A Traffic Scheduling Algorithm for Bandwidth Fragmentation Minimization and QoS Guarantee in Data Center Network
-
摘要:
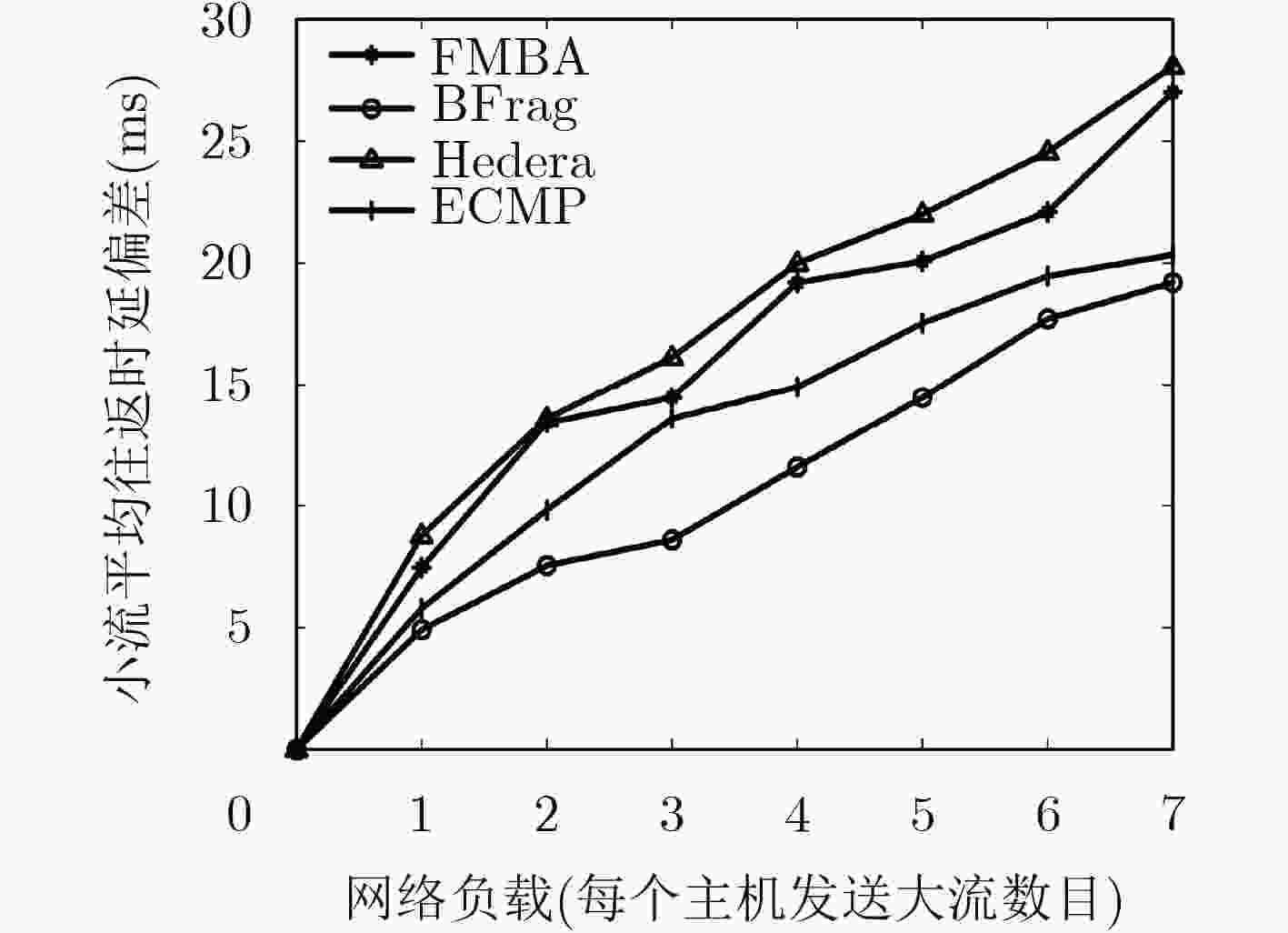
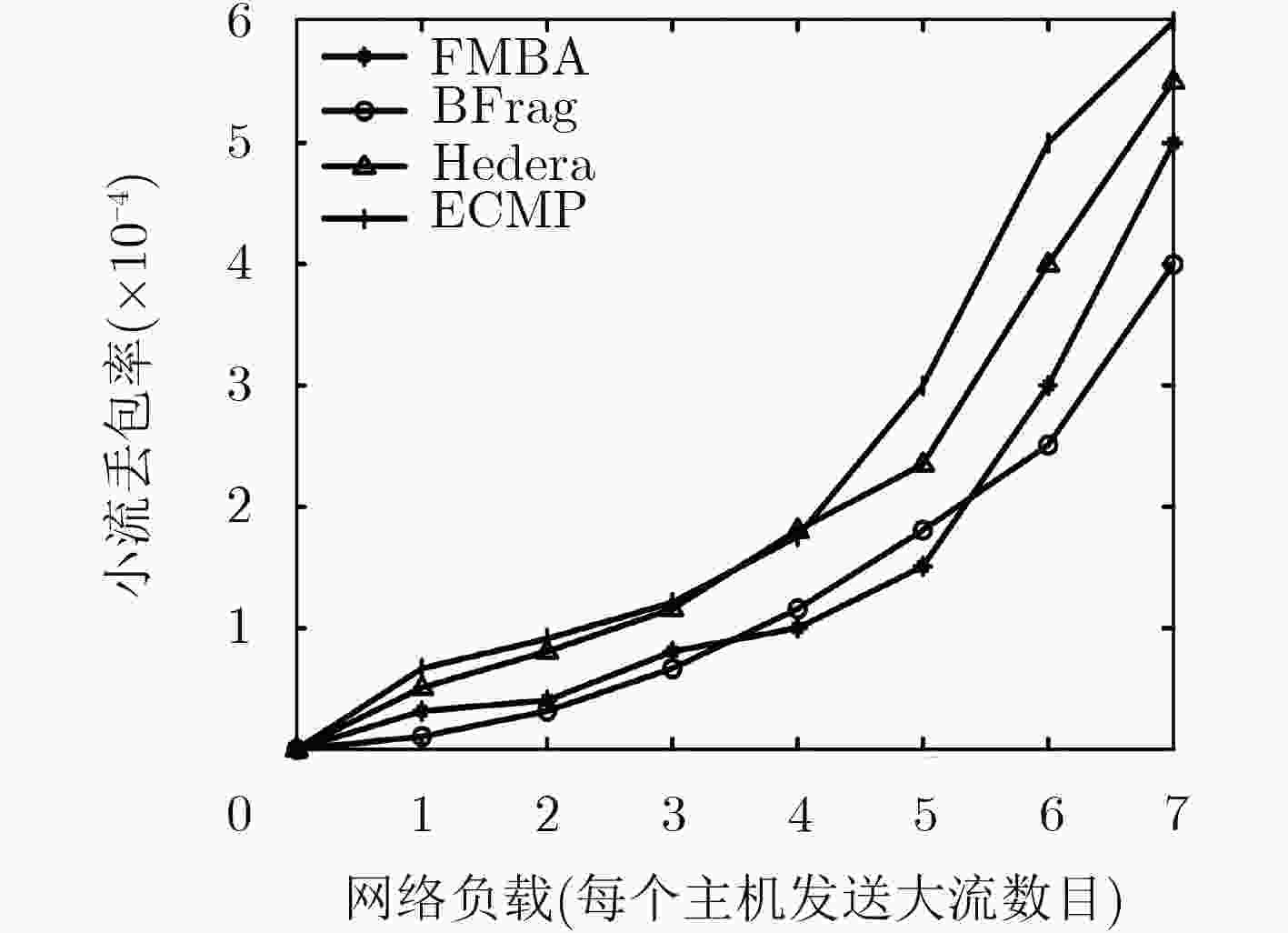
随着数据中心网络流量的迅速增长,如何提高数据中心网络性能和服务质量成为了研究热点。然而现有的流量调度算法在网络负载加大时,一方面会导致网络带宽碎片化从而使得网络吞吐量降低,另一方面忽视了流量应用需求导致网络服务质量较差。为此,该文提出一种面向带宽碎片最小化和QoS保障的动态流量调度算法,算法综合考虑了带宽敏感的大流、时延与丢包敏感的小流的不同需求,首先根据待调度流的源地址和目的地址建立最短路径集,其次从中筛选出满足待调度流的带宽需求的所有路径,然后根据路径剩余带宽信息和小流应用需求情况为每条路径建立权重函数,最后根据权重函数值利用轮盘赌算法选择转发路径。实验仿真结果显示,与其它算法相比,所提算法降低了小流的丢包率和时延,同时在网络负载较大时提升了网络吞吐量。
Abstract:With the rapid growth of Data Center Network (DCN) traffic, how to improve the performance and service quality of data center network become a research hotspot. However, when the network load increases, the existing traffic scheduling algorithm on the one hand may cause bandwidth fragmentation results in the network throughput decrease, on the other hand, it neglects the traffic application requirements to lead to poor QoS. Therefore, a dynamic traffic scheduling algorithm for bandwidth fragmentation minimization and QoS guarantee is proposed. The algorithm takes into account the different requirements of the bandwidth-sensitive large flows, and delay sensitive and packet-loss sensitive small flows. Firstly, the shortest path set is established according to the source address and destination address of the to-be-scheduled flow. Secondly, all the paths that satisfy the bandwidth requirement of the to-be-scheduled flow are selected. Then, the weight function is established for each path according to the free bandwidth of the path and the application requirements of the small flow. Finally, the forwarding path is selected based on the weight function value by roulette algorithm. The network simulation results show that when the network load increases, the proposed algorithm reduces the packet loss rate and delay of small flows, and improves the network throughput compared with other algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Data Center Network(DCN) /
- Traffic scheduling /
- Bandwidth fragmentation /
- QoS
-
表 1 FMBA算法伪代码
$\begin{array}{l}\left( 1 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm for\;each\;path} \in {K_{\rm src \to dst}}\;{\rm do}\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 2 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm if}\;{B_{\rm \min }} \cdot \mu > {B_n}\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 3 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm selectedPath \leftarrow {\mathop{\rm path}\nolimits} .\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 4 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm return\;selectedPath\end{array}$ 表 2 BFrag算法伪代码
$\begin{array}{l}\left( 1 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm for\;each\;path} \in {K_{\rm src \to dst}}\;\rm do\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 2 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm if}\;{B_{\rm \min }} > {B_{\rm n}}\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 3 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm candidatePath.add(path);\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 4 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm if\;candidatePath\;is\;empty\;then\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 5 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;k + = 1\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 6 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm for\;each\;p \in candidatePath\;do\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 7 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm weight}1 \leftarrow \left( {{B_{\rm \min }} \cdot \mu - {B_n}} \right)/B\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 8 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm weight}2 \leftarrow ({B_{\rm \max }} - {B_{\rm \min }})/B\\{\rm{}}\\\left( 9 \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm weight \leftarrow weight1 \cdot \alpha + weight2 \cdot \left( {1{\rm{ - }}\alpha } \right)\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {10} \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm totalProbability + = 1/weight\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {11} \right)\;\;\;\;\;{\rm for\;each}\;p \in \rm candidatePath\;do\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {12} \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm probabilty \leftarrow totalProbability/weight\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {13} \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm cumulativeProbabilty + = probabilty\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {14} \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\rm while\;cumulativeProbabilty \ge fslice\;do\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {15} \right)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\rm selectedPath} \leftarrow p\\{\rm{}}\\\left( {16} \right)\;\;\;\;\;\rm return\;selectedPath\end{array}$ 表 3
${μ} $ 取不同值时算法结果对比$\mu $取值 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 平均吞吐量(Gbps) 7.821 7.756 6.601 6.416 标准化吞吐量 0.488 0.484 0.413 0.401 小流时延(ms) 14.43 12.69 17.50 10.18 小流时延偏差(ms) 19.27 14.82 10.64 12.82 小流丢包率(‰) 0.127 0.094 0.104 0.115 表 4
${α}$ 取不同值时算法结果对比$\alpha $取值 平均吞吐量
(Gbps)标准化吞
吐量小流时延(ms) 小流时延
偏差(ms)小流丢
包率(‰)0.1 6.765 0.423 17.93 10.09 0.142 0.2 6.778 0.424 26.88 10.81 0.280 0.3 6.527 0.408 14.73 10.13 0.135 0.4 6.672 0.417 28.39 10.83 0.176 0.5 6.945 0.434 80.55 14.79 0.091 0.6 7.019 0.438 20.13 15.49 0.129 0.7 7.100 0.443 20.07 16.33 0.200 0.8 7.095 0.443 21.24 14.81 0.164 0.9 7.228 0.452 25.20 16.45 0.221 表 5 算法运行时间结果对比(s)
发送大流数目 1 2 3 4 5 FMBA运行时间 198.34 258.81 300.12 349.97 403.88 BFrag运行时间 200.56 246.20 295.54 345.68 391.74 Hedera运行时间 201.39 255.50 298.81 343.10 392.15 ECMP运行时间 141.58 190.96 239.35 286.76 335.00 -
GAO Yongqiang and WU Yonghao. Profit-aware workload management for geo-distributed data centers[C]. International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies, Taipei, China, 2017: 60–66. MRUDUAL S and SWAPNASUDHA K. A dynamic and energy efficient greedy scheduling algorithm for cloud Data Centers[C]. IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computiong in Emerging Markets, Bangalore, India, 2017: 1–3. SONG Ziyan and ZHANG Ting. START: Sensible traffic scheduling in dynamic data center networks[C]. IEEE International Performance Computing and Communications Conference, San Diego, USA, 2017: 1–8. ZHANG Hailong and GUO Xiao. SDN-based ECMP algorithm for data center networks[C] Computing, Communications and IT Applications Conference, Beingjing, China, 2015: 13–18. LI Cong and WU Yonghao. Strategy of data manage center network traffic scheduling based on SDN[C]. International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data & Smart City, Changsha, China, 2016: 29–34. LIU Jing and LI Jie. SDN based load balancing mechanism for elephant flow in data center networks[C]. International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications, Sydney, Australia, 2015: 486–490. ALFARES M, RADHAKRISHNAN S, RAGHAVAN B, et al. Hedera: Dynamic flow scheduling for data center networks[C]. NSDI’10 Proceedings of the 7th Usenix Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, San Jose, USA, 2010: 19. CURTIS A, KIM W, and YALAGANDULA P. Mahout: Low-overhead datacenter traffic management using end-host-based elephant detection[C] IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, China, 2011: 1629–1637. 李龙, 付斌章, 陈明宇. Nimble: 一种适用于OpenFlow网络的快速流调度策略[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(5): 1056–1068 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.01056LIN Long, FU Zhangshou, and CHEN Mingyu. Nimble: A fast flow scheduling strategy for OpenFlow networks[J]. Journal of Computer, 2015, 38(5): 1056–1068 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.01056 陈琳, 张富强. 面向SDN数据中心网络最大概率路径流量调度算法[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(2): 254–260CHEN Lin and ZHANG Fuqiang. Maximum probability path scheduling algorithm for elephant flow in data center networks based on SDN[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(2): 254–260 段洁, 高江明, 程克非, 等. 基于流类型的SDN数据平面故障恢复算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 30(1): 134–140 doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.01.017DUAN Jie, GAO Jiangming, CHENG Kefei, et al. Failure recovery algorithm based on flow type in SDN data plane[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications(Natural Science Edition) , 2018, 30(1): 134–140 doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2018.01.017 左青云, 陈鸣, 赵广松, 等. 基于OpenFlow的SDN技术研究[J]. 软件学报, 2013, 24(5): 1078–1097 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2013.04390ZUO Qingyun, CHEN Ming, ZHAO Guangsong, et al. Research on OpenFlow-based SDN technologies[J]. Journal of Software, 2013, 24(5): 1078–1097 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2013.04390 SONG Tao, LIU Yuchen, WANG Yiding, et al. Ashman: A bandwidth fragmentation-based dynamic flow scheduling for data center networks[J]. Computer Journal, 2017, 60(10): 1498–1509 doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxx042 林智华, 高文, 吴春明, 等. 基于离散粒子群算法的数据中心网络流量调度研究[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(9): 2197–2202 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.09.026LIN Zhihua, GAO Wen, WU Chunming, et al. Data center network flow scheduling based on DPSO algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(9): 2197–2202 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.09.026 VAHADAT A, AlFARES M, and LOUKISSAS A. Scalable commodity data center network architecture[P]. USA Patent, US8483096, 2013. -





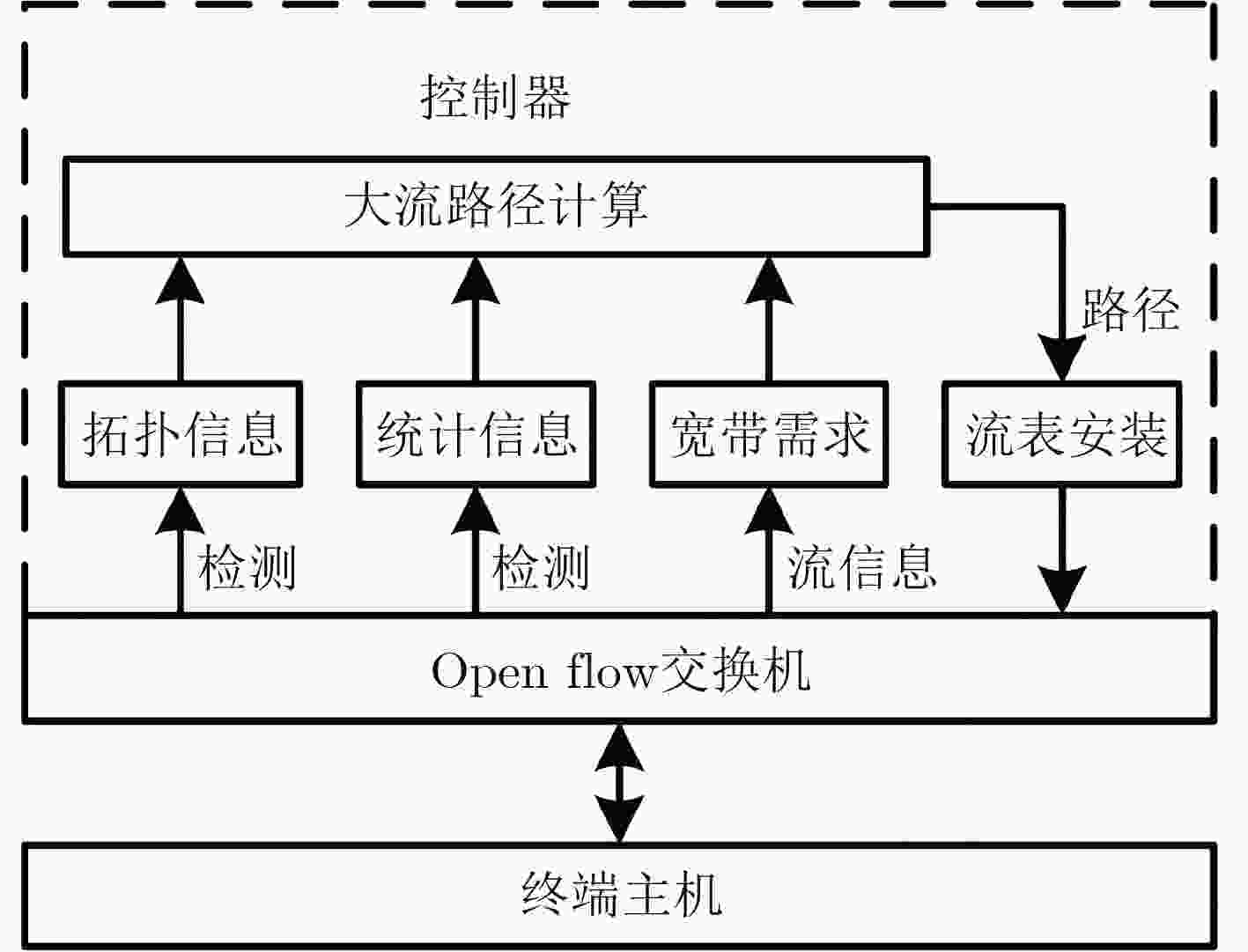
 下载:
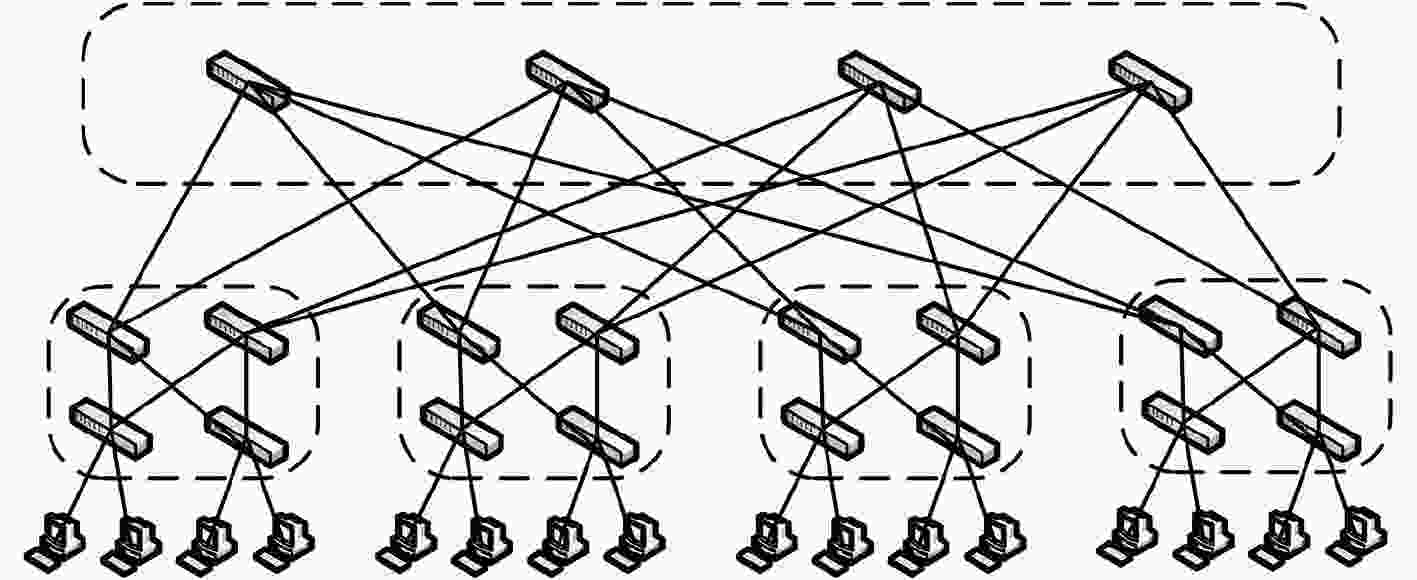
下载:
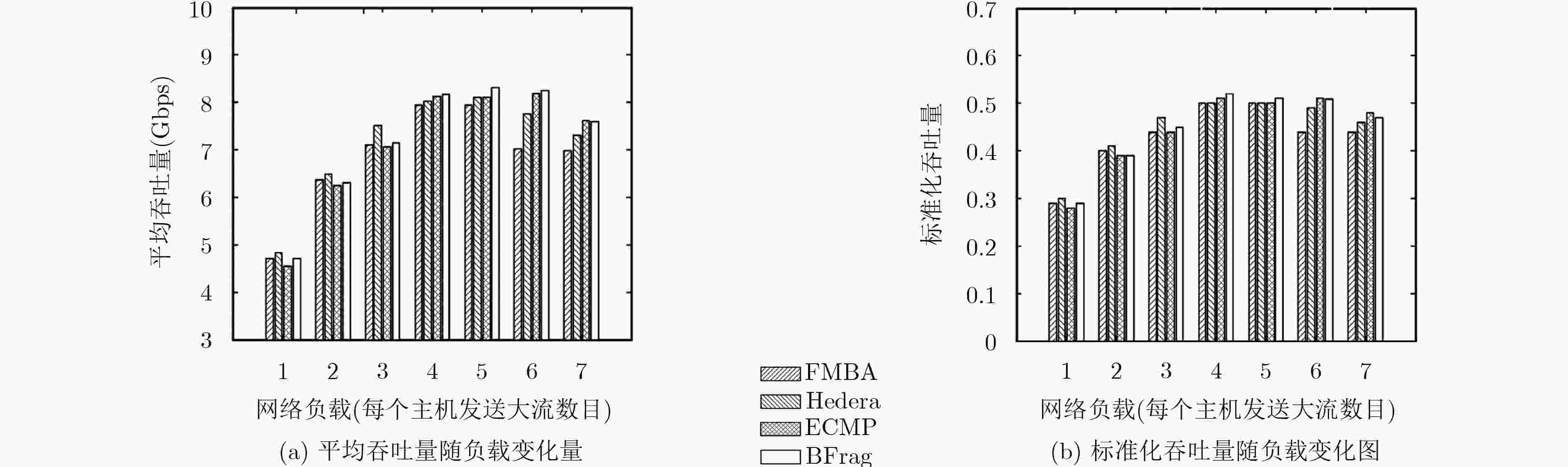
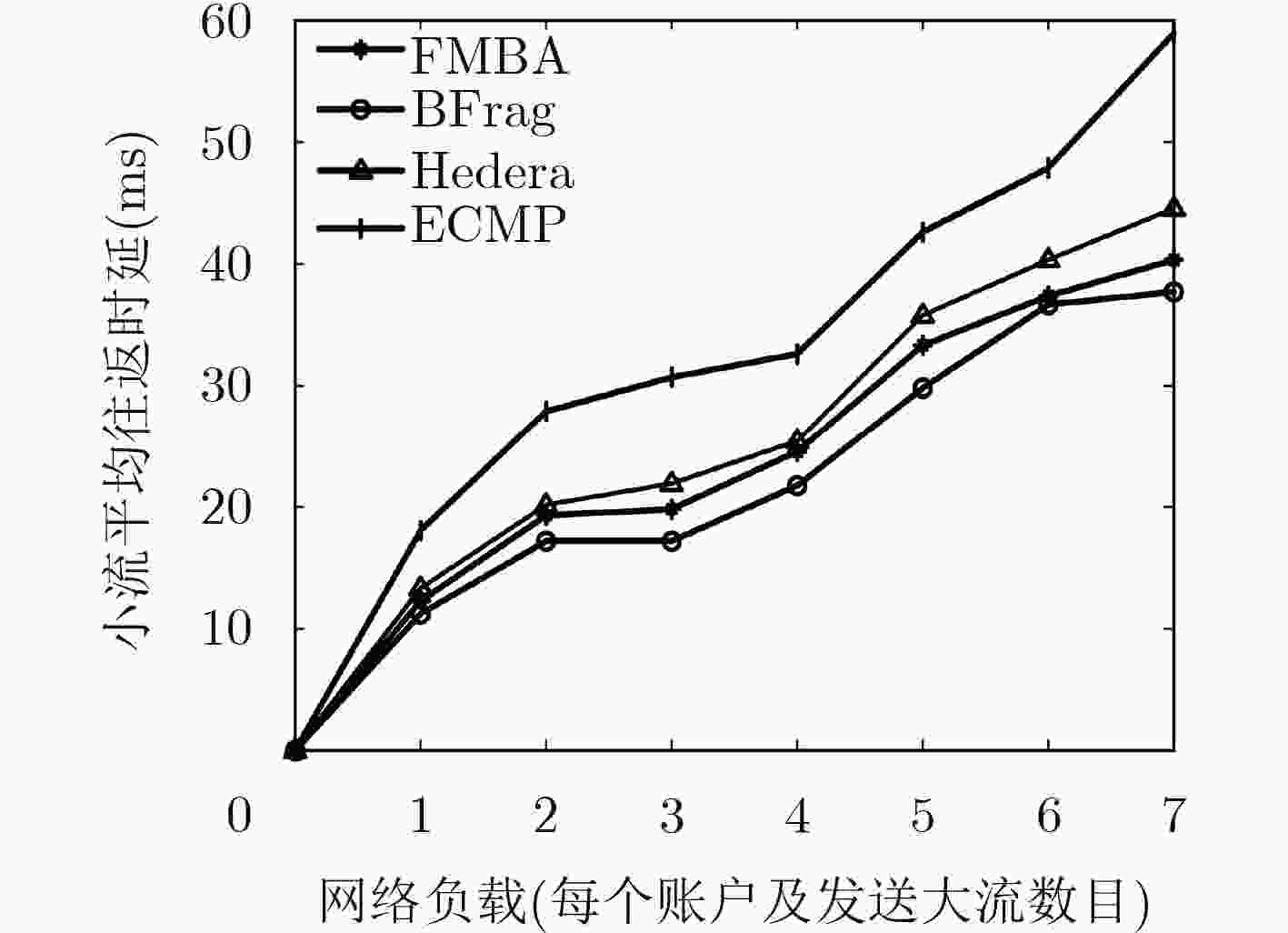




 下载:
下载:
