Radar Emitter Signal Identification Based on Multi-scale Information Entropy
-
摘要:
随着雷达信号的日益复杂,从实数序列中提取特征变得越来越困难,但当它们表示成符号序列时,通常能更容易地挖掘出有效的特征参数。因此,该文提出一种基于多尺度信息熵(MSIE)的雷达信号识别方法。首先通过符号聚合近似(SAX)算法在不同字符集尺度下将雷达信号转换为符号化序列;然后联合各符号序列的信息熵值,组成MSIE特征向量;最后,使用k邻近算法(k-NN)作为分类器实现雷达信号的分类识别。通过仿真6种典型的雷达信号进行验证,结果表明该方法在信噪比(SNR)为5 dB时,不同雷达信号的识别正确率大于90%,并且优于传统的基于复杂度特征(盒维数和稀疏性)的识别方法。
Abstract:With the increasing complexity of radar signals, it is more and more difficult to extract features of the real sequences, but when they are transformed to a symbol sequence, it is usually easier to mine the effective feature parameters. Therefore, a radar signal recognition method based on Multi-Scale Information Entropy (MSIE) is proposed. Firstly, the radar signal is transformed into symbolic sequence by Symbolic Aggregate approXimation (SAX) algorithm under different character number scales. Then, the information entropy of each symbol sequence is combined to form the MSIE feature vector. Finally, the k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) is used as a classifier to realize the classification and identification of radar signals. The simulation results of 6 typical radar signals show that using the proposed method the correct recognition rate of different radar signals is greater than 90% when Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is 5 dB, and better performance can be obtaned conpared with the traditional identification method based on complexity characteristics (box-dimension and sparseness).
-
表 1 参数a从3~8的等概率断点查询表[12]
断点(${\beta _i}$) 字符集大小(a) 3 4 5 6 7 8 ${\beta _{{1}}}$ 0.43 0.67 0.84 0.97 1.07 1.15 ${\beta _{{2}}}$ 0.43 0 0.25 0.43 0.57 0.67 ${\beta _{{3}}}$ – 0.67 0.25 0 0.18 0.32 ${\beta _{{4}}}$ – – 0.84 0.43 0.18 0 ${\beta _{{5}}}$ – – – 0.97 0.57 0.32 ${\beta _{{6}}}$ – – – – 1.07 0.67 ${\beta _{{7}}}$ – – – – – 1.15 表 2 不同SNR下6种雷达信号的识别率
雷达信号 信噪比SNR (dB) 20 15 10 5 LFM 1.000 1.000 1.000 0.985 CP 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 BPSK 0.975 0.990 0.990 1.000 BFSK 0.930 0.910 0.800 0.700 NLFM 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 COSTAS 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 表 3 提取两种特征耗费的时间对比
特征向量 耗费时间(s) WRFCCF 135.102 MSIE 1.704 表 4 两种方法的总体识别正确率比较(%)
识别方法 总体识别率 WRFCCF+k-NN 92.13 MSIE+k-NN 95.63 表 5 3种方法的总体识别正确率比较(%)
识别方法 信噪比SNR(dB) 20 15 10 5 MSIE+k-NN 98.42 97.25 94.25 91.25 CC+k-NN 80.25 73.08 54.33 <50 SIE+k-NN 81.42 79.08 71.25 62.92 -
WILEY R G. ELINT: The Interception and Analysis of Radar Signals[M]. Norwood, USA: Artech House, 2006: 1–15. 韩俊, 何明浩, 朱振波, 等. 基于复杂度特征的未知雷达辐射源信号分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(11): 2552–2556.HAN Jun, HE Minghao, ZHU Zhenbo, et al. Sorting unknown radar emitter signal based on the complexity characteristics[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(11): 2552–2556. 曲志昱, 毛校洁, 侯长波. 基于奇异值熵和分形维数的雷达信号识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 303–307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.10QU Zhiyu, MAO Xiaojie, and HOU Changbo. Radar signal recognition based on singular value entropy and fractal dimension[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 303–307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.10 LI Jingchao and YING Yulong. Radar signal recognition algorithm based on entropy theory[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Systems and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 2014: 718–723. GUO Yuanyuan and ZHANG Xudong. Radar signal classification based on cascade of STFT, PCA and naïve Bayes[C]. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation, Bangkok, Thailand, 2016: 191–196. DUDCZYK J. A method of feature selection in the aspect of specific identification of radar signals[J]. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences, 2017, 65(1): 113–119. doi: 10.1515/bpasts-2017-0014 GUO Qiang, NAN Polong, and WAN Jian. Signal classification method based on data mining for multi-mode radar[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27(5): 1010–1017. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2016.05.09 KONOPKO K, GRISHIN Y P, and JAŃCZAK D. Radar signal recognition based on time-frequency representations and multidimensional probability density function estimator[C]. Proceedings of 2015 Signal Processing Symposium, Dębe, Poland, 2015: 1–6. 陈韬伟, 金炜东. 雷达辐射源信号符号化脉内特征提取方法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2008, 23(5): 521–526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2008.05.004CHEN Taowei and JIN Weidong. Intra-pulse feature extraction of radar emitter signals based on symbolization method[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2008, 23(5): 521–526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2008.05.004 CHEN Taowei and JIN Weidong. Feature extraction of radar emitter signals based on symbolic time series analysis[C]. Proceedings of 2007 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 2007: 1277–1282. CHEN Taowei, LIU Zugen, LI Jie, et al. Symbolic time series analysis for measuring complexity in radar emitter signals[C]. Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Dalian, China, 2014: 918–922. LIN J, KEOGH E, WEI Li, et al. Experiencing SAX: A novel symbolic representation of time series[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2007, 15(2): 107–144. doi: 10.1007/s10618-007-0064-z SONG Wei, WANG Zhiguang, ZHANG Fan, et al. Empirical study of symbolic aggregate approximation for time series classification[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2017, 21(1): 135–150. doi: 10.3233/IDA-150351 向馗, 蒋静坪. 时间序列的符号化方法研究[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2007, 20(2): 154–161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2007.02.003XIANG Kui and JIANG Jingping. Study on symbolization analysis of time series[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2007, 20(2): 154–161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2007.02.003 KEOGH E, CHAKRABARTI K, PAZZANI M, et al. Dimensionality reduction for fast similarity search in large time series databases[J]. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2001, 3(3): 263–286. doi: 10.1007/PL00011669 余志斌. 基于脉内特征的雷达辐射源信号识别研究[D]. [博士论文], 西南交通大学, 2010: 1–56.YU Zhibin. Study on radar emitter signal identification based on intra-pulse features[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010: 1–56. VAN DER MAATEN A and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008(9): 2579–2605. -





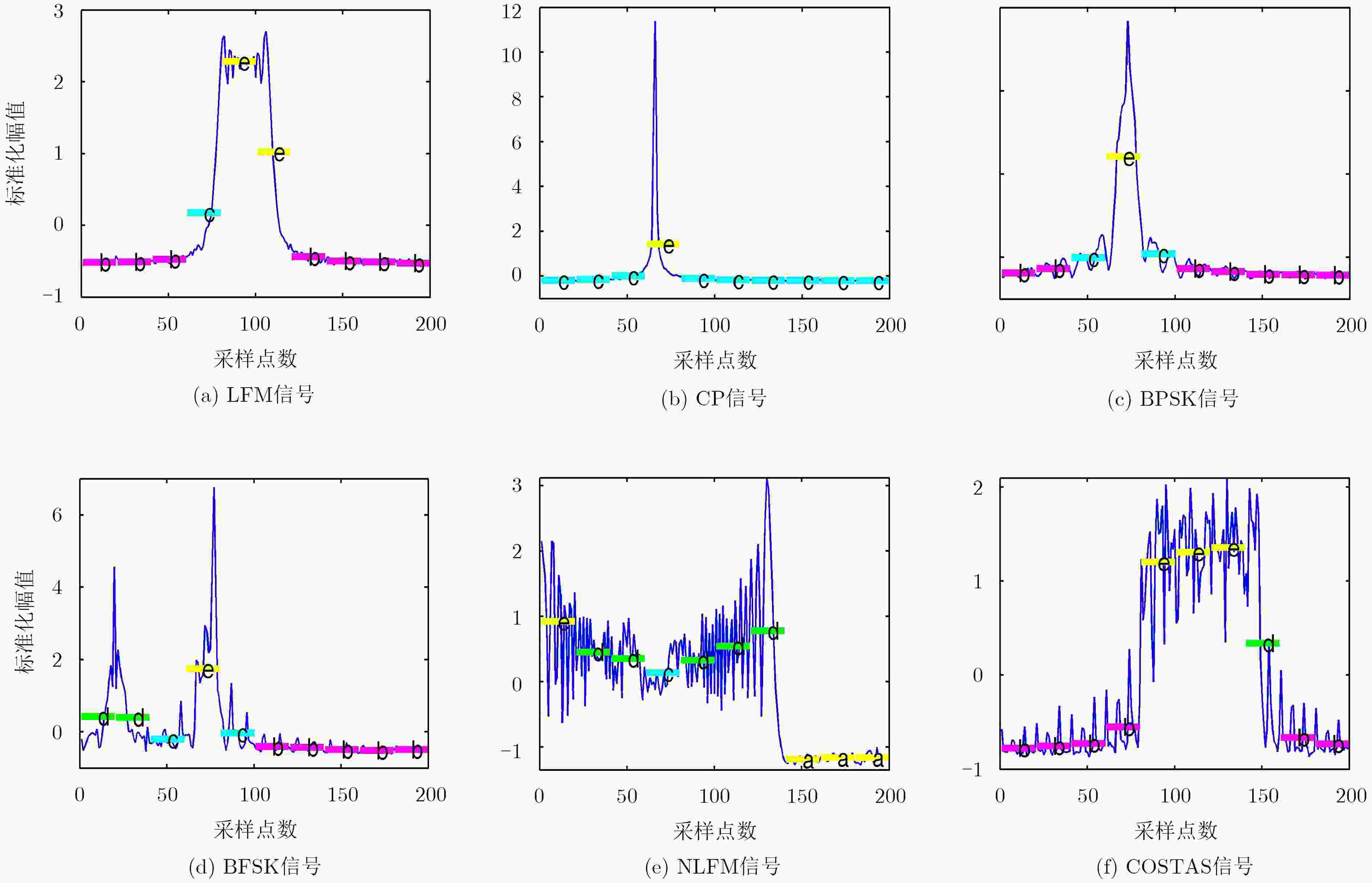
 下载:
下载:
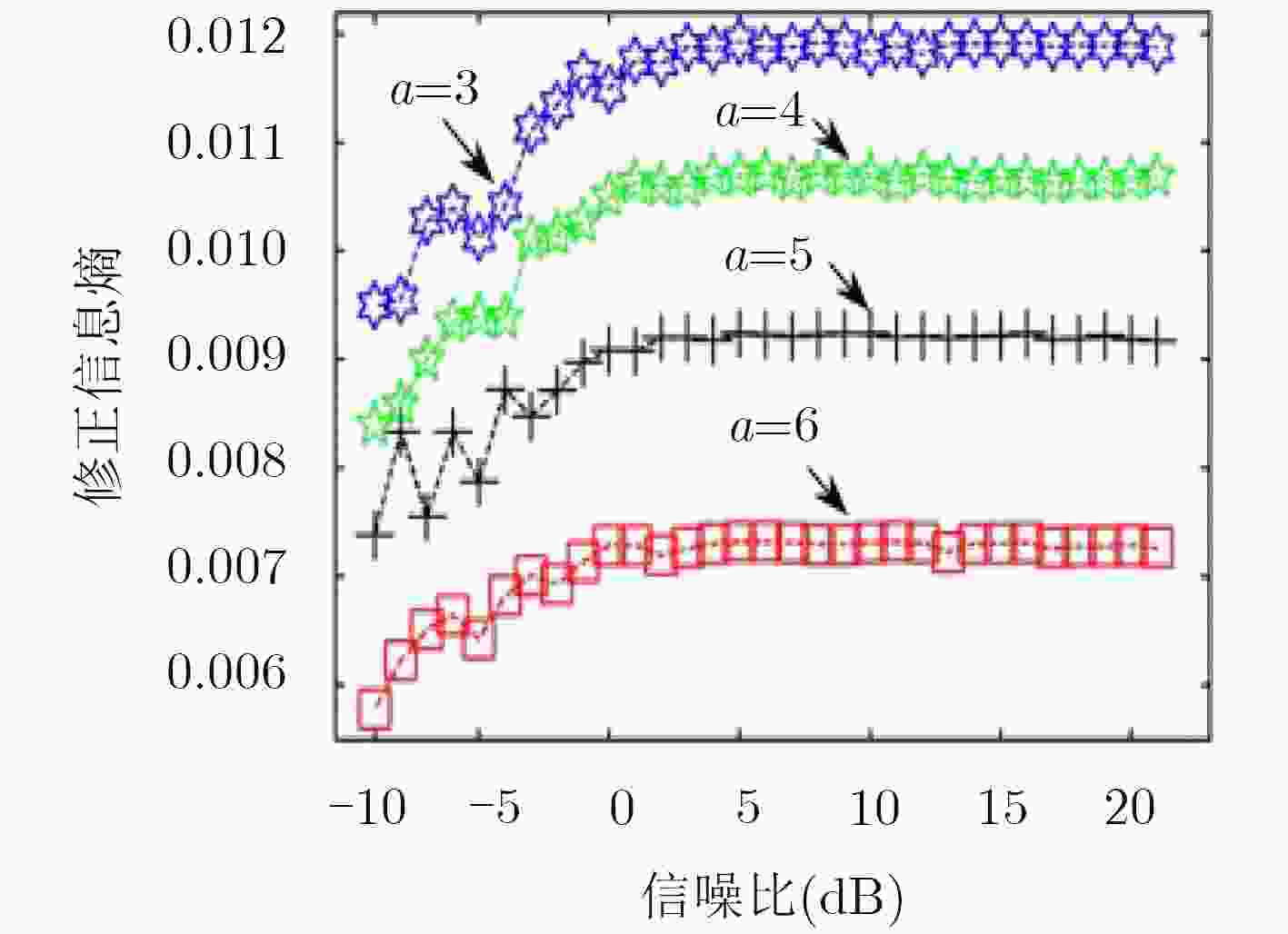
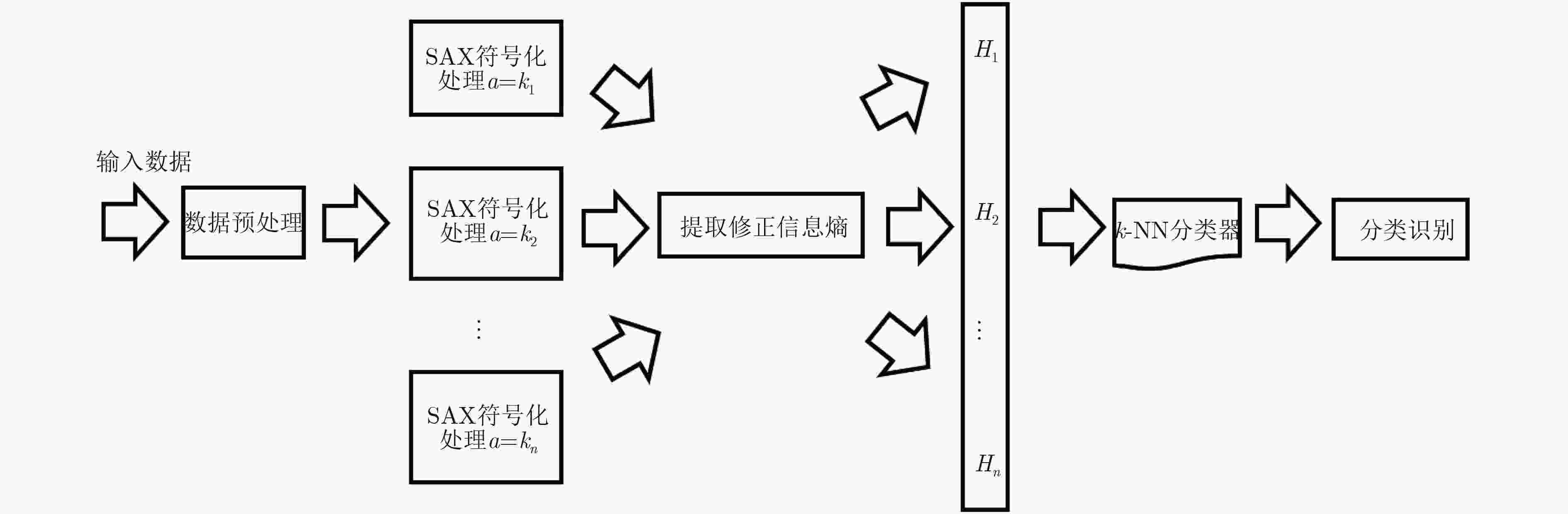
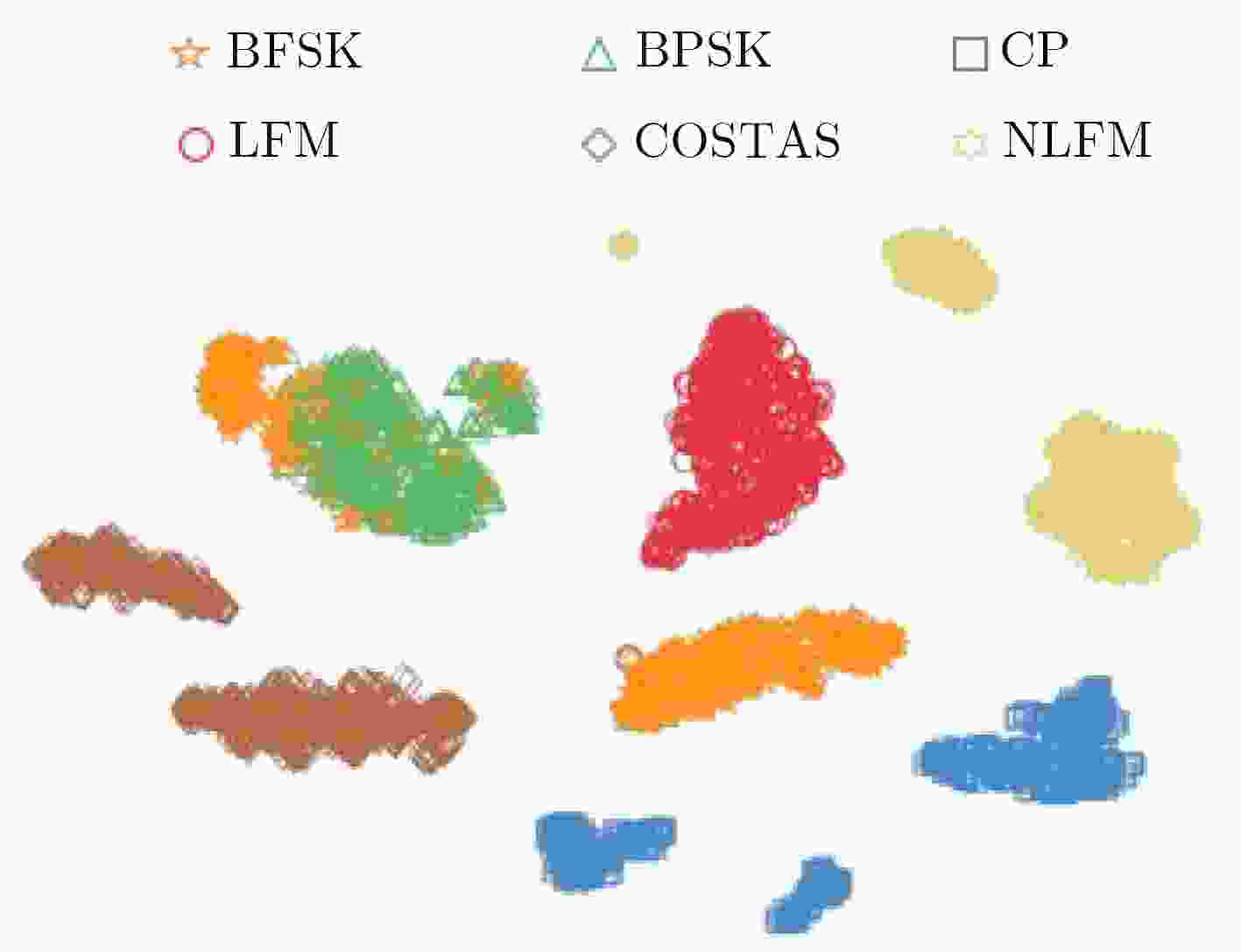
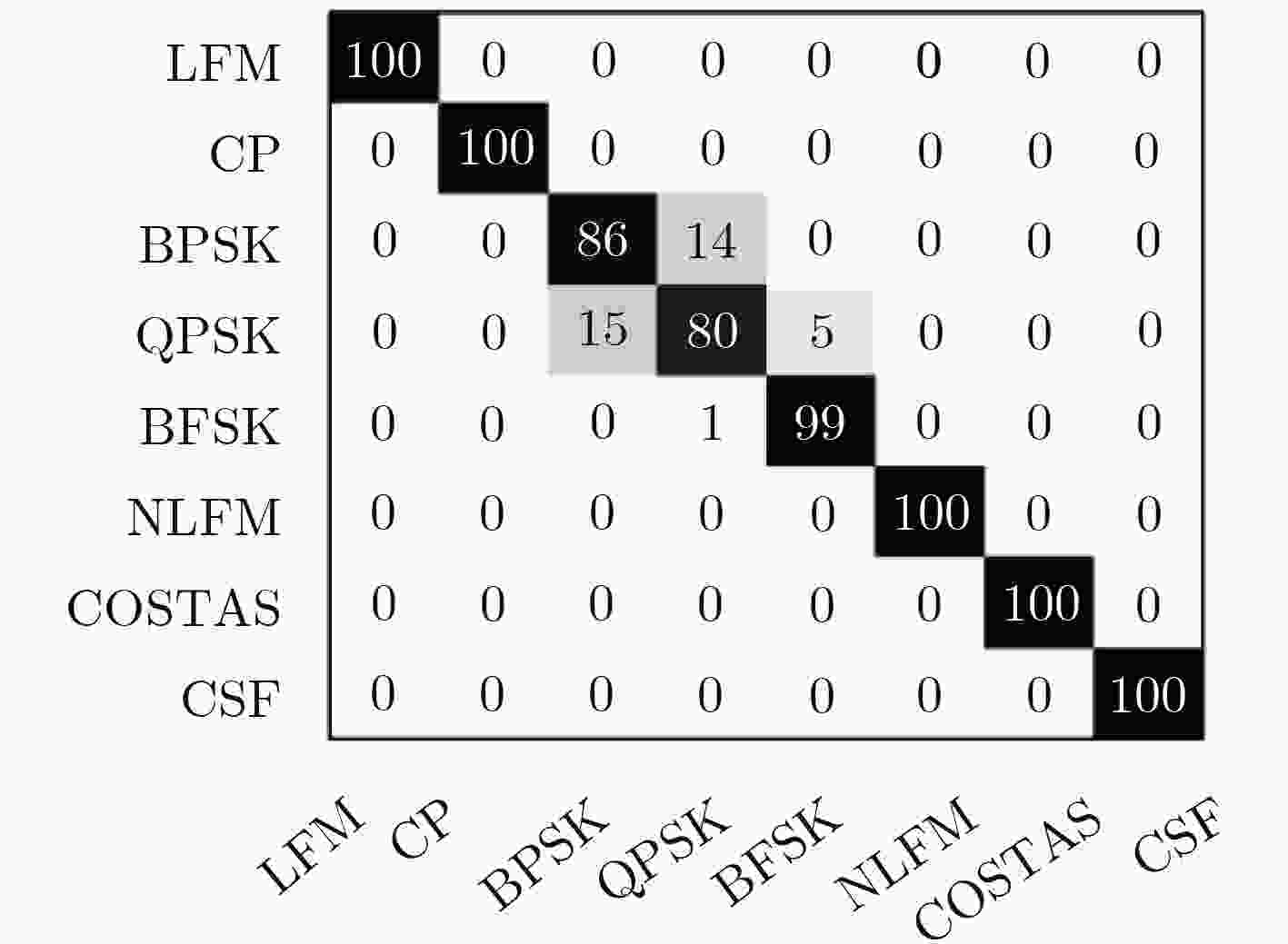
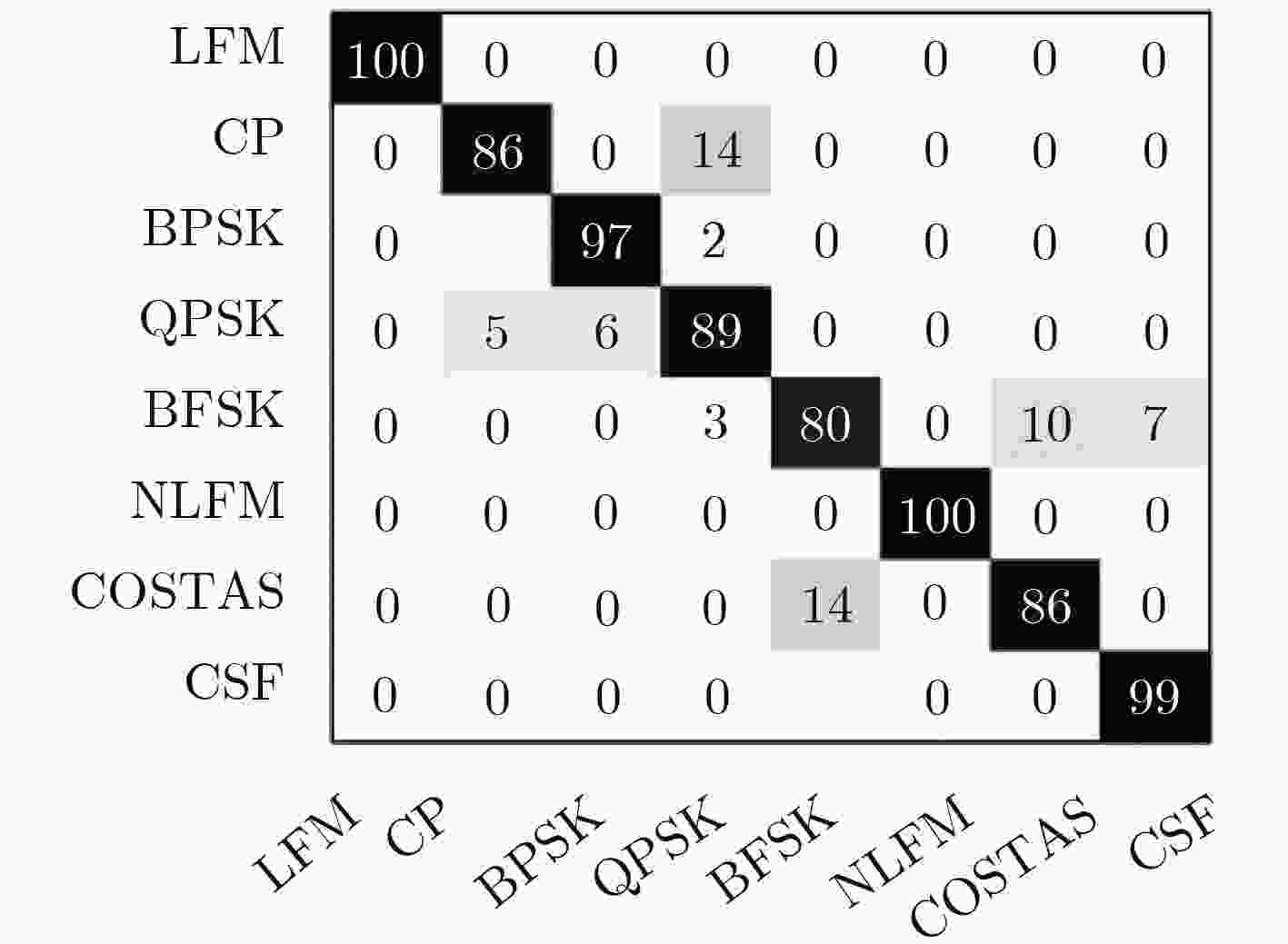
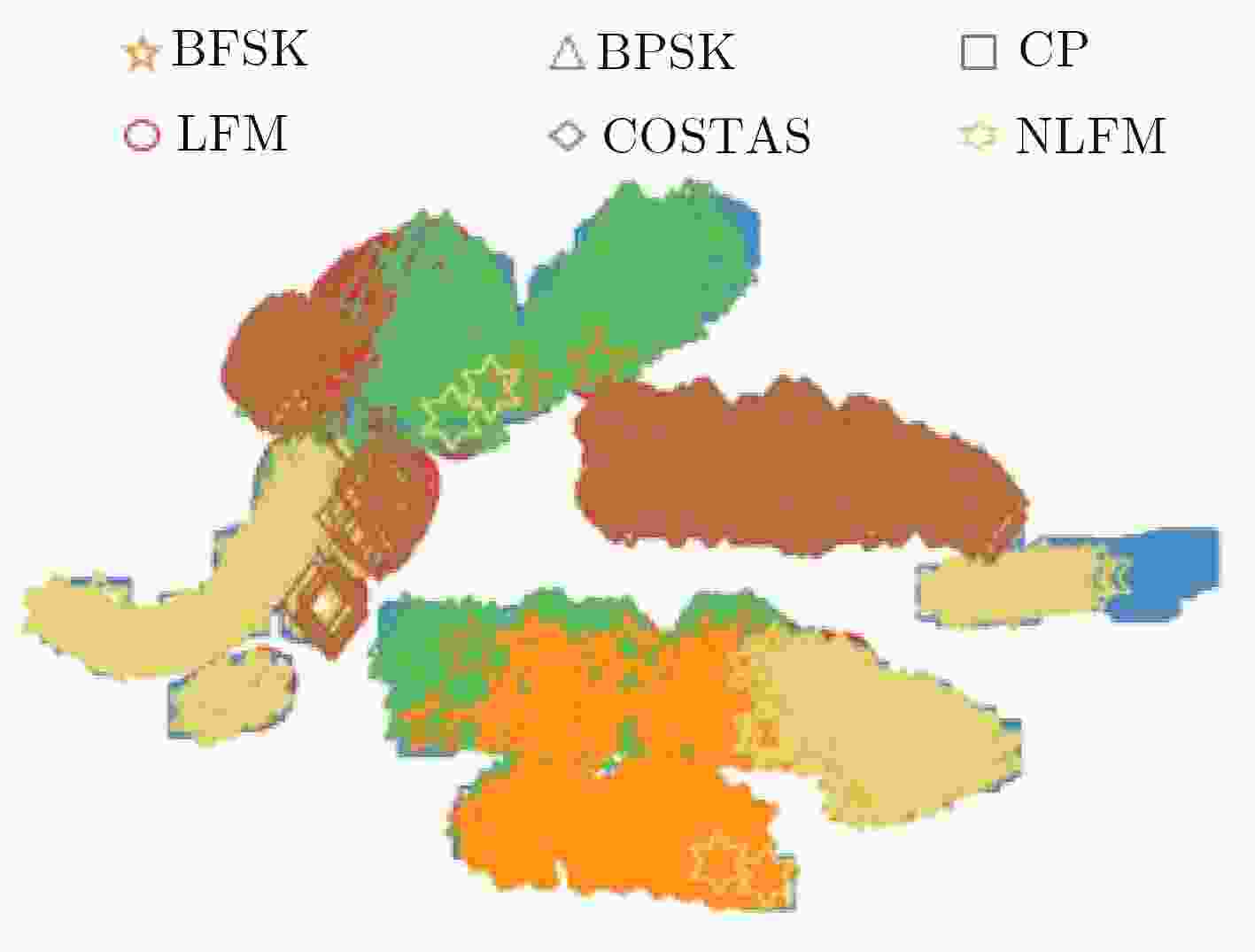


 下载:
下载:
