Gridless Sparse Method for Direction of Arrival Estimation for Two-dimensional Array
-
摘要:
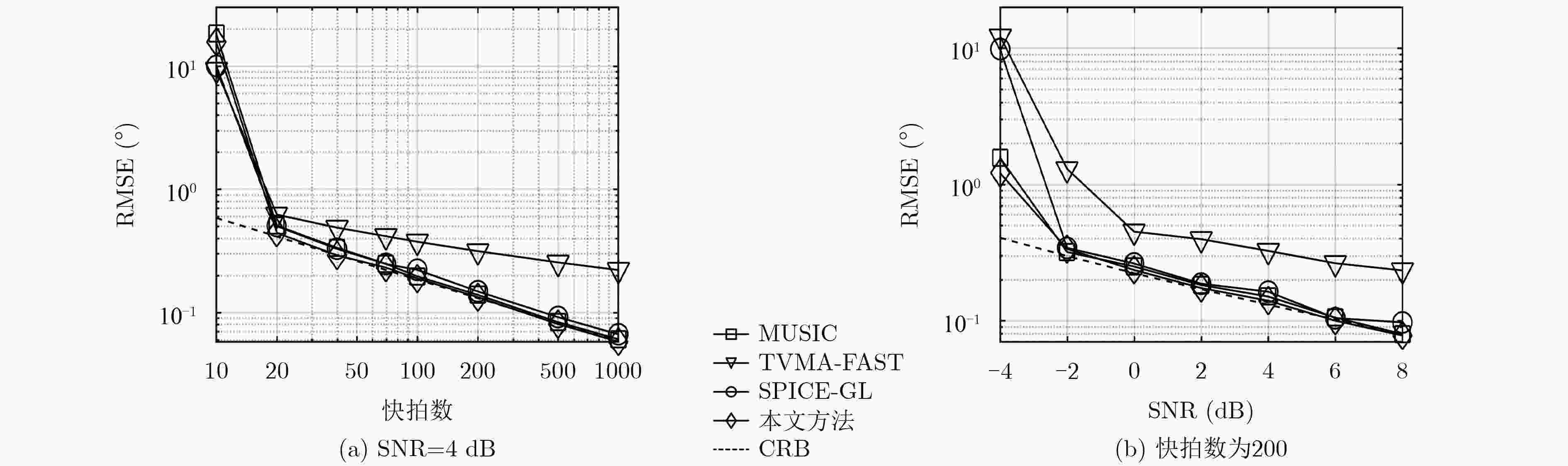
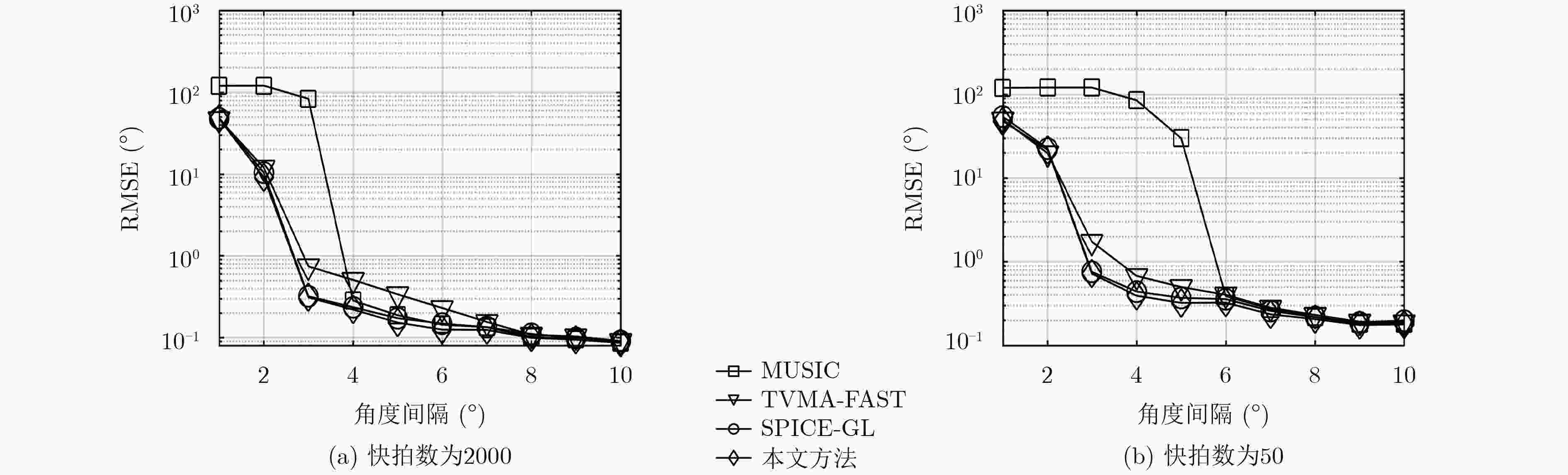
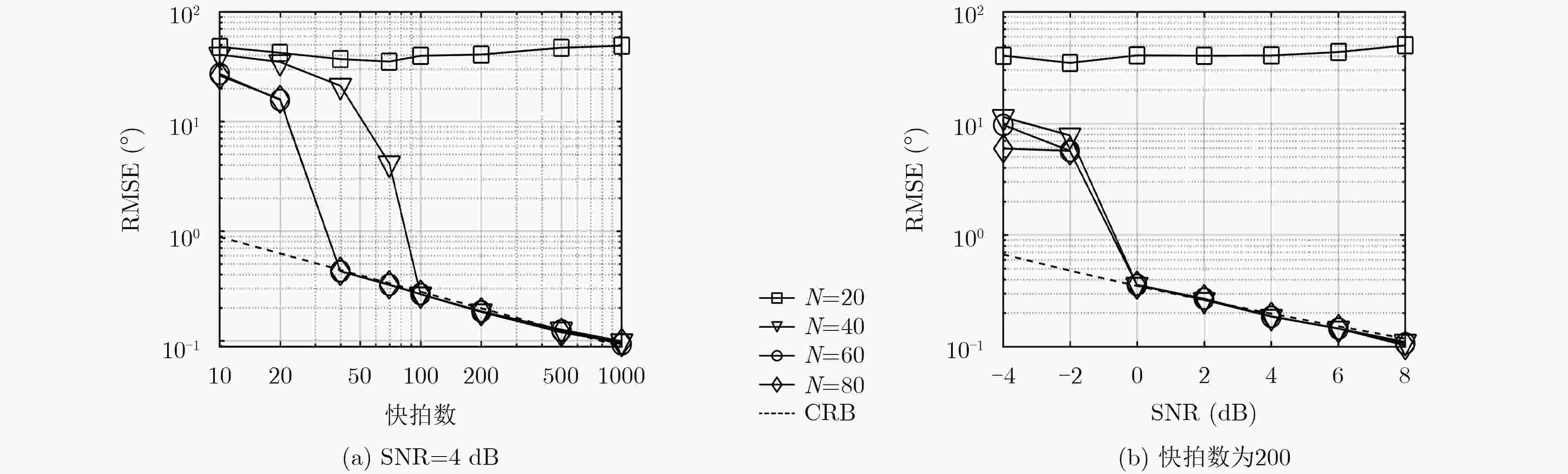
针对现有的适用于2维阵列的无格稀疏波达方向(DOA)估计方法性能不足的问题,该文提出一种新的方法。对2维阵列,从原子L0范数出发,证明其值等于一个以矩阵秩为目标函数的半定规划(SDP)问题的最优解。对该矩阵使用第1类有限阶贝塞尔函数近似表达,构造新的秩优化SDP问题。根据低秩矩阵恢复理论,对该SDP问题的目标函数使用log-det函数方法平滑替代,然后使用优化最小(MM)算法求解,最后通过(半)正定Toeplitz矩阵的范德蒙分解方法实现无格DOA估计。在MM算法求解模型时,使用样本协方差矩阵构造初始优化问题,减少算法迭代。仿真实验结果表明,相较于基于网格的MUSIC和其他无格DOA估计方法,该文方法具有更好的均方根误差(RMSE)性能与对相邻源的分辨能力;在快拍数充足且信噪比(SNR)较高时,适当的第1类贝塞尔函数阶数选择可以实现与较大阶数接近的RMSE性能,同时能减少运行时间。
Abstract:For the fact that current gridless Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation methods with two-dimensional array suffer from unsatisfactory performance, a novel girdless DOA estimation method is proposed in this paper. For two-dimensional array, the atomic L0-norm is proved to be the solution of a Semi-Definite Programming (SDP) problem, whose cost function is the rank of a Hermitian matrix, which is constructed by finite order of Bessel functions of the first kind. According to low rank matrix recovery theorems, the cost function of the SDP problem is replaced by the log-det function, and the SDP problem is solved by Majorization-Minimization (MM) method. At last, the gridless DOA estimation is achieved by Vandermonde decomposition method of semidefinite Toeplitz matrix built by the solutions of above SDP problem. Sample covariance matrix is used to form the initial optimization problem in MM method, which can reduce the iterations. Simulation results show that, compared with on-grid MUSIC and other gridless methods, the proposed method has better Root-Mean-Square Error (RMSE) performance and identifiability to adjacent sources; When snapshots are enough and Signal-Noise-Ratio (SNR) is high, proper choice of the order of Bessel functions of the first kind can achieve approximate RMSE performance as that of higher order ones, and can reduce the running time.
-
表 1 不同贝塞尔函数阶数的本文方法平均运行时间(s)
N 20 40 60 80 运行时间 0.7453 1.7536 4.0365 8.0497 -
QIN Si, ZHANG Yimin D, and AMIN M G. DOA estimation of mixed coherent and uncorrelated targets exploiting coprime MIMO radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 61: 26–34. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.06.006 SAUCAN A A, CHONAVEL T, SINTES C, et al. CPHD-DOA tracking of multiple extended sonar targets in impulsive environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(5): 1147–1160. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2504349 HE Saijuan and CHEN Huawei. Closed-form DOA estimation using first-order differential microphone arrays via joint temporal-spectral-spatial processing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(4): 1046–1060. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2641449 WAN Liangtian, HAN Guangjie, JIANG Jinfang, et al. A DOA estimation approach for transmission performance guarantee in D2D communication[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2017, 22(6): 998–1009. doi: 10.1007/s11036-017-0820-2 CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278 SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT—Estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276 MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, and WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010–3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882 WIPF D P and RAO B D. An empirical Bayesian strategy for solving the simultaneous sparse approximation problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3704–3716. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894265 LIU Zhangmeng, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. An efficient maximum likelihood method for direction-of-arrival estimation via sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(10): 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.090312.111912 BHASKAR B N, TANG Gongguo, and RECHT B. Atomic norm denoising with applications to line spectral estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(23): 5987–5999. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273443 QIAN Tong, TIAN Jing, ZHANG Xu, et al. Atomic norm method for DOA estimation in random sampling condition[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4. ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Gong, and WANG Xinhai. Array covariance matrix-based atomic norm minimization for off-grid coherent direction-of-arrival estimation[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, USA, 2017: 3196–3200. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2017.7952746. CHEN Yuxin and CHI Yuejie. Robust spectral compressed sensing via structured matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(10): 6576–6601. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2343623 YANG Zai, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Sparse methods for direction-of-arrival estimation[OL]. http://cn.arxiv.org/pdf/1609.09596v2, 2017.3. YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. A discretization-free sparse and parametric approach for linear array signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(19): 4959–4973. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2339792 YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. On gridless sparse methods for multi-snapshot direction of arrival estimation[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2017, 36(8): 3370–3384. doi: 10.1007/s00034-016-0462-9 ZHANG Youwen, HONG Xiaoping, WANG Yonggang, et al. Gridless SPICE applied to parameter estimation of underwater acoustic frequency hopping signals[C]. 2016 IEEE/OES Chian Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 2016: 1–6. MAHATA K and HYDER M M. Grid-less TV minimization for DOA estimation[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 132: 155–164. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.09.018 RAO B D and HARI K V S. Performance analysis of root-MUSIC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(12): 1939–1949. doi: 10.1109/29.45540 TANG Gongguo, BHASKAR B N, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465–7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451 MOHAN K and FAZEL M. Iterative reweighted algorithms for matrix rank minimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2012, 13(11): 3441–3473. SUNDIN M, ROJAS C R, JANSSON M, et al. Relevance singular vector machine for low-rank matrix reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5327–5339. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2597121 SUN Ying, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Majorization-minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 794–816. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2601299 HORN R A and JOHNSON C R. Matrix Analysis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 495–497. LANDAU H J. The classical moment problem: Hilbertian proofs[J]. Journal of Functional Analysis, 1980, 38(2): 255–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-1236(80)90065-8 STOICA P and MOSES R L. Spectral Analysis of Signals[M]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2005: 172–177. YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. Enhancing sparsity and resolution via reweighted atomic norm minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(4): 995–1006. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2493987 FERNANDEZGRANDA C. Super-resolution of point sources via convex programming[C]. IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, Cancun, Mexico, 2015: 41–44. CANDES E J and FERNANDEZ-GRANDA C. Towards a mathematical theory of super-resolution[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2014, 67(6): 906–956. doi: 10.1002/cpa.v67.6 STURM J F. Using SeDuMi 1.02, a MATLAB toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 1999, 11(1/4): 625–653. doi: 10.1080/10556789908805766 TOH K C, TODD M J, and TUTUNCU R H. SDPT3—A Matlab software package for semidefinite programming, Version 1.3[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 1999, 11(1/4): 545–581. doi: 10.1080/10556789908805762 STURM J F. Implementation of interior point methods for mixed semidefinite and second order cone optimization problems[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 2002, 17(6): 1105–1154. doi: 10.1080/1055678021000045123 STOICA P and NEHORAI A. Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1990, 38(10): 1783–1795. doi: 10.1109/29.60109 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
