Multi-scale Local Region Structure Dominant Binary Pattern Learning for Image Representation
-
摘要:
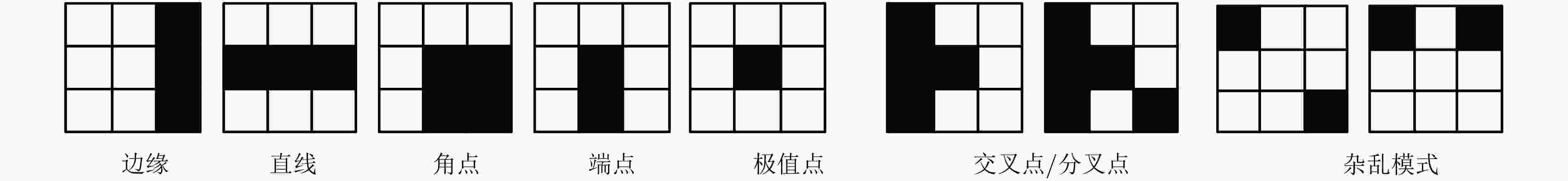
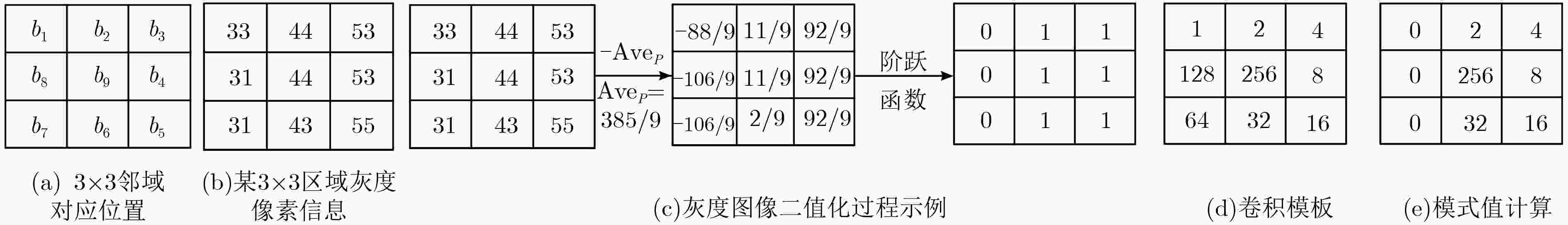
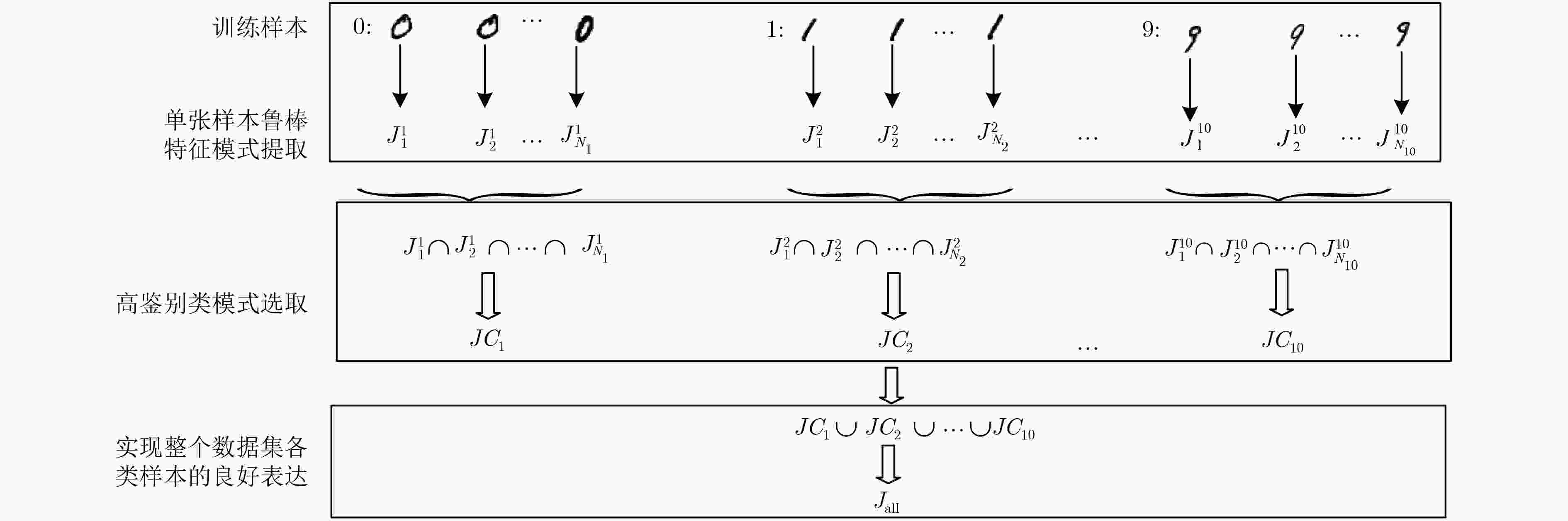
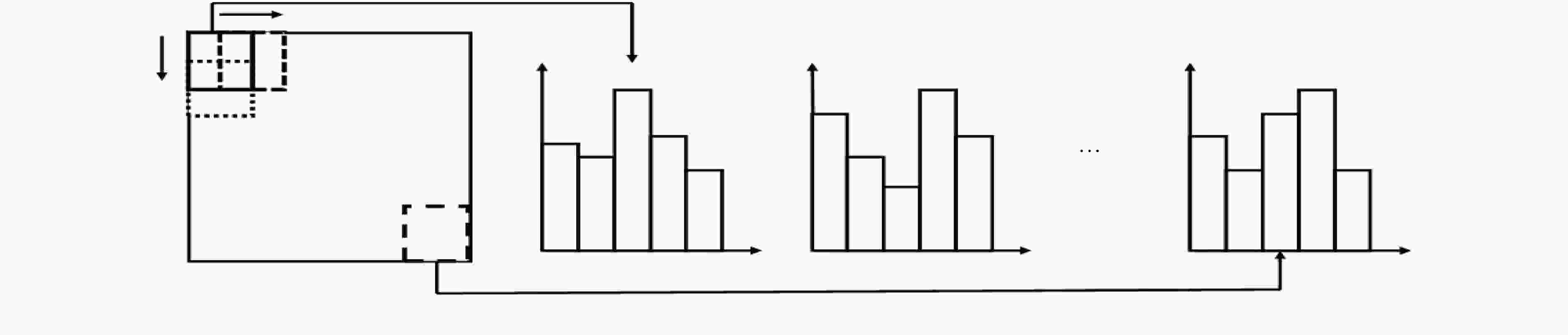
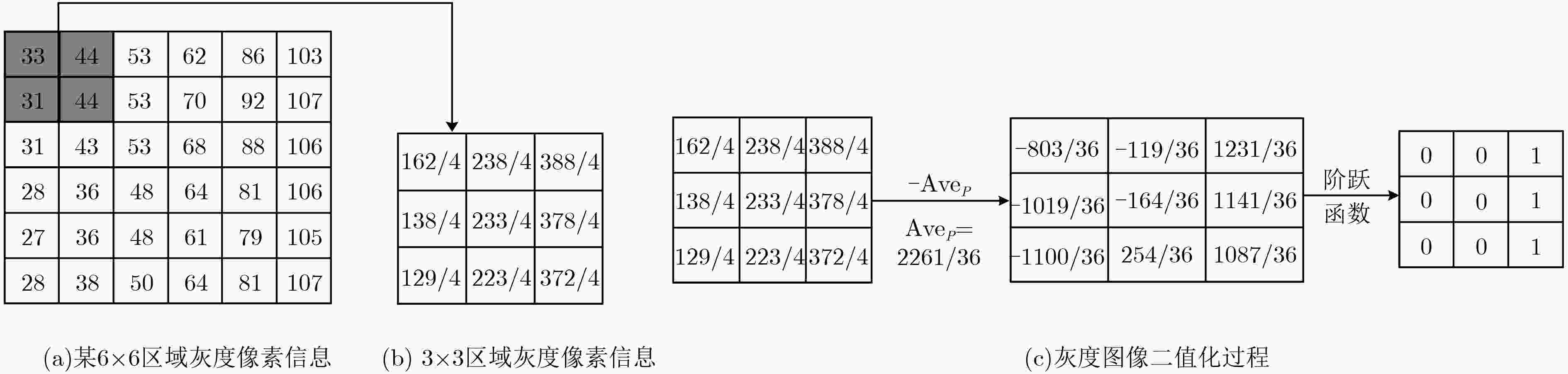
通过零均值化的微观结构模式二值化(ZMPB)处理,该文提出一种立足于局部图像多尺度结构二值模式提取的图像表示方法。该方法能够表达图像中可能出现的各种具有视觉意义的重要模式结构,同时通过主导二值模式学习模型,可以获得适应于图像数据集的主导特征模式子集,在特征鲁棒性、鉴别力和表达能力上达到优异性能,同时可以有效降低特征编码的维度,提高算法的执行速度。实验结果表明该算法性能优异,具有很强的鉴别能力和鲁棒性,优于传统LBP和GIMMRP方法,和很多最新算法结果相比,也具有竞争优势。
-
关键词:
- 目标识别 /
- 零均值化的微观结构模式二值化 /
- 主导二值模式学习 /
- 局部结构
Abstract:By means of Zero-mean Microstructure Pattern Binarization (ZMPB), an image representation method based on image local microstructure binary pattern extraction is proposed. The method can express all the important patterns with visual meaning that may occur in the image. Moreover, through the dominant binary pattern learning model, the dominant feature pattern set adapted to the different data sets is obtained, which not noly achieves excellent ability in feature robustness, discriminative and representation, but also can greatly reduce the dimension of feature coding and improve the execution speed of the algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed method has strong discriminative power and outperformes the traditional LBP and GIMMRP methods. Compared with many recent algorithms, the proposed method also presents a competitive advantage.
-
表 1 各种算法人脸识别率比较(%)
表 2 各种算法在手写数字库MNIST的识别率比较(%)
表 3 各种算法的车标识别率比较(%)
训练样本数 10 20 30 40 50 LBP 97.95 99.42 99.69 99.87 99.92 GIMMRP[9] 99.64 99.88 99.95 99.96 99.96 本文算法 99.87 99.98 100 100 100 表 4 本文算法与相关算法性能比较
数据库 1×1识别率(%) 2×2识别率(%) 1×1+2×2识别率(%) 特征维度 1×1尺度单张图片特征提取时间(s) YALE 本文算法 95.56 95.40 99.30 4050/5670/9720 0.020 LBP 92.96 4779 0.016 GIMMRP 94.11 10611 0.062 ORL 本文算法 97.70 97.45 99.40 7290/6966/14256 0.020 LBP 96.00 4779 0.016 GIMMRP 97.50 10611 0.061 车标 本文算法 99.11 99.10 99.76 4212/5670/9882 0.018 LBP 97.95 4779 0.012 GIMMRP 99.64 10611 0.053 MNIST 本文算法 98.32 98.93 99.01 720/792/1512 0.016 LBP 93.56 2124 0.015 GIMMRP 98.91 4716 0.044 -
LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant key points[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 BAY H and TUYTELAARS T. SURF: Speeded up robust features[J]. Computer Vision & Image Understanding, 2006, 110(3): 404–417 doi: 10.1007/11744023_32 MIKOLAJCZYK K and SCHMID C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(10): 1615–1630 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.188 ENGIN T, LEPETIT V, and FUA P. Daisy: An efficient dense descriptor applied to wide-baseline stereo[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(5): 815–830 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.77 DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2005: 886–893. OJALA T, VALKEALAHTI K, OJA E, et al. Texture discrimination with multidimensional distributions of signed gray-level differences[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2001, 34(3): 727–739 doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(00)00010-8 OJALA T, PIETIKAINEN M, and MAENPAA T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 971–987 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623 LIAO S, LAW M W K, and CHUNG A C S. Dominant local binary patterns for texture classification[J]. IEEE Transactionson Image Processing, 2009, 18(5): 1107–1118 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2015682 张东波, 陈治强, 易良玲, 等. 图像微观结构的二值化表示与目标识别应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(3): 633–640 doi: 10.11999/JEIT170513ZHANG Dongbo, CHEN Zhiqiang, YI Liangling, et al. Binarization representation of image microstructure and the application of object recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(3): 633–640 doi: 10.11999/JEIT170513 HAMDAN B and MOKHTAR K. Face recognition using Angular Radial Transform[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2016, 30(2): 141–151 doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2016.10.006 ZHU Ningbo, TANG Ting, and TANG Shi. A sparse representation method based on kernel and virtual samples for face recognition[J]. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2013, 124(23): 6236–6241 doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.05.017 ZHANG Yuanyuan and ZHAO Dong. Adaptive convolutional neural network and its application in face recognition[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2016, 43(2): 389–399 doi: 10.1007/s11063-015-9420-y HUANG Pu and LAI Zhihui. Adaptive linear discriminant regression classification for face recognition[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 55: 78–84 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.05.001 WANG Sujing and ZHOU Chunguang. Face recognition using second-order discriminant tensor subspace analysis[J]. Neurocomputing, 2011, 74(12/13): 2142–2156 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2011.01.024 WANG Guoqiang and SHI Nianfeng. Embedded manifold-based kernel fisher discriminant analysis for face recognition[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2016, 43(1): 1–16 doi: 10.1007/s11063-014-9398-x SINGH G and CHHABRA I. Integrating global zernike and local discriminative HOG features for face recognition[J]. International Journal of Image & Graphics, 2016, 16(4): 1650021–1650042 doi: 10.1142/S0219467816500212 SHAO Hong and CHEN Shuang. Face recognition based on subset selection via metric learning on manifold[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2015, 16(12): 1046–1058 doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1500085 DING Shifei and GUO Lili. Extreme learning machine with kernel model based on deep learning[J]. Neural Computing & Applications, 2017, 28(8): 1975–1984 doi: 10.1007/s00521-015-2170-y ZHOU Yang and SUN Shiliang. Manifold partition discriminant analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(4): 830–840 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2529299 WU Tingfang and LIN C J. Probability estimates for multi-class classification by pairwise coupling[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2004, 5(4): 975–1005. SCHMIDHUBER J, CIRES D, and MEIER U. Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, Rod Aprovendis, USA, 2012: 3642–3649. ZHANG Ziming and LADICKY L. Learning anchor planes for Classification[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Granada, Spain, 2011: 1611–1619. EBRAHIMZADEH R and JAMPOUR M. Efficient handwritten digit recognition based on histogram of oriented gradients and SVM[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2014, 104(9): 10–13 doi: 10.5120/18229-9167 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
