High-precision Digital Surface Model Inversion Approach in Forest Region Based on PolInSAR
-
摘要:
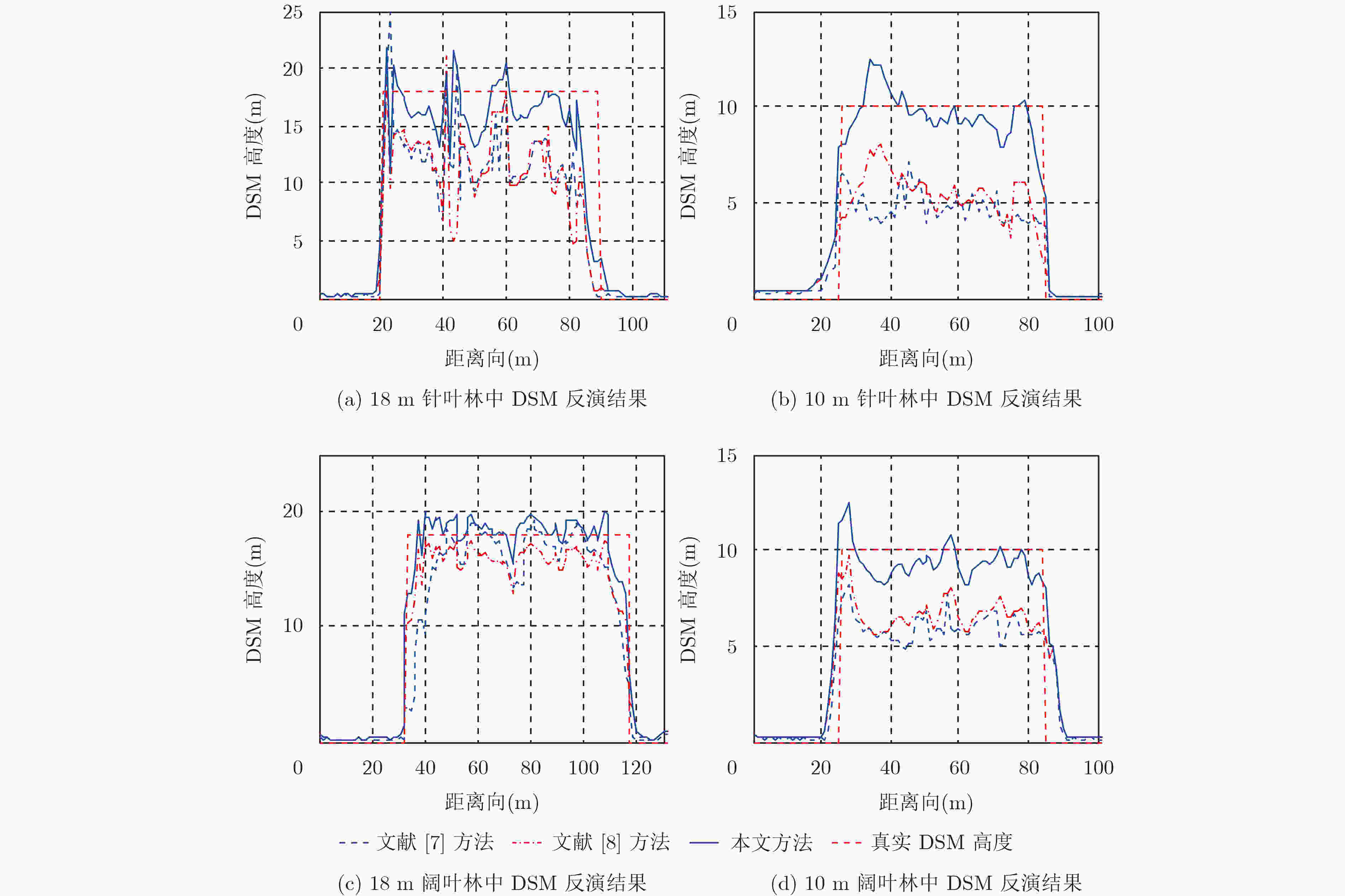
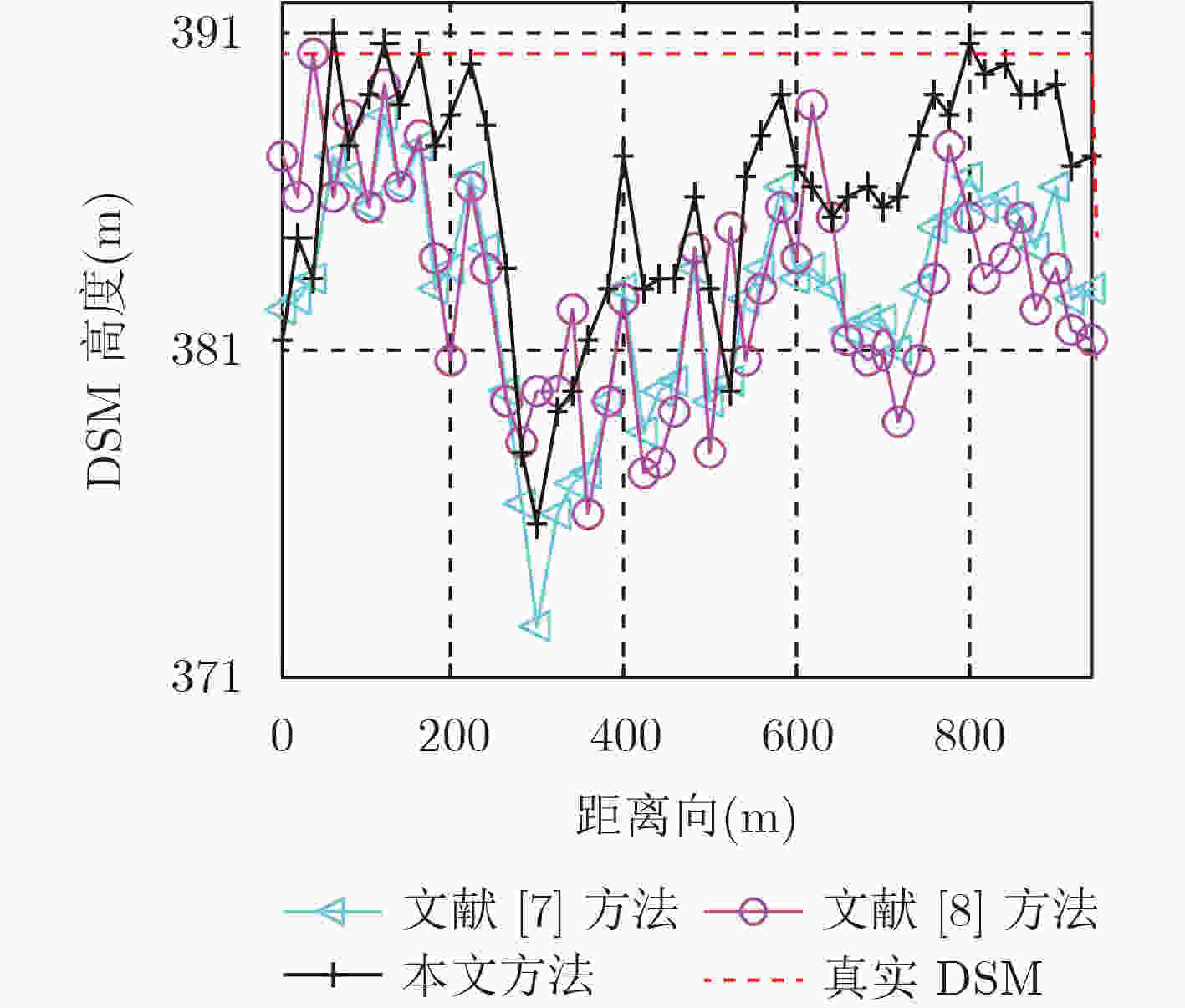
针对传统方法无法估计电磁波在植被中的穿透深度导致植被数字表面模型(DSM)反演误差较大的问题,该文提出一种高精度DSM估计方法。该方法首先通过极化干涉相干最优中最大化相位差法分离得到电磁波在植被中高、低散射相位中心的干涉相位。然后提出一种归一化高、低散射相位中心高度随消光系数变化的模型,基于该模型搜索得到电磁波在植被中的最浅穿透深度。最后利用干涉处理方法得到高散射相位中心的高程,将最浅穿透深度补偿到该高程中,从而提升植被区DSM估计精度。利用PolSARpro软件在不同植被种类和不同植被高度下进行仿真试验以及机载全极化数据进行实测数据试验,试验结果表明该方法能有效提高植被区DSM反演精度。
Abstract:The general method for inversion of Digital Surface Model (DSM) in forest region has great errors due to the inestimable waves’ penetration depth. For this problem, an approach to inversion of high-precision DSM is proposed. First, the phases of high and low scattering phase centers of the waves in forest are obtained by maximizing the phase separation of the coherence optimization. Then, the normal height variation models of the high and low scattering centers with extinction factors are constructed. According to the models, the least penetration depth of the waves in forest is acquired. Eventually, by implementing the interferometric technique on the phase of high scattering phase center, a coarse DSM is retrieved, and a high-precision DSM is developed by compensating the least penetration depth to the coarse one. The validation of the method is investigated by simulated datasets of PolSARpro under different tree species and different forest heights and by airborne real datasets. It shows that the proposed method can improve the accuracy on the inversion of DSM effectively in forest region.
-
表 1 雷达几何参数
参数名 参数值 雷达平台高度(m) 3000 有效基线长度(m) 6.33 雷达下视角(°) 45 雷达工作频率(GHz) 1.3 表 2 场景参数
参数名 参数值 树种类型 阔叶林/针叶林 植被高度(m) 18/10 树种密度(株/Ha) 600 距离向地形坡度(°) 0 -
ROSEN P A, HENSLEY S, JOUGHIN I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of IEEE, 2000, 88(3): 333–382. doi: 10.1109/5.838084 CLARK M L, CLARK D B, and ROBERTS D A. Small-footprint Lidar estimation of sub-canopy elevation and tree height in a tropical rain forest landscape[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2004, 91(1): 68–89. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.02.008 ANDERSEN H E, REUTEBUCH S E, and MCGAUGHEY R J. Active Remote Sensing[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2006: 43–66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-4387-1_3. GUSTAVO H X, KARLUS A, CAMARA D M, et al. The dual-band PolInSAR method for forest parametrization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 3189–3201. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2520900 GONZÁLEZ C, BRÄUTIGAM B, RIZZOLI P, et al. Relative height accuracy analysis of Tandem-X DEM products[C]. The 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1172–1176. YASER S, BENOÎT S, BRIGITTE L, et al. Canopy Height Model (CHM) derived from a TanDEM-X InSAR DSM and an airborne lidar DTM in boreal forest[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(1): 381–397. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2512230 周伟, 陈尔学, 刘国林, 等. 基于ALOS极化干涉SAR数据的DEM提取方法研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2013, 28(1): 44–51. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2013.1.44ZHOU Wei, CHEN Erxue, LIU Guolin, et al. Extract DEM from ALOS based on polarinetric SAR Interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2013, 28(1): 44–51. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2013.1.44 龙江平, 刘峰, 段祝庚. 联合干涉相位和相干性幅度的极化干涉SAR最优相干性估计[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(1): 73–82. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20150509LONG Jiangping, LIU Feng, and DUAN Zhugeng. A new method of coherence optimization based on the phase and coherence magnitude in polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(1): 73–82. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20150509 KUGLER F, LEE S K, HAJNSEK I, et al. Forest height estimation by means of Pol-InSAR data inversion: The role of the vertical wavenumber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(10): 5294–5311. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2420996 CLOUDE S R. Polarization Application in Remote Sensing[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009: 265–274. 卢红喜, 宋文青, 李飞, 等. 基于幅相一致性校正的稳健植被参数反演方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(2): 283–290. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140261LU Hongxi, SONG Wenqing, LI Fei, et al. Forest parameters inversion based on nonstationarity compensation and mapping space regularization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(2): 283–290. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140261 孙宁霄, 吴琼之, 孙林. 基于PolInSAR相干区域的最优正规矩阵近似解的地形与树高估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1051–1057. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160774SUN Ningxiao, WU Qiongzhi, and SUN Lin. Topography and tree height estimation based on the best normal matrix approximation for polinsar coherence region[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1051–1057. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160774 FRANCK G and THUY L T. Forest modeling for height inversion using single-baseline InSAR/Pol-InSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3): 1528–1539. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2032538 LAGARIAS J C, REEDS J A, WRIGHT M H, et al. Convergence properties of the nelder-mead simplex method in low dimensions[J]. SIAM Journal of Optimization, 1998, 9(1): 112–147. doi: 10.1137/S1052623496303470 BANDA F and TEBALDINI S. Texture-free absolute DEM retrieval from opposite-side multibaseline InSAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 43–47. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2494684 CHOI C and KIM D J. Optimum baseline of a single-pass InSAR system to generate the best DEM in tidal flats[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(3): 919–929. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2795107 BRYAN M, ZHANG Q P, MARCUS S, et al. Extraction of DTM beneath forest canopy using a combination of X-Band InSAR and L-band PolInSAR data[C]. European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 821–824. -





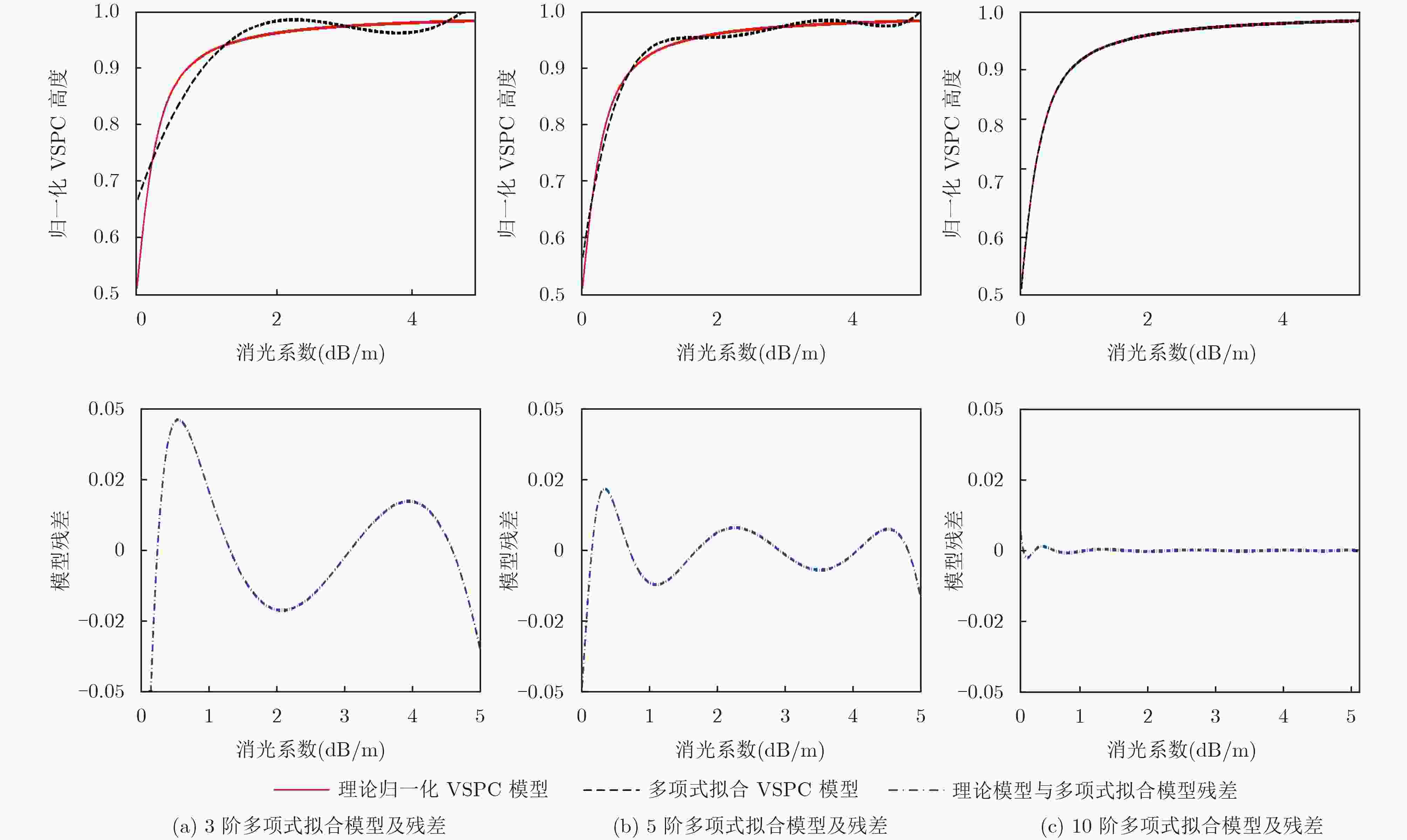
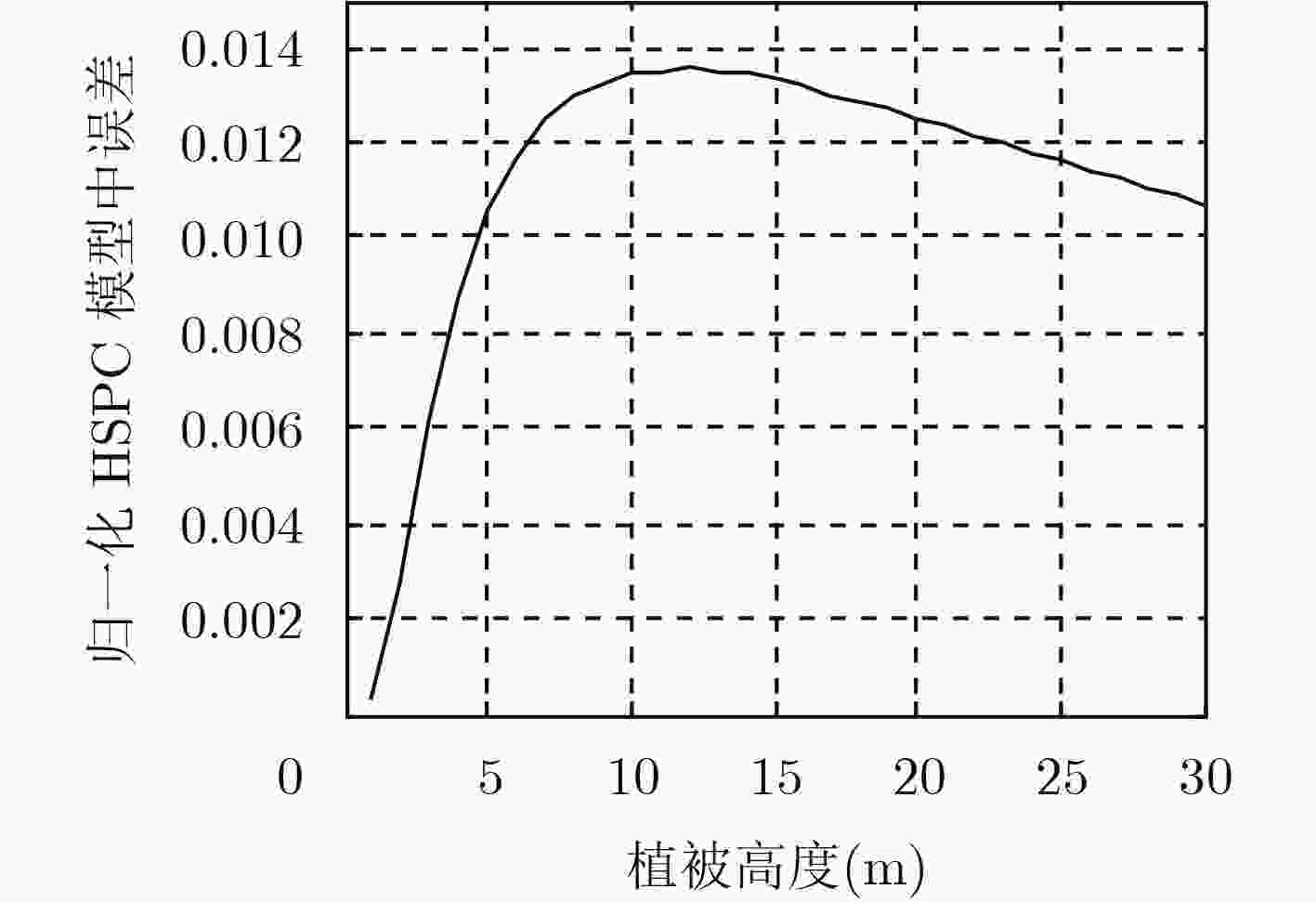
 下载:
下载:
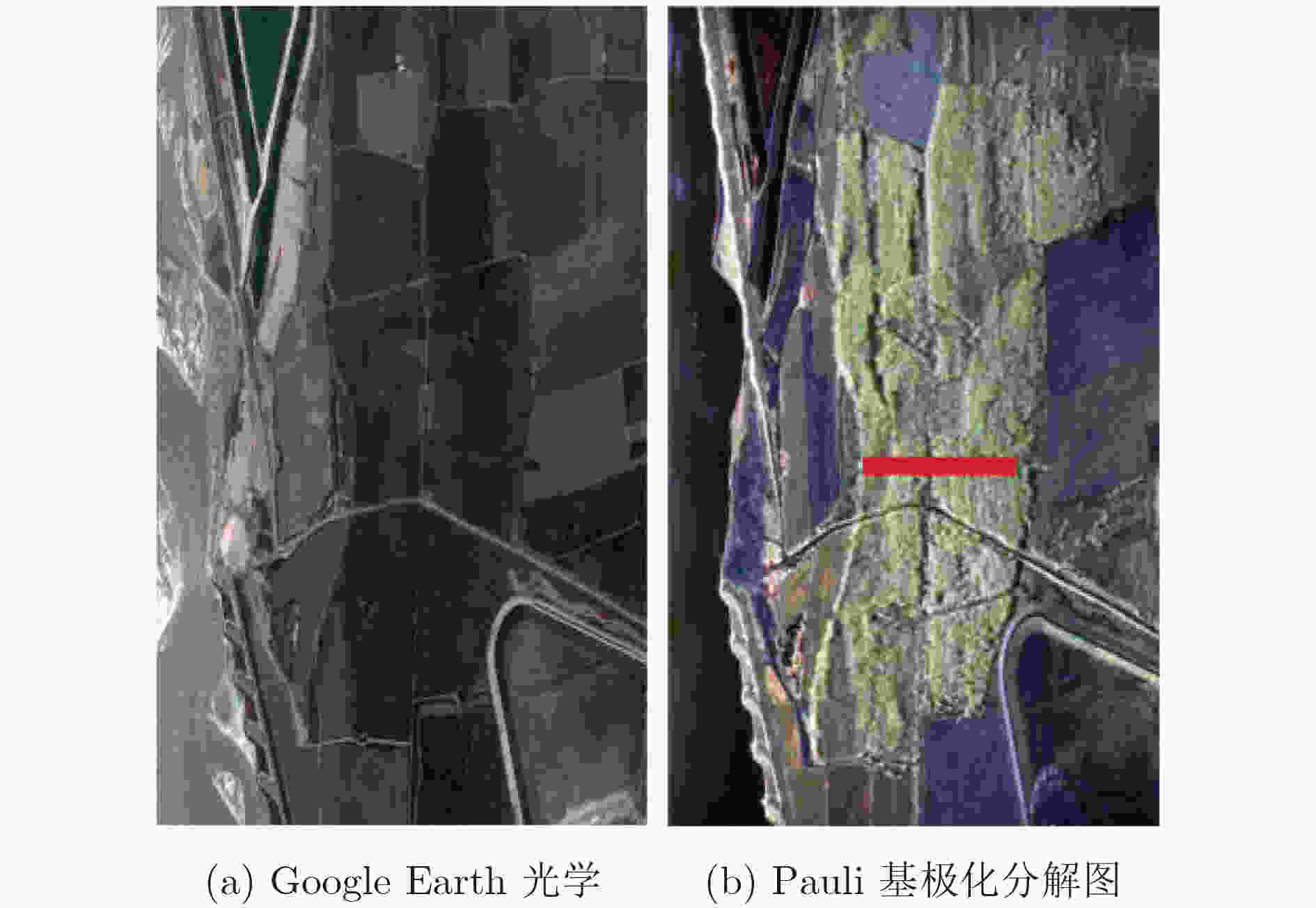
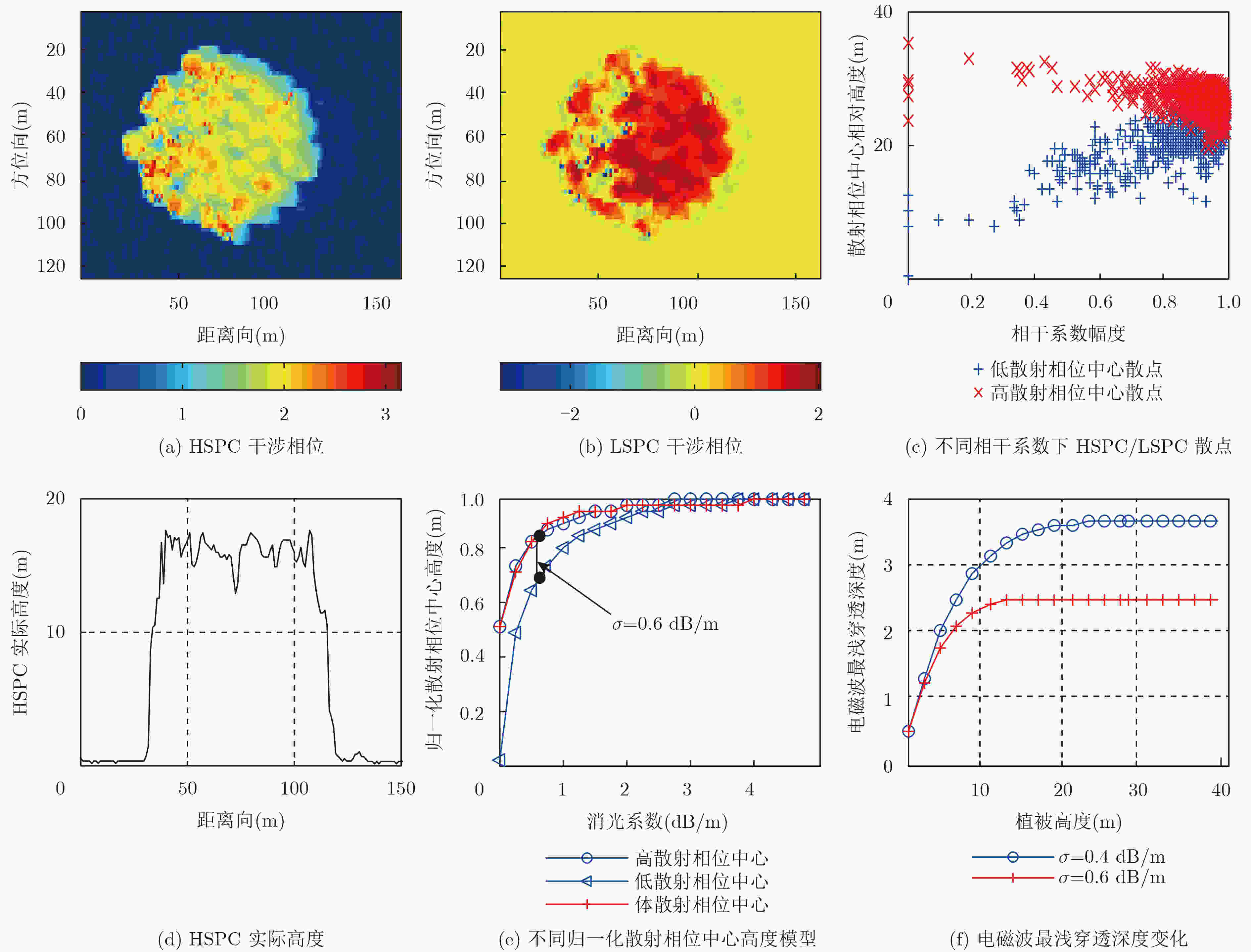
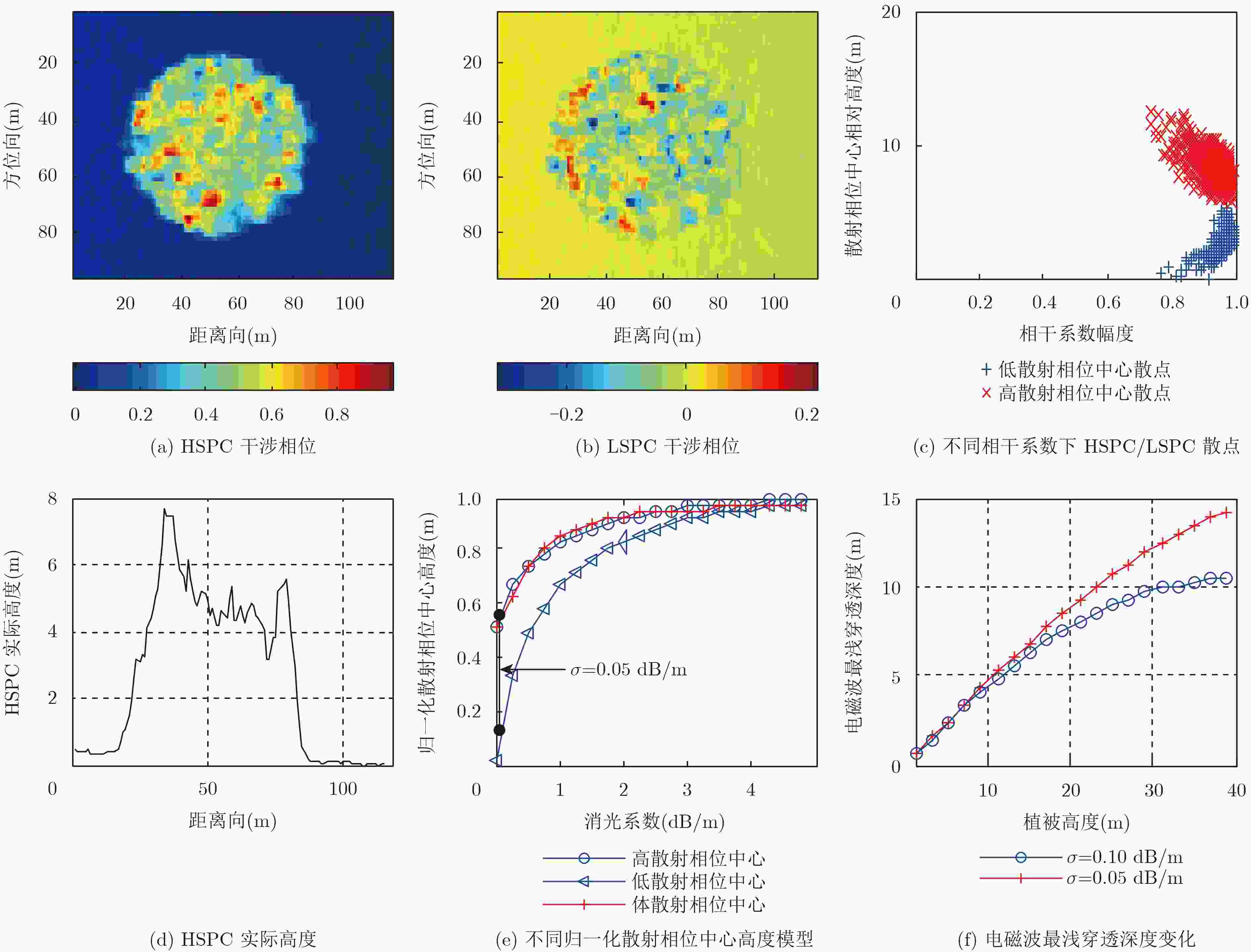



 下载:
下载:
