Gesture Recognition with Multi-dimensional Parameter Using FMCW Radar
-
摘要:
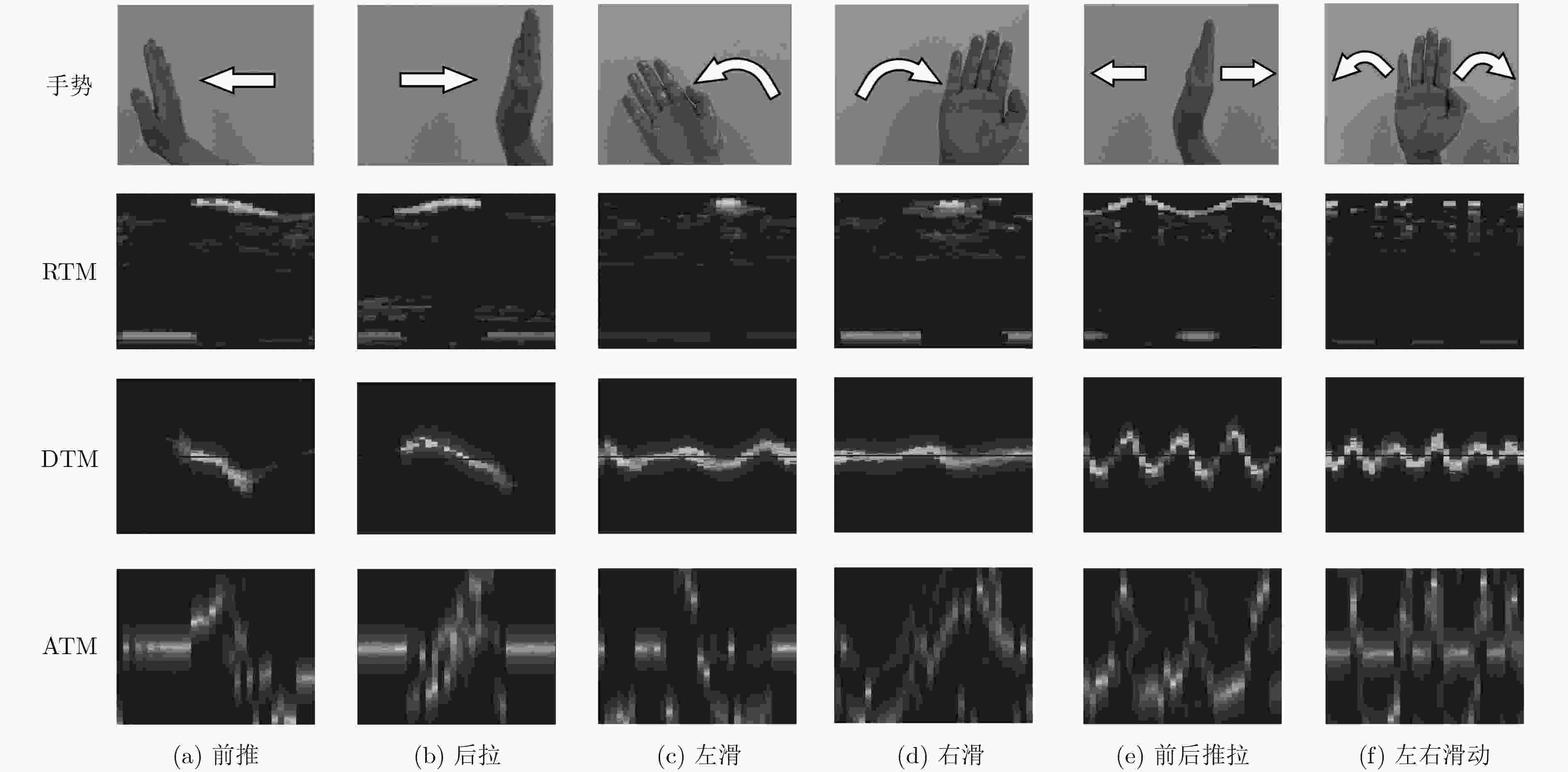
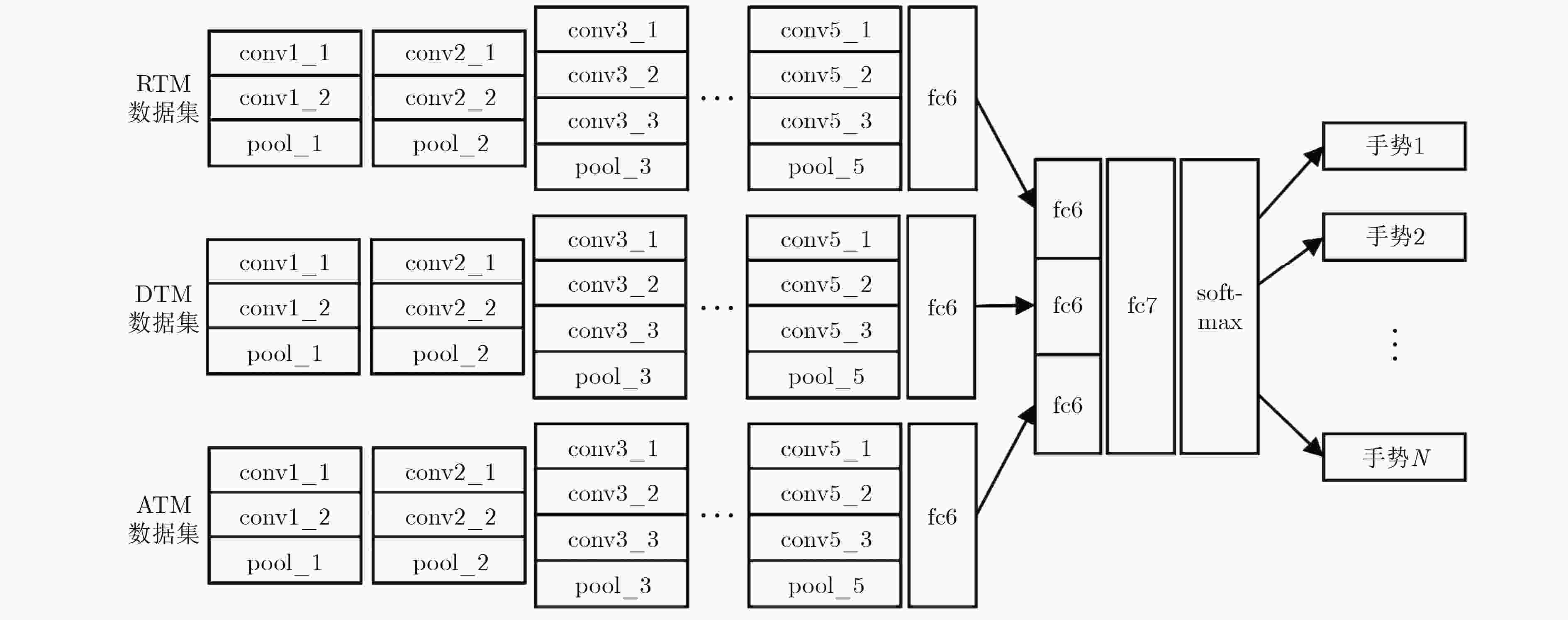
该文提出一种基于调频连续波(FMCW)雷达多维参数的卷积神经网络手势识别方法。通过对雷达信号进行时频分析,估计手势目标的距离、多普勒和角度参数,构建出手势动作的多维参数数据集。同时,为了进行手势特征提取和精确分类,提出多分支网络结构和高维特征融合的方案,设计出具有端到端结构的RDA-T多维参数卷积神经网络。实验结果表明,结合手势动作的距离、多普勒和角度信息进行多维参数学习,所提方法有效解决了单维参数手势识别方法中手势描述信息量低的问题,且手势识别准确率相较于单参数方法提高了5%~8%。
Abstract:A multi-parameter convolutional neural network method is proposed for gesture recognition based on Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar. A multidimensional parameter dataset is constructed for gestures by performing time-frequency analysis of the radar signal to estimate the distance, Doppler and angle parameters of the gesture target. To realize feature extraction and classification accurately, an end-to-end structured Range-Doppler-Angle of Time (RDA-T) multi-dimensional parameter convolutional neural network scheme is further proposed using multi-branch network structure and high-dimensional feature fusion. The experimental results reveal that using the combined gestures information of distance, Doppler and angle for multi-parameter learning, the proposed scheme resolves the problem of low information quantity of single-dimensional gesture recognition methods, and its accuracy outperforms the single-dimensional methods in terms of gesture recognition by 5%~8%.
-
Key words:
- FMCW radar /
- Gesture recognition /
- Deeplearning /
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
-
表 1 不同帧数下的准确率比较结果(%)
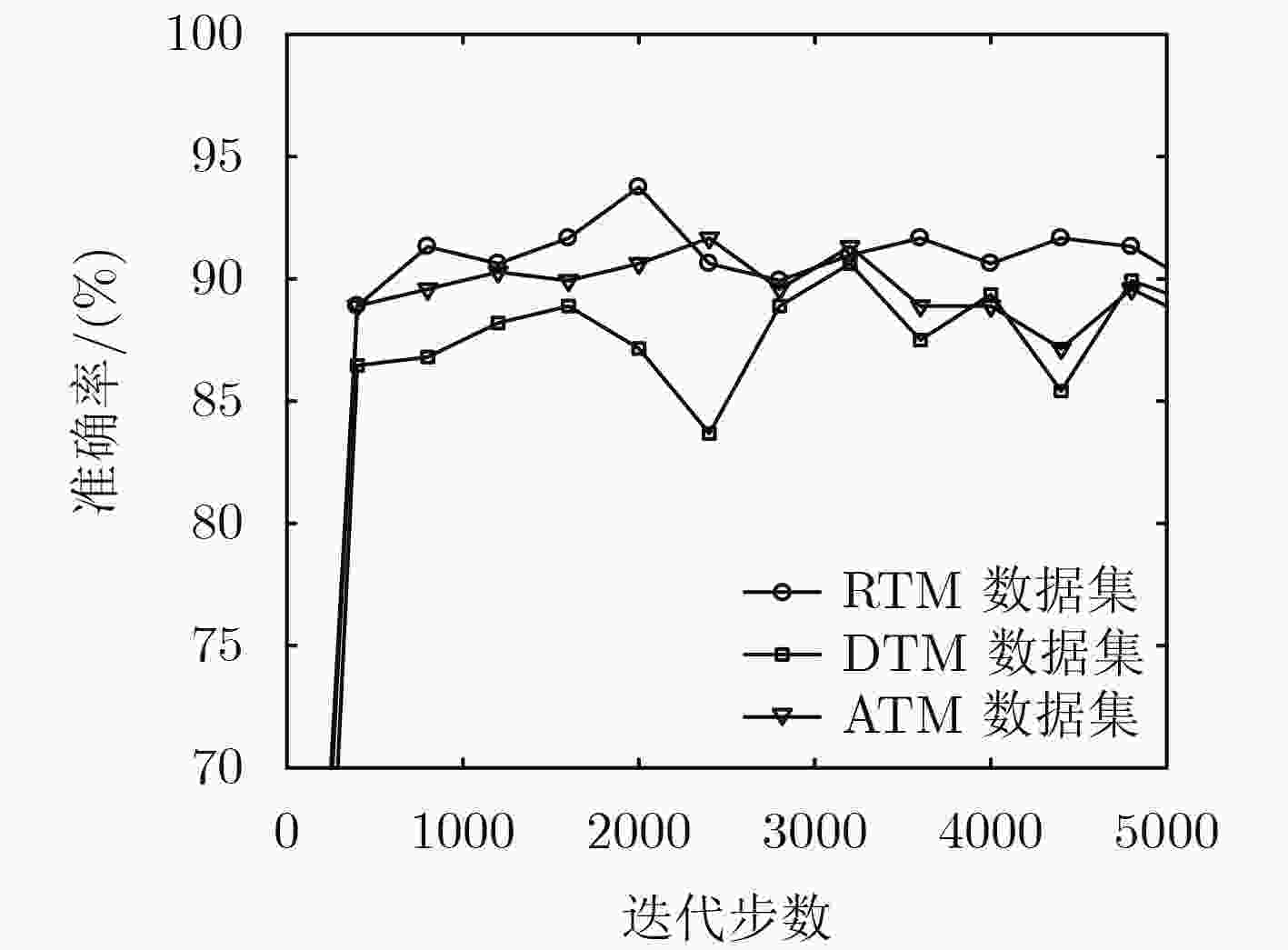
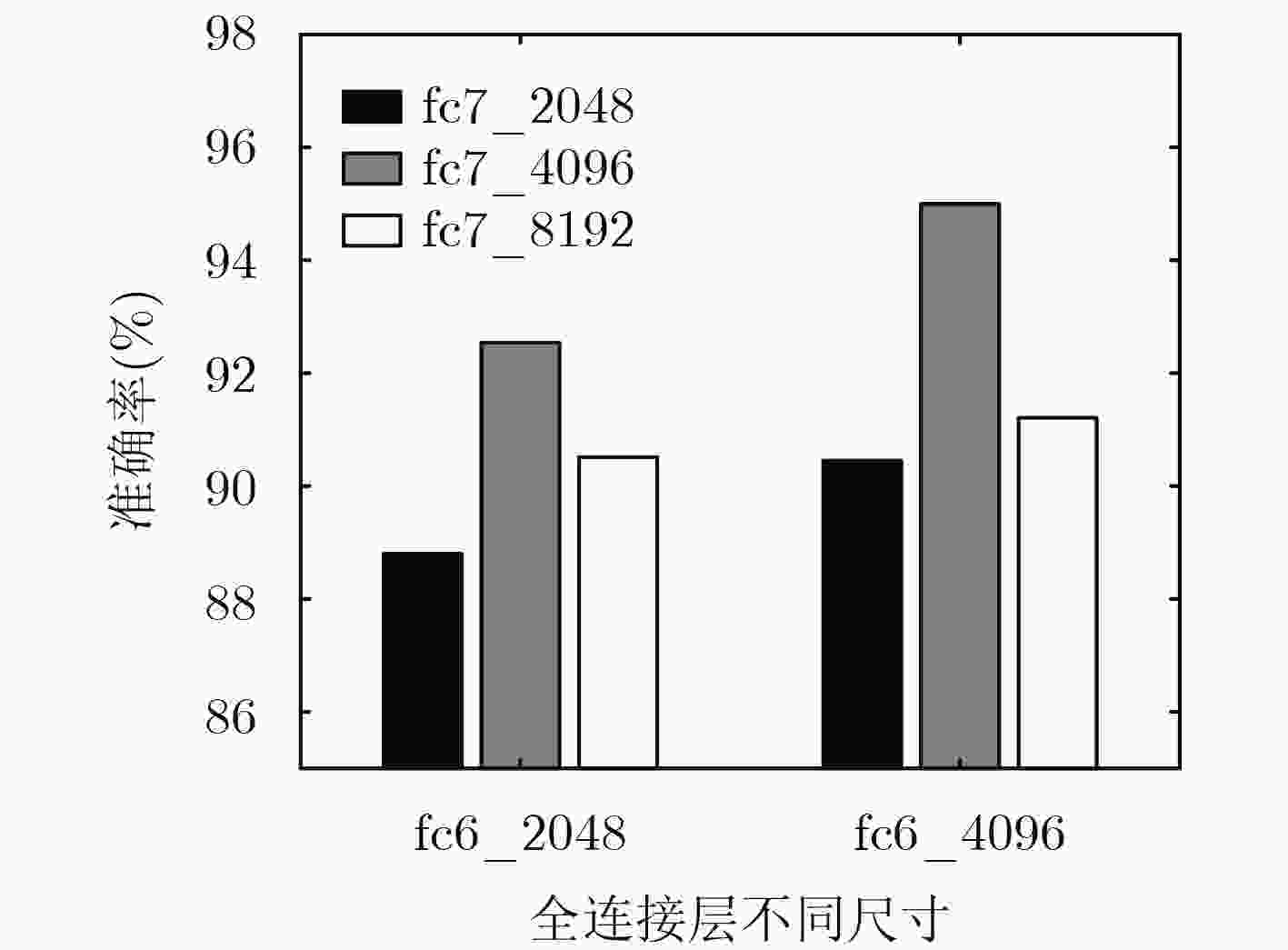
8帧数据集 16帧数据集 24帧数据集 32帧数据集 准确率 70.3 79.7 88.3 95.3 表 2 手势分类混淆矩阵(%)
预测类别 前推 后拉 左滑 右滑 前后推拉 左右滑动 真实类别 前推 90 0 4 0 0 6 后拉 0 100 0 0 0 0 左滑 0 0 98 2 0 0 右滑 0 2 0 94 0 4 前后推拉 4 0 0 0 94 2 左右滑动 2 0 0 0 2 96 表 3 本文方法与其他方法准确率和算法复杂度对比
-
LI Yunan, MIAO Qiguang, TIAN Kuan, et al. Large-scale gesture recognition with a fusion of RGB-D data based on the C3D model[C]. 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 25–30. HE Yiwen, YANG Jianyu, SHAO Zhanpeng, et al. Salient feature point selection for real time RGB-D hand gesture recognition[C]. IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics, Okinawa, Japan, 2017: 103–108. ALMASRE M A and AL-NUAIM H. Recognizing Arabic Sign Language gestures using depth sensors and a KSVM classifie[C]. Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, Colchester, UK, 2016: 146–151. AUGUSTAUSKAS R and LIPNICKAS A. Robust hand detection using arm segmentation from depth data and static palm gesture recognition[C]. Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications, Bucharest, Romania, 2017, 2: 664–667. DEKKER B, JACOBS S, KOSSEN A S, et al. Gesture recognition with a low power FMCW radar and a deep convolutional neural network[C]. Radar Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2017: 163–166. MOLCHANOV P, GUPTA S, KIM K, et al. Multi-sensor system for driver's hand-gesture recognition[C]. Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2015, 1: 1–8. LIN J J, LI Yuanping, HSU W C, et al. Design of an FMCW radar baseband signal processing system for automotive application[J]. Springerplus, 2016, 5(1): 42–57 doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1583-5 LI Gang, ZHANG Rui, RITCHIE M, et al. Sparsity-driven micro-Doppler feature extraction for dynamic hand gesture recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(2): 655–665 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2761229 ZHANG Shimeng, LI Gang, RITCHIE M, et al. Dynamic hand gesture classification based on radar micro-Doppler signatures[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4. KIM Y and TOOMAJIAN B. Hand gesture recognition using micro-Doppler signatures with convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 7125–7130 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2617282 MOLCHANOV P, GUPTA S, KIM K, et al. Short-range FMCW monopulse radar for hand-gesture sensing[C]. Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 1491–1496. WANG Saiwen, SONG Jie, LIEN J, et al. Interacting with soli: Exploring fine-grained dynamic gesture recognition in the radio-frequency spectrum[C]. Proceedings of the 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, New York, USA, 2016: 851–860. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2012: 1097–1105. SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409. 1556, 2014. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xianyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167, 2015. SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]. International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4489–4497. MOLCHANOV P, GUPTA S, KIM K, et al. Hand gesture recognition with 3D convolutional neural networks[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–7. SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 568–576. SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280 doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 HE Kaiming and SUN Jian. Convolutional neural networks at constrained time cost[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5353–5360. -





 下载:
下载:
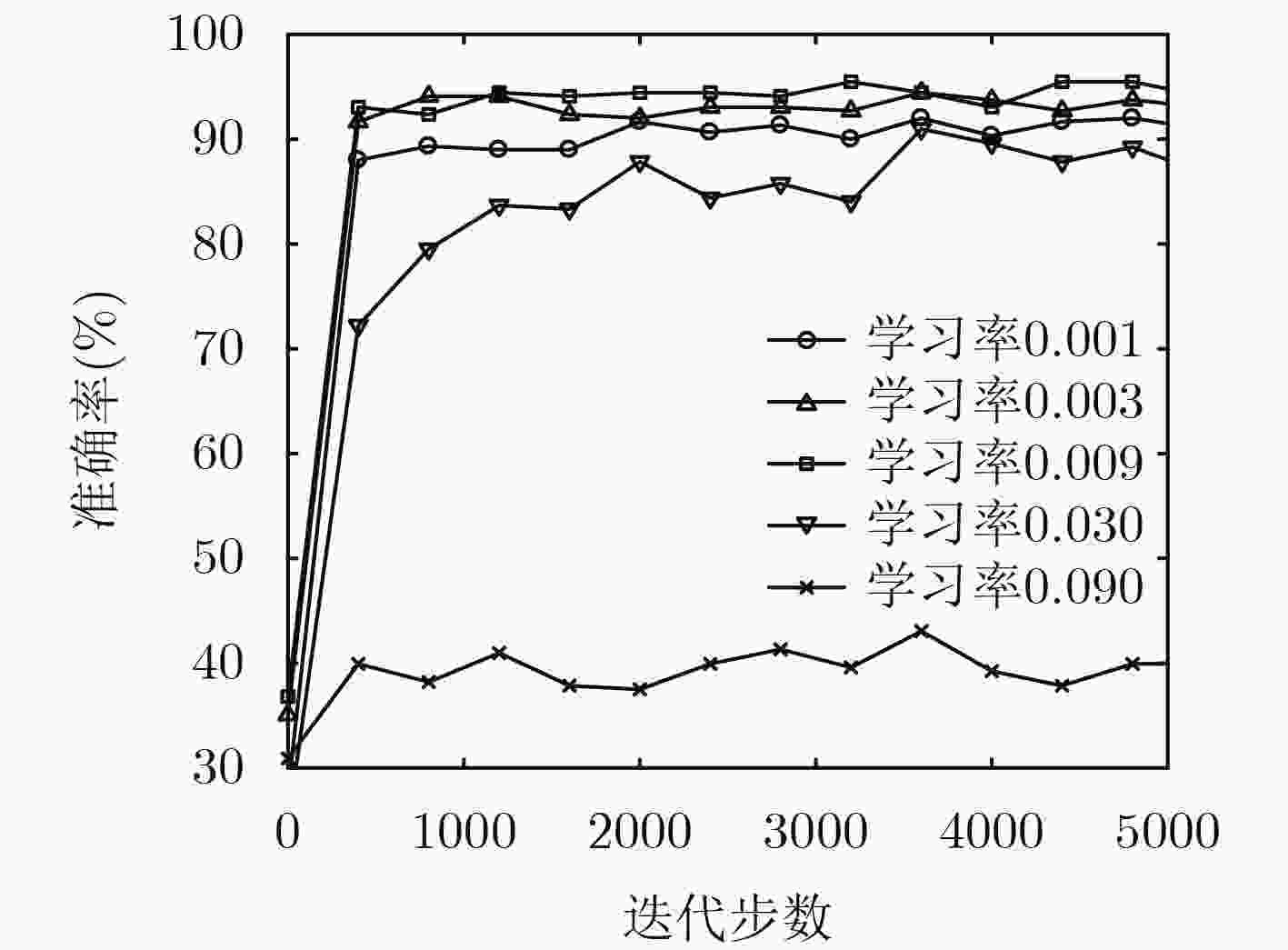
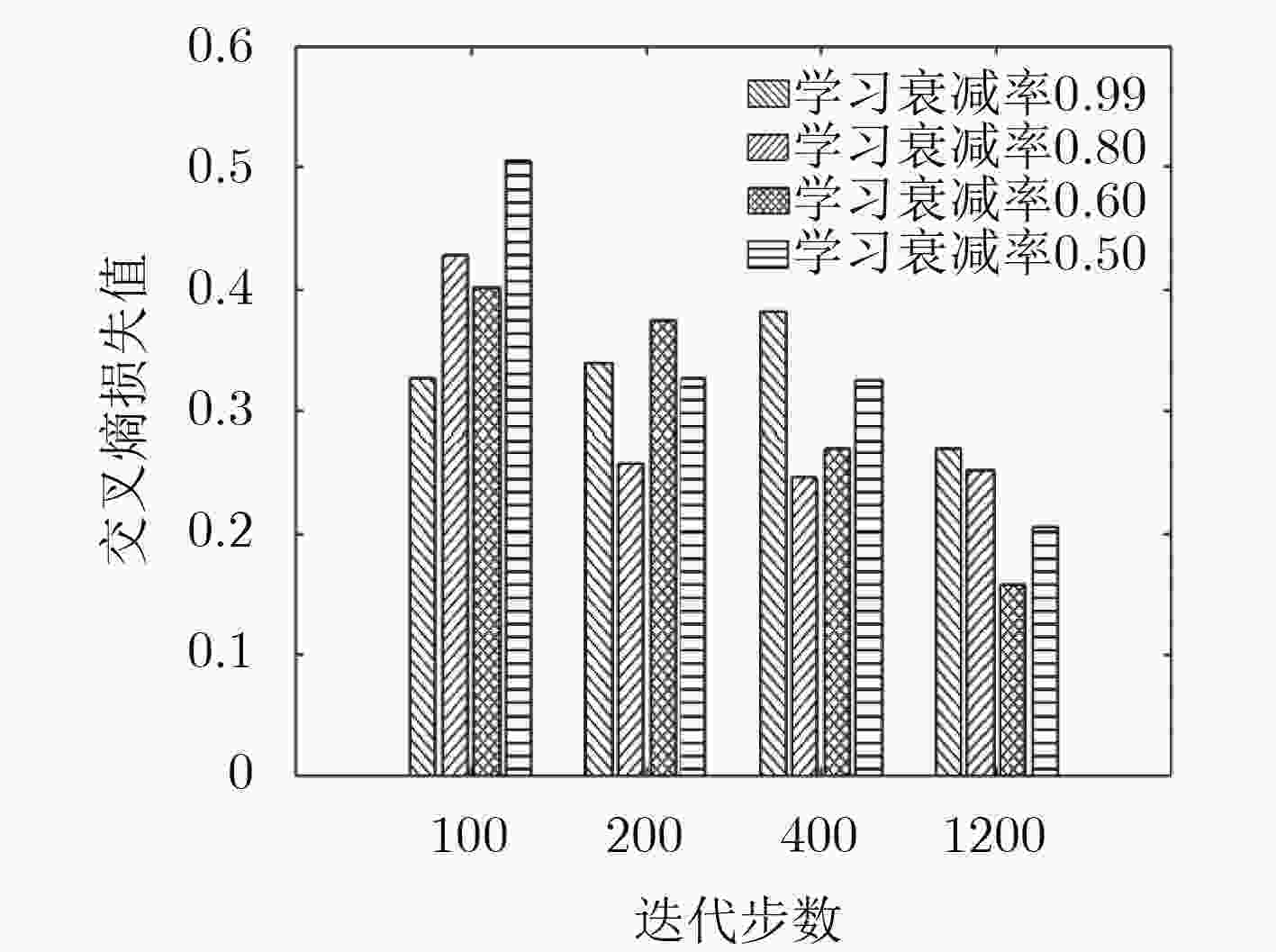
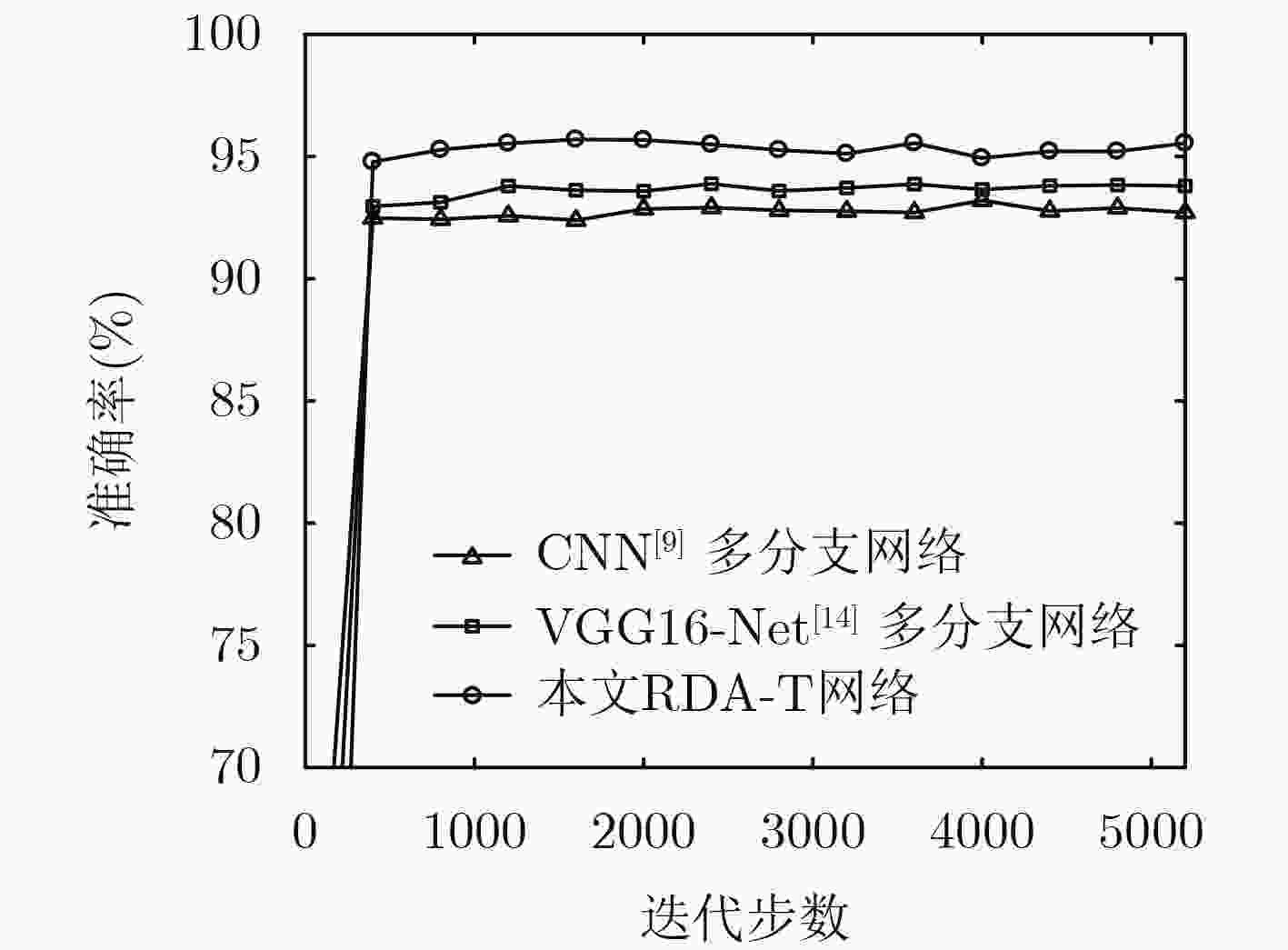


 下载:
下载:
