Dictionary Refinement Method for Compressive Sensing Based Multi-target Device-free Localization
-
摘要:
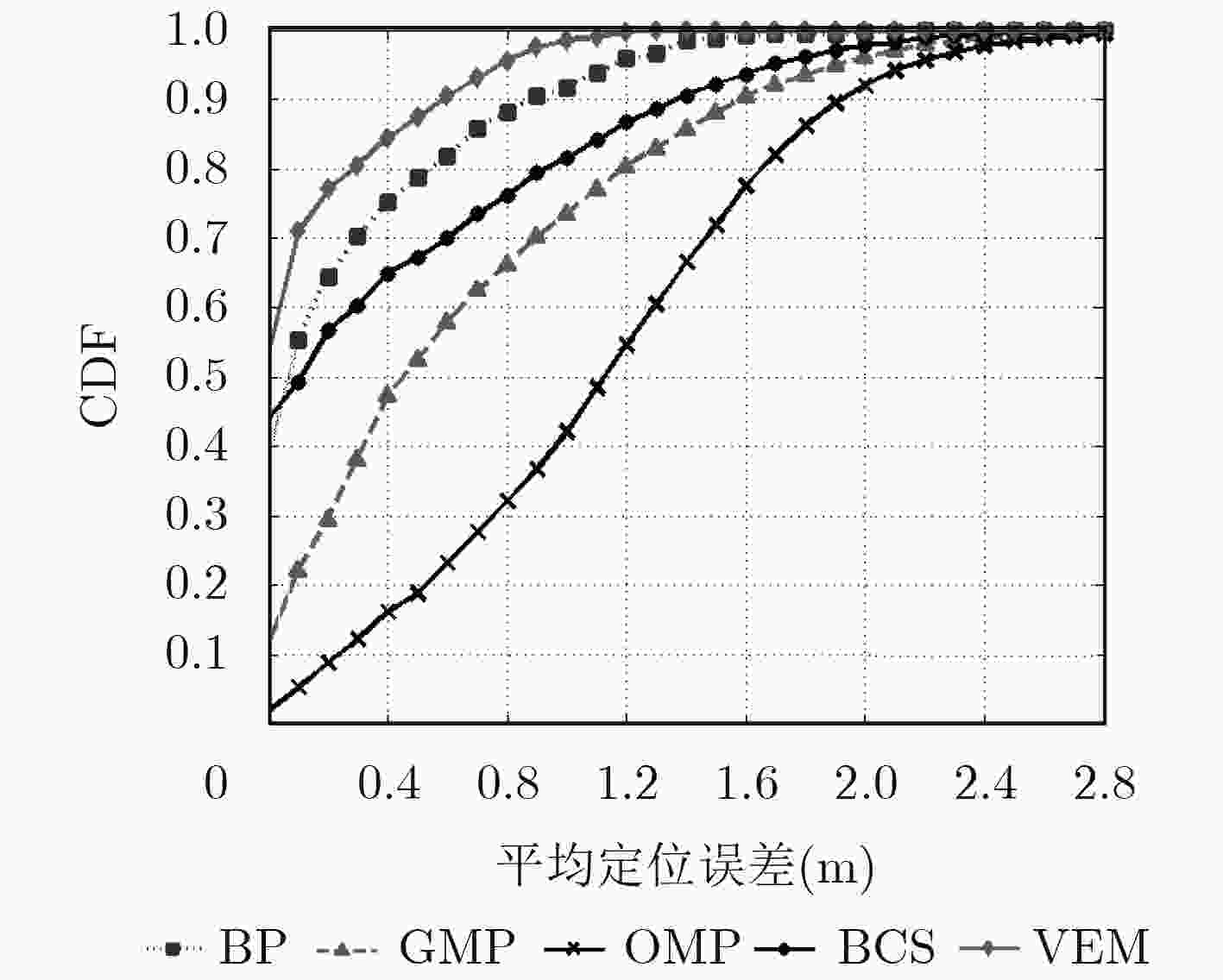
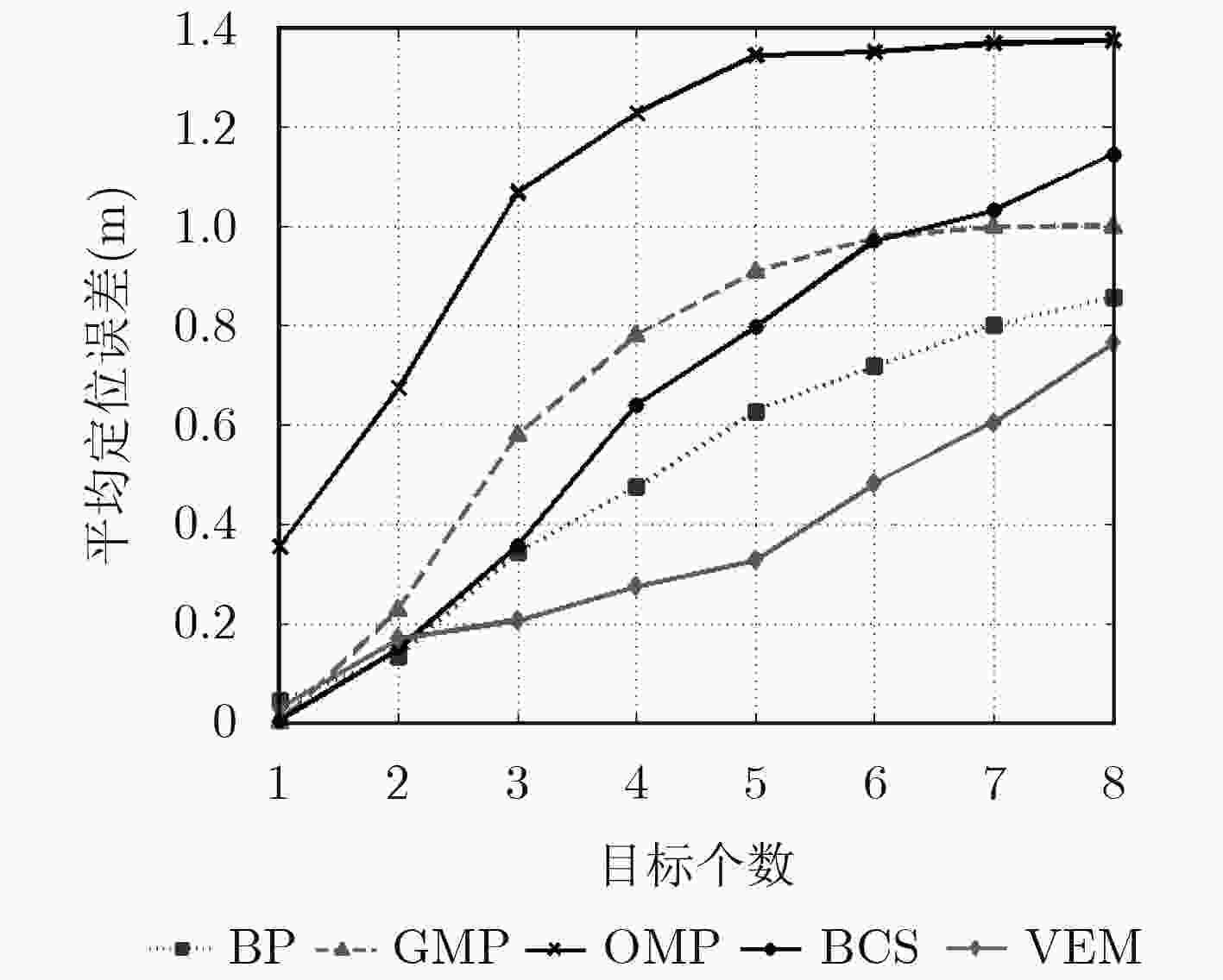
该文针对压缩感知多目标无源定位在无线定位环境中的字典失配问题,提出基于变分期望最大化算法的字典适配方法。该方法首先根据鞍面模型建立无源字典,并将与定位环境相关的字典参数作为可调参数。然后,为目标位置向量建立两层的混合高斯先验模型以诱导其稀疏性。最后,利用变分期望最大化算法估计隐藏变量的后验分布以及优化字典环境参数,实现多目标位置估计和字典适配。仿真结果表明,相较于传统的压缩感知多目标无源定位方法,在变化的无线定位环境下,所提定位方法的性能优势尤为明显。
Abstract:In order to solve the dictionary mismatch problem of Compressive Sensing (CS) based multi-target Device-Free Localization (DFL) under the wireless localization environments, a Variational Expectation Maximization (VEM) based dictionary refinement method is proposed. Firstly, this method builds the dictionary based on the saddle surface model, and models the environment-related dictionary parameters as tunable parameters. Then, a two-layer hierarchical Gaussian prior model is imposed on the location vector to induce its sparsity. Finally, the VEM algorithm is adopted to estimate the posteriors of hidden variables and optimize the environment-related dictionary parameter, thus the estimation of target locations and dictionary refinement can be realized jointly. Compared with the conventional CS based multi-target DFL schemes, the simulation results demonstrate that the performance of the proposed algorithm is especially excellent in changing wireless localization environments.
-
表 1 目标位置估计算法
(1) 令${\gamma _{{\text{th}}}} = {10^{ - 3}}$, ${r_{\max }} = {10^3}$, ${\eta _{{\text{th}}}} = - 10\;{\text{dB}}$, $\gamma = \tau = 0$。 (2) while($\gamma \ge {\gamma _{{\text{th}}}}$或$r \le {r_{\max }}$)do (3) 根据式(17)和式(18),计算${{Σ}} $和${{μ}} $; (4) 根据式(20)和式(21),更新参数${a^ * }$和${b^ * }$; (5) 根据式(23)和式(24),更新参数${c^ * }$和$d_n^ * $; (6) while($\tau \le {\tau _{\max }}$)do (7) 根据式(30)更新$\rho $; (8) end while (9) 令$\gamma \leftarrow \parallel {{y}} - {{Φ}} ({\rho ^ * }){{μ}} \parallel_2^2$, $r \leftarrow r + 1$; (10) end while (11) $\forall n \in \{ 1,2, ·\!·\!· , N\} $,若$20\lg ({\mu _n}/\mathop {\max }\nolimits_i |{\mu _i}|) < {\eta _{{\text{th}}}}$,则${\mu _n} \!=\! 0$; (12) 令恢复的位置向量$\hat {{θ}} = {{μ }}$,目标个数$\hat K = |\hat {{θ}} |$。 -
WANG Jie, GAO Qinhua, PAN Miao, et al. Device-free wireless sensing: Challenges, opportunities, and applications[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(2): 132–137 doi: 10.1109/MNET.2017.1700133 YOUSSEF M, MAH M, and AGRAWALA A. Challenges: Device-free passive localization for wireless environments[C]. Proceedings of the ACM MobiCom’07, Montreal, 2007: 222–229. doi: 10.1145/1287853.1287880. ZHANG Dian, MA Jian, CHEN Quanbin, et al. An RF-based system for tracking transceiver-free objects[C]. Proceeding of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom’07), White Plains, 2007: 135–144. doi: 10.1109/percom.2007.8. WANG Ju, CHEN Xiaojiang, FANG Dingyi, et al. Transferring compressive-sensing-based device-free localization across target diversity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(4): 2397–2409 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2360140 KE Wei, WANG Tingting, and SHAO Jianhua. CS-based device-free localization in the presence of model errors[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, 2016: 4443–4447. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2016.7472517. WANG Ju, FANG Dingyi, and YANG Zhe. E-HIPA: An energy-efficient framework for high-precision multi-target adaptive device-free localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(3): 716–729 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2567396 TALAMPAS M and LOW K. A geometric filter algorithm for robust device-free localization in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(5): 1670–1678 doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2433211 LEI Qian, ZHANG Haijian, SUN Hong, et al. Fingerprint-based device-free localization in changing environments using enhanced channel selection and logistic regression[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 2569–2577 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2784387 CHEN Xi, MA Chen, ALLEGUE M, et al. Taming the inconsistency of Wi-Fi fingerprints for device-free passive indoor localization[C]. Proceeding of the IEEE INFOCOM 2017, Atlanta, 2017: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2017.8057185. WILSON J and PATWARI N. Ratio tomographic imaging with wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2010, 9(5): 621–632 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2009.174 WANG Qinghua, YIGITLER H, JANTTI R, et al. Localizing multiple objects using radio tomographic imaging technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(5): 3641–3656 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2432038 DONOHO D. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 WANG Ju, FANG Dingyi, CHEN Xiaojing, et al. LCS: Compressive sensing based device-free localization for multiple targets in sensor networks[C]. Proceeding of the IEEE INFOCOM 2013, Turin, 2013: 14–19. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2013.6566752. SONG Chaobing and XIA Shutao. Sparse signal recovery by minimization under restricted isometry property[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(9): 1154–1158 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2323238 WANG Jie, GAO Qinhua, PAN Miao, et al. Towards accurate device-free wireless localization with a saddle surface model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(8): 6665–6677 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2476495 SEEGER M and WIPF D. Variational Bayesian inference techniques[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(6): 81–91 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.938082 CANDES E and WAKIN M. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 JI Shihao, XUE Ya, and CARIN L. Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2346–2356 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.914345 -





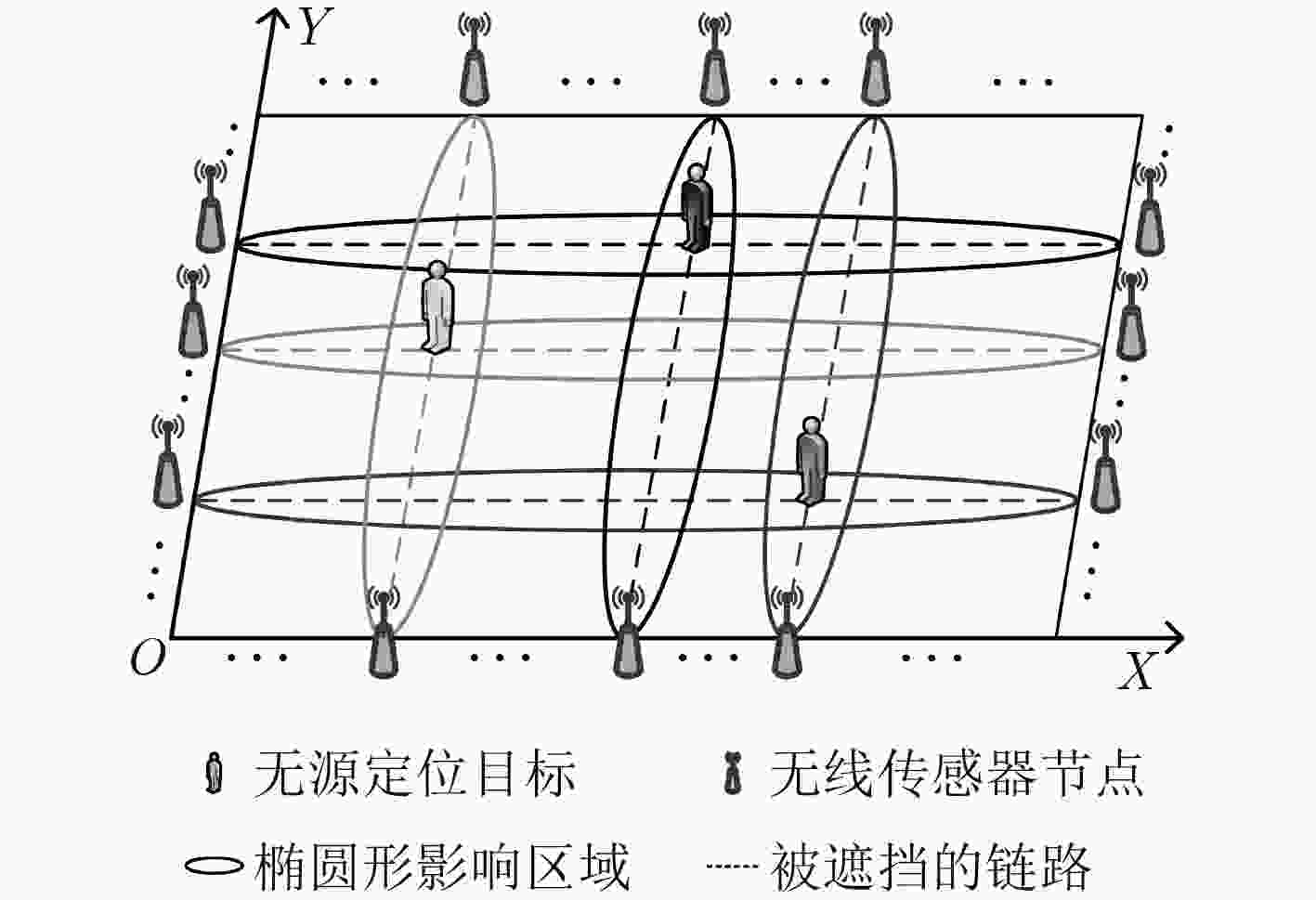
 下载:
下载:
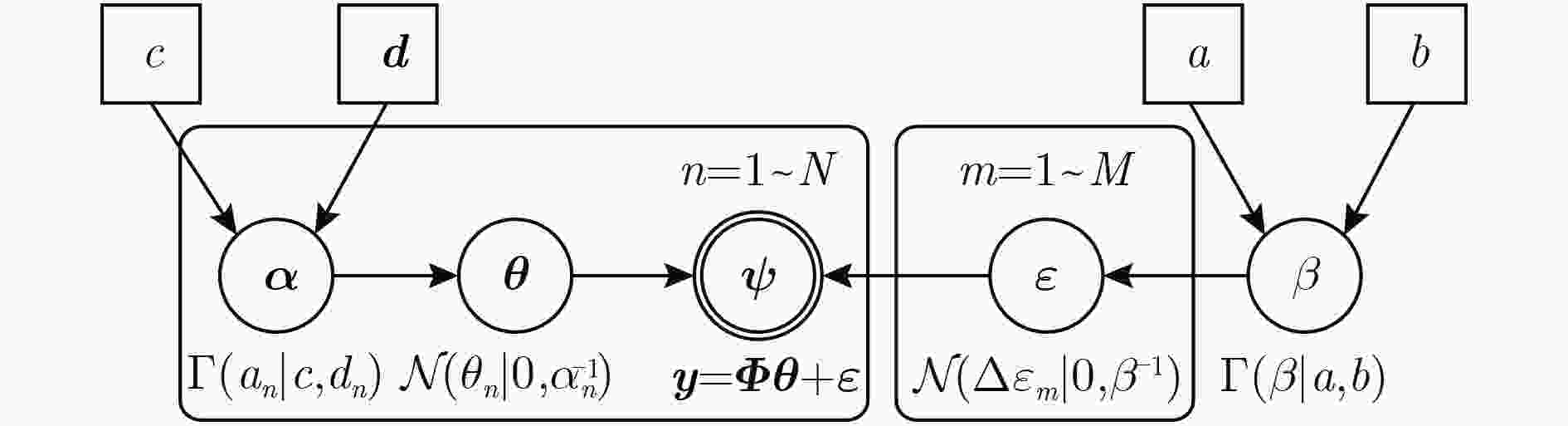
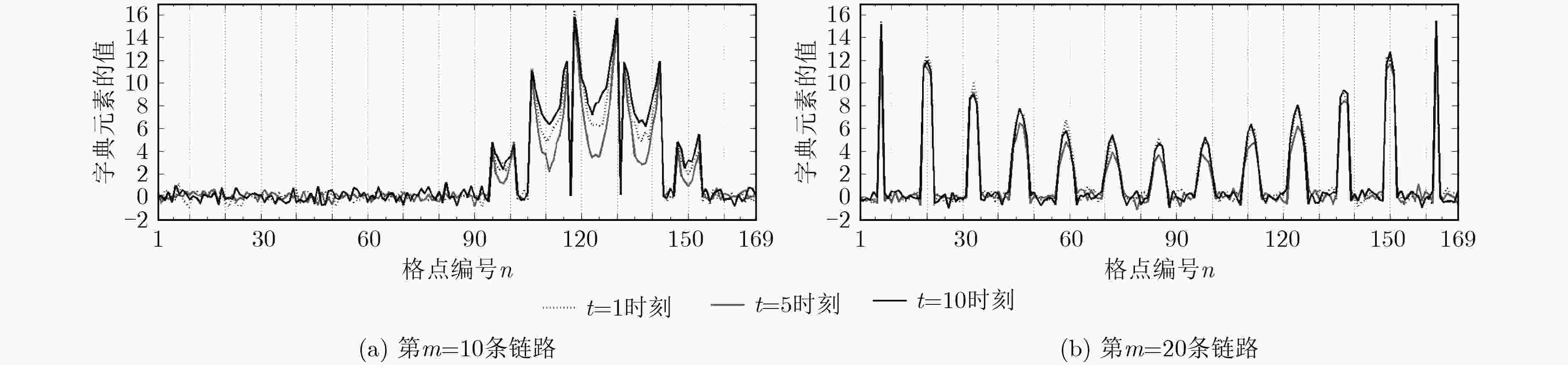
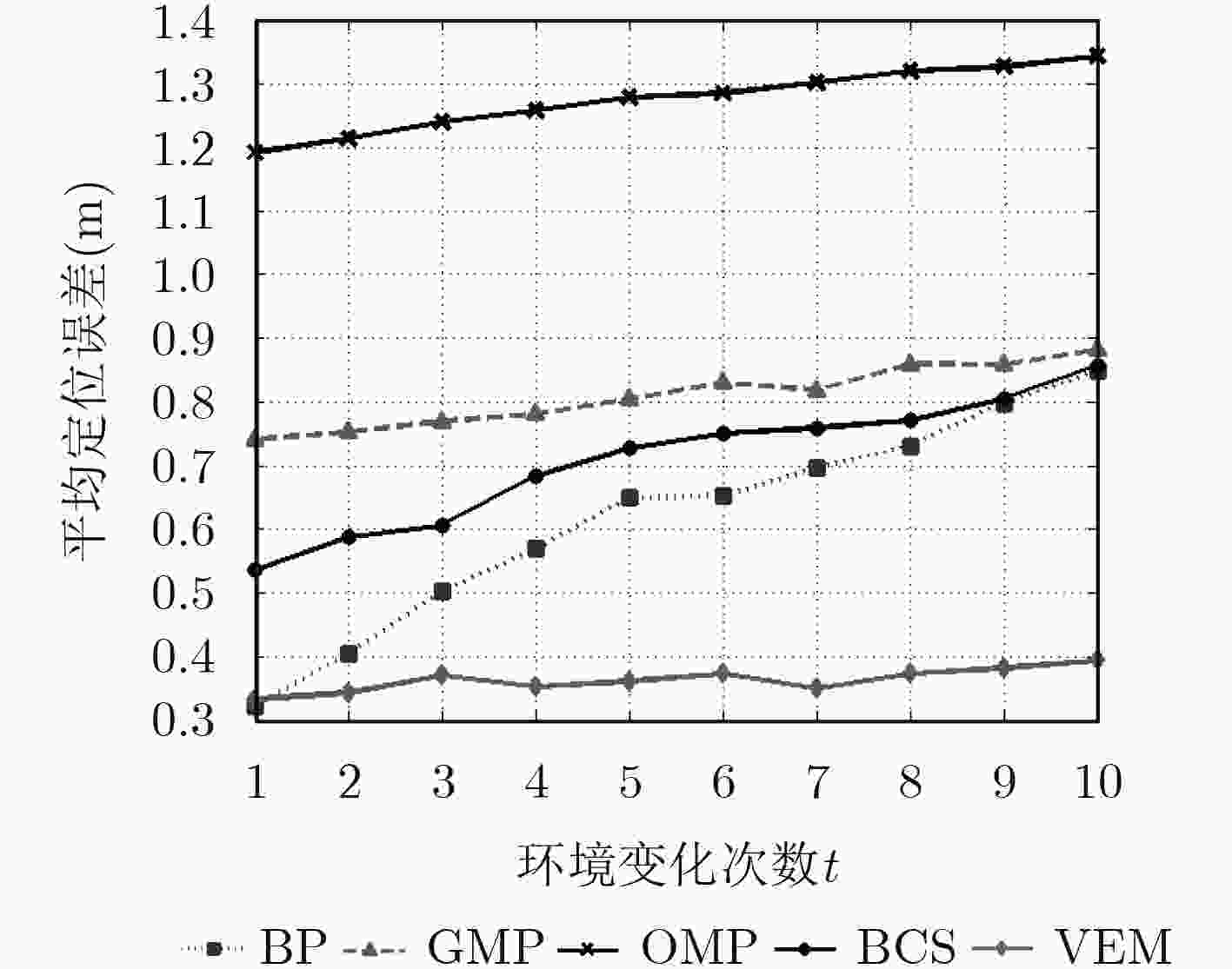


 下载:
下载:
