Frequency Domain Blind Source Separation Permutation Algorithm Based on Regional Growth Correction
-
摘要:
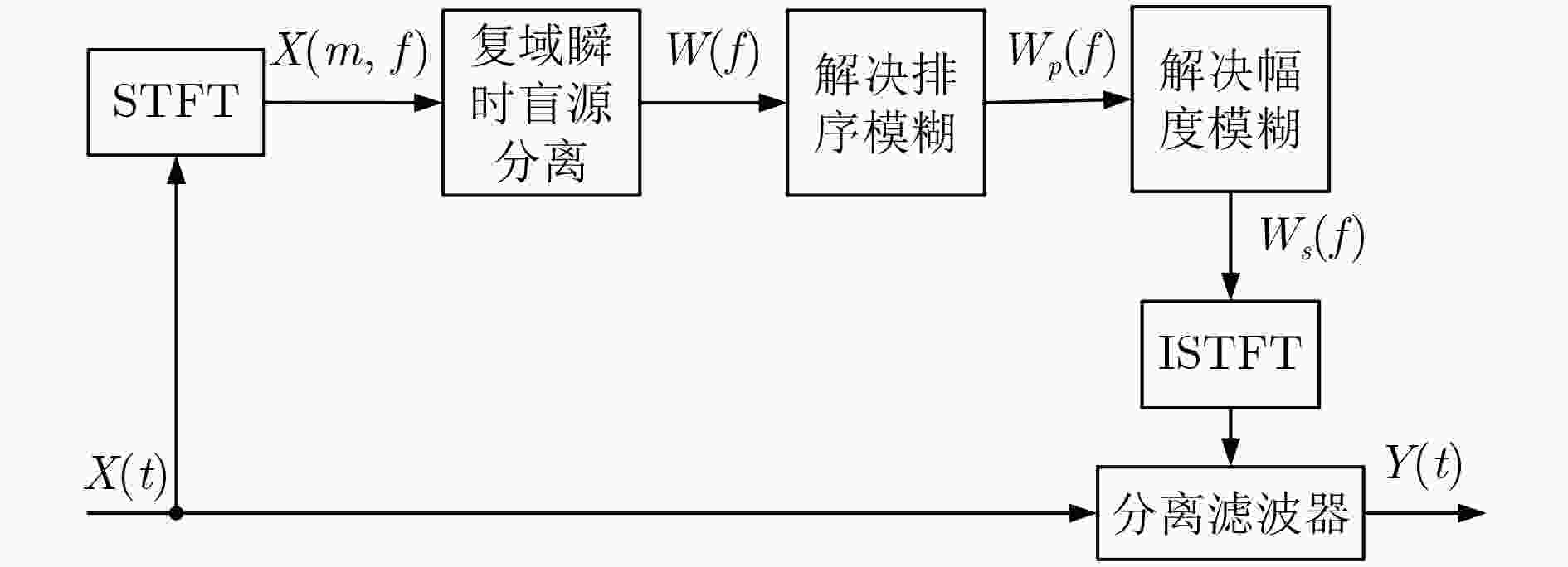
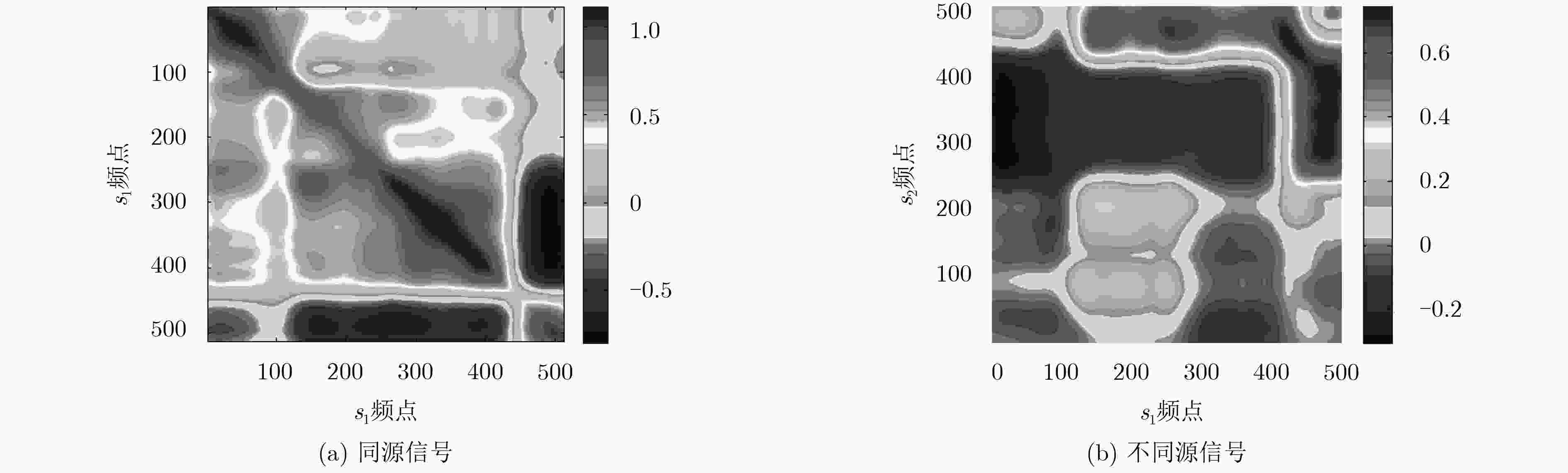
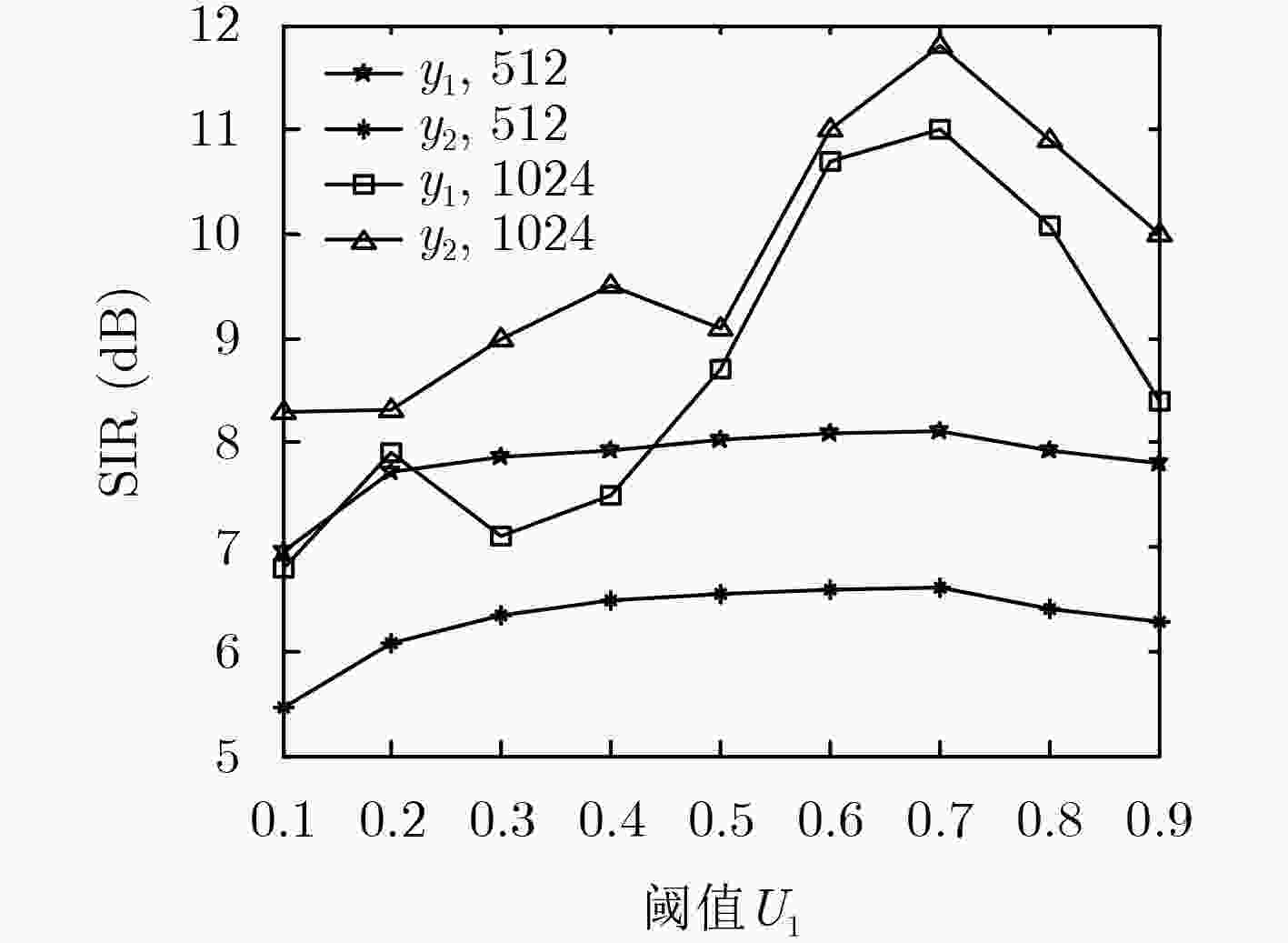
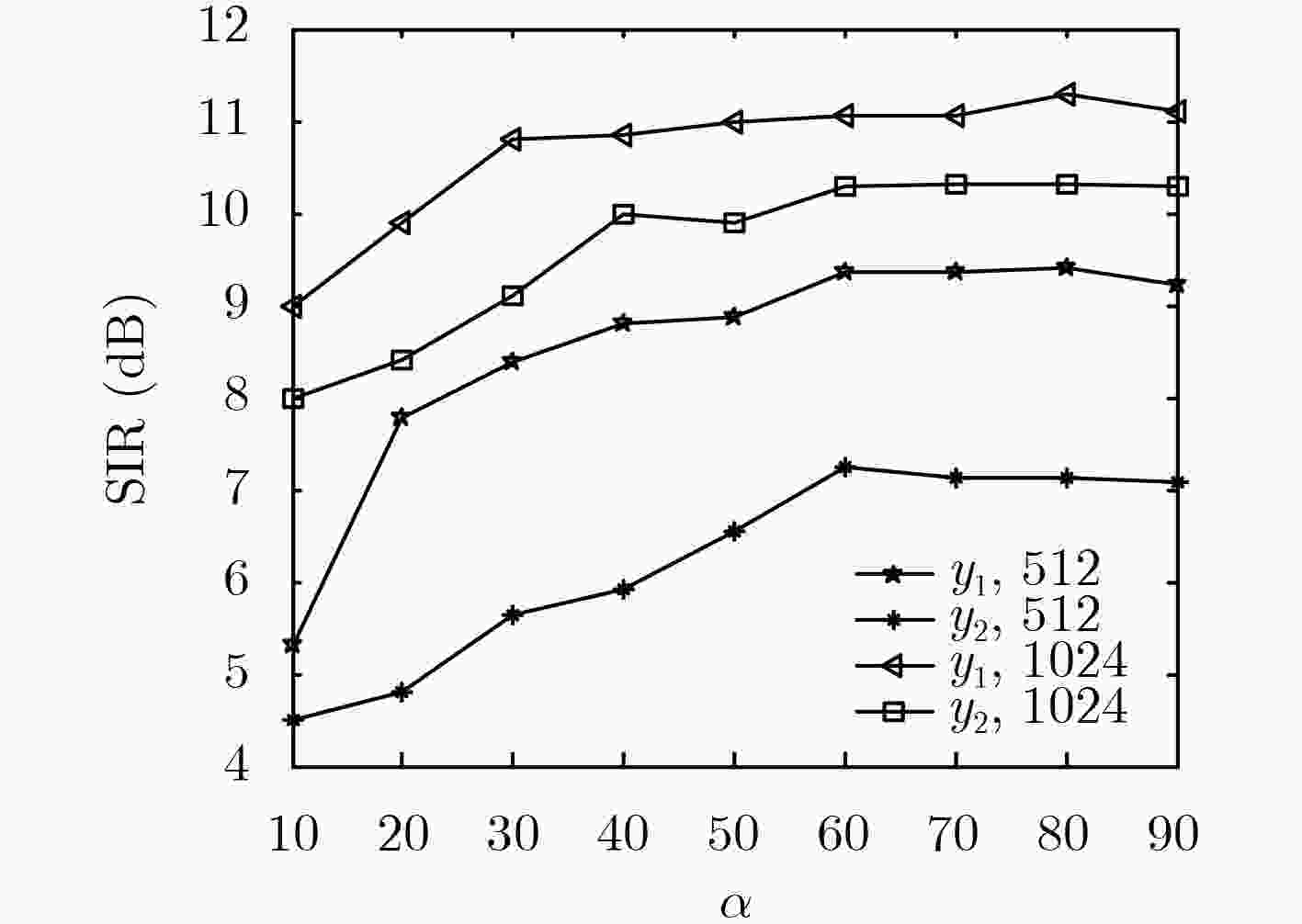
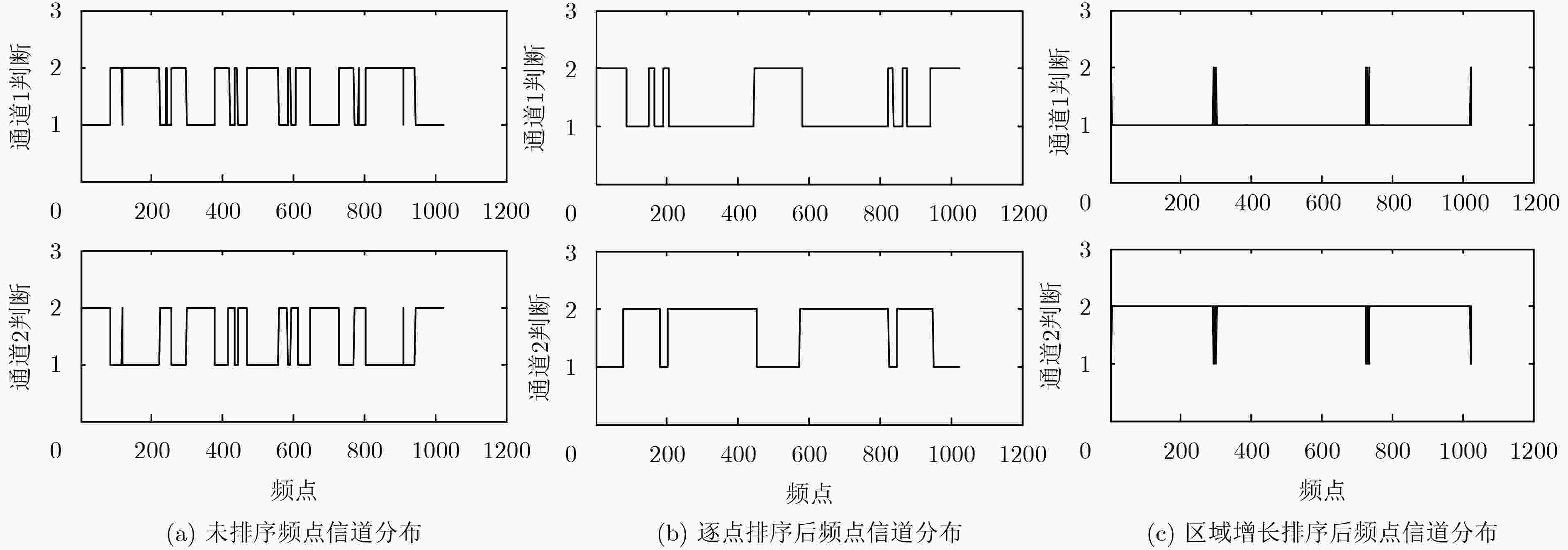
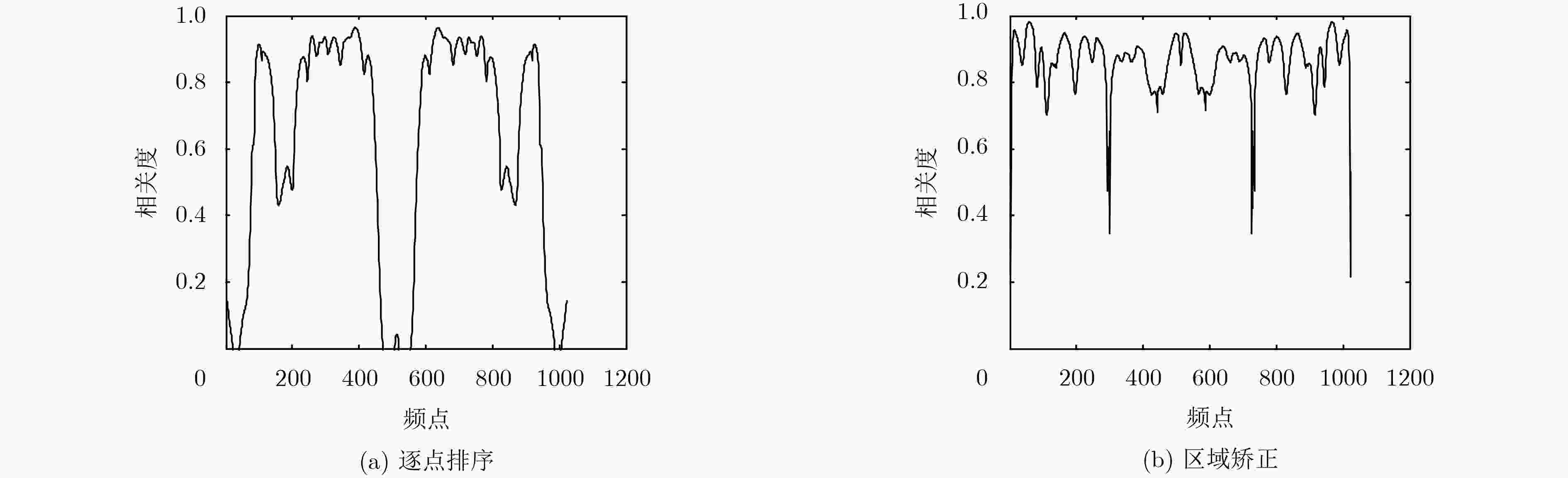
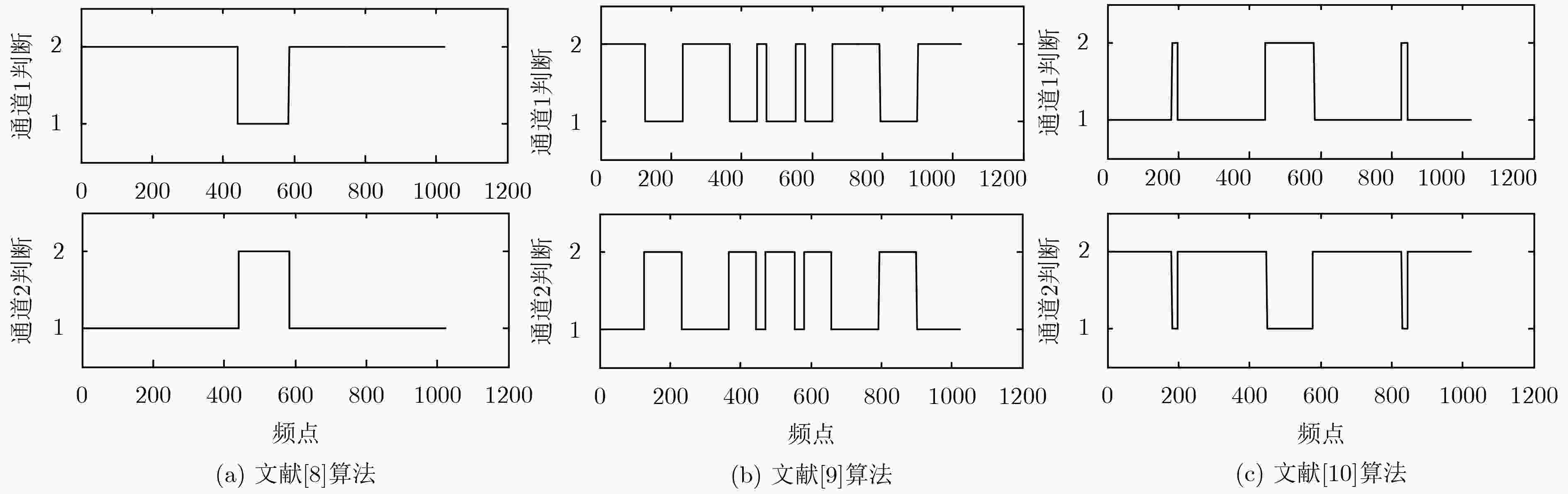
卷积盲源分离可以在频域得到有效解决,但频域盲源分离必须解决排序模糊问题。该文提出一种基于区域增长校正的频域盲源分离排序算法。首先对卷积混合信号短时傅里叶变换,在频域的各个频点处建立瞬时模型进行独立分量分析,在此基础上使用分离信号功率比的相关性,对所有频点进行逐点排序置换。其次根据阈值将排序后的结果划分为若干个小区域。最后按区域增长方式进行区域置换与合并,最终得到正确的分离信号。区域增长校正可最大限度地减少频点排序错误扩散现象,从而改善分离效果。在模拟和真实环境中分别进行语音盲源分离实验,结果表明所提算法的有效性。
Abstract:The convolutive blind source separation can be effectively solved in frequency domain, but blind source separation in frequency domain must solve the problem of ranking ambiguity. A frequency-domain blind source separation sorting algorithm is proposed based on regional growth correction. First, the convolutional mixed signal short-time Fourier transform is used to establish an instantaneous model at each frequency point in the frequency domain for independent component analysis. Based on this, the correlation of the power ratio of the separated signal is used to sort all frequency points one by one replacement. Second, according to the threshold, the sorted result is divided into several small areas. Finally. regional replacement and merging is performed according to the regional growth method, and the correct separation signal is finally obtained. Regional growth correction minimizes the mis-proliferation of frequency sorting and improves separation results. The speech blind source separation experiments are performed in the simulated and real environments respectively. The results show the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 算法性能对比(dB)
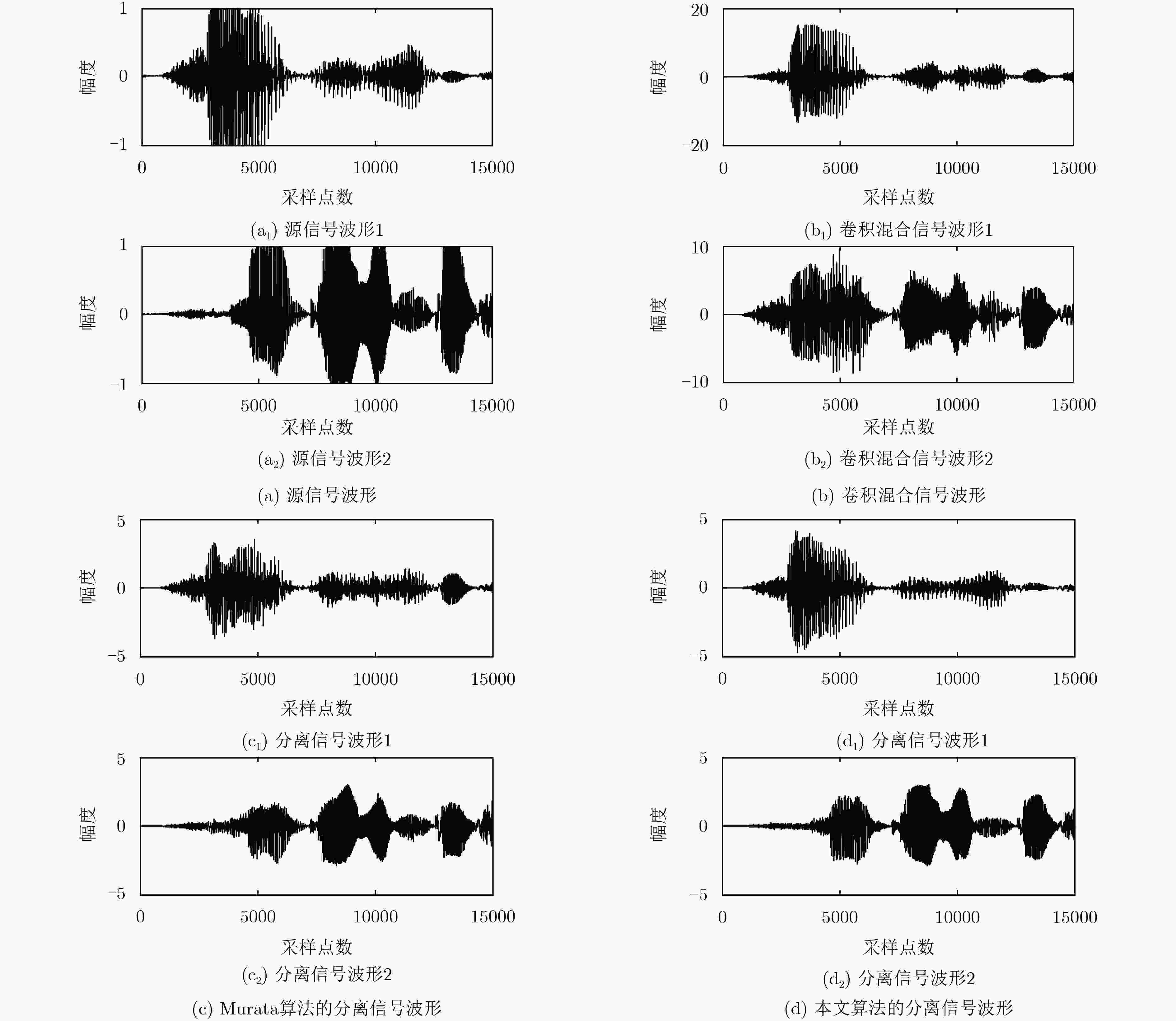
性能指标 分离信号1 分离信号2 Murata算法 本文算法 Murata算法 本文算法 SIR 6.4071 15.8474 8.5336 18.7533 SDR 5.3447 7.6937 5.6878 9.4011 SAR 4.8792 8.8522 8.0340 10.1978 表 2 本文算法复杂度
各算法块 计算量 功率比计算 $\left( {L/2} \right) \left( {{N^2}B + NB} \right)$ 逐点排序 $\left( {L/2} \right) {N^2}B$ 区域排序 $R {N^2}B$ -
张天骐, 马宝泽, 强幸子, 等. 一种引入自适应动量项的变步长混沌信号盲分离算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(4): 908–914. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160578ZHANG Tianqi, MA Baoze, QIANG Xingzi, et al. Variable-step blind source separation algorithm with adaptive momentum item for chaotic signals[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(4): 908–914. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160578 欧世峰, 耿超, 高颖. 动量项盲源分离算法及其性能优化策略[J]. 电子学报, 2014, 42(1): 42–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-21122014.01.007OU Shifeng, GENG Chao, and GAO Ying. Momentum term based blind source separation algorithm and its performance modified strategies[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(1): 42–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-21122014.01.007 徐成发, 郝宇星, 陆潞, 等. 基于互相关的快速角度估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1446–1451. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151021XU Chengfa, HAO Yuxing, LU Lu, et al. Fast angle estimation algorithm based on cross-correlation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1446–1451. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151021 胡可, 汪增福. 一种基于时频分析的语音卷积信号盲分离算法[J]. 电子学报, 2006, 34(7): 1246–1254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.07.014HU Ke and WANG Zengfu. A time-frequency analysis based blind source deconvolution method[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(7): 1246–1254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.07.014 YOSHIOKA T, NAKATANI T, MIYOSHI M, et al. Blind separation and dereverberation of speech mixtures by joint optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 2011, 19(1): 69–84. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2010.2045183 欧旭东, 张天骐, 闫振华, 等. 基于多频段能量相关排序的语音卷积混合盲源分离[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2016, 33(5): 1481–1485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.05.046OU Xudong, ZHANG Tianqi, YAN Zhenhua, et al. Blind convolution speech separation based on multi-band ordering[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2016, 33(5): 1481–1485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.05.046 PARRA L and SPENCE C. Convolutive blind separation of non-stationary sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech Audio Process, 2000, 8(3): 320–327. doi: 10.1109/89.841214 IKRAM M and MORGAN D. Permutation inconsistency in blind speech separation: Investigation and solutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech & Audio Process, 2005, 13(1): 1–13. 张华, 冯大政, 庞继勇. 基于二阶统计量的语音信号时域卷积盲分离算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(5): 1083–1086. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00574ZHANG Hua, FENG Dazheng, and PANG Jiyong. A time-domain blind convolutive separation algorithm for speech signals based on second-order statistic[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(5): 1083–1086. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00574 SAWADA H, MUKAI R, ARAKI S, et al. A robust and precise method for solving the permutation problem of frequency domain blind source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech Audio Process, 2004, 12(5): 530–538. doi: 10.1109/TSA.2004.832994 MIETTINEN J, NORDHAUSEN K, and TASKINEN S. Blind source separation based on joint diagonalization in R: The packages JADE and BSSasymp[J]. Journal of Statistical Software, 2017, 76(2): 1–31. doi: 10.18637/jss.v076.i02 MURATA N, IKEDA S, and ZIEHE A. An approach to blind source separation based on temporal structure of speech signals[J]. Neurocomputing, 2001, 41(1): 1–24. 薄祥雷, 何怡刚, 尹柏强, 等. 基于影响因子的频域盲源分离排序算法[J]. 电子学报, 2013, 42(2): 360–365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.02.023BO Xianglei, HE Yigang, YIN Baiqiang, et al. Algorithm to eliminate permutation of frequency domain blind source separation based on influence factor[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 42(2): 360–365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.02.023 SAITO S, OISHI K, and FURUKAWA T. Convolutive blind source separation using an iterative least-squares algorithm for non-orthogonal approximate joint diagonalization[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio Speech & Language Processing, 2015, 23(12): 2434–2448. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
