A Fragment-aware Secure Virtual Network Reconfiguration Method
-
摘要:
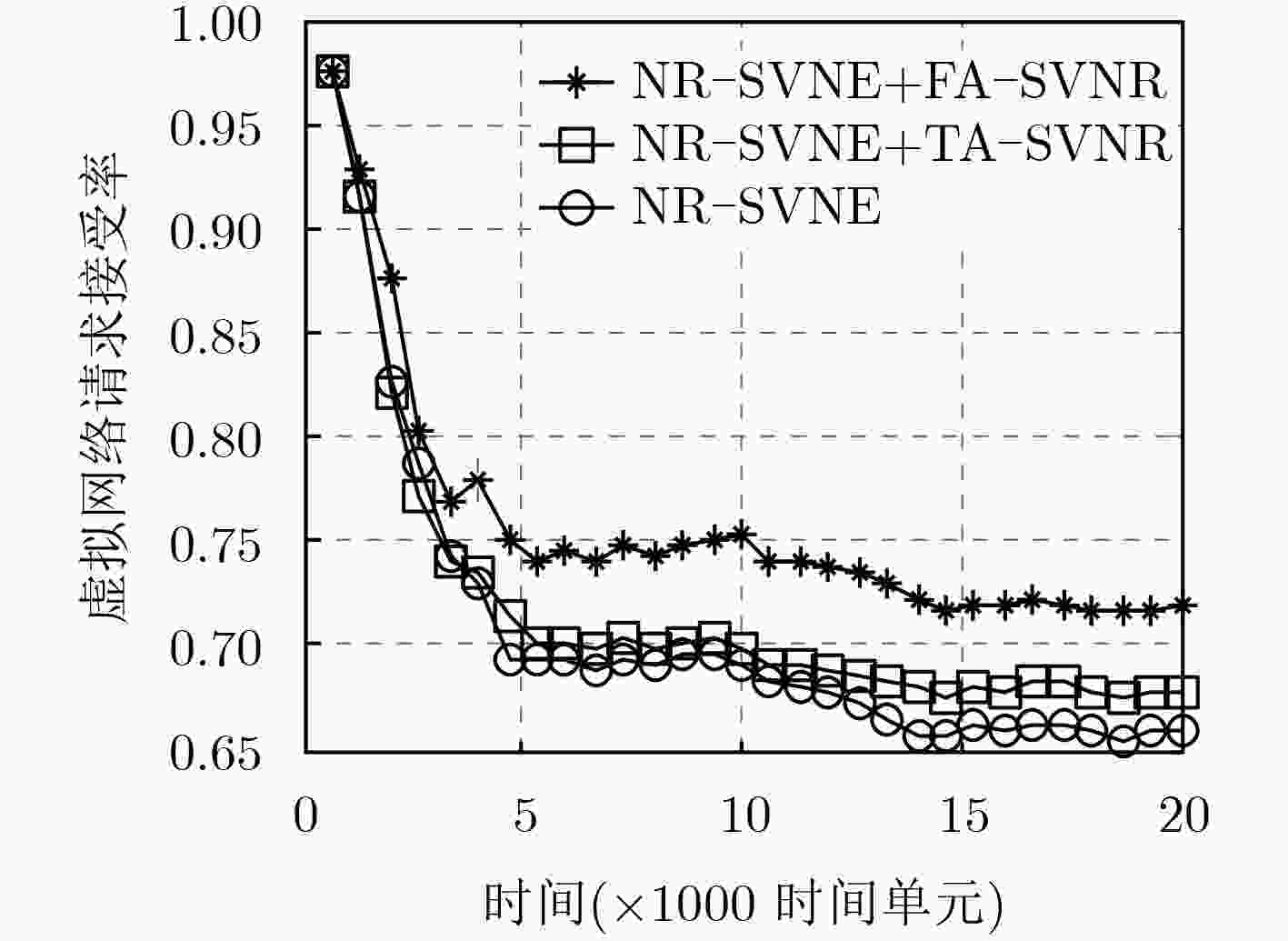
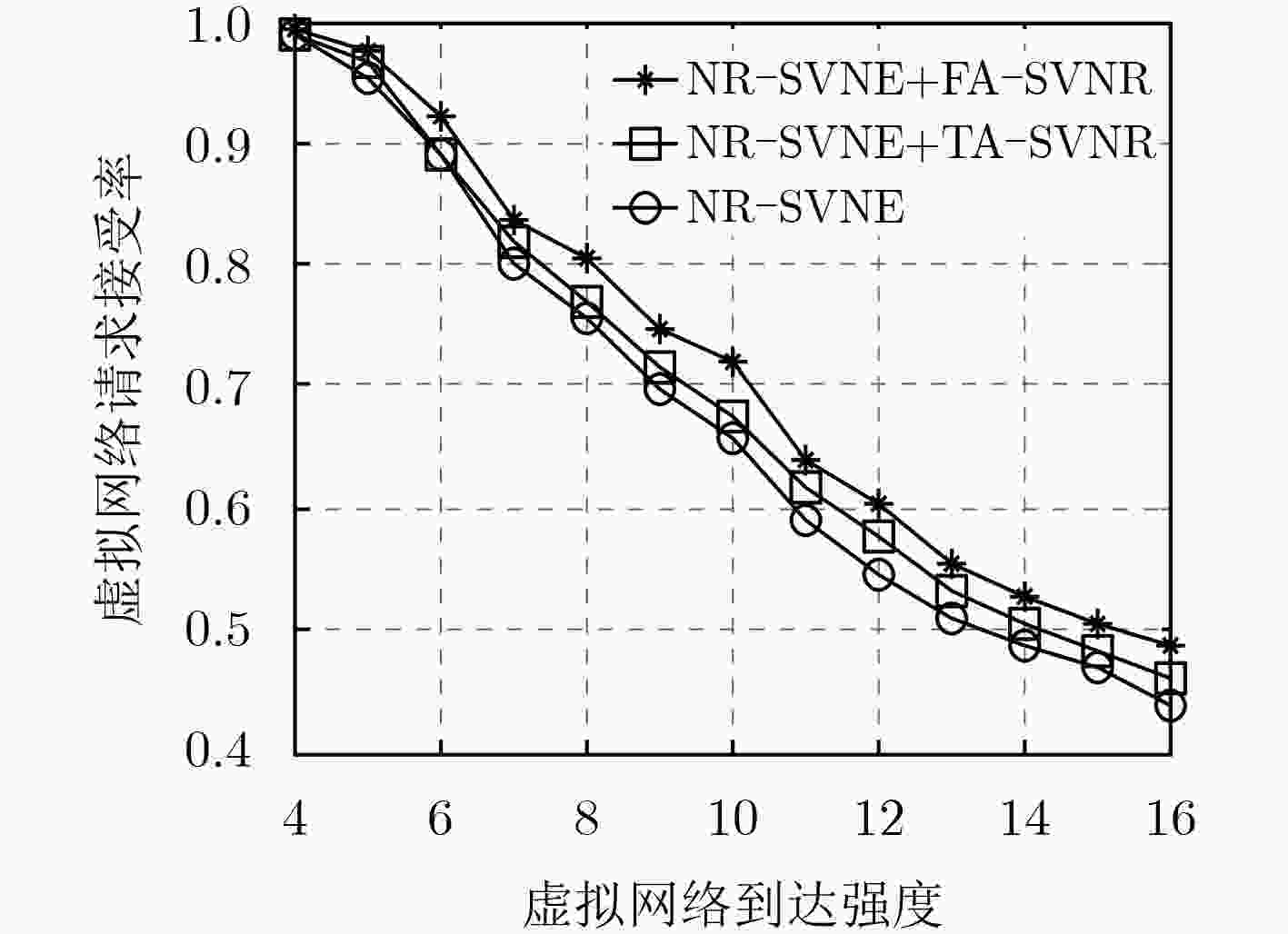
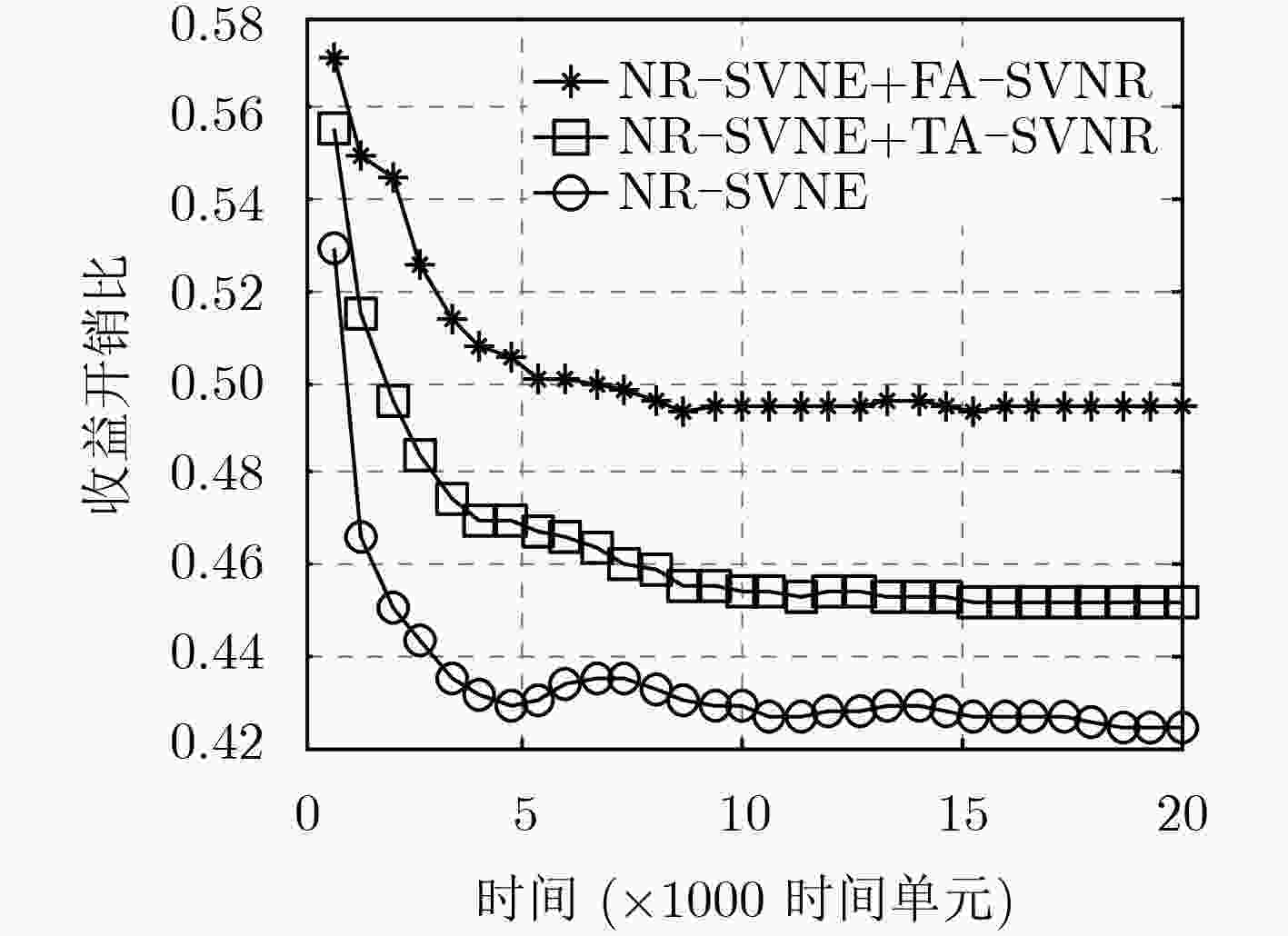
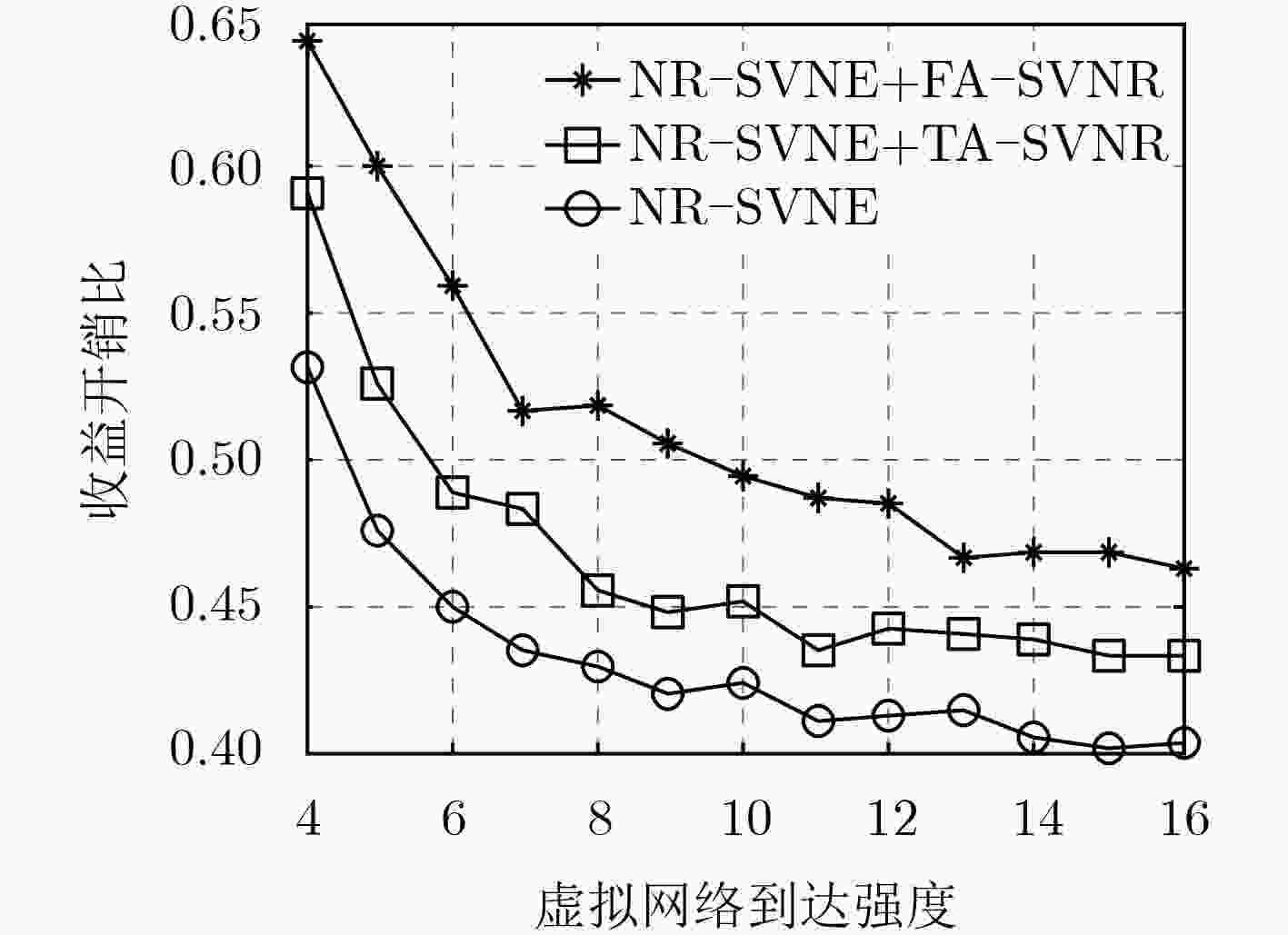
针对现有的虚拟网络重构算法对物理网络中产生的碎片资源考虑不够周到,导致其对在线虚拟网络映射算法的性能改善不够显著的问题,该文定义了一种网络资源碎片度度量方法,并提出一种碎片感知的安全虚拟网络重构算法。该算法通过周期性考虑物理网络中节点的碎片度,选择出待迁移虚拟节点集合;通过综合考虑物理网络的碎片度减小量和虚拟网络的映射开销减少量,选择出最佳的虚拟节点迁移方案。仿真结果表明,该算法的请求接受率和收益开销比均优于当前的重构算法,特别是在收益开销比方面的优势更加明显。
Abstract:The existing virtual network reconfiguration algorithms do not consider the fragment resources generated in the physical network, which results in the improvement of the performance of the online virtual network embedding algorithms is not obvious. To solve this problem, a definition of network resource fragmentation is given, and a Fragment-Aware Secure Virtual Network Reconfiguration (FA-SVNR) algorithm is proposed. In the process of reconfiguration, the virtual node set to be migrated is selected by considering the fragmentation of nodes in the physical network periodically, and the best virtual node migration scheme is selected by considering the reduction of the fragmentation of the physical network and the reduction of the embedding cost of the virtual network. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has the higher acceptance ratio and revenue to cost ratio compared with the existing virtual network reconfiguration algorithm, especially in the metric of revenue to cost ratio.
-
表 1 仿真时网络参数详情
参数 物理网络 虚拟网络 节点数量 100 [4, 8]均匀分布 节点CPU资源 [50, 100]均匀分布 [2, 30]均匀分布 节点安全等级 [1, 5]均匀分布 [1, 5]均匀分布 节点安全需求等级 [1, 5]均匀分布 [1, 5]均匀分布 链路数量 500 每对虚拟节点间存在一条虚拟链路的概率为50% 链路带宽资源 [50, 100]均匀分布 [2, 30]均匀分布 表 2 稳定状态下物理网络负载情况对比
比较的参数 NR-SVNE+FA-SVNR NR-SVNE+TA-SVNR NR-SVNE 物理节点负载强度均值 0.7883 0.7559 0.7453 物理节点负载强度均方差 0.1859 0.1940 0.2254 物理链路负载强度均值 0.6334 0.6739 0.6974 物理链路负载强度均方差 0.2483 0.2620 0.2789 -
RAZZAQ A and RATHORE M S. An approach towards resource efficient virtual network embedding[C]. International Conference on Evolving Internet, Valcencia, Spain, 2010: 68–73. ZHANG Sheng, QIAN Zhuzhong, WU Jie, et al. Virtual network embedding with opportunistic resource sharing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(3): 816–827 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.64 YU Chunyan, LIAN Qi, ZHANG Dong, et al. PAME: Evolutionary membrane computing for virtual network embedding[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2018, 111: 136–151 doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2017.08.005 RUBIO-LOYOLA J, AGUILAR-FUSTER C, TOSCANO-PULIDO G, et al. Enhancing metaheuristic-based online embedding in network virtualization environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2018, 15(1): 200–216 doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2017.2742666 ZHANG Zhongbao, SU Sen, ZHANG Junchi, et al. Energy aware virtual network embedding with dynamic demands: Online and offline[J]. Computer Networks, 2015, 93: 448–459 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2015.09.036 FISCHER A, BOTERO J F, BECK M T, et al. Virtual network embedding: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2013, 15(4): 1888–1906 doi: 10.1109/SURV.2013.013013.00155 TRAN P N and TIMM-GIEL A. Reconfiguration of virtual network mapping considering service disruption[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications, Budapest, Hungary, 2013: 3487–3492. HSU W H, SHIEH Y P, WANG C H, et al. Virtual network mapping through path splitting and migration[C]. International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Fukuoka, Japan, 2012: 1095–1100. ZANGIABADY M, AGUILAR-FUSTER C, and RUBIO-LOYOLA J. A virtual network migration approach and analysis for enhanced online virtual network embedding[C]. International Conference on Network and Service Management, Montreal, Canada, 2016: 324–329. CHOWDHURY S R, AHMED R, SHAHRIAR N, et al. ReViNE: Reallocation of virtual network embedding to eliminate substrate bottlenecks[C]. IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management, Lisbon, Portugal, 2017: 116–124. 曲桦, 赵季红, 郭爽乐, 等. 基于最小代价的虚拟网络重配置方法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2014, 37(5): 114–118 doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2014.05.024QU Hua, ZHAO Jihong, GUO Shuangle, et al. Resource reconfiguration method based on minimum cost for network virtualization[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2014, 37(5): 114–118 doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2014.05.024 彭利民. 一种拓扑感知的虚拟网络重构算法[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2015, 47(5): 110–115 doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2015.05.016PENG Limin. A topology-awareness virtual network reconfiguration algorithm[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition) , 2015, 47(5): 110–115 doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2015.05.016 FISCHER A and DE MEER H. Position paper: Secure virtual network embedding[J]. PIK-Praxis der Informationsverarbeitung und Kommunikation, 2011, 34(4): 190–193 doi: 10.1515/piko.2011.040 LIU Shuhao, CAI Zhiping, XU Hong, et al. Towards security-aware virtual network embedding[J]. Computer Networks, 2015, 91: 151–163 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2015.08.014 刘新波, 王布宏, 刘帅琦, 等. 安全虚拟网络映射的启发式算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(3): 676–681 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.29LIU Xinbo, WANG Buhong, LIU Shuaiqi, et al. Heuristic algorithm for secure virtual network embedding[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(3): 676–681 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.29 CHOWDHURY N M M K, RAHMAN M R, and BOUTABA R. Virtual network embedding with coordinated node and link mapping[C]. IEEE INFOCOM, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009: 783–791. EHRGOTT M and GANDIBLEUX X. A survey and annotated bibliography of multiobjective combinatorial optimization[J]. OR-Spektrum, 2000, 22(4): 425–460 doi: 10.1007/s002910000 YANG Zeheng and GUO Yongan. An exact virtual network embedding algorithm based on integer linear programming for virtual network request with location constraint[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(8): 177–183 doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7563720 CAO Haotong, YANG Longxiang, LIU Zeyuan, et al. Exact solutions of VNE: A survey[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(6): 48–62 doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7513202 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
