Sensing Matrix Optimization for Sparse Signal under Structured Noise Interference
-
摘要:
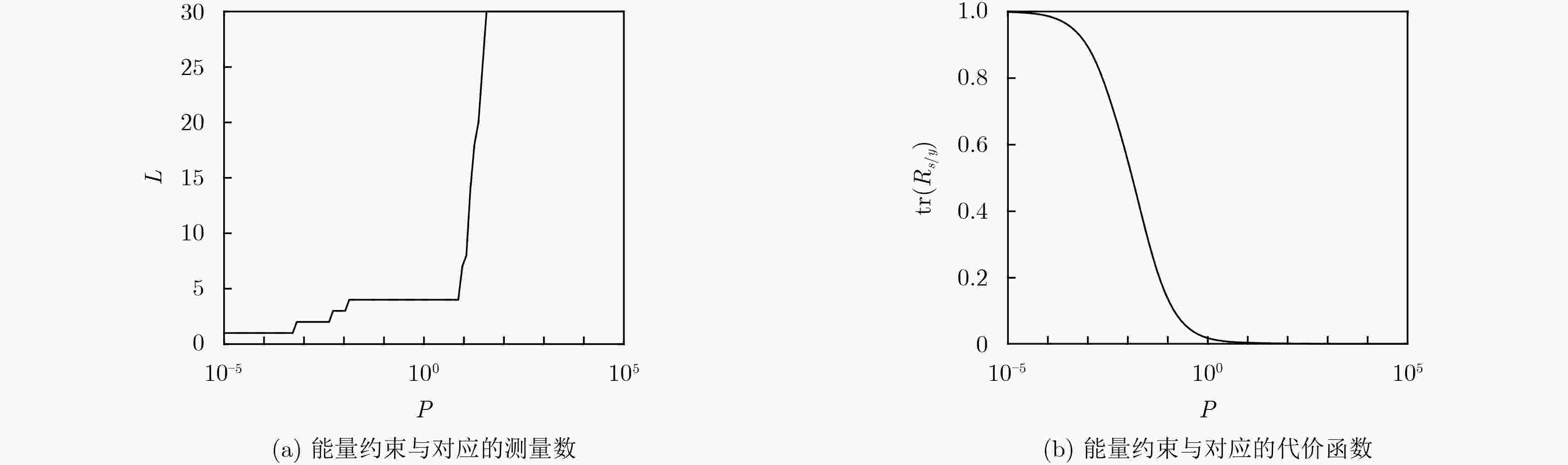
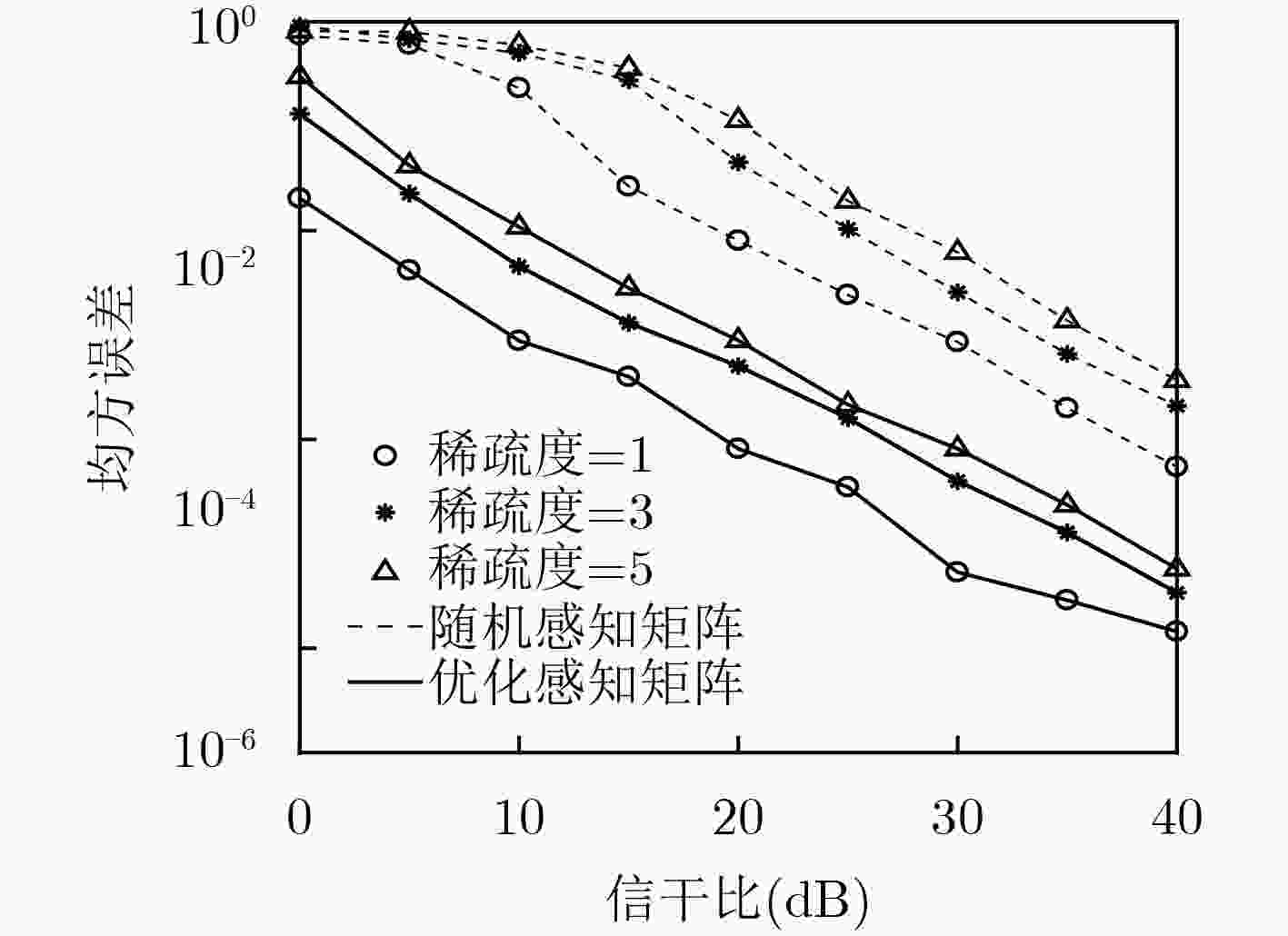
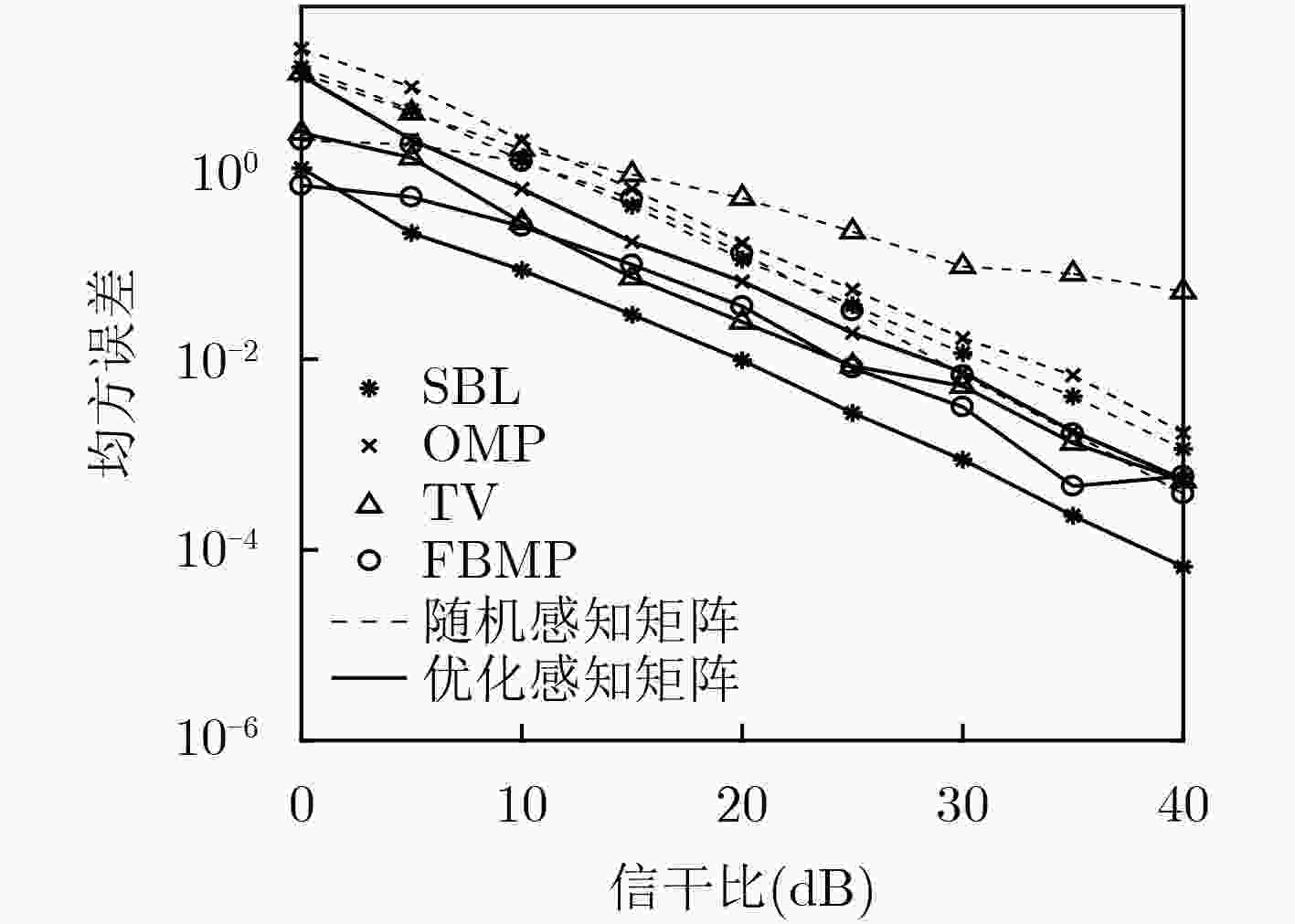
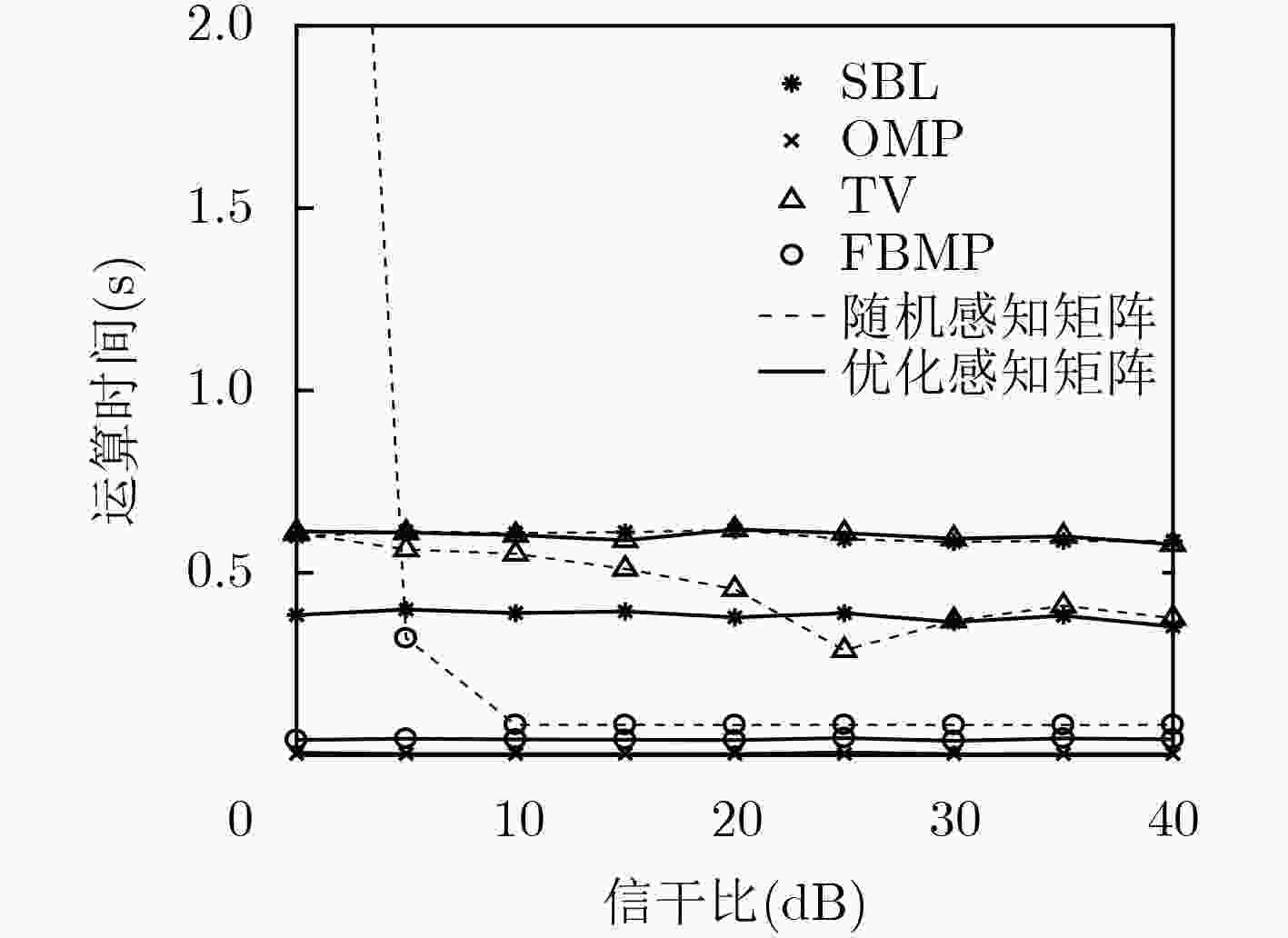
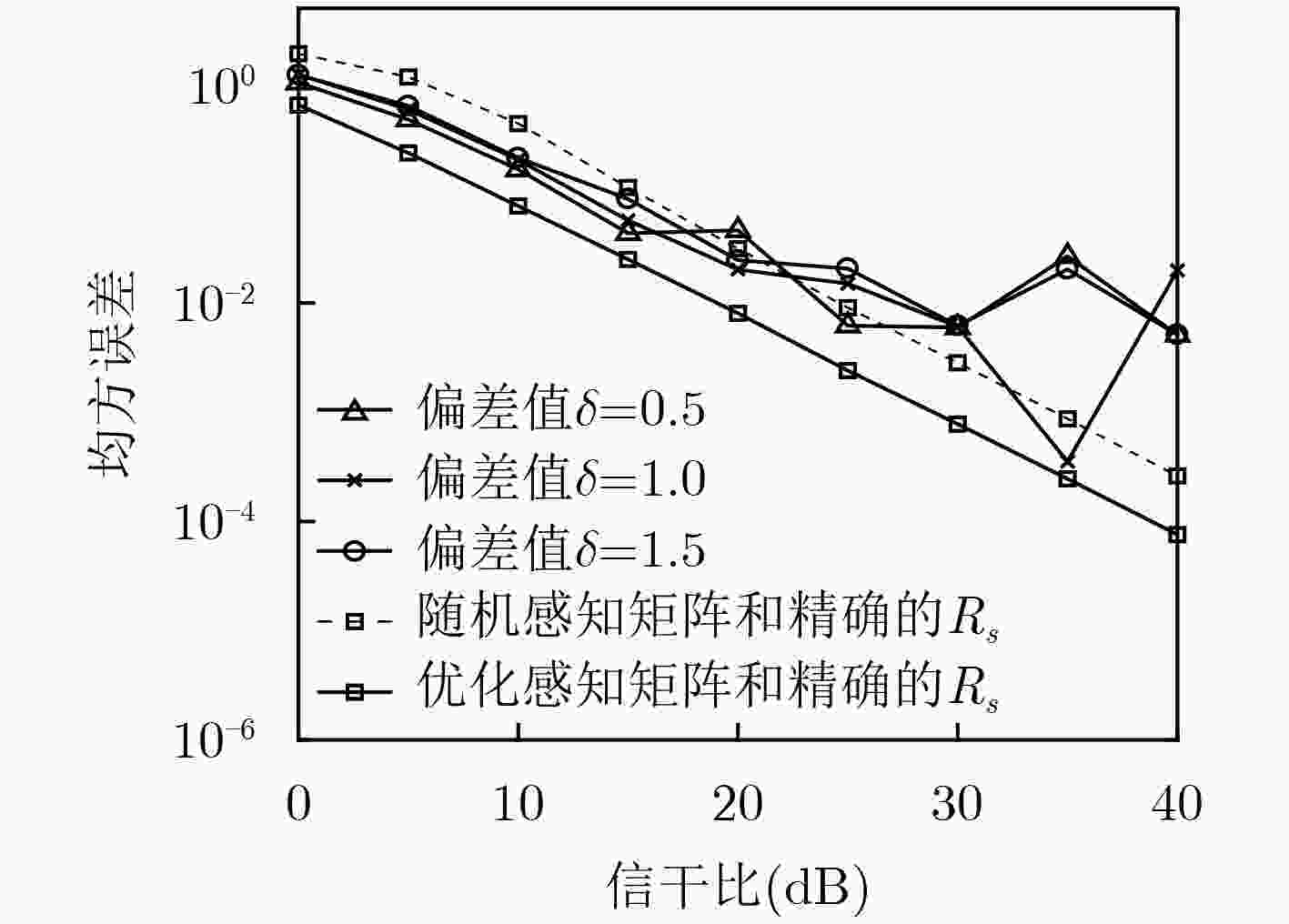
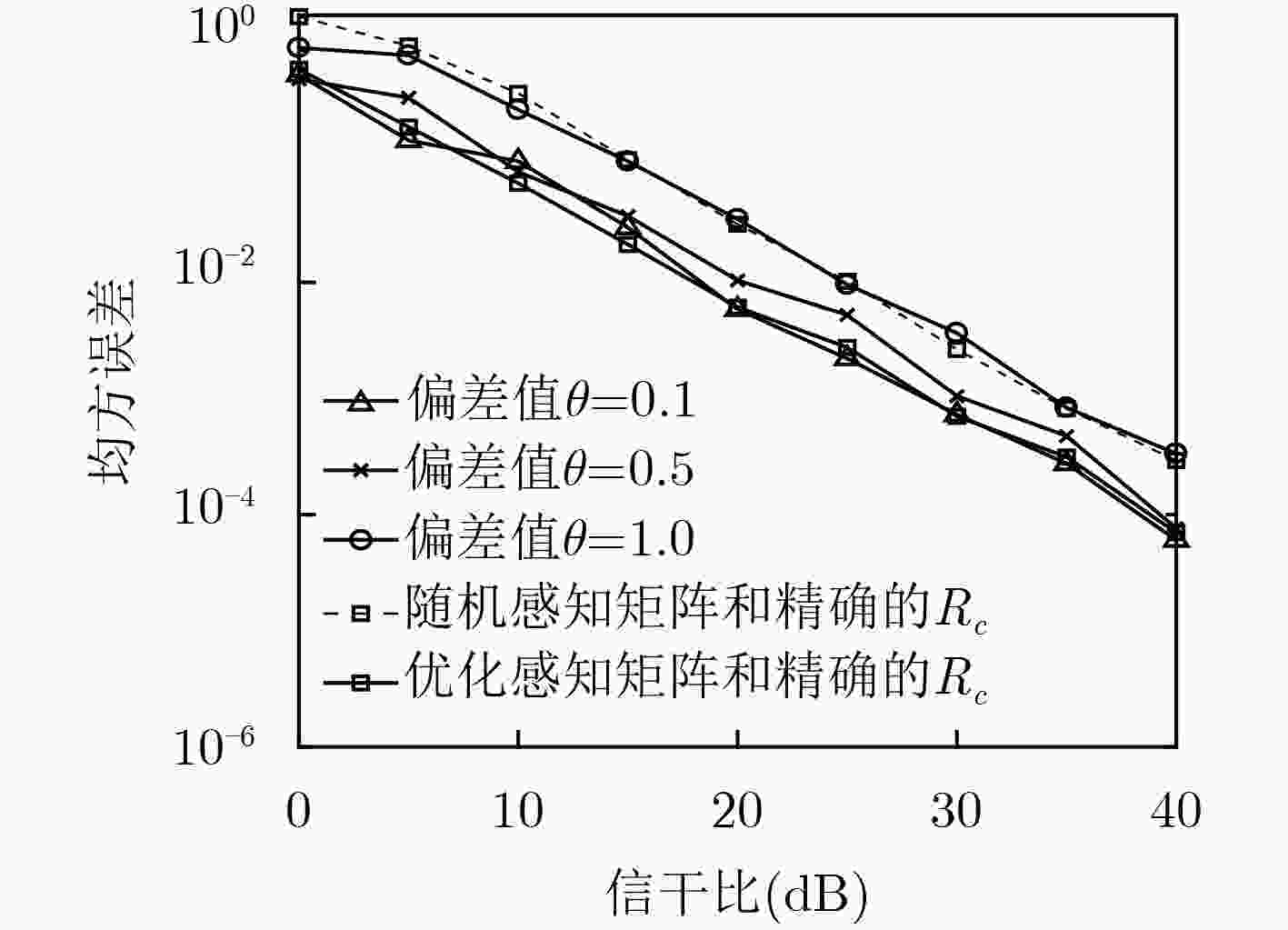
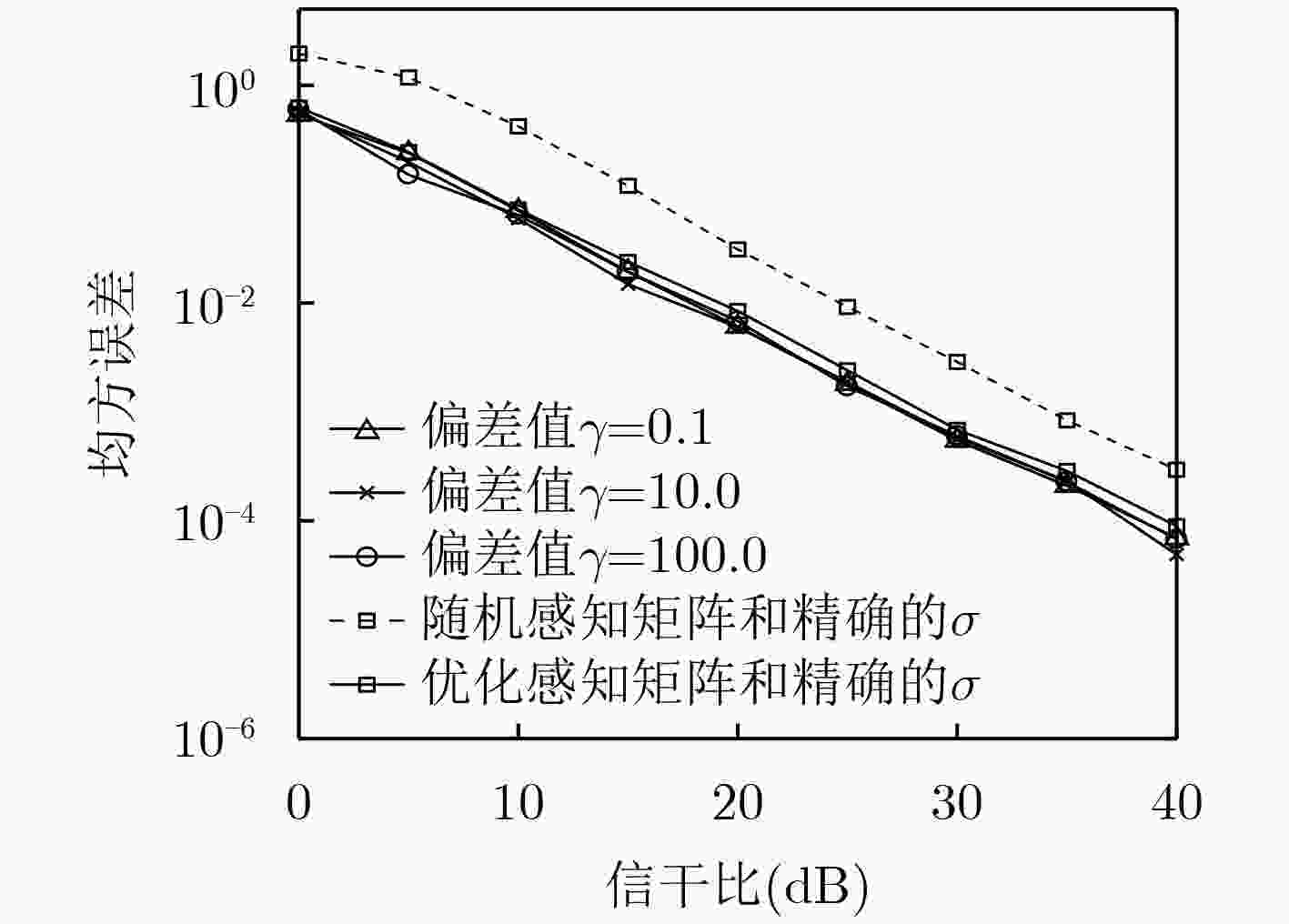
针对具有结构性噪声干扰的稀疏信号处理问题,该文提出一种基于贝叶斯理论的感知矩阵优化设计方法。结合具有加性干扰的稀疏信号模型,通过对感知矩阵进行能量约束,最小化信号的后验协方差矩阵的迹,实现感知矩阵的优化设计。仿真不同信号稀疏度和重构算法时,感知矩阵优化对信号重构误差和重构时间的影响;分析信号先验信息存在偏差时,感知矩阵优化对重构效果的影响。仿真结果表明,优化后的感知矩阵能够更好地获取稀疏信号中的重要信息,信号重构精度的均方误差减小约15~25 dB,重构时间减少约40%。
Abstract:To solve sparse signal processing problem with structural noise interference, a method of sensing matrix optimization design based on sparse Bayesian theory is proposed. Combining the sparse signal model with additive interference, the design of the sensing matrix is realized by minimizing the trace of the posterior covariance matrix and the energy constraint of sensing matrix. The effects of sensing matrix optimization on the reconstruction error and reconstruction time are simulated using difference sparse signal and reconstruction algorithms, and the effects of the sensing matrix optimization on the reconstruction effect are analyzed when there is a bias in the prior information. The simulation results show that the optimized sensing matrix can obtain the important information in the sparse signal, the mean square error of the signal reconstruction accuracy is reduced by about 15~25 dB, and the reconstruction time is reduced by about 40%.
-
FOUCART S. Flavors of compressive sensing[C]. International Conference Approximation Theory, San Antonio, USA, 2016: 61–104. NOUASRIA H and ET-TOLBA M. A novel sensing matrix for cluster structured sparse signals[C]. International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference, Valencia, Spain, 2017: 998–1003. JI Shihao, XUE Ya, and CARIN L. Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2346–2356 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.914345 FUHRMANN D R. One-step optimal measurement selection for linear Gaussian estimation problems[C]. International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference. Pisa, Italy, 2007: 224–227. ZELNIK-MANOR L, ROSENBLUM K, and ELDAR Y C. Sensing matrix optimization for block-sparse decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(9): 4300–4312 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2159211 DAS A. A Bayesian sparse-plus-low-rank matrix decomposition method for direction-of-arrival tracking[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(15): 4894–4902 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2715347 NANNURU S, GERSTOFT P, and GEMBA K L. Sparse Bayesian learning with uncertain sensing matrix[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, USA, 2017: 3964–3968. YANG Linxiao, FANG Jun, and LI Hongbin. Sparse Bayesian dictionary learning with a Gaussian hierarchical model[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2016: 2564–2568. FISHER R A S. Theory of Statistical Estimation[M]. Institute of Mathematics, University of Tsukuba, 2008: 51–65. PETERSEN K B and PEDERSEN M S. The Matrix Cookbook[M]. Technical University of Denmark, 2008: 18–19. BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. World Book Inc, 2013: 243–249. WIPF D P and RAO B D. Sparse Bayesian Learning for basis selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2153–2164 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831016 SCHNITER P, POTTER L C, and ZINIEL J. Fast Bayesian matching pursuit[C]. Information Theory and Applications Workshop, San Diego, USA, 2008: 326–333. TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108 KAMILOV U. Parallel proximal algorithm for anisotropic total variation minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 26(2): 539–548 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2629449 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
