Improved Metric Learning Algorithm for Person Re-identification Based on Equidistance
-
摘要:
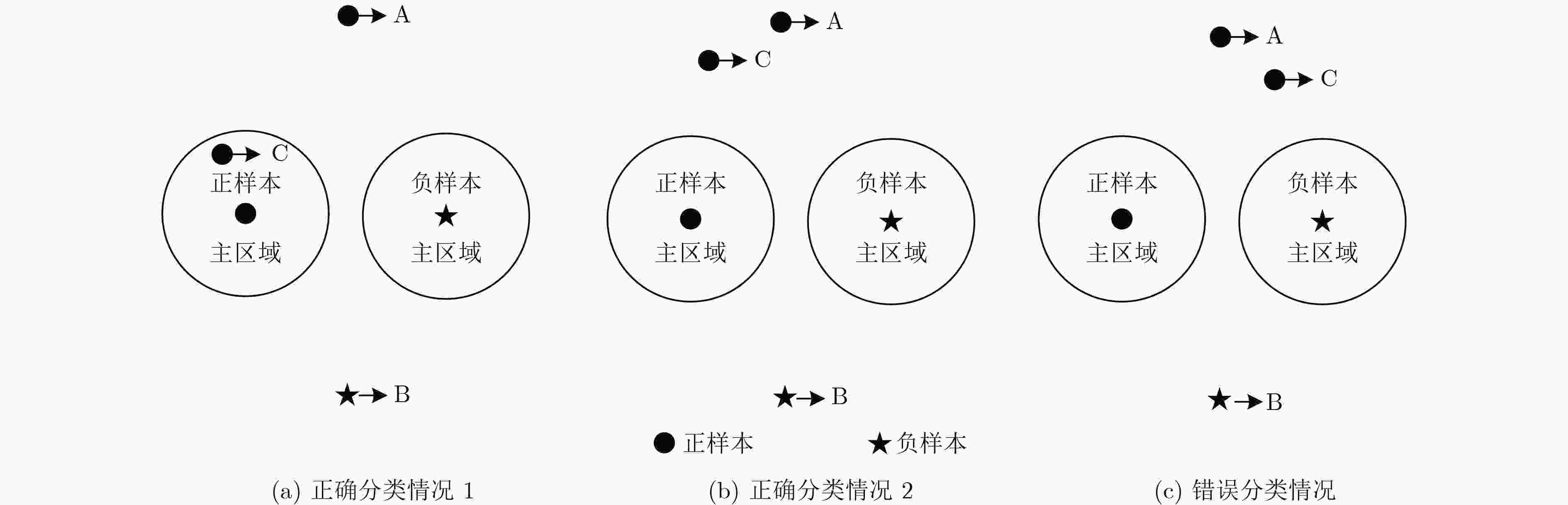
为了提高行人重识别距离度量MLAPG算法的鲁棒性,该文提出基于等距度量学习策略的行人重识别Equid-MLAPG算法。 MLAPG算法中正负样本对在映射空间的分布不均衡导致间距超参数受负样本对距离影响更大,因此该文设计的Equid-MLAPG算法要求正样本对映射成为变换空间中的一个点,即正样本对在变换空间中距离为零,使算法收敛时正负样本对距离分布不存在交叉部分。实验表明Equid-MLAPG算法能在常用的行人重识别数据集上取得良好的实验效果,具有更好的识别率和广泛的适用性。
Abstract:In order to improve the robustness of MLAPG algorithm, a person re-identification algorithm, called Equid-MLAPG algorithm is proposed, which is based on the equidistance measurement learning strategy. Due to the imbalanced distribution of positive and negative sample pairs in the mapping space, sample spacing hyper-parameter of MLAPG algorithm is more affected by the distance of negative sample pairs. Therefore, Equid-MLAPG algorithm tends to map the positive sample pair to be a point in the transform space. That is, the distance of a positive sample pair in the transform space is mapped to be zero, resulting in no intersection in the distribution of positive and negative sample pairs in the transform space when algorithm convergences. Experiments show that the Equid-MLAPG algorithm can achieve better experimental results on commonly used person re-identification datasets with better recognition rate and wide applicability.
-
Key words:
- Person re-identification /
- Equidistance /
- MLAPG algorithm
-
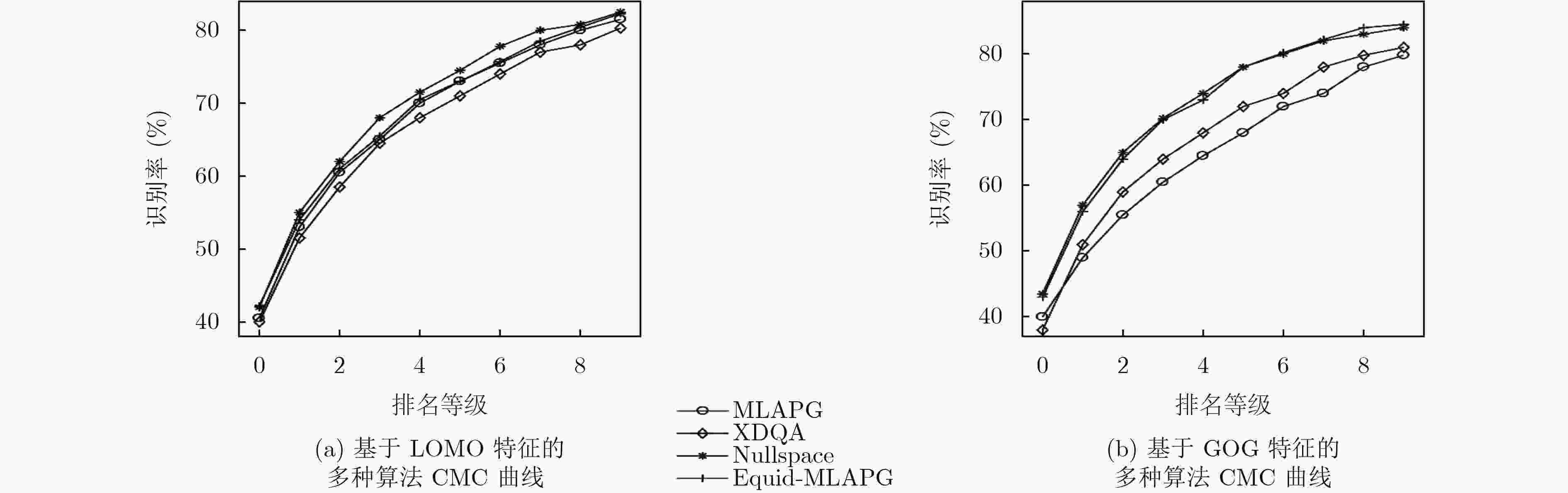
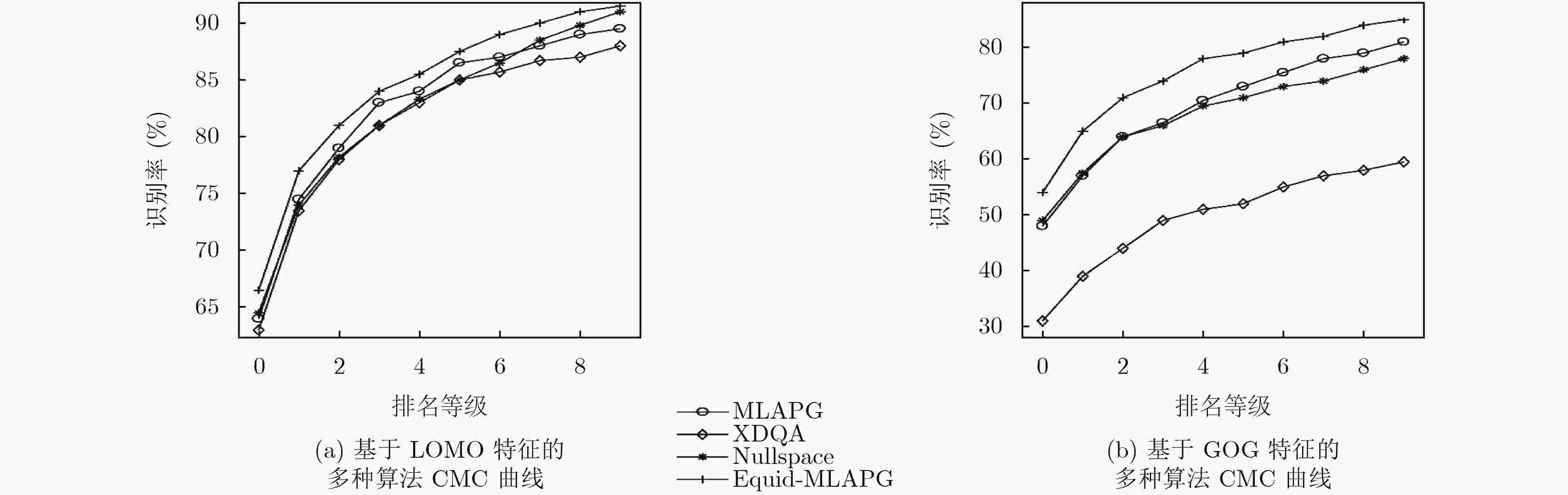
表 1 CUHK03数据集上多种距离度量算法对比
算法 检测标注 人工标注 第1匹配率(%) 第5匹配率(%) 第10匹配率(%) 第1匹配率(%) 第5匹配率(%) 第10匹配率(%) XQDA 46.25 78.90 88.55 52.20 82.23 92.14 MLAPG 51.15 83.55 92.05 57.96 87.09 94.74 Nullspace 53.70 83.05 90.30 58.90 85.60 92.45 Equid-MLAPG 52.41 85.25 92.84 58.72 89.07 95.28 表 2 Marlet1501,DukeMTMC-reID数据集上多种距离度量算法对比
算法 Market1501数据集 DukeMTMC-reID数据集 第1匹配率(%) 平均准确率(%) 第1匹配率(%) 平均准确率(%) XQDA 43.23 22.00 31.37 17.17 MLAPG 42.52 21.45 36.58 19.10 Nullspace 54.60 29.80 45.02 26.11 Equid-MLAPG 44.25 24.38 39.25 21.54 -
ZHENG Liang, YANG Yi, and HAUPTMANN A G. Person re-identification: Past, present and future[OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.02984, 2016. SHAH J H, LIN Mingqiang, and CHEN Zonghai. Multi-camera handoff for person re-identification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 191: 238–248. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.037 REHMAN S U, CHEN Zonghai, RAZA M, et al. Person re-identification post-rank optimization via hypergraph-based learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 287: 143–153. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.01.086 PEDAGADI S, ORWELL J, VELASTIN S, et al. Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Protland, USA, 2013: 3318–3325. WEINBERGER K Q, BLITZER J, and SAUL L K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada, 2006: 1473–1480. DAVIS J V, KULIS B, JAIN P, et al. Information-theoretic metric learning[C]. Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, Corvalis, USA, 2007: 209–216. DIKMEN M, AKBAS E, HUANG T S, et al. Pedestrian recognition with a learned metric[C]. Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Queenstown, New Zealand, 2010: 501–512. ZHENG Weishi, GONG Shaogang, and XIANG Tao. Person re-identification by probabilistic relative distance comparison[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Colorado, USA, 2011: 649–656. KOESTINGER M, HIRZER M, WOHLHART P, et al. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Rhode Island, USA, 2012: 2288–2295. TAO Dapeng, JIN Lianwen, WANG Yongfei, et al. Person re-identification by regularized smoothing kiss metric learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2013, 23(10): 1675–1685. doi: 10.1109/tcsvt.2013.2255413 LIAO Shengcai, and LI S Z. Efficient PSD constrained asymmetric metric learning for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, USA, 2015: 3685–3693. NESTEROV Y. Introductory Lectures on Convex Optimization: A Basic Course[M]. New York, USA, Springer Science & Business Media, 2013: 15–20. TSENG P. On accelerated proximal gradient methods for convex-concave optimization[OL]. http://www.mit.edu/~dimitrib/PTseng/papers/apgm.pdf. GRAY D and TAO Hai. Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 2008: 262–275. LI Wei, ZHAO Rui, and WANG Xiaogang. Human reidentification with transferred metric learning[C]. Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Daejeon, Korea, 2012: 31–44. LI Wei, ZHAO Rui, XIAO Tong, et al. Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA, 2014: 152–159. ZHENG Liang, SHEN Liyue, TIAN Lu, et al. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, USA, 2015: 1116–1124. ZHENG Zhedong, ZHENG Liang, and YANG Yi. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy, 2017: 3774–3782. LIAO Shengcai, HU Yang, ZHU Xiangyu, et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2197–2206. ZHANG Li, XIANG Tao, and GONG Shaogong. Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1239–1248. 曾明勇, 吴泽明, 田畅, 等. 基于外观统计特征融合的人体目标再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(8): 1844–1851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01389ZENG Mingyong, WU Zeming, TIAN Chang, et al. Fusing appearance statistical features for person re-identification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(8): 1844–1851. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01389 MATSUKAWA T, OKABE T, SUZUKI E, et al. Hierarchical gaussian descriptor for person re-identification[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1363–1372. -





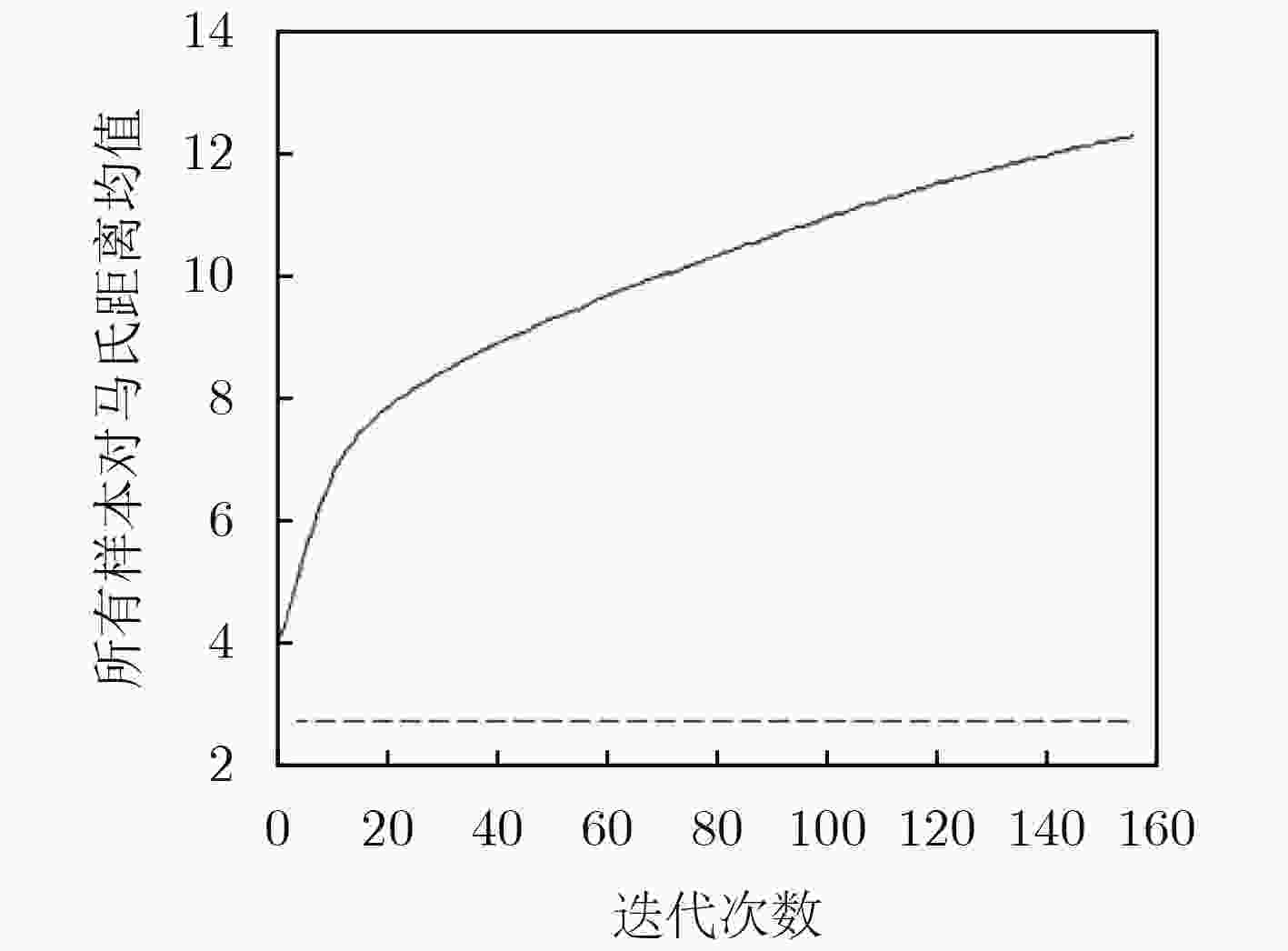

 下载:
下载:
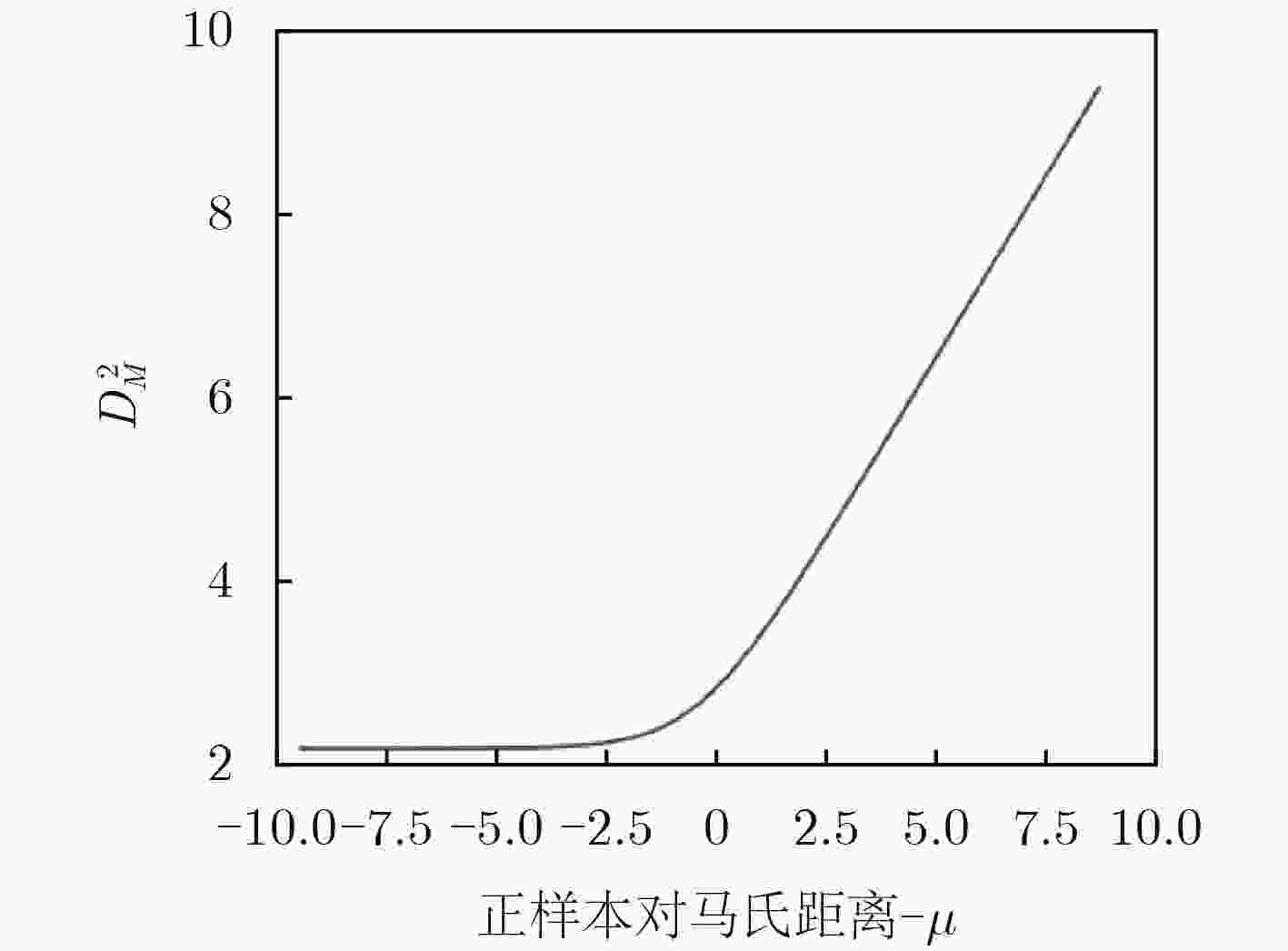
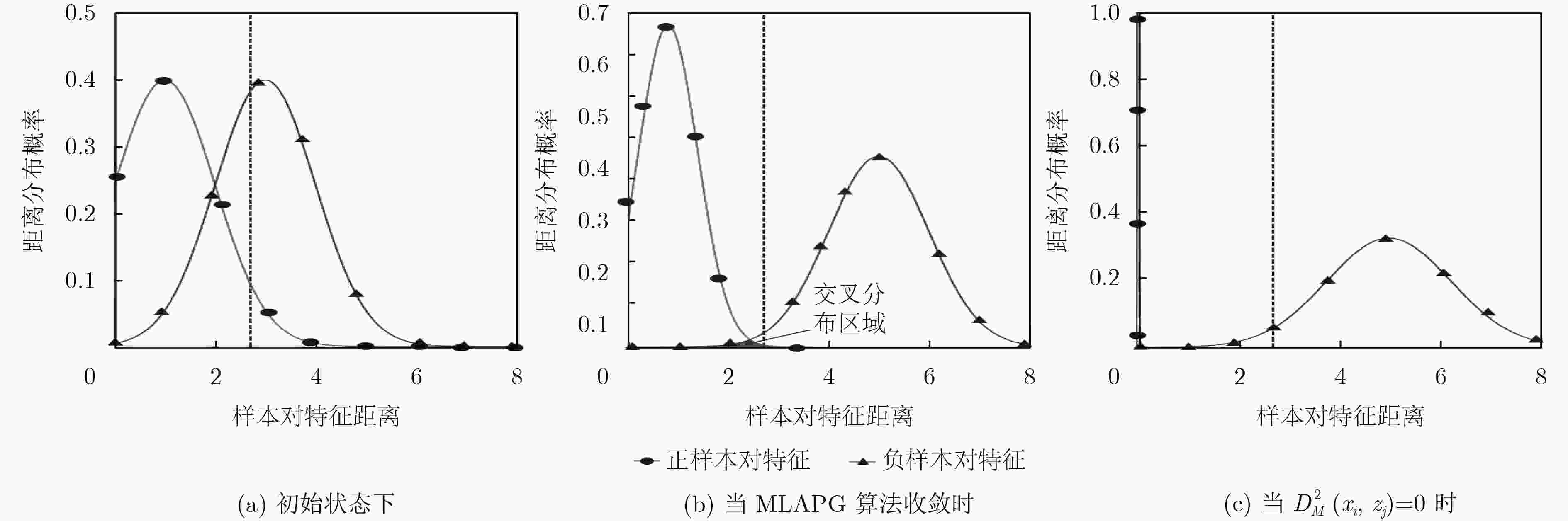
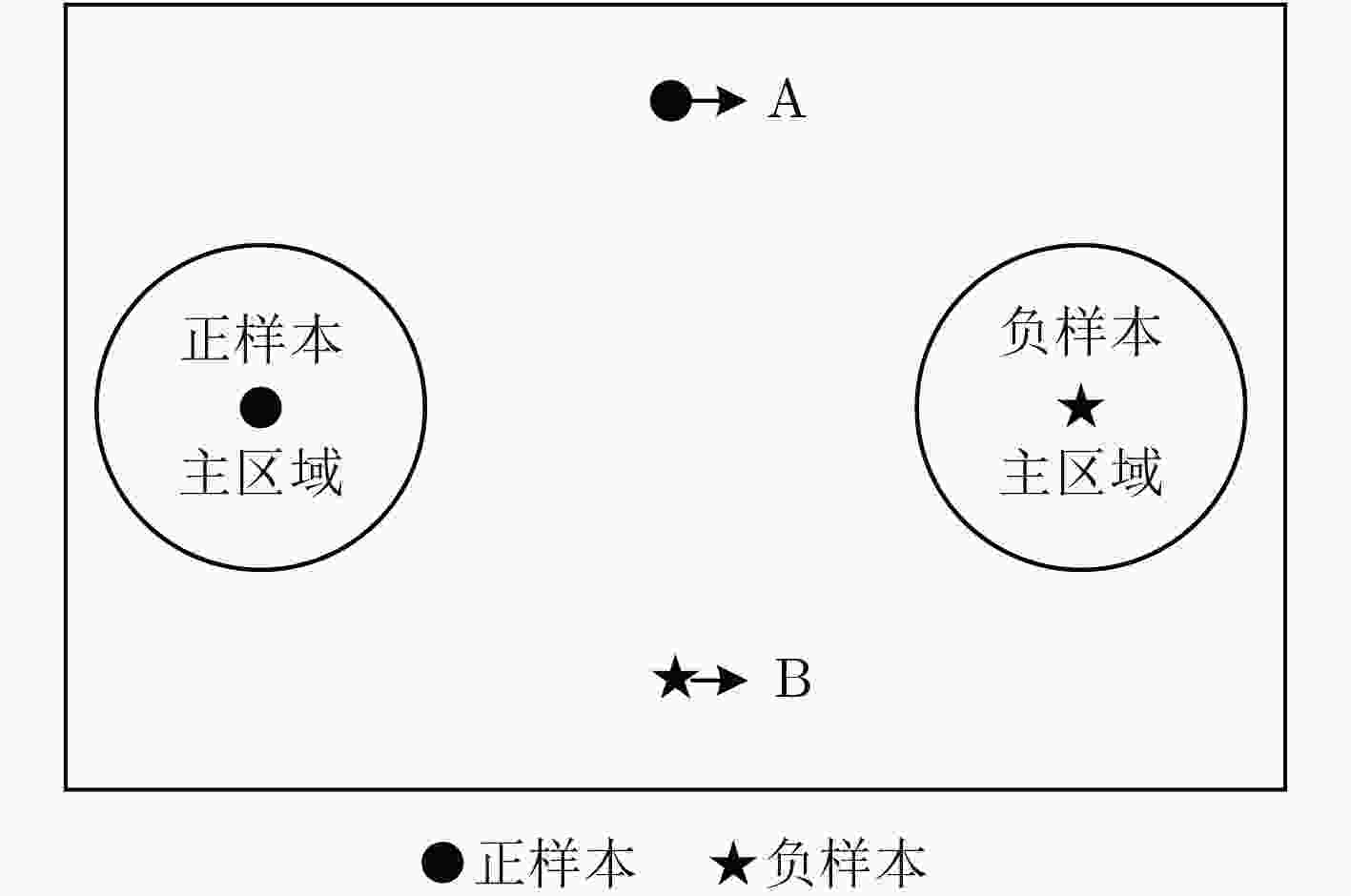


 下载:
下载:
