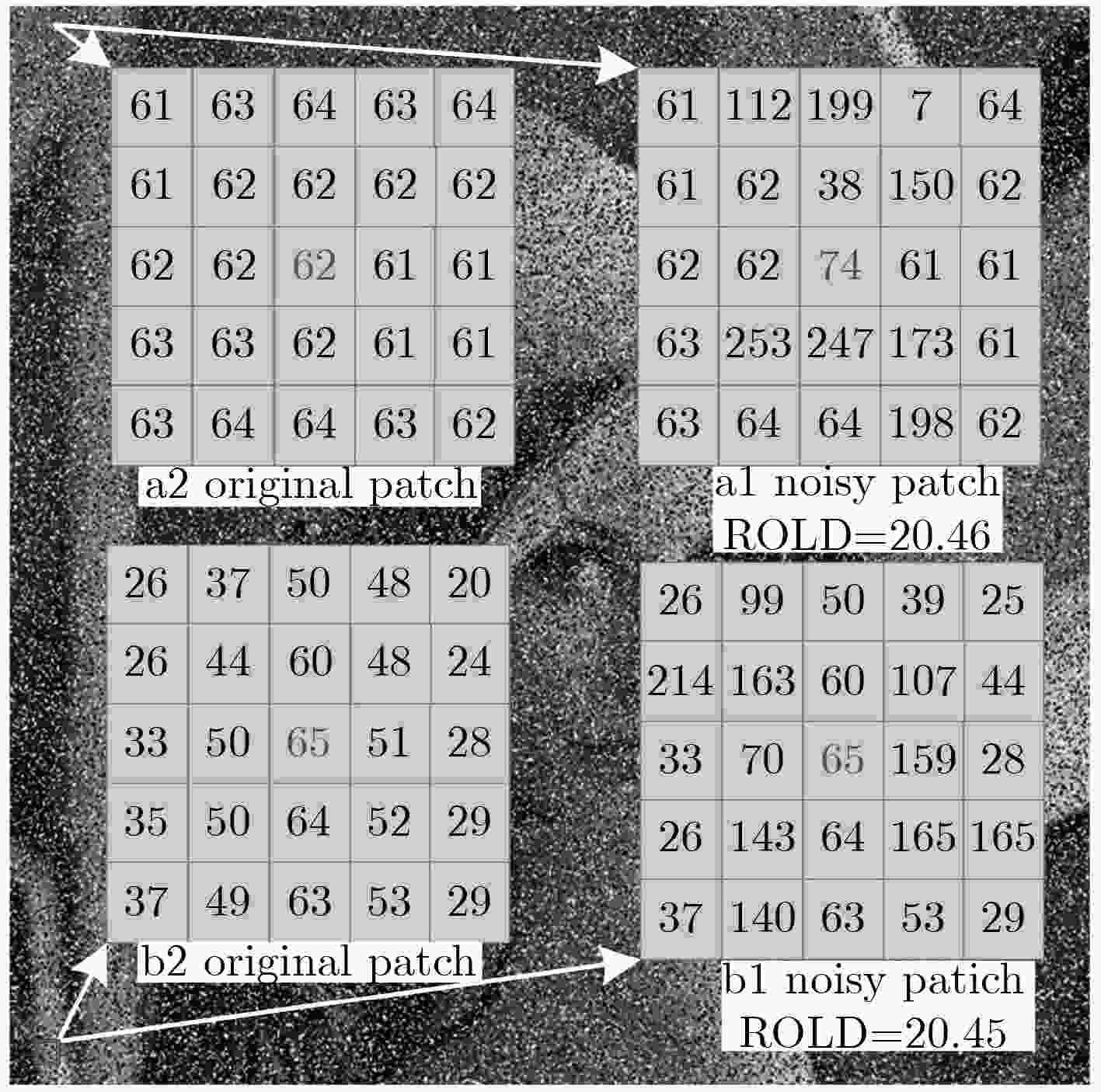
表 1 图1中a1和b1图块上所提取的前m阶ROLD值比较
图块 阶数m 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 a1 1.63 3.29 4.99 6.68 8.37 10.09 11.80 13.52 15.24 16.98 18.72 20.46 b1 1.00 2.20 3.66 5.12 6.84 8.62 10.50 12.44 14.40 16.40 18.42 20.45 表 2 各噪声检测算法在常用图像集合上的各项性能指标的平均值比较
方法 含噪20% 含噪40% 含噪60% 漏检数 误检数 错检总数 MEMH 漏检数 误检数 错检总数 MEMH 漏检数 误检数 错检总数 MEMH ASWM 3462 10687 14149 14.23 7478 10005 17483 16.40 14720 9804 24524 23.17 PSMF 10695 3585 14279 15.14 23038 3603 26641 30.27 39096 5634 44730 45.81 ROLD-EPR 6567 5106 11673 18.77 9462 8956 18419 15.95 10417 11616 22034 14.04 ROR-NLM 5068 9354 14421 14.91 11906 8873 20779 17.13 22553 12856 35408 23.60 MLP-EPR 8505 2081 10586 22.78 13244 5759 19003 18.09 15017 10113 25130 16.18 本文方法 4084 5909 9992 11.77 7975 8586 16561 12.17 10076 12594 22670 11.53 表 3 各检测算法统一用相同修复算法降噪后在PSNR指标上的比较(dB)
方法 含噪20% 含噪40% 含噪50% 含噪60% Lena House Bridge Lena House Bridge Lena House Bridge Lena House Bridge ASWM 39.06 33.31 25.76 34.27 31.21 24.33 30.66 28.81 23.25 26.04 26.13 21.61 PSMF 30.24 27.82 23.25 29.26 26.03 22.77 26.03 24.09 21.91 22.04 21.98 20.00 ROLD-EPR 34.77 33.31 26.75 31.77 31.21 24.25 30.54 28.81 23.12 28.78 26.13 22.20 ROR-NLM 36.94 28.92 25.28 31.58 28.91 23.59 27.61 27.39 22.35 22.92 24.68 20.39 MLP--EPR 36.45 39.36 27.71 33.83 37.49 24.40 31.86 36.48 23.33 29.42 33.96 22.25 本文方法 40.35 42.95 26.97 35.89 40.31 24.91 33.04 38.27 23.36 29.66 36.12 22.18 表 4 各噪声检测算法平均执行时间的比较(s)
方法 ASWM PSMF ROLD-EPR ROR-NLM MLP-EPR 本文方法 时间 102.72 0.86 10.40 77.19 0.79 0.70 -
LIU Licheng, Chen C L P, and ZHOU Yicong. A new weighted mean filter with a two-phase detector for removing impulse noise[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 315(September): 4052–4057. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.03.067 SINGH N, THILAGAVATHY T, LAKSHMIPRIYA R T, et al. Some studies on detection and filtering algorithms for the removal of random valued impulse noise[J]. IET Image Processing, 2017, 11(11): 953–963. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr. 2017.0346 DONG Yiqiu and XU Shufang. A new directional weighted median filter for removal of random-valued impulse noise[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2007, 14(3): 193–196. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.884014 刘万军, 梁雪剑, 曲海成. 自适应增强卷积神经网络图像识别[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2017, 22(12): 1723–1736. doi: 10.11834/jig.170079LIU Wanjun, LIANG Xuejian, and QU Haicheng. Adaptively enhanced convolutional neural network algorithm for image recognition[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2017, 22(12): 1723–1736. doi: 10.11834/jig.170079 于海平, 何发智, 潘一腾, 等. 一种基于多特征的距离正则化水平集快速分割方法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(3): 534–539. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.003.004YU Haiping, HE Fazhi, PAN Yiteng, et al. A fast distance regularized level set method for segmentation based on multi-features[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(3): 534–539. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.003.004 王森, 王余, 王易川, 等. 水下高速目标声谱图特征提取及分类设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(11): 2684–2689. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170283WANG Sen, WANG Yu, WANG Yichuan, et al. Feature extraction and classification of spectrum of radiated noise of underwater high speed vehicle[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(11): 2684–2689. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170283 周箩鱼, 汤佳欣. 基于图像稀疏表达的模拟退火图像复原[J]. 光电子·激光, 2018, 29(2): 218–223. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2018.02.0088ZHOU Luoyu and TANG Jiaxin. Image restoration based on simulated annealing with image sparse representation[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics · Laser, 2018, 29(2): 218–223. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2018.02.0088 AKKOUL S, LEDEE R, LECONGE R, et al. A new adaptive switching median filter[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(6): 587–590. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2048646 YU Hancheng, ZHAO Li, and WANG Haixian. An efficient procedure for removing random-valued impulse noise in images[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2008, 15(12): 922–925. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2008.2005051 GARNETT R, HUEGERICH T, CHUI C, et al. A universal noise removal algorithm with an impulse detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(11): 1747–1754. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.857261 DONG Yiqiu, RAYMOND H C, and XU Shufang. A detection statistic for random-valued impulse noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(4): 1112–1120. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.891348 XIONG Bo and YIN Zhouping. A universal denoising framework with a new impulse detector and nonlocal means[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1663–1675. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2172804 ROY A, SINGHA J, DEVI S S, et al. Impulse noise removal using SVM classification based fuzzy filter from gray scale images[J]. Signal Processing, 2016, 128(11): 262–273. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.04.007 TURKMEN I. The ANN based detector to remove random-valued impulse noise in images[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 34(10): 28–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.10.011 SOLEIMANY S and HAMGHALAM M. A novel random-valued impulse noise detector based on MLP neural network classifier[C]. Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (IRANOPEN), Qazvin, Iran, 2017: 165–169. HINTON G, DENG Li, YU Dong, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82–97. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597 WANG Zhou and ZHANG D. Progressive switching median filter for the removal of impulse noise highly corrupted images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits System II: Analog Digital Signal Processing, 1999, 46(1): 78–80. doi: 10.1109/82.749102 CHAN S H, WANG Xiran, and ELGENDY O A. Plug-and-play ADMM for image restoration: Fixed-point convergence and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(1): 84–98. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2629286 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
