A Collaborative Mapping Method for Service Chain Based on Matching Game
-
摘要:
针对软件定义网络(SDN)/网络功能虚拟化(NFV)环境下服务链映射难以兼顾效率与物理资源利用率的问题,该文提出一种基于匹配博弈的服务链协同映射方法。首先,以最大化网络资源效用为目标,建立服务链映射模型MUSCM;然后,分虚拟网络功能(VNF)部署和组链两个部分解决服务链映射问题,VNF部署部分,设计基于多对一匹配博弈理论的算法协同服务链和服务节点双方互相进行选择,有效提升了服务链的映射效率和物理资源的利用率,在此基础上,设计基于分段路由策略的算法实现各VNF实例间的流量牵引以完成VNF组链,有效降低了链路传输时延。实验结果表明,与经典算法相比,该算法在保证映射请求接受率的同时,有效降低了服务链的平均传输延时,提升了系统的物理资源利用率。
Abstract:Considering that it is difficult to balance efficiency and resource utilization of Service Chain (SC) mapping problem in Software Defined Network (SDN)/Network Function Virtualization (NFV) environment, this paper proposes a collaborative mapping method for SC based on matching game. Firstly, it defines a SC mapping model named MUSCM to maximize the utility of network resources. Secondly, it divides the SC mapping problem into Virtual Network Function (VNF) deployment and connection parts. As for the VNF deployment part, an algorithm is designed to collaborate the selection of the SC and the service node based on many-to-one matching game, improving the mapping efficiency of SC and utilization of physical resource effectively. On the basis of it, an algorithm is designed based on segment routing strategy to accomplish the traffic steering between VNF instances to finish the VNF connection part, reducing the link transmission delay effectively. The experiment result shows that, compared with the classical algorithm, this algorithm ensures the mapping request received rate, and at the same time, it reduces the average transmission delay of the service chain and improves the physical resources utilization of the system effectively.
-
表 1 主要符号列表
符号 描述 $G$ 物理基础设施无向图$G = (N,E)$ $N$ 物理节点集合,$n \in N$ $E$ 物理链路集合,$e\left( {{n_i},{n_j}} \right) \in E$ ${N^F}$ 转发节点集合 ${N^S}$ 服务节点集合 ${I_k}$ 资源种类,${I_k} = \left\{ {{\rm{CPU}},{\rm{Me}},{\rm{Th}}} \right\}$ ${\rm{vol}}_n^{{I_k}}$ 服务节点$n$的${I_k}$类资源的容量 ${\rm{vol}}_{e\left( {{n_i},{n_j}} \right)}^{\rm band}$ 服务节点${n_i}$和${n_j}$间物理链路的带宽资源容量 $P$ 网络中可提供的所有VNF种类集合 ${F^p}$ 类型为$p$的VNF实例集合,${f^p} \in {F^p}$ ${R^c}$ 构成服务链$c$的VNF实例集合 $d_{{f^p}}^{{I_k}}$ VNF实例${f^p}$的${I_k}$类资源需求 $C$ 服务链集合,$c \in C$ $d_c^{{I_k}}$ 服务链$c$的${I_k}$类资源需求 $d_{{f^p},{f^{p'}}}^c$ 服务链$c$中实例${f^p}$和${f^{p'}}$间的带宽资源需求 $X_{{f^p},n}^c$ 服务链$c$中VNF实例${f^p}$与服务节点$n$映射关系 表 2 服务链匹配偏好表构建算法
算法1 服务链匹配偏好表构建算法 输入:构成服务链$c$的VNF实例集合${R^c}$,服务节点集合${N^S}$,物 理基础设施图$G$ 输出:服务链匹配偏好表${\rm SC}\left( {{N^S}} \right)$ (1) 根据输入初始化; (2) for each $n$ in ${N^S}$ do 依据式(8)计算资源偏差$\Delta R$; 选择$\Delta R$最小的服务节点${n_0}$; ${\rm{SC}}\left( {{N^S}} \right) \leftarrow \left\{ {{n_0}} \right\}$;//将${n_0}$作为起始节点,并加入偏好表 将${n_0}$标记为已读; end for (3) while ${N^S}$中存在未读节点 do 依据NNA算法寻找图$G$中距离当前节点最近的且满足资源 约束条件(式(3)、式(4))的下一服务节点${n_w}$; ${\rm{SC}}\left( {{N^S}} \right) \cup \left\{ {{n_w}} \right\}$;//将${n_w}$加入偏好表
将${n_w}$标记为已读;(4) 所有服务节点已读则终止; (5) 返回步骤(3); (6) 输出服务链匹配偏好表${\rm{SC}}\left( {{N^S}} \right)$ 表 3 服务节点匹配偏好表构建算法
算法2 服务节点匹配偏好表构建算法 输入:构成服务链$c$的VNF实例集合${R^c}$,服务节点集合${N^S}$ 输出:服务节点匹配偏好表${N^S}\left( {\rm{SC}} \right)$ (1) 根据输入初始化; (2) for each ${f^p}$ in ${R^c}$ do 按资源需求对${f^p}$进行排序; //资源需求优先级依次为
$\rm{CPU} > \rm{Me} > \rm{Th}$依据BFA算法选择剩余资源空间最小的VNF实例${f^p}$; ${N^S}\left( {\rm{SC}} \right) \cup \left\{ {{f^p}} \right\}$; //将${f^p}$加入偏好表
将VNF实例${f^p}$标记为已读;end for (3) 所有VNF实例已读则终止; (4) 返回步骤(2) (5) 输出服务节点匹配偏好表${N^S}\left( {\rm{SC}} \right)$ 表 4 博弈选择算法
算法3 博弈选择算法
输入:构成服务链$c$的VNF实例集合${R^c}$,服务节点集合${N^S}$
输出:服务链和服务节点的平稳匹配结果
根据输入初始化;
if 服务链$c$是不饱和的 do
for each ${f^p}$ in ${R^c}$ do
$n \leftarrow $get highest rank in ${\rm \rm{SC}}\!\left( {{N^S}} \right)$;
if $\left( {{\rm{vol}}_n^{{I_k}} > d_{{f^p}}^{{I_k}}} \right)\& \& \left( {{f^p} \ \ {\rm in} \ \ {N^S}\left( {\rm{SC}} \right)} \right)$ then
将${f^p}$匹配给$n$;
${\rm{vol}}_n^{{I_k}} = {\rm{vol}}_n^{{I_k}} - d_{{f^p}}^{{I_k}}$;
end
else
找出所有满足${f^p}\mathop \succ \limits_n {f^{p'}}$的${f^{p'}}$;
拒绝所有${f^{p'}}$并更新服务节点$n$的资源;
${\rm{vol}}_n^{{I_k}} = {\rm{vol}}_n^{{I_k}} - d_{{f^p}}^{{I_k}}$;
将${f^{p'}}$从服务节点映射偏好表${N^S}\left( {\rm{SC}} \right)$中移除;
将$n$从服务链映射偏好表${\rm{SC}}\left( {{N^S}} \right)$中移除;
end
end for
输出匹配结果;
else
return表 5 分段路由连接算法
算法4 分段路由连接算法 输入:VNF实例与服务节点间的映射关系$\varOmega $ 输出:服务链$c$的路由路径 根据输入初始化; 依据式(11)表达$\varOmega $中服务节点的分段路径,构成集合$S$ for each ${\rm{FG}}\left( {n_{i - 1}^{ma},n_i^{ma}} \right)$ in $S$ do 利用SPA算法计算连接路径; end for 输出计算结果; return 表 6 服务节点参数设置
CPU 内存 吞吐量 32 100 GB 10 Gbps 表 7 VNF参数设置
VNF种类 CPU 内存(GB) 吞吐量(Mbps) Firewall 8 4 200 IDS 8 4 80 IPS 4 4 268 WAN-opt 2 2 10 -
KREUTZ D, RAMOS F M V, VERÍSSIMO P E, et al. Software-defined networking: A comprehensive survey[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2015, 103(1): 14–76. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2371999 MIJUMBI R, SERRAT J, GORRICHO J L, et al. Network function virtualization: State-of-the-art and research challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2017, 18(1): 236–262. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2477041 OCAMPO A F, GIL-HERRERA J, ISOLANI P H, et al. Optimal service function chain composition in network functions virtualization[C]. International Conference on Autonomous Infrastructure, Management and Security, Zurich, Switzerland, 2017: 62–76. LI Yong and CHEN Min. Software-defined network function virtualization: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 2542–2553. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2015.2499271 BHAMARE D, JAIN R, SAMAKA M, et al. A survey on service function chaining[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2016, 75: 138–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2016.09.001 DWARAKI A and WOLF T. Adaptive service-chain routing for virtual network functions in software-defined networks[C]. The Workshop on Hot Topics in Middleboxes and Network Function Virtualization, Salvador, Brazil, 2016: 32–37. XIONG Gang, HU Yunxiang, LAN Julong, et al. A mechanism for configurable network service chaining and its implementation[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2016, 10(8): 3701–3727. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2016.08.016 SEKAR V, EGI N, RATNASAMY S, et al. Design and implementation of a consolidated middlebox architecture[C]. Usenix Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Lombard, Italy, 2012: 24–34. KUO Tunwei, LIOU Bangheng, LIN Chingju, et al. Deploying chains of virtualnetwork functions: On the relation between link and server usage[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–9. ZHANG Qixia, XIAO Yikai, LIU Fangming, et al. Joint optimization of chain placement and request scheduling for network function virtualization[C]. IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, Atlanta, USA, 2017: 731–741. GALE D and SHAPLEY L S. College admissions and the stability of marriage[J]. American Mathematical Monthly, 1962, 69(1): 9–15. doi: 10.4169/amer.math.monthly.120.05.386 XU Hong and LI Baochun. Anchor: A versatile and efficient framework for resource management in the cloud[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2013, 24(6): 1066–1076. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2012.308 ZHANG Yan and ANSARI N. Heterogeneity aware dominant resource assistant heuristics for virtual machine consolidation[C]. Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 1297–1302. CORMEN T T, LEISERSON C E, RIVEST R L, et al. Introduction to Algorithms[M]. McGraw, USA, MIT Press, 2002: 145–167. MANLOVE D. Algorithmics of Matching under Preferences[M]. Glasgow, UK, World Scientific Pub. Co, 2013: 266–278. FILSFILS C, NAINAR N K, PIGNATARO C, et al. The segment routing architecture[C]. Global Communications Conference, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–6. CALVERT K L and BHATTACHARJEE S. How to model an internetwork[C]. IEEE Conference of Computer Societies, San Francisco, USA, 1996: 594–602. -





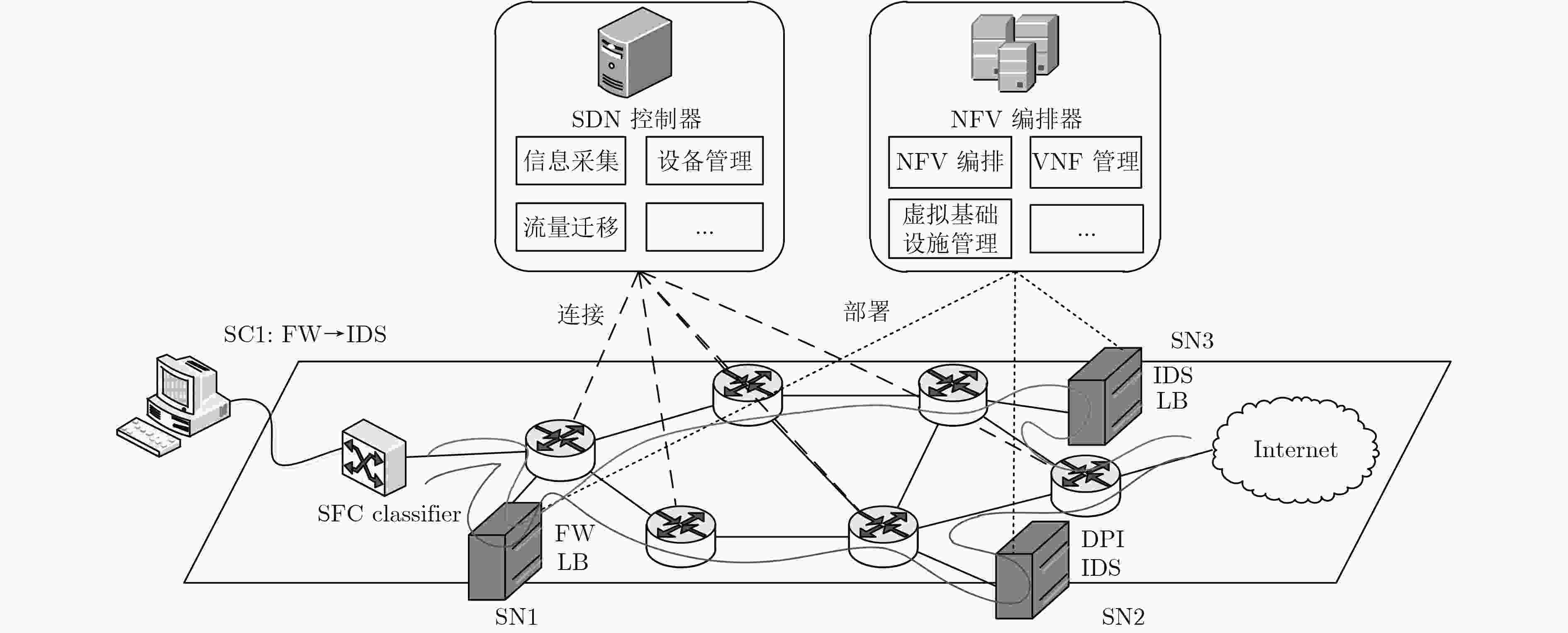
 下载:
下载:
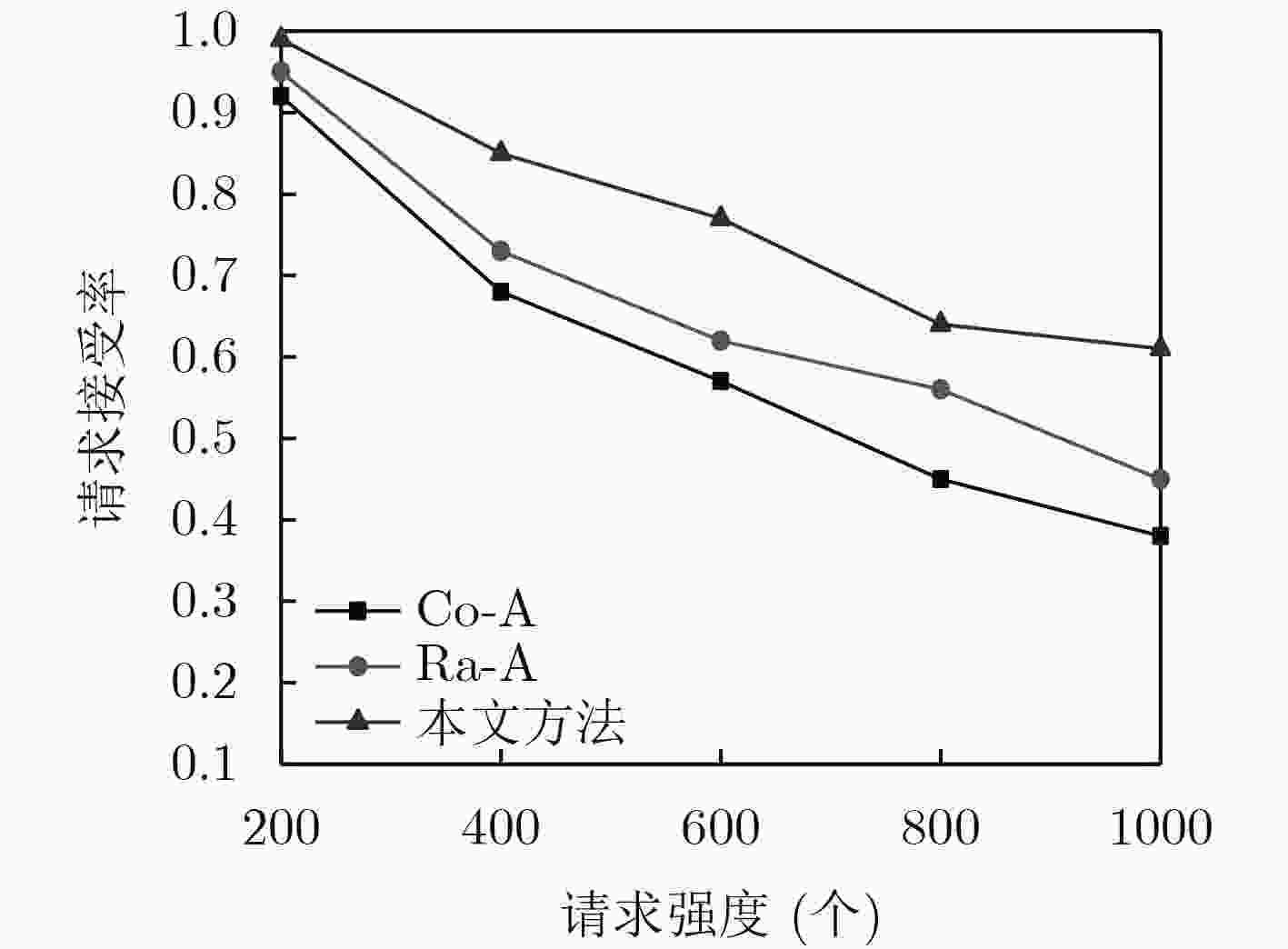
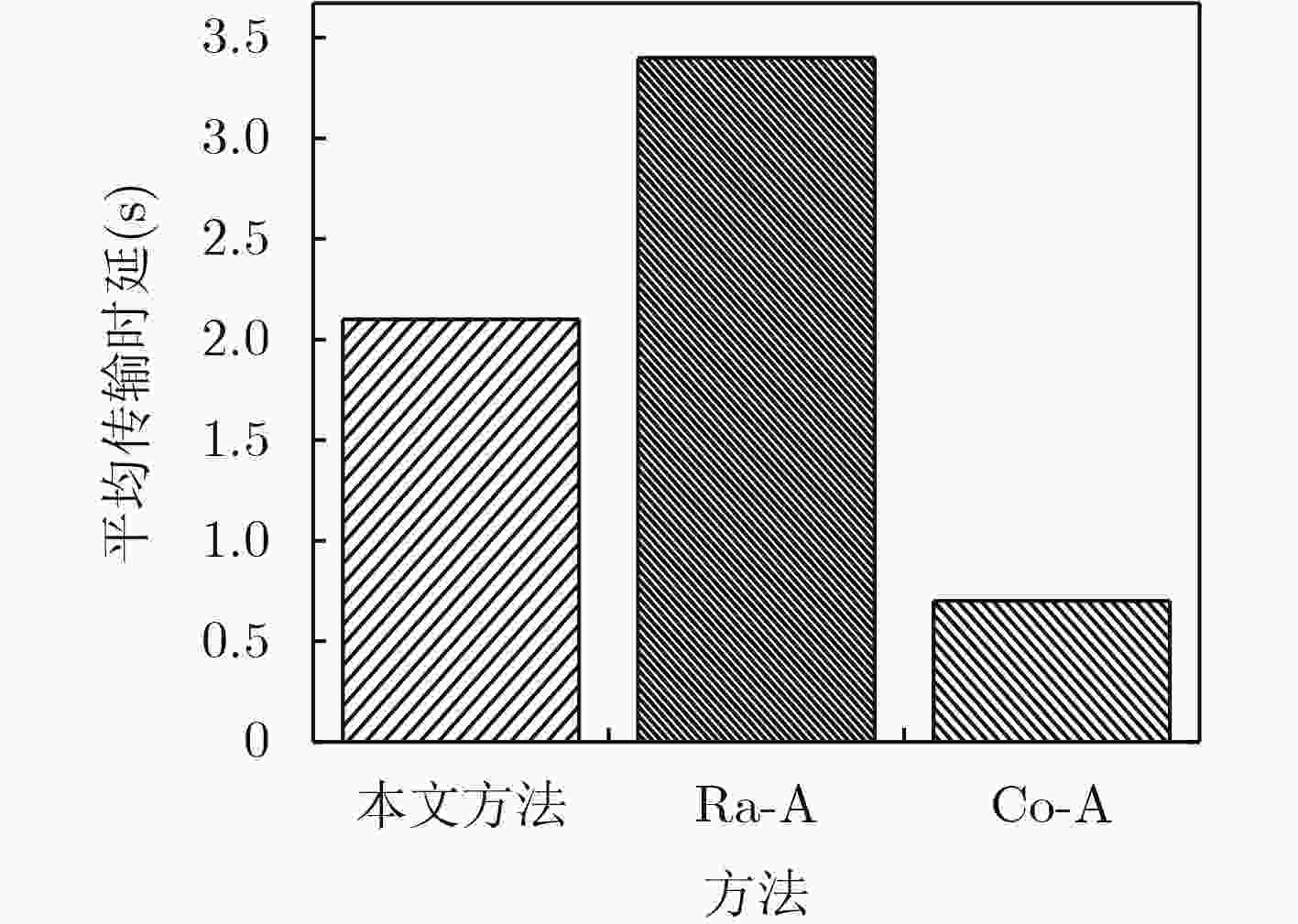
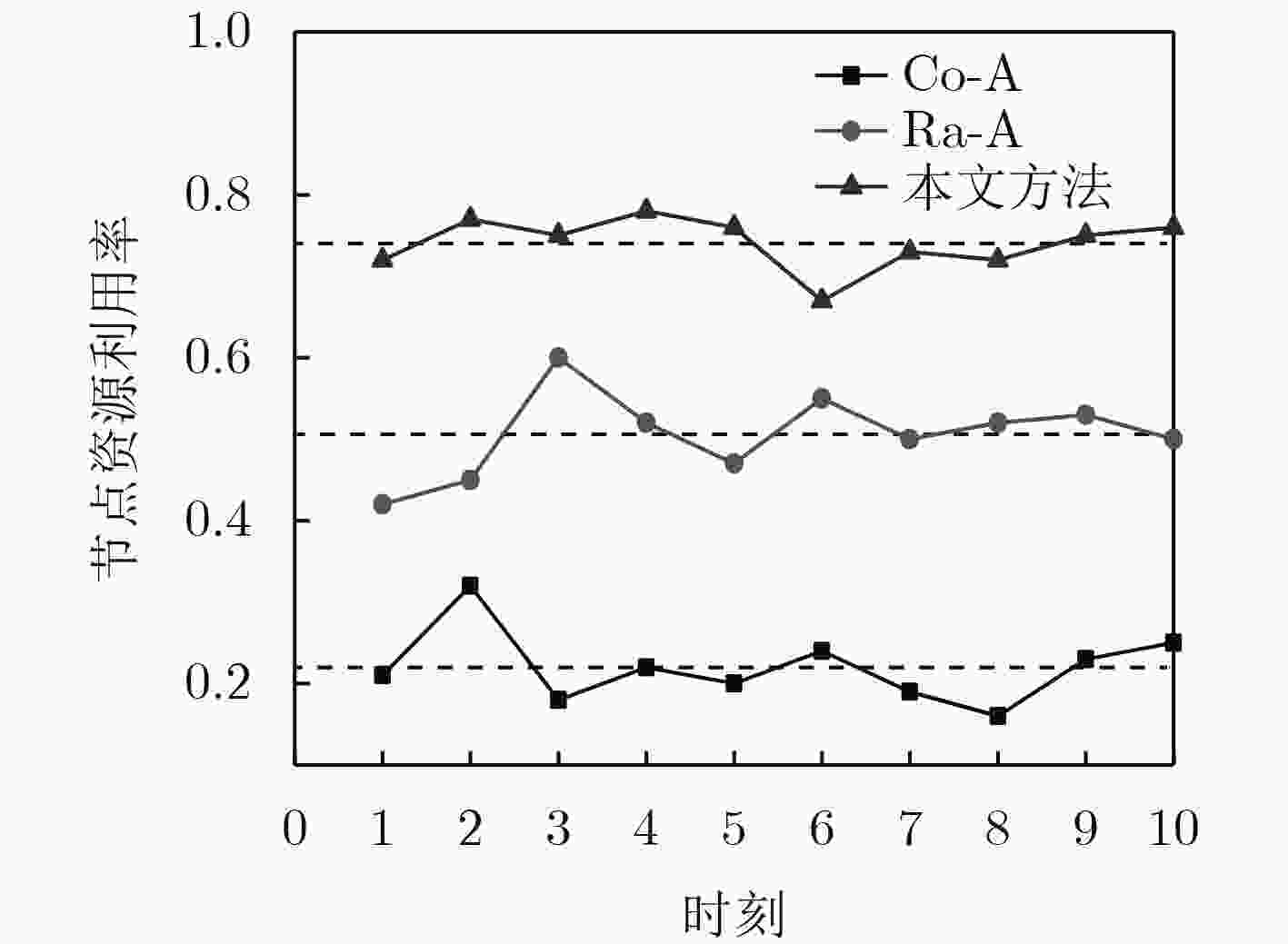
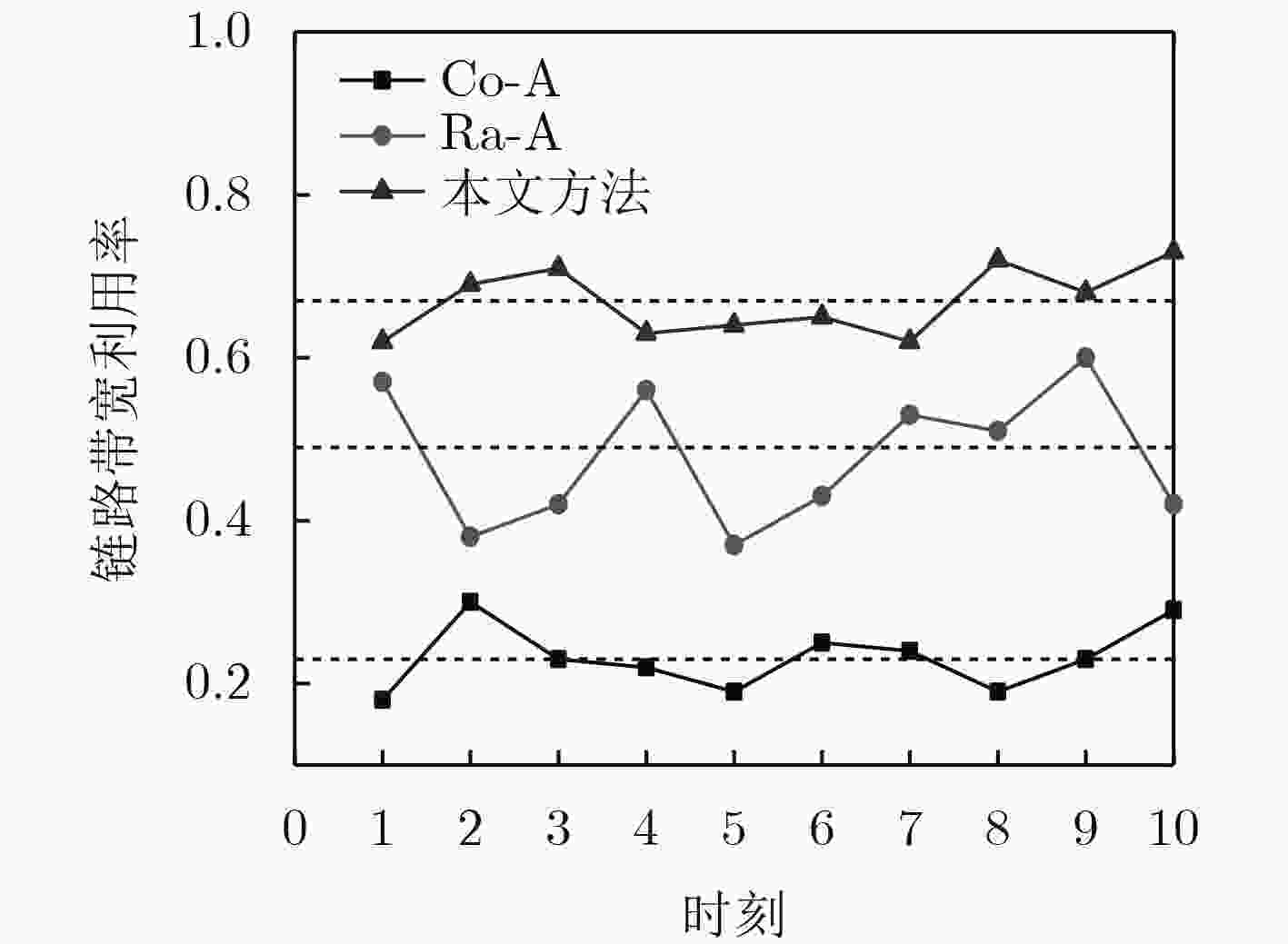


 下载:
下载:
