Incentive and Restraint Mechanism of Rewards and Punishment in Access Control Based on Game Theory
-
摘要:
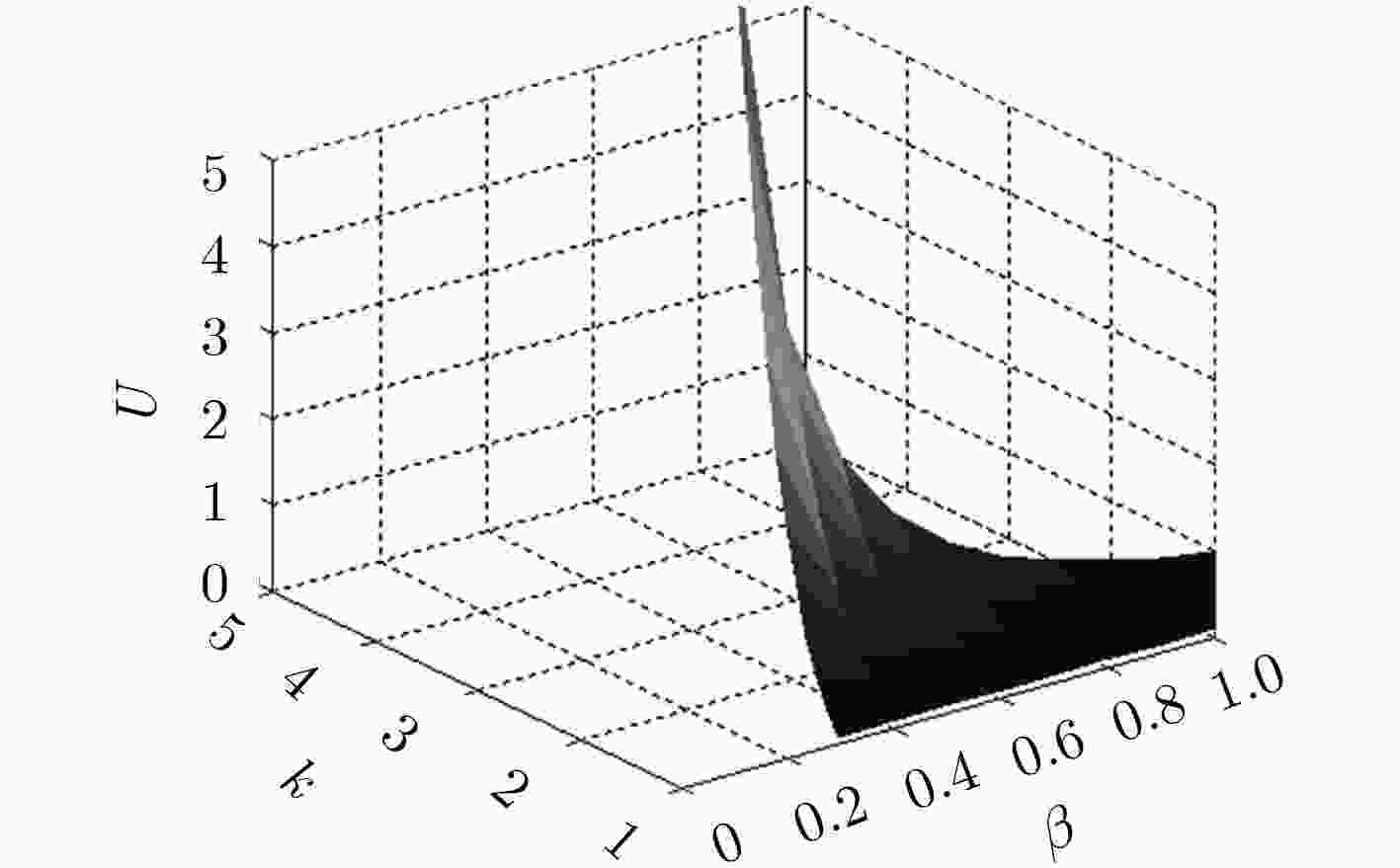
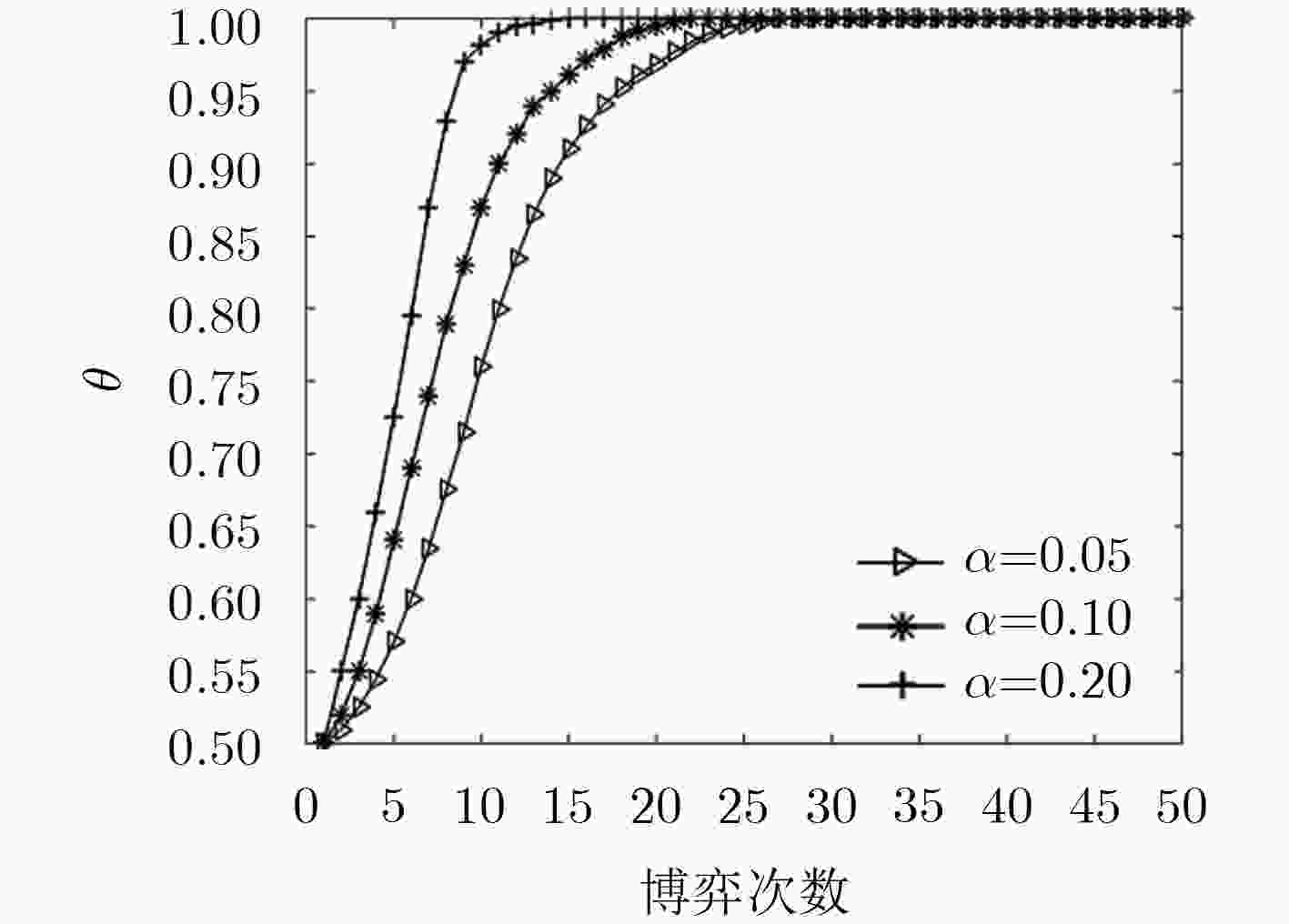
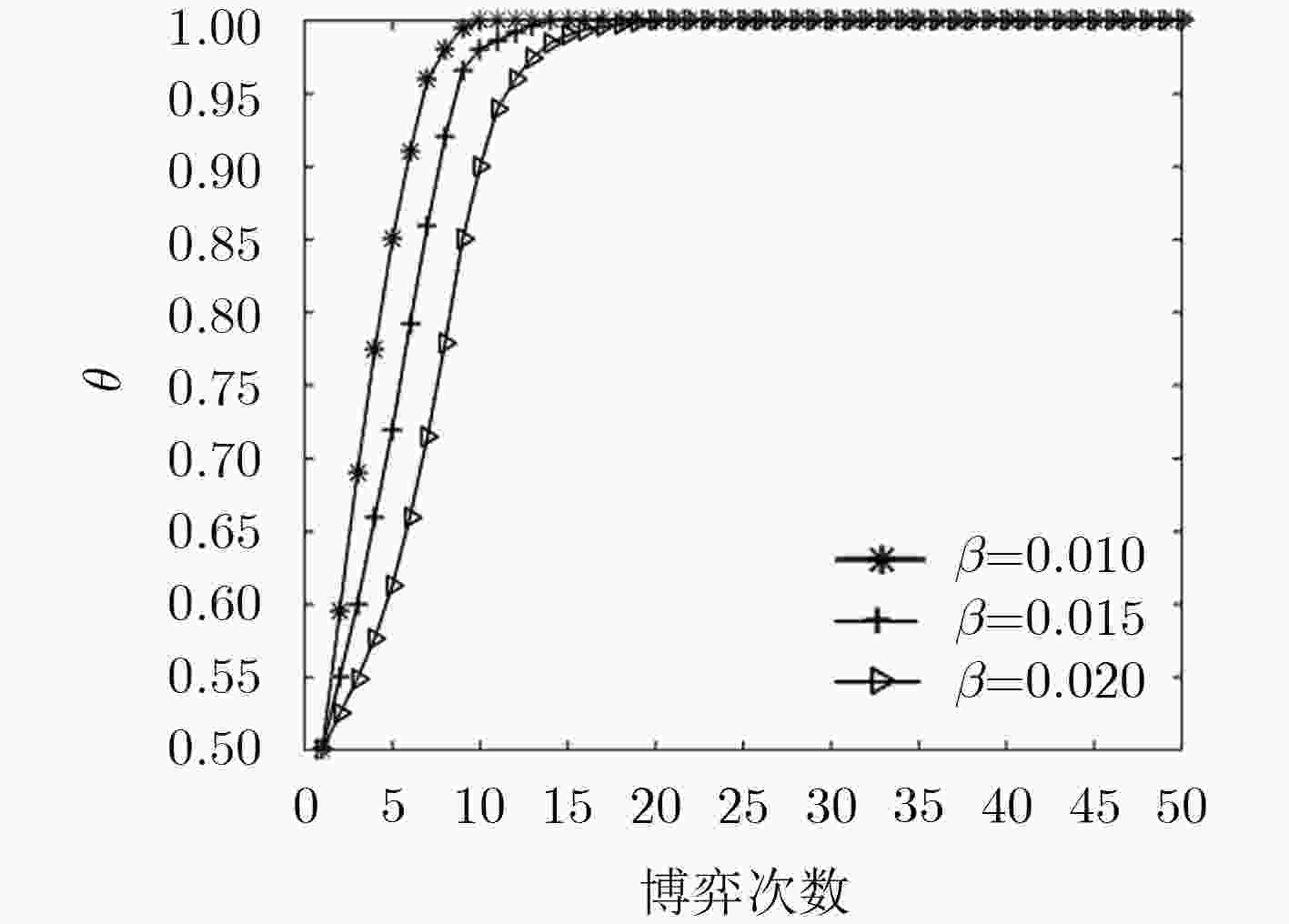
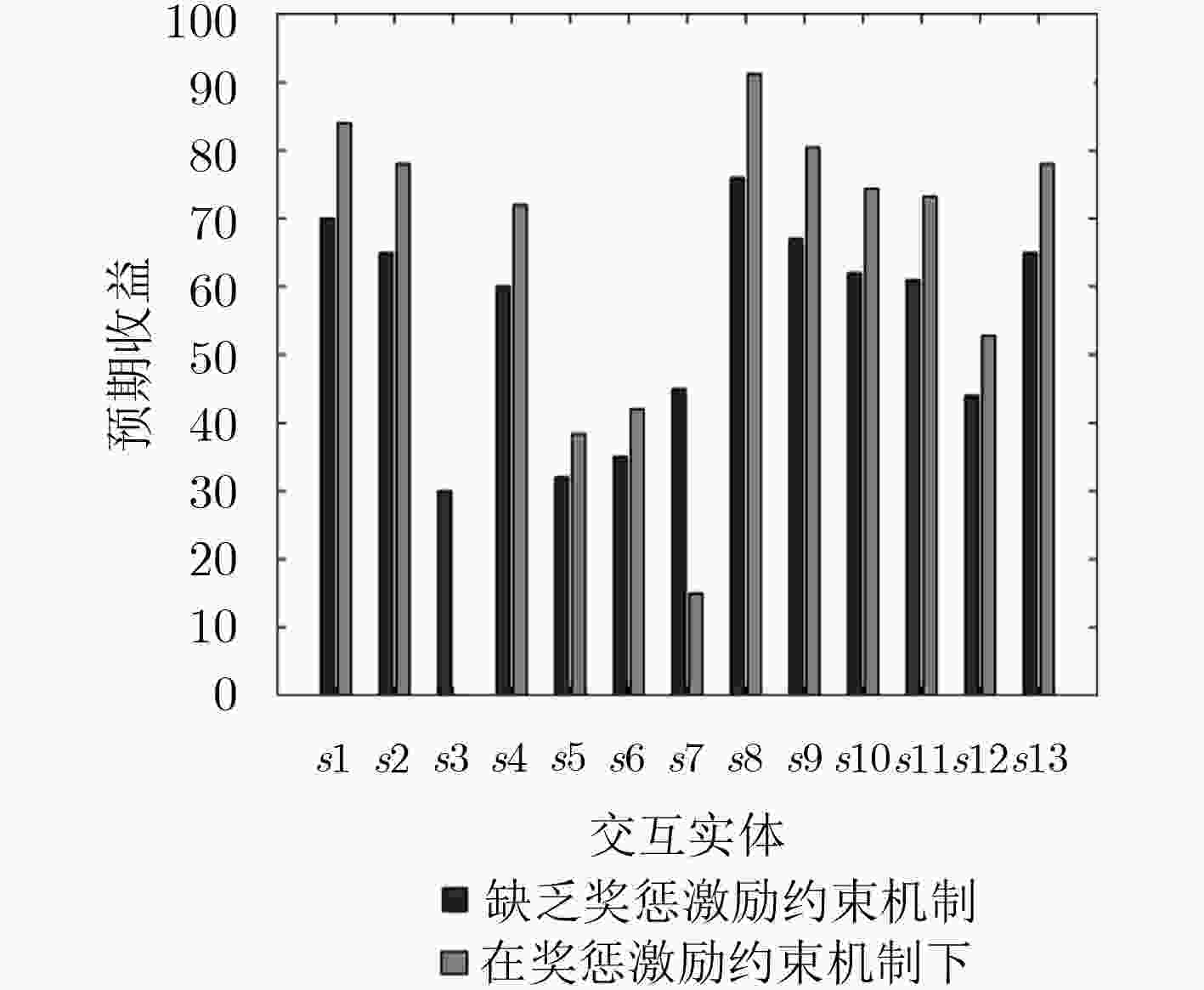
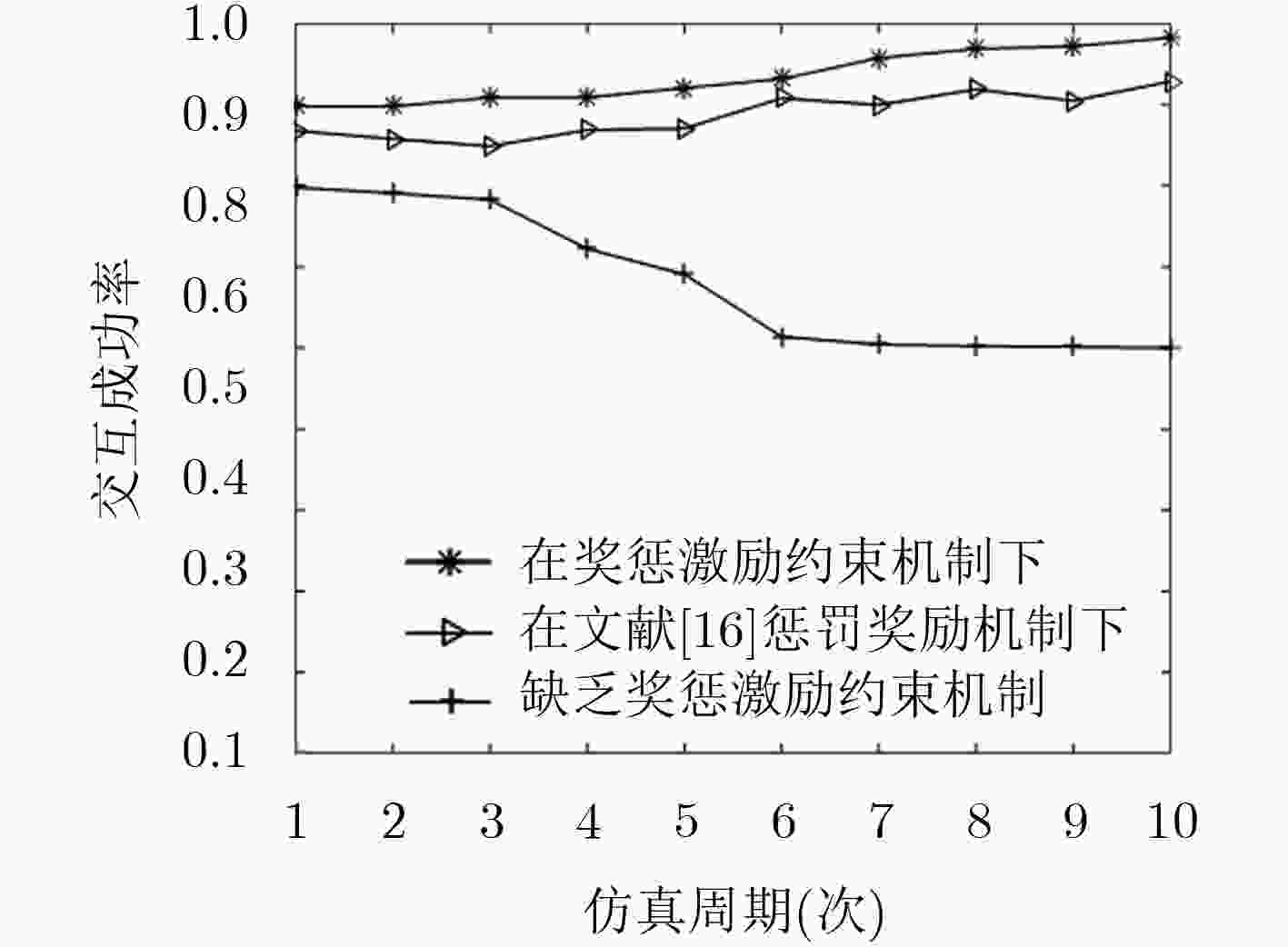
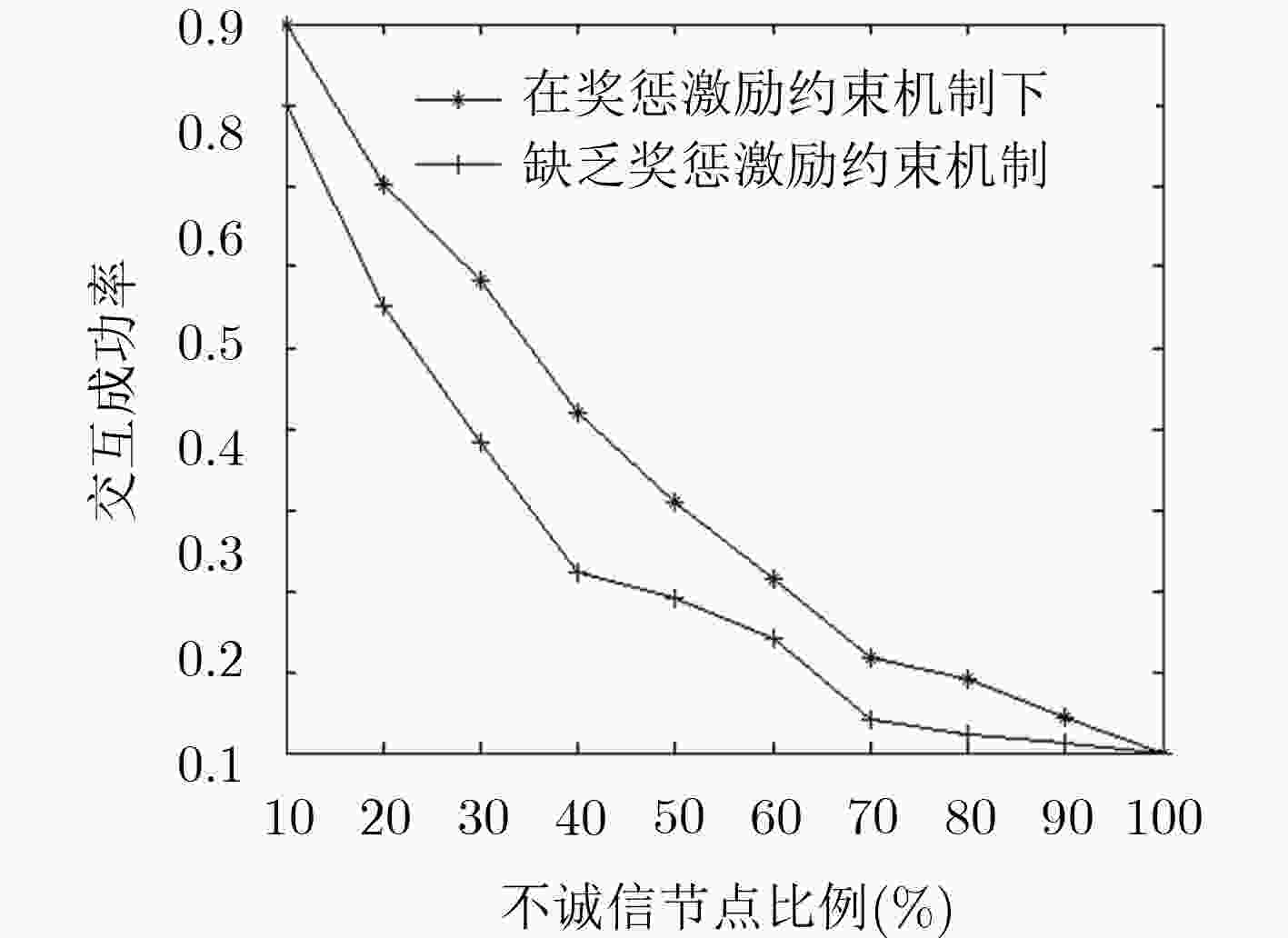
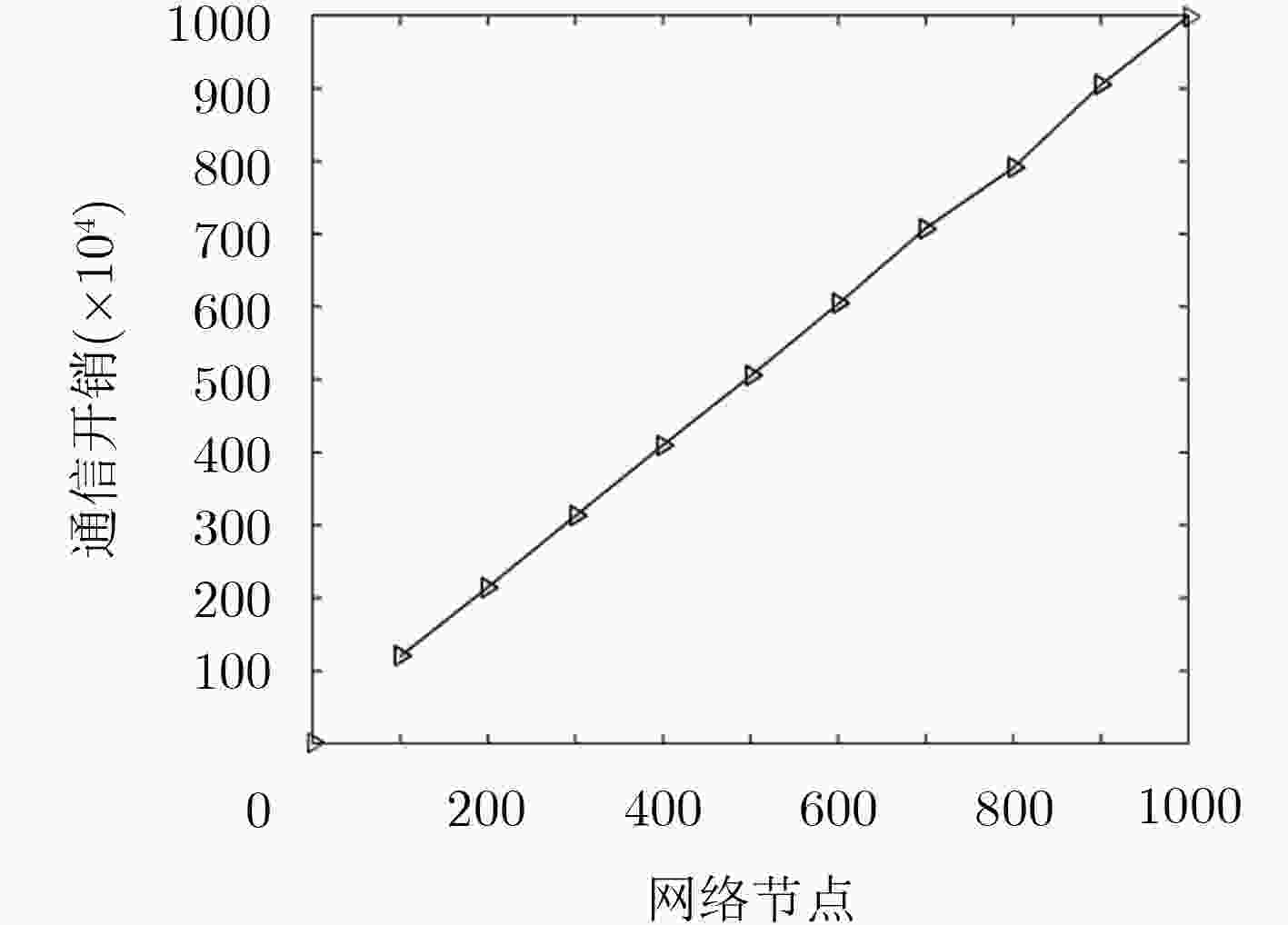
基于信任的访问控制问题是面向开放式网络访问控制中研究的热点。该文针对开放式网络环境下网络交互实体不诚信合作的交互访问行为,建立了基于信任的动态访问控制博弈模型,并通过设计的奖惩激励约束机制促使交互实体在自身利益驱动下理性选择系统(设计者)期望的策略,以利益作为驱动力,奖励诚信节点,惩罚约束激励不诚信节点,实现符合目标要求实体间的总体均衡状态。仿真实验和结果分析表明,在网络交互实体的不诚信访问问题上该激励约束机制是有效的。
Abstract:Trust based access control is a research hotspot in open network that access control is one of the importation technology of information security. For the interactive access behaviors of non-honest cooperation between network interactive entities in open network, the dynamic game access control model is established based on trust, and interactive entities are encouraged to rationally choose strategies expected by the system (the designer) driven by its own benefits through the designed mechanism. Taking benefits as the driven force, the mechanism rewards the honest nodes and punishes and restrains the non-honest nodes, and then reaches the general state of equalization between entities which meets the goal. The simulation experiment and result analysis show that the incentive and restraint mechanism is valid and necessary on the issue of non-honest access between network interactive entities.
-
Key words:
- Open network /
- Game theory /
- Access control /
- Incentive /
- Restraint mechanism
-
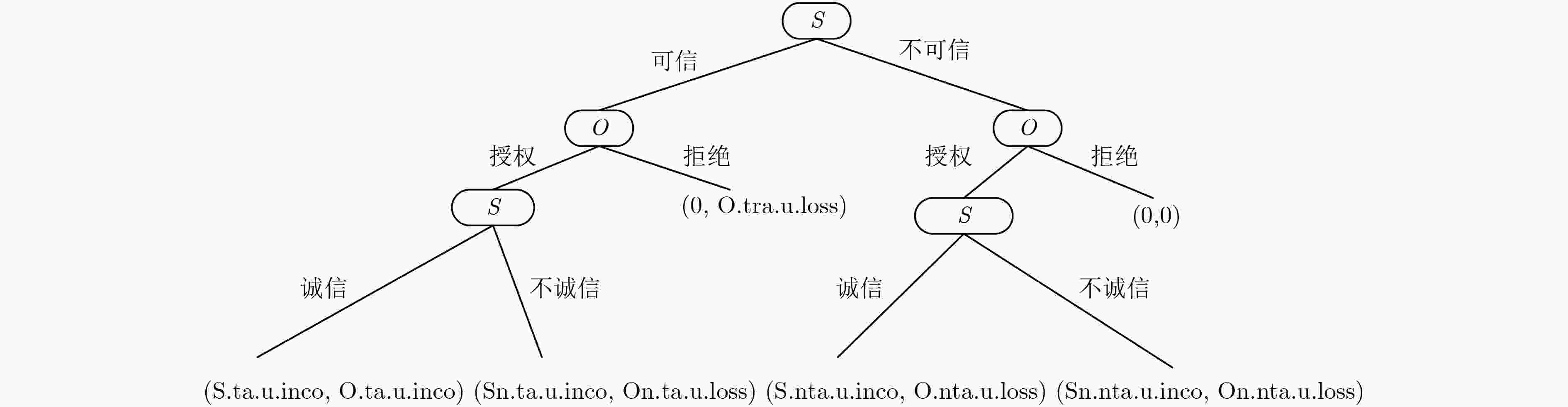
表 1 基于信任的访问控制博弈支付矩阵
参与者 客体O 主体S 行动 授权 拒绝 可信 诚信 S.ta.u.inco, O.ta.u.inco 0, O.tra.u.loss 不诚信 Sn.ta.u.inco, On.ta.u.loss 不可信 诚信 S.nta.u.inco, O.nta.u.loss 0, 0 不诚信 Sn.nta.u.inco, On.nta.u.loss 表 2 可信情况下主客体的支付矩阵
参与者 客体$O$ 主体$S$ 行动 授权 拒绝 可信 不诚信 (20, 0) (1, 1) 诚信 (5, 5) (0, 10) 表 3 实体间博弈支付矩阵
参与者 Ej ${E_i}$ 行动 授权 拒绝 可信(P) 不诚信 (5, 5) (0, –2) 诚信 (4, –4) (0, –2) -
FUDENBERG D and TIROLE J. Game Theory[M]. Cambridge, Massachusetts, US, MIT Press, 1991: 275–277. 赵斌, 何泾沙, 张伊璇, 等. 基于灰色关联分析的推荐信任评估方法[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(2): 314–320 doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2016.112ZHAO Bin, HE Jingsha, ZHANG Yixuan, et al. Recommendation trust evaluation method based on grey relational analysis[J]. Journal of Peking University (Natural Science Edition) , 2017, 53(2): 314–320 doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2016.112 GHARAM M, ABDALLAH W, and BOUDRIGA N. The design of a game-theoretic based multiple access scheme for 5G millimeter wave communication networks[C]. ACM International Conference on Advances in Mobile Computing & Multimedia, Salzburg, Austria, 2017: 166–17. 刘琴, 刘旭辉, 胡柏霜, 等. 个人健康记录云管理系统中支持用户撤销的细粒度访问控制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1206–1212 doi: 10.11999/JEIT16062LIU Qin, LIU Xuhui, HU Baishuang, et al. Personal health record cloud management system in support of user revocation fine grained access control[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1206–1212 doi: 10.11999/JEIT16062 郭树行, 张禹. 基于动态情景网关的系统协同访问控制模型[J]. 通信学报, 2013, 34(Z1): 142–147GUO Shuxing and ZHANG Yu. Collaborative access control model based on dynamic situational gateway[J]. Journal of Communications, 2013, 34(Z1): 142–147 HELIL N, HALIK N, and RAHMAN K. Non-zero-sum cooperative access control game model with user trust and permission risk[J]. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 2017, 307: 299–310 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2017.03.006 CHEN Lijun, LOW S H, and DOYLE J C. Random access game and medium access control design[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2010, 18(4): 1303–1316 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2010.2041066 ALAVI S M and ZHOU Chi. Resource allocation scheme for orthogonal frequency division multiple access networks based on cooperative game theory[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2014, 27(8): 1105–1125 doi: 10.1002/dac.2398 ZHAO Bin, XIAO Chuangbai, ZHANG Yu, et al. Assessment of recommendation trust for access control in open networks[J]. Cluster Computing, 2018(4): 1–7 doi: 10.1007/s10586-017-1338-x 郭子溢, 刘立, 叶牡丹, 等. 层次化社交网络中直销激励机制的研究与设计[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2017, 38(8): 2111–2115 doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2017.08.022GUO Ziyi, LIN Li, YE Mudan, et al. Research and design of direct selling incentive mechanism in hierarchical social network[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2017, 38(8): 2111–2115 doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2017.08.022 IOSIFIDIS G, GAO Lin, and HUANG Jianwei. Incentive mechanisms for user-provided networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(9): 20–27 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6894448 CHANG Junsheng, PANG Zhengbin, XU Weixia, et al. An incentive compatible reputation mechanism for P2P systems[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2014, 69(3): 1382–1409 doi: 10.1007/s11227-014-1204-z WU Tinyu, LEE Weitsong, GUIZANI N, et al. Incentive mechanism for P2P file sharing based on social network and game theory[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2014, 41(5): 47–55 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2013.10.006 王博, 黄传河, 杨文忠, 等. Ad Hoc网络中基于惩罚机制的激励合作转发模型[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2011, 48(3): 398–406WANG Bo, HUANG Chuanhe, YANG Wenzhong, et al. Incentive cooperation forwarding model based on penalty mechanism in Ad Hoc networks[J]. Computer Research and Development, 2011, 48(3): 398–406 王杨, 王汝传, 徐小龙, 等. 资源共享P2P网络的进化博弈激励模型[J]. 计算机工程, 2011, 37(11): 19–21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2011.11.007WANG Yang, WANG Ruchuan, XU Xiaolong, et al. Evolutionary game incentive model of resource sharing P2P network[J]. Computer Engineering, 2011, 37(11): 19–21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2011.11.007 CIOBANU R, DOBRE C, DASCALU M, et al. SENSE: A collaborative selfish node detection and incentive mechanism for opportunistic networks[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2014, 41(5): 240–249 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2014.01.009 -





 下载:
下载:






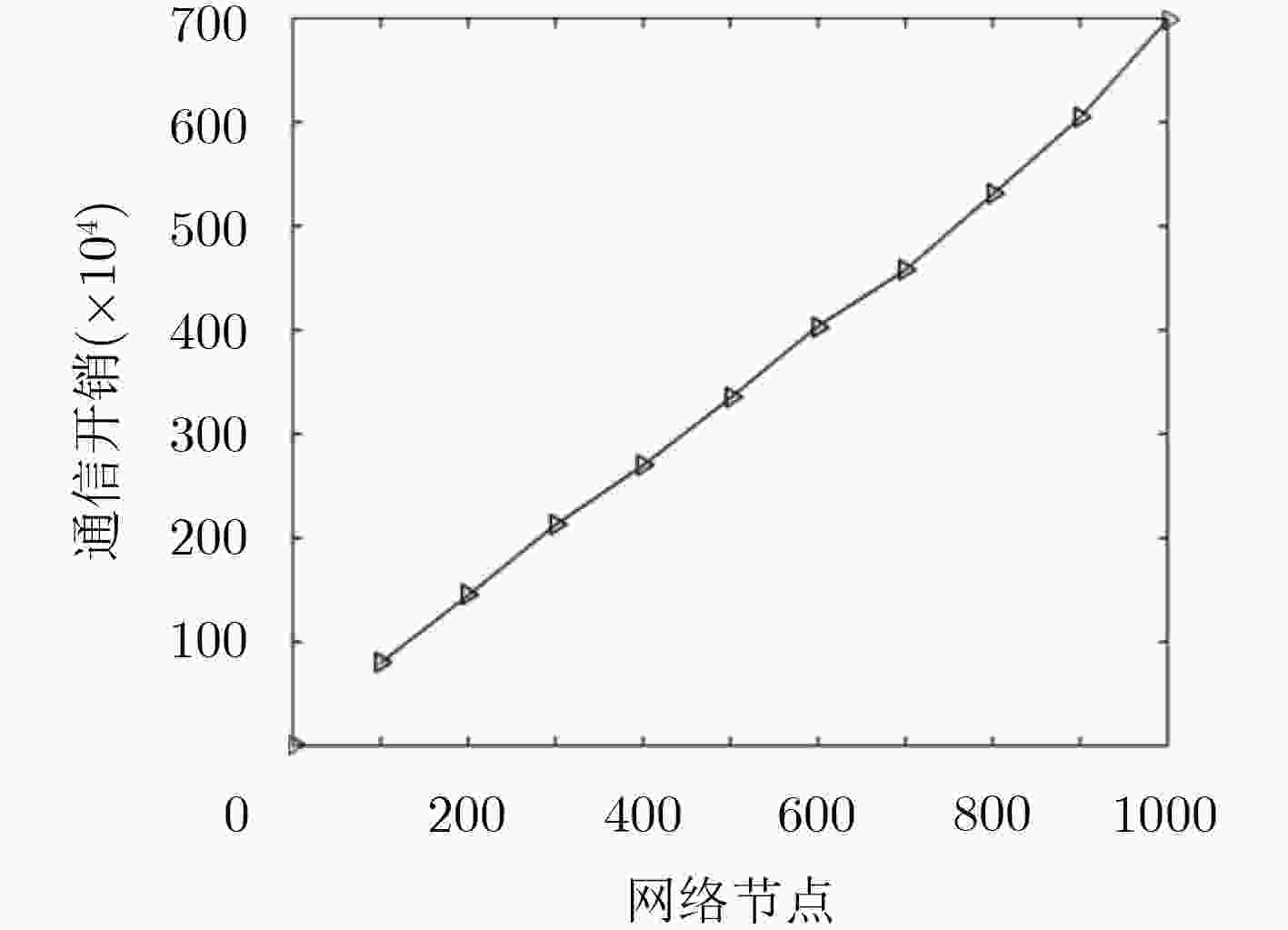


 下载:
下载:
