Joint Admission Control and Resource Allocation Algorithm for Access and Backhaul Integrated Small Base Station
-
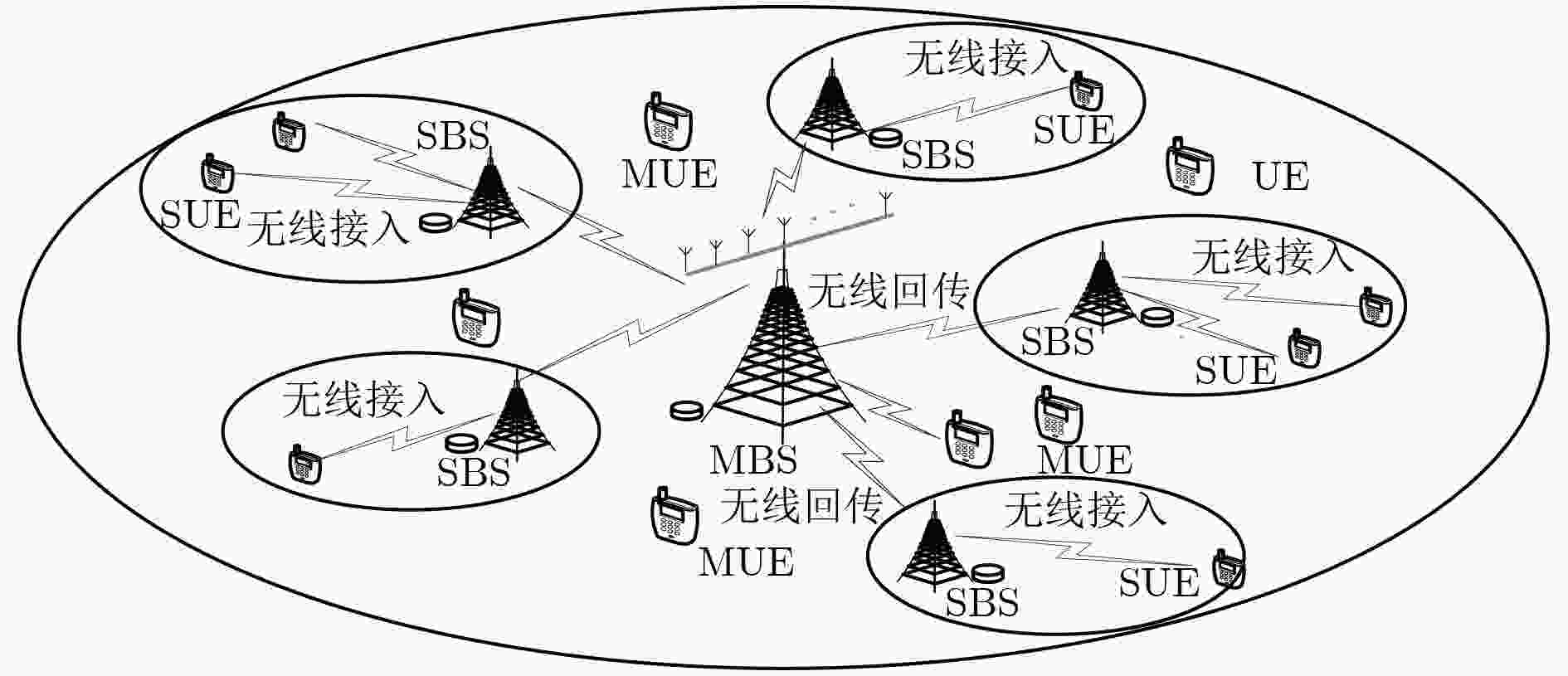
摘要: 针对全双工无线接入与回传一体化小基站场景下长期的频谱效率和能效同时最大化问题,该文提出一种基于近似动态规划理论的接入与回传一体化小基站接入控制与资源分配联合优化算法。该算法首先联合考虑当前基站的资源使用和功率配置情况,在任一用户需求动态到达以及平均时延、小基站回传速率和传输功率约束下,使用受限马尔科夫决策过程(CMDP)建立频谱效率最大化和功率消耗最小化的多目标优化模型,其次运用切比雪夫理论将多目标优化问题转化为单目标问题,并使用拉格朗日对偶分解法进一步转化为非受限的马尔科夫决策过程(MDP)问题。最后,为了解决其求解时存在的“维度灾”爆炸问题,该文提出基于近似动态规划的无线接入与回传一体化小基站资源动态分配算法进行求解,得到此时的接入与资源分配策略。仿真结果表明,所提算法能在保证平均时延约束、小基站回传速率约束和传输功率约束的同时最大化长期平均频谱效率和能效。
-
关键词:
- 接入与回传一体化小基站 /
- 近似动态规划理论 /
- 受限马尔科夫决策过程 /
- 切比雪夫理论
Abstract: To maximize the long-term spectral efficiency and energy efficiency of a full duplex wireless access and backhaul integrated small base station scene, approximate dynamic programming based joint admission control and resource allocation optimization algorithm is proposed. The algorithm firstly considers the resource usage and power configuration of the current base station, the dynamic demand of user, the constraints of average delay as well as backhaul rate and transmission power. The corresponding multi-objective optimization model of maximum spectrum efficiency and minimizes power consumption is established by using the Constrained Markov Decision Process(CMDP). Then, the Chebyshev theory is used to transform the multi-objective into a single-objective optimization, and the Lagrange dual decomposition method is then used to convert the single-objective problem into unrestricted Markov decision process problem. Finally, To solve the " dimension disaster” explosion that generated when solving this unrestricted Markov Decision Process(MDP) problem, a dynamic resource allocation algorithms based on approximate dynamic programming is presented, and the access and resource allocation strategy is obtained during this process. The simulation results show that the algorithm can maximize the long-term average spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency, within the constraints of the average delay, backhaul rate and transmission power, under the scenario of integrated access and backhaul small base station. -
表 1 基函数的定义
基函数 含义 1 常数 ${Q_{i,j}}(t)$ 用户$j$在基站$i$处队列积压的长度 ${U_i}(t)$ 新用户需求到达前基站$i$的资源使用状态 ${[{Q_{i,j}}(t)]^2}$ 用户$j$在基站$i$处队列积压长度的平方 ${Q_{i,j}}(t){U_i}(t)$ 用户$j$在基站$i$处队列积压长度和新用户需求到达前基站$i$资源使用状态的乘积 ${[{U_i}(t)]^2}$ 新用户需求到达前基站$i$资源使用状态的平方 表 2 基于随机梯度法更新待估参数的样本值函数逼近近似值函数算法
(1) 输入目标函数:
${{\text{μ}} ^*} = \arg {\rm{ }}\mathop {{\rm{min}}}\limits_\text{μ} {\rm E}\left\{ \frac{1}{2}{[{V^a}({S^a}(t - 1)|{\text{μ}} ) - \widehat {{V^{\text{π}} }(S)}]^2}\right\} $(2) 初始化步长$\gamma {}_t$,均方差误差门限$\delta $等; (3) 使用${\rm TD}(0)$方法取样本值函数的初始值; (4) 用数值微分法对待估参数${\mu _f}$取样本$\widehat {{\mu _f}}$; (5) 计算当前状态$S(t)$的值函数样本$\widehat {{V^{\text{π}} }(S)}$; (6) 根据式(36),按随机梯度法沿着梯度方向更新待估参数向量
${\text{μ}}$, ${\gamma _t}$值为$0.1 \sim 0.7$;(7) 根据式(33),求最优近似值函数; (8) 判定(1)中目标函数是否小于$\delta = {10^{ - 5}}$,若不满足,则执行(6),
否则依次执行;(9) 获得最接近样本值函数的近似值函数${V^a}$。 表 3 基于蒙特卡罗方法的外部用户需求随机变量采样算法
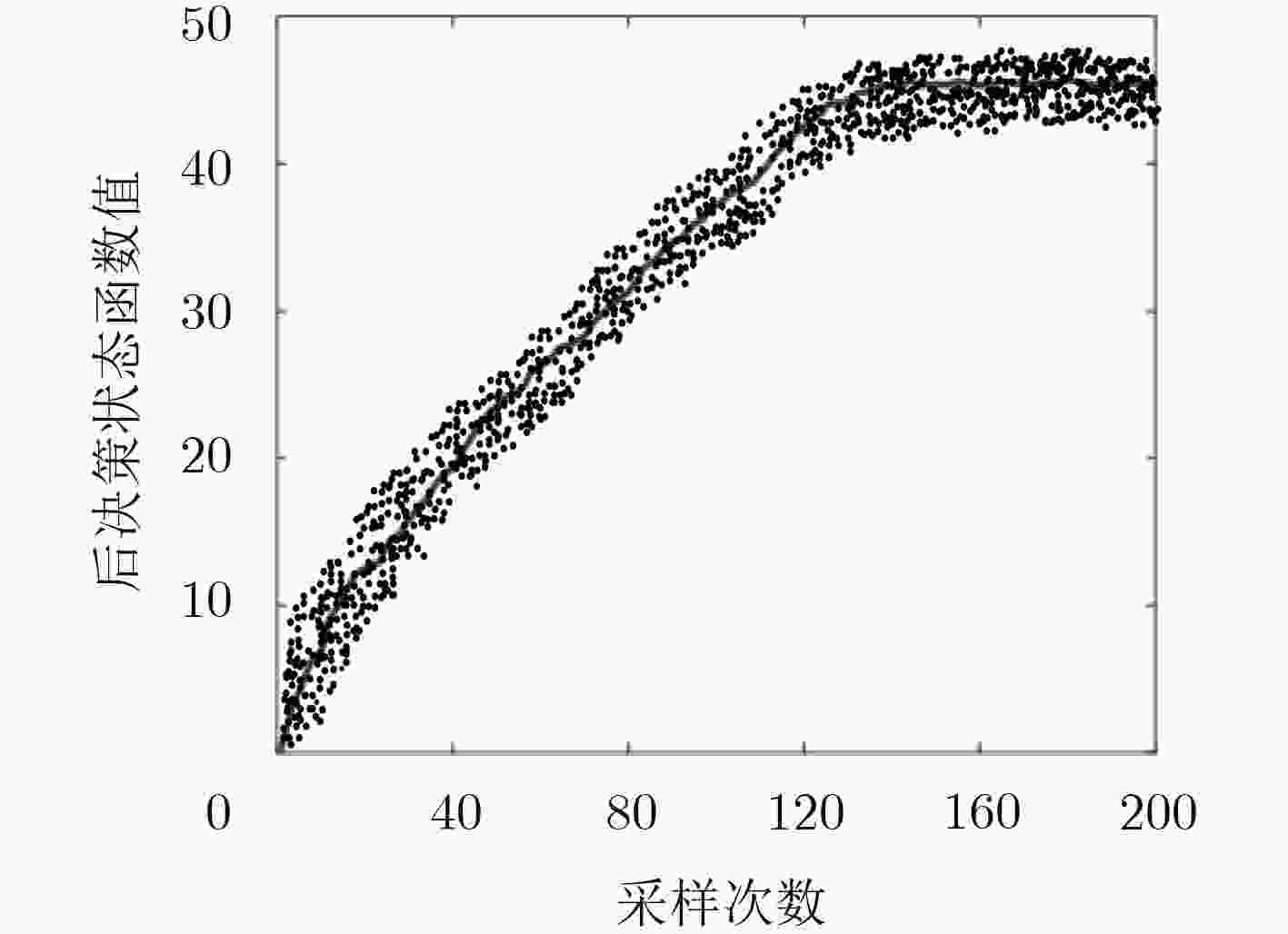
(1) 初始化采样路径$k$, $k = 1$,总采样次数$K$, $K = 200$,折扣因
子$\alpha $等参数;(2) for $k = 1$ to $K$ do (3) 选择一条采样路径${\omega ^k}$; (4) 对于每一个采样时刻$t = 1,2, ·\!·\!·,20$,令$\omega _t^k = {W_t}({\omega ^k})$表示
采样的实现;(5) 得到数据包数${a_{i,j}}(t)$与无线资源量${\beta _{ij}}(t)$; (6) $k = k + 1$,重复1。 表 4 基于近似动态规划的动态资源分配算法
(1) 对每个状态$S(t)$,初始化其初始值函数${V^*}(S)$,探索率
$\varepsilon = 0.1$等参数;(2) for $t = 0$ to $T\;$ do (3) 根据式(37),使用$\varepsilon {\tiny{-}} $贪心策略对行为空间进行探索; (4) 根据式(33)求解,并令此时的${{\text{π}} ^*}(S)$为以上优化问题的解; (5) 根据表2求近似值函数${V^a}$,得到此时的接入与频谱和功率
资源分配策略;(6) 根据表3进行1次采样; (7) 根据梯度法更新拉格朗日乘子${\lambda _{ij}}$; (8) 更新$t = t + 1$,并更新$t + 1$时隙的系统状态,重复3。 表 5 仿真参数
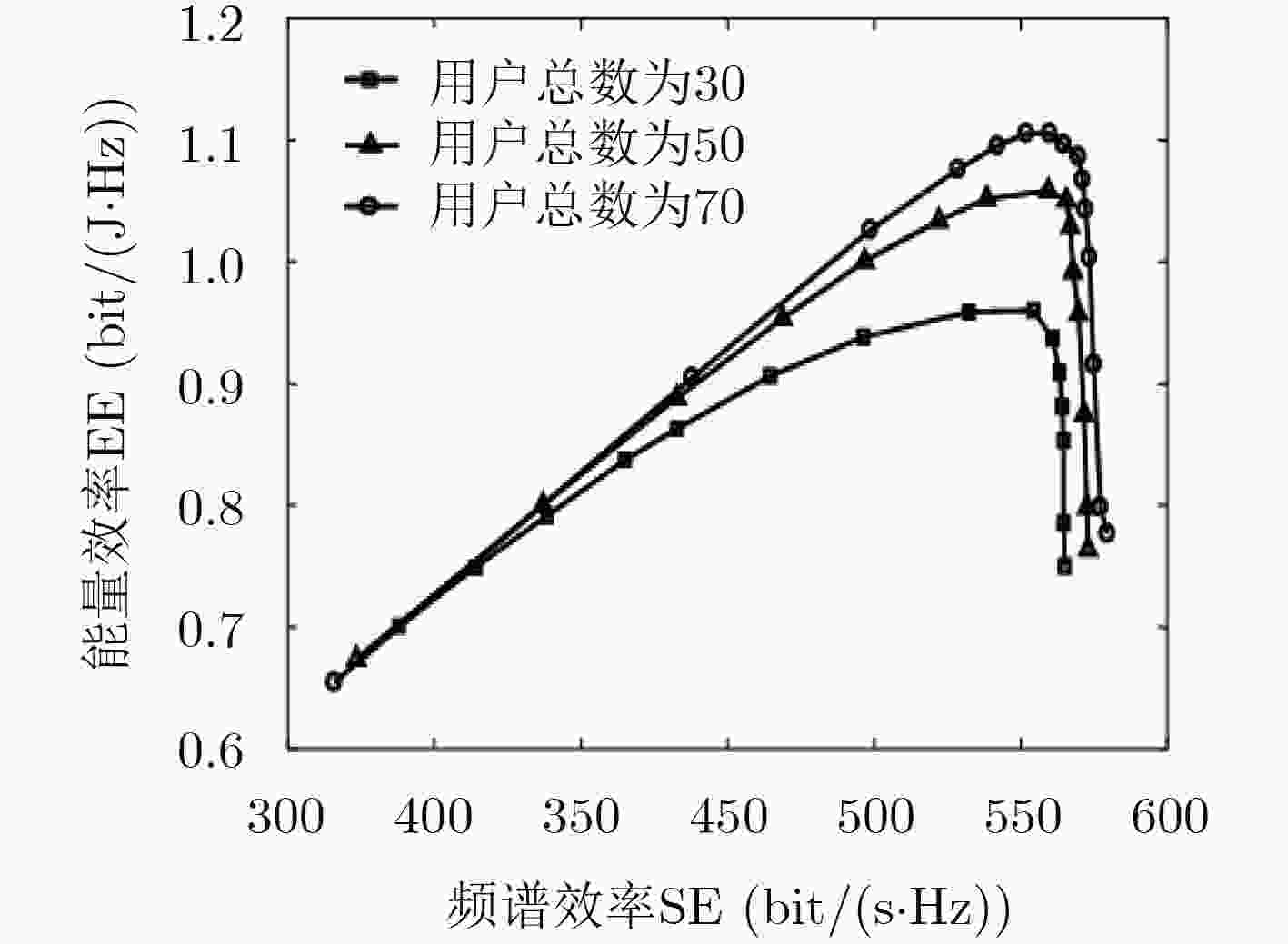
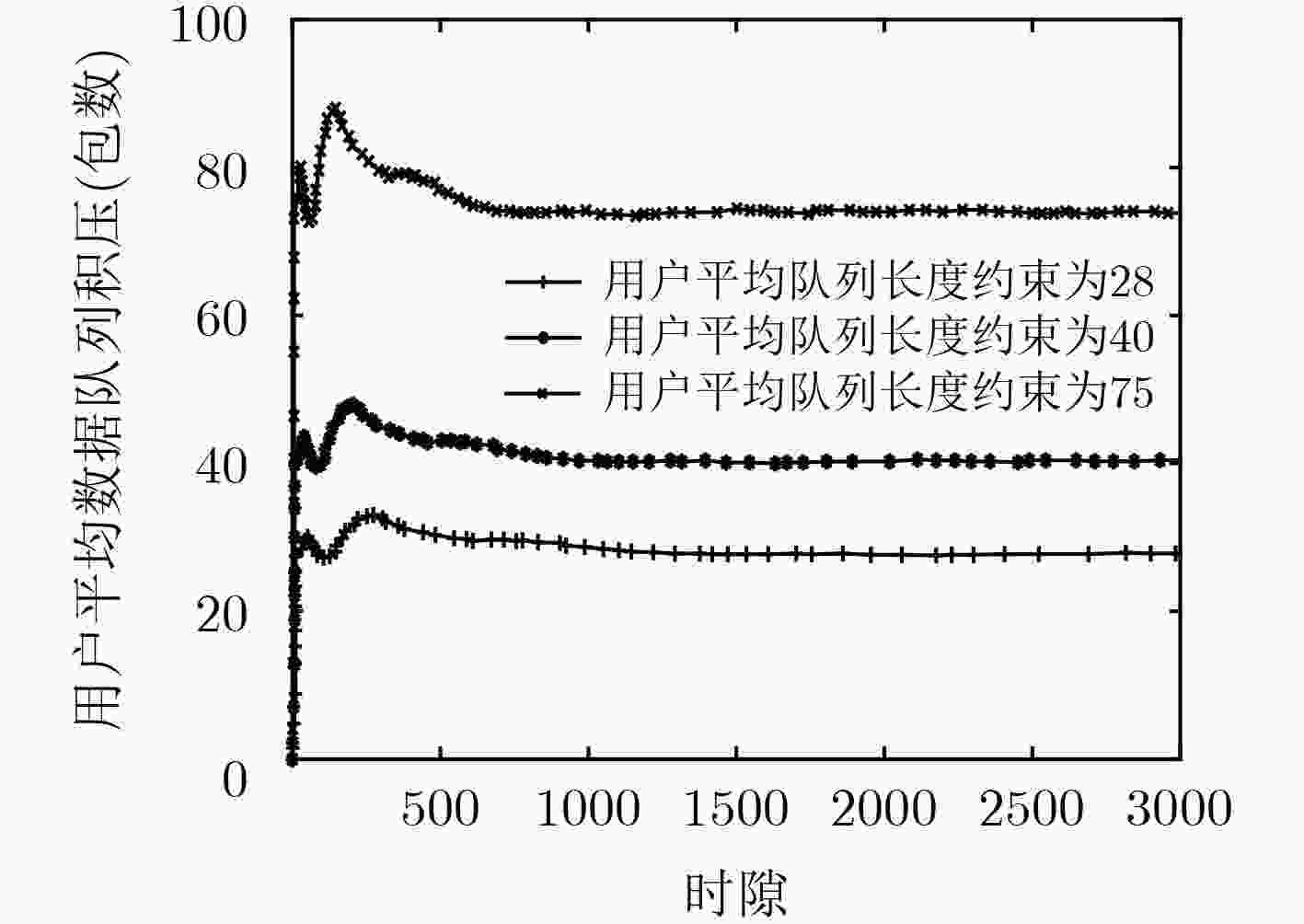
参数 数值 信道模型 瑞利衰落 噪声功率谱密度${N_0}$ –174 dBm/Hz 训练周期$T\;$ 30 宏基站发送功率${P_0}$ 43 dBm 小基站发送功率${P_{}}$ 33 dBm 基站个数$I$ 4 时隙时长 1 ms 总用户数 30, 50, 70 折扣因子$\alpha $ 0.3, 0.5, 0.9 天线阵列数为$M$ 100 波束成形组大小$N$ 10 平均队列长度门限值${\varepsilon _{i,j}}$ 28, 40, 75 -
BENCHAABENE Y, BOUJNAH N, and ZARAI F. 5G cellular: Survey on some challenging techniques[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies, Taipei, China, 2017: 348–353. MESODIAKAKI A, ADELANTADO F, ALONSO L, et al. Energy- and spectrum-efficient user association in millimeter-wave backhaul small-cell networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(2): 1810–1821. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2565539 OGAWA H, TRAN G K, SAKAGUCHI K, et al. Traffic adaptive formation of mmWave meshed backhaul networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, Paris, France, 2017: 185–191. LI Yuzhou, SHI Yan, SHENG Min, et al. Energy-efficient transmission in heterogeneous wireless networks: A delay-aware approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(9): 7488–7500. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2472578 LIU Yanping and FANG Xuming. Joint user association and resource allocation for self-backhaul ultra-dense networks[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(2): 1–10. doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7405718 YANG H H, GERACI G, and QUEK T Q S. Energy-efficient design of MIMO heterogeneous networks with wireless backhaul[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(17): 4914–4927. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2549529 MASOUDI M, ZAEFARANI H, MOHAMMADI A, et al. Energy and spectrum efficient resource allocation in two-tier networks: A multiobjective approach[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. LI Yi, FAN Pingzhi, LIU Lingjia, et al. Distributed MIMO precoding for in-band full-duplex wireless backhaul in heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(3): 2064–2076. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2713413 TANG Lun, WEI Yannan, CHEN Wan, et al. Delay-aware dynamic resource allocation and ABS configuration algorithm in HetNets based on Lyapunov optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 23764–23775. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2761863 ZORDAN D, MELODIA T, and ROSSI M. On the design of temporal compression strategies for energy harvesting sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(2): 1336–1352. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2489200 DEVRAJ A M and MEYN S P. Differential TD learning for value function approximation[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 6347–6354. XIANG Lin, NG D W K, SCHOBER R, et al. Secure video streaming in heterogeneous small cell networks with untrusted cache helpers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2645–2661. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2800005 MI Xiang, ZHAO Ming, XIAO Limin, et al. Delay-aware resource allocation and power control for device-to-device communications[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops, New Orleans, USA, 2015: 115–122. -





 下载:
下载:
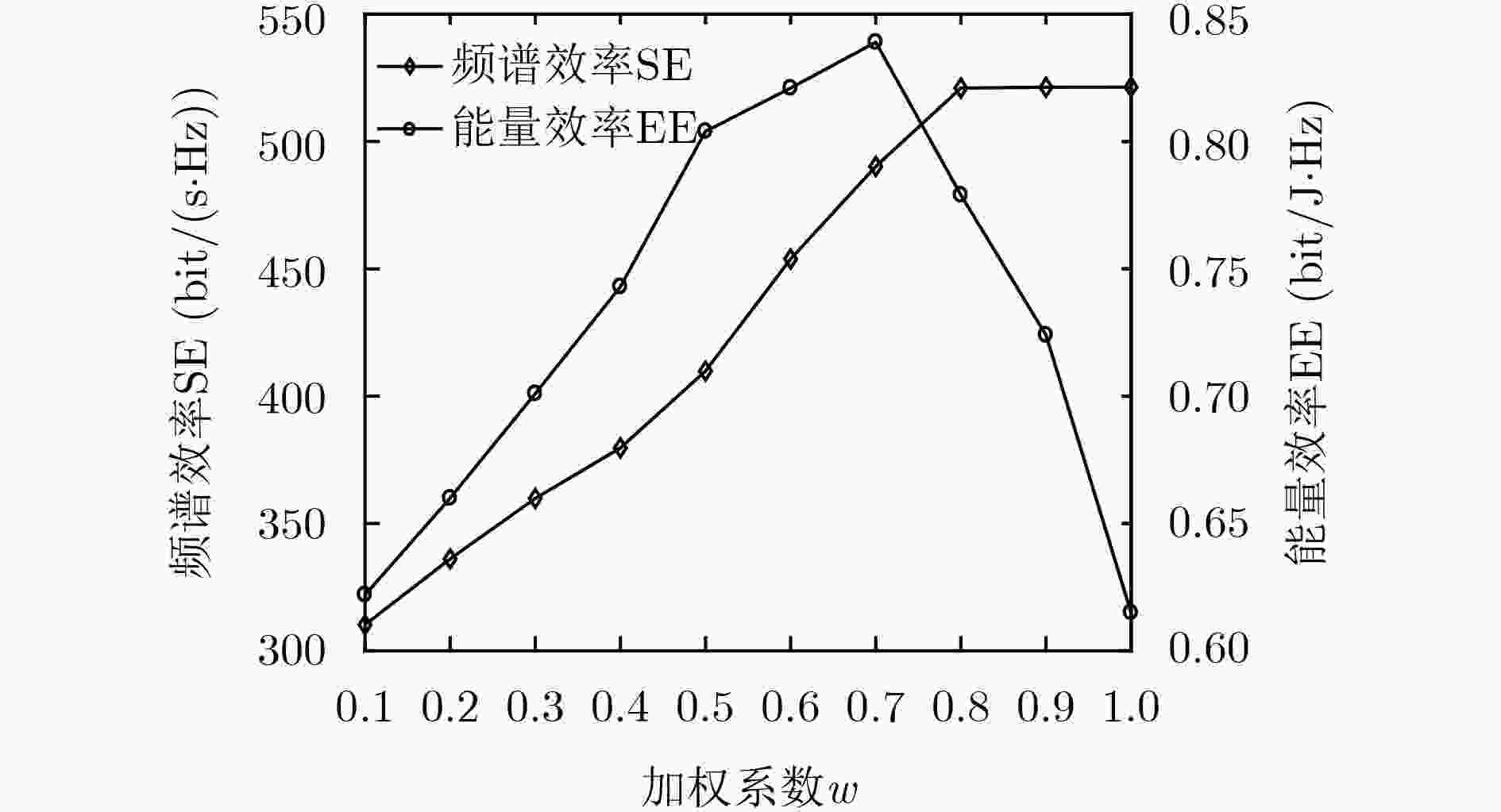

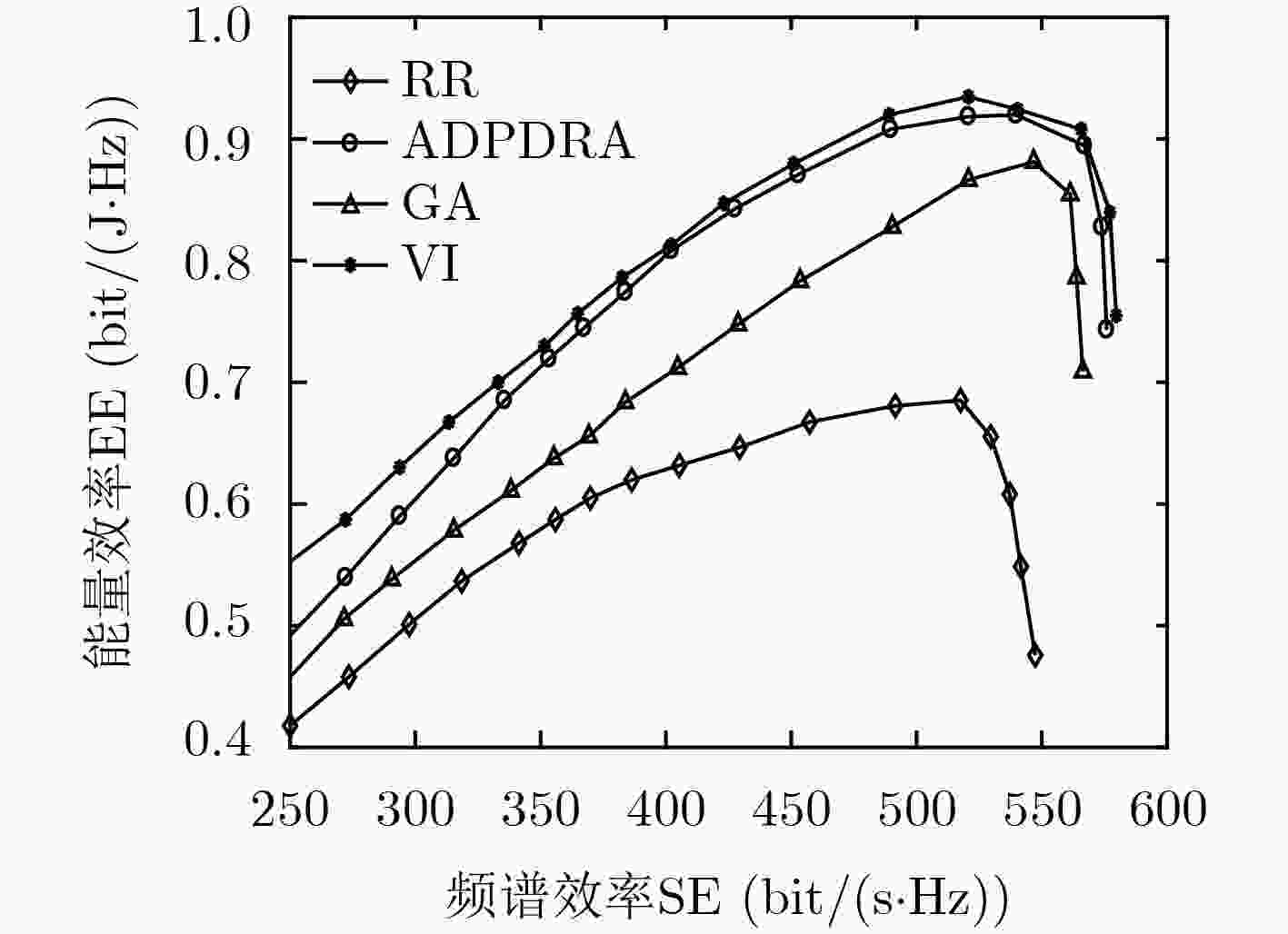
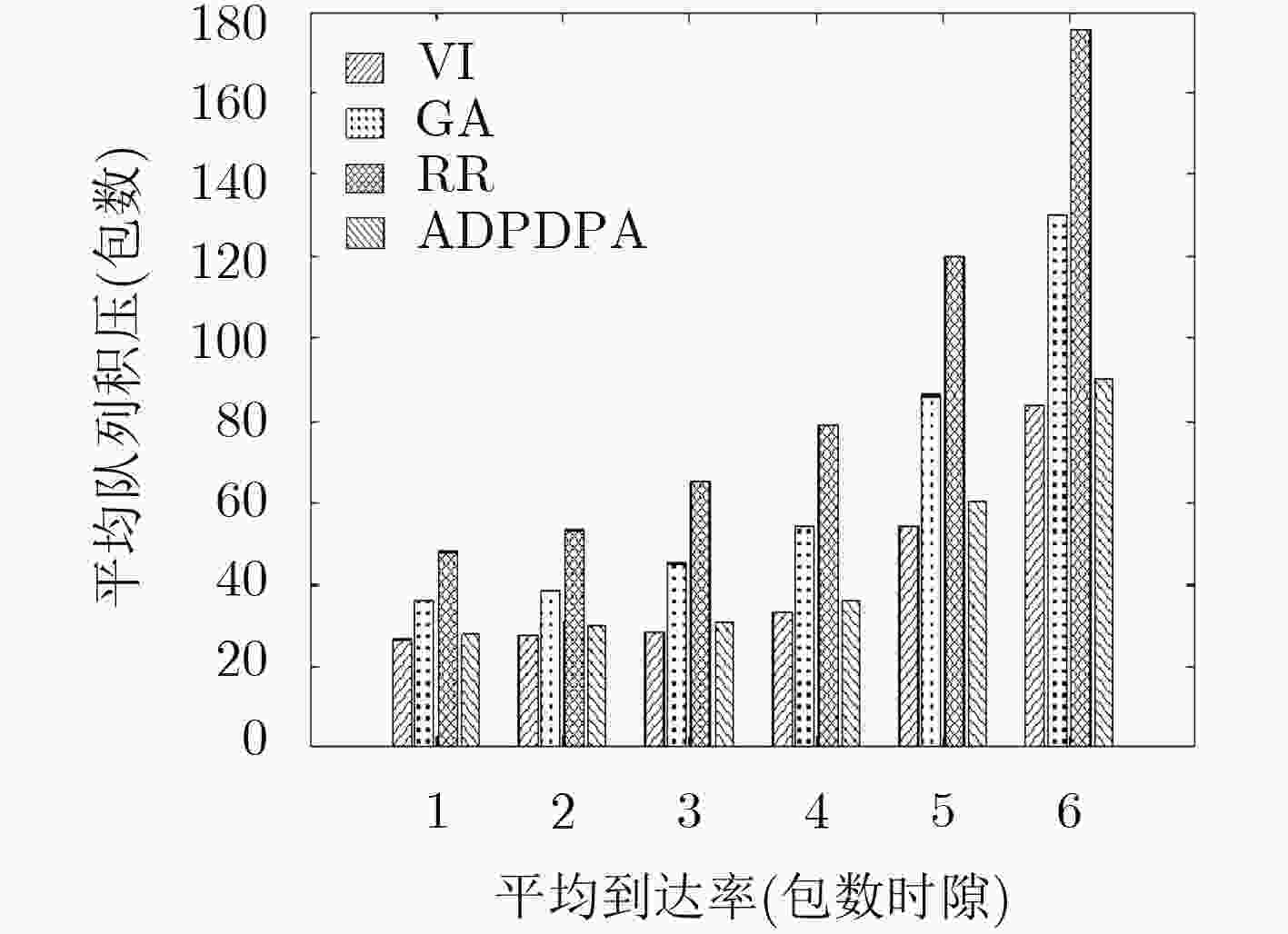


 下载:
下载:
